
Finance
What Happens When The Fed Buys Bonds
Published: November 3, 2023
Discover how the finance industry responds to the Federal Reserve's bond purchases and the effects it has on the economy.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
The Federal Reserve, commonly referred to as the Fed, plays a crucial role in the economy of the United States. As the country’s central banking system, the Fed is responsible for implementing monetary policy, maintaining stability in the financial system, and promoting economic growth.
One of the tools the Federal Reserve uses to fulfill its objectives is buying government bonds. Bond purchasing, also known as open market operations, allows the Fed to inject liquidity into the financial system, influencing interest rates and the overall money supply.
Understanding the implications and consequences of the Fed’s bond purchases is essential for investors, economists, and individuals who want to stay informed about the state of the economy. In this article, we will explore the effects of the Fed buying bonds and the potential impact it can have on the financial markets and the economy as a whole.
From the manipulations of the nation’s money supply to the influence on interest rates and inflation expectations, the Fed’s bond purchases have far-reaching consequences. It is crucial to have a comprehensive understanding of this process to navigate the intricacies of the financial world and make informed investment decisions.
Let’s dive into the world of the Federal Reserve and explore what happens when the Fed buys bonds.
Understanding the Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve System, often referred to as the Fed, is the central banking system of the United States. Established in 1913, its main purpose is to provide stability and support to the country’s financial system while promoting sustainable economic growth.
The Federal Reserve operates independently within the government and is composed of several key components, including the Board of Governors, the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), and the regional Federal Reserve Banks. Together, they work to implement monetary policy, oversee banking regulations, and maintain the stability of the entire financial system.
One of the primary goals of the Federal Reserve is to regulate the money supply within the economy. By controlling the money supply, the Fed can impact interest rates, control inflation, and stimulate or restrict economic growth as needed.
The Federal Reserve has various tools at its disposal to achieve these objectives. One of the most commonly used tools is open market operations, which involves the buying and selling of government bonds. When the Fed buys bonds, it aims to increase the money supply in the economy, thereby stimulating lending and economic activity.
It is important to note that the Federal Reserve’s actions are not arbitrary or based solely on the preferences of its policymakers. Instead, they rely on data-driven analysis and discussions within the FOMC to determine the appropriate course of action. These decisions take into account a wide range of economic indicators, including inflation rates, employment levels, and GDP growth.
Understanding the role and function of the Federal Reserve is crucial for comprehending the implications of its bond purchasing activities. By gaining insight into its mandate, structure, and decision-making processes, individuals can better evaluate the potential impact of the Fed’s actions and make informed financial decisions.
Now that we have a basic understanding of the Federal Reserve, let’s delve deeper into the process of bond purchasing and its effects on the economy.
Bond Purchasing: An Overview
Bond purchasing, also known as open market operations, is a key monetary policy tool used by the Federal Reserve to manage the money supply in the economy. Through the purchase of government bonds, the Fed injects liquidity into the financial system, influencing interest rates and stimulating economic activity.
When the Federal Reserve decides to buy bonds, it does so through primary dealers, which are authorized financial institutions that have an ongoing relationship with the Fed. These dealers participate in auctions where the bonds are issued, and the Fed purchases them in the open market.
The Federal Reserve has the flexibility to choose which bonds it buys. However, it typically focuses on buying Treasury bonds issued by the U.S. government. These bonds are considered safe and highly liquid, making them an attractive choice for the Fed.
By purchasing government bonds, the Fed increases the amount of money in circulation. This injection of liquidity has a ripple effect throughout the economy. When primary dealers receive payment from the Fed for the bonds, they deposit this money into their bank accounts.
This influx of funds allows banks to have more money available for lending. Increased lending can then lead to economic growth as individuals and businesses have greater access to credit, which can be used for investment, consumption, or other financial activities.
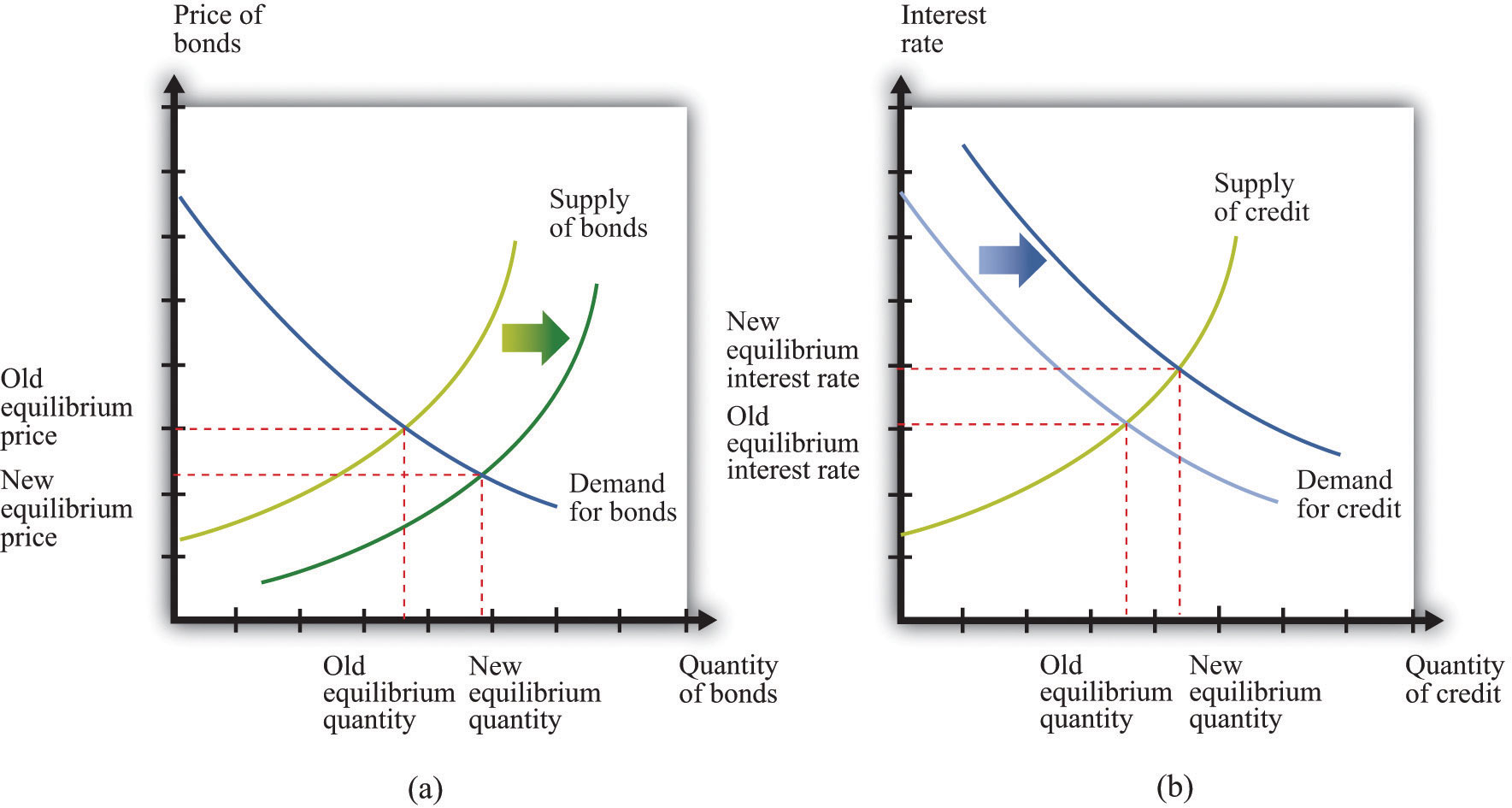
Furthermore, when the Fed buys bonds, it creates demand for these securities, driving up their prices. As bond prices increase, bond yields decrease. This inverse relationship between bond prices and yields means that when the Fed engages in bond purchases, it puts downward pressure on interest rates.
Lower interest rates make borrowing more affordable, encouraging individuals and businesses to take on new debt. This increased borrowing can lead to higher spending, investment, and economic expansion.
In addition to the direct impact on interest rates and money supply, bond purchasing by the Fed can also have psychological effects on market participants. When investors see the central bank actively buying bonds, it signals confidence and support for the financial markets and can impact investor sentiment.
Overall, bond purchasing by the Federal Reserve is a powerful tool that can be used to influence the economy. By injecting liquidity, lowering interest rates, and fostering confidence, the Fed aims to support economic growth and stability.
Now that we understand the basic mechanics of bond purchasing, let’s explore the effects it has on the money supply.
The Effect on the Money Supply
The Federal Reserve’s bond purchasing activities have a direct impact on the money supply in the economy. When the Fed buys bonds, it injects money into the financial system, increasing the overall money supply.
Let’s take a closer look at how this process works. When the Federal Reserve purchases bonds from primary dealers, it pays for them by depositing funds into the dealers’ bank accounts. These funds, known as reserves, become part of the banking system’s total reserves.
With greater reserves, banks have more money available to lend. They can extend credit to individuals and businesses, allowing them to make purchases, invest, or meet their financial needs. As a result, the money supply in the economy expands.
Increasing the money supply can have a stimulating effect on the economy. It provides individuals and businesses with access to additional funds, fostering economic growth and activity. This injection of liquidity can support increased consumer spending, business investment, and overall economic expansion.
However, it is important to note that the impact on the money supply may not always be immediate. The effectiveness of the Federal Reserve’s bond purchasing program in increasing the money supply depends on various factors, such as the willingness of banks to lend and the demand for credit in the economy.
Moreover, the money supply is not solely determined by the Fed’s actions. Other factors, such as consumer and business borrowing behavior, government spending, and the overall health of the financial system, also contribute to changes in the money supply.
It’s also worth noting that the Federal Reserve has the ability to adjust the money supply by selling bonds as well. When the Fed sells bonds, it takes money out of circulation, reducing the money supply. This action can be used when the central bank wants to tighten monetary policy or combat inflationary pressures.
The relationship between the money supply and economic growth is complex. While an increase in the money supply can promote economic activity, an excessive expansion of the money supply can lead to inflationary pressures. Therefore, the Federal Reserve carefully monitors and adjusts its bond purchasing activities to maintain a balance between supporting economic growth and controlling inflation.
By understanding the impact on the money supply, investors and individuals can gain insights into the potential effects of the Federal Reserve’s bond purchases on the overall economy. This knowledge can inform financial decisions and help navigate the ever-changing economic landscape.
Next, let’s explore the impact that the Fed’s bond purchases have on interest rates.
Impact on Interest Rates
The Federal Reserve’s bond purchasing activities have a profound impact on interest rates. By buying bonds, the Fed increases the demand for these securities, which in turn influences the interest rates throughout the economy.
When the Federal Reserve buys bonds, it creates demand in the market. This increased demand drives up the prices of bonds. As bond prices rise, the yield on these bonds decreases, since the yield is inversely related to the price. So, when the Fed engages in bond purchases, it exerts downward pressure on interest rates.
Lower interest rates can have far-reaching effects on the economy. First and foremost, they make borrowing more affordable for individuals and businesses. Lower interest rates stimulate borrowing and encourage consumers to take out mortgages, auto loans, and other forms of credit. This increased borrowing can spur economic growth by boosting consumer spending and business investment.
Moreover, lower interest rates can also benefit businesses by reducing their capital costs. When interest rates are low, companies can borrow funds at a cheaper rate, allowing them to undertake expansion projects, invest in new technologies, and create jobs.
Additionally, lower interest rates can incentivize individuals and businesses to refinance existing debt. When interest rates decrease, homeowners may refinance their mortgages at lower rates, reducing their monthly payments and freeing up additional disposable income.
On the other hand, lower interest rates can present challenges for certain groups, such as savers and retirees. With lower interest rates, returns on savings accounts and fixed-income investments may decrease, affecting individuals who rely on these income streams for their financial security.
It is important to note that the impact of the Federal Reserve’s bond purchases on interest rates may vary depending on market conditions and other economic factors. Market expectations, inflation pressures, and global economic developments can also influence interest rates, sometimes offsetting the direct effect of the Fed’s actions.
As part of its mandate, the Federal Reserve carefully monitors and adjusts its bond purchasing activities to achieve its objectives of promoting economic growth and maintaining price stability. This includes analyzing interest rate movements and market dynamics to ensure that its policy actions are aligned with the broader economic landscape.
By understanding the interplay between the Federal Reserve’s bond purchases and interest rates, investors and individuals can anticipate how changes in interest rates may influence their financial decisions. Whether it’s deciding to refinance a mortgage or exploring investment opportunities, awareness of interest rate dynamics is crucial for making informed choices.
Next, let’s explore the relationship between the Fed’s bond purchases and inflationary or deflationary pressures in the economy.
Inflation and Deflationary Pressures
The Federal Reserve’s bond purchasing activities can have significant implications for inflation and deflationary pressures in the economy. These effects arise from the increased money supply and the influence on interest rates resulting from the Fed’s bond purchases.
When the Federal Reserve buys bonds, it increases the money supply by injecting liquidity into the financial system. This infusion of funds can stimulate spending as individuals and businesses have more access to credit. Increased consumer spending and business investment can lead to higher demand for goods and services, potentially driving up prices.
In this way, the Fed’s bond purchases can contribute to inflationary pressures. Inflation refers to the sustained increase in the general level of prices for goods and services over time. While moderate inflation is generally seen as a sign of a healthy economy, an excessive rise in prices can erode purchasing power and impact the standard of living.
Conversely, bond purchases by the Federal Reserve can also act as a countermeasure against deflationary pressures. Deflation occurs when there is a sustained decrease in the general price level, leading to a decline in consumer spending and business investment. Deflation can hinder economic growth as consumers and businesses delay purchases in anticipation of even lower prices in the future.
By injecting liquidity into the economy through bond purchases, the Federal Reserve aims to stimulate economic activity and prevent deflationary spirals. Lower interest rates resulting from bond purchases can incentivize borrowing and spending, thereby boosting demand and mitigating deflationary pressures.
Nevertheless, it is important to note that the relationship between the Federal Reserve’s bond purchases and inflation or deflation is complex. Inflationary and deflationary factors are influenced by various economic indicators, such as consumer confidence, labor market conditions, and global economic trends.
Furthermore, the effectiveness of the Fed’s bond purchases in combating inflation or deflation depends on several factors, including the overall health of the financial system, market expectations, and the monetary policy transmission mechanism.
The Federal Reserve closely monitors inflationary and deflationary trends to ensure price stability and support economic growth. It utilizes various tools, including bond purchases, to calibrate its monetary policy and address any emerging imbalances in the economy.
Understanding the implications of the Fed’s bond purchases on inflation and deflation can help investors and individuals make informed decisions about their savings, investments, and financial planning. By keeping an eye on these trends, individuals can adjust their strategies to align with the prevailing economic conditions.
Next, let’s explore how the stock market reacts to the Federal Reserve’s bond purchasing activities.
Stock Market Reactions
The Federal Reserve’s bond purchasing activities can have a significant impact on the stock market. The stock market is influenced by a variety of factors, including investor sentiment, corporate performance, and macroeconomic conditions. The actions of the Federal Reserve, particularly its bond purchases, can directly and indirectly affect the stock market.
When the Federal Reserve buys bonds, it injects liquidity into the financial system, which can lead to increased investor demand for stocks. As interest rates decline due to the Fed’s bond purchases, investors may seek higher returns in the stock market. Lower interest rates can make stocks more attractive compared to fixed-income investments, prompting investors to allocate more of their portfolios into equities.
In addition to the direct impact on investor sentiment, the Federal Reserve’s bond purchases can stimulate economic growth. The injection of liquidity and lower interest rates resulting from bond purchases can encourage consumer spending and business investment. When businesses perform well and the economy expands, it can positively affect corporate earnings, which, in turn, may boost stock prices.
However, stock market reactions to the Federal Reserve’s bond purchases are not always straightforward. The stock market is also sensitive to other factors such as earnings reports, geopolitical events, and market sentiment. Moreover, uncertainties and surprises in the Fed’s monetary policy actions can cause volatility in the stock market.
Furthermore, the stock market may react differently to the Fed’s bond purchases depending on the phase of the economic cycle. During periods of economic expansion, the stock market may respond positively to the Fed’s actions as it signals support for economic growth. Conversely, during periods of economic contraction or uncertainty, the stock market may view the Fed’s bond purchases as a reflection of underlying weaknesses in the economy.
Given the importance of the Federal Reserve’s actions to the overall economy, stock market participants closely monitor the central bank’s bond purchasing activities and try to anticipate their impact. Market participants analyze statements and clues provided by the Federal Reserve to gauge the trajectory of its policy actions, as well as economic data that may influence the Fed’s decisions.
Investors and individuals should be aware that stock market reactions to the Federal Reserve’s bond purchases can be temporary or uncertain. It is essential to consider a broad range of factors, conduct thorough research, and seek professional guidance when making investment decisions in the stock market.
Next, let’s delve into potential risks and concerns associated with the Federal Reserve’s bond purchasing activities.
Potential Risks and Concerns
While the Federal Reserve’s bond purchasing activities serve as a critical tool to support economic growth and stability, there are potential risks and concerns associated with these actions. It is important to be aware of these factors to have a comprehensive understanding of the broader implications.
One of the concerns is the potential impact on inflation. As the Federal Reserve buys bonds and injects liquidity into the financial system, there is a risk that excessive money supply growth can lead to inflationary pressures. If inflation rises too quickly, it can erode purchasing power, reduce the value of savings, and create economic instability.
Furthermore, the Federal Reserve’s bond purchases can contribute to the distorting of asset prices. As the central bank buys bonds, it increases demand for these securities, which can drive up prices. This can create a distortion in the bond market and other related markets, leading to misallocations of capital and potential asset bubbles.
Another concern is the potential unintended consequences of the Fed’s actions. While the aim is to stimulate economic growth, there may be unintended side effects or spillover risks. For example, low-interest rates resulting from bond purchases can incentivize excessive risk-taking in the financial markets, potentially leading to financial instability or asset price volatility.
Moreover, the Federal Reserve’s bond purchasing activities can have international implications. As the Fed buys bonds, it can weaken the value of the U.S. dollar relative to other currencies. This can impact global trade dynamics, exchange rates, and even lead to potential trade tensions or competitive devaluations.
Another risk to consider is the potential for market dependence on the Federal Reserve’s actions. Overreliance on the central bank’s bond purchases to stimulate economic growth can create a situation where market participants become overly sensitive to the Fed’s policy decisions. This dependency can make the market vulnerable to sudden shifts in sentiment and expectations, leading to heightened volatility and instability.
It is also crucial to acknowledge that the Federal Reserve’s bond purchasing activities may not always have the desired impact on the economy. The effectiveness of these actions can be influenced by various factors, such as market conditions, business and consumer sentiment, and the overall health of the financial system.
Furthermore, as the Federal Reserve unwinds its bond purchases or adjusts its monetary policy stance, there is the risk of market disruptions or negative market reactions. The timing and pace of these policy adjustments can have significant consequences for interest rates, asset prices, and market confidence.
Understanding and monitoring these risks and concerns helps market participants, policymakers, and individuals better navigate the complex economic landscape. It is crucial to consider the potential implications and be aware of the various dynamics at play when evaluating the impact of the Federal Reserve’s bond purchasing activities.
Now, let’s conclude our exploration of the effects of the Federal Reserve’s bond purchases.
Conclusion
The Federal Reserve’s bond purchasing activities have far-reaching effects on the economy, financial markets, and individuals. By buying government bonds, the central bank seeks to influence the money supply, interest rates, and stimulate economic growth.
Through bond purchases, the Federal Reserve injects liquidity into the financial system, increasing the money supply and promoting lending. This can stimulate economic activity, encourage borrowing, and support consumer spending and business investment.
The impact of the Federal Reserve’s bond purchases extends to interest rates. By creating demand for bonds, the central bank drives down interest rates, making borrowing more affordable for individuals and businesses. Lower interest rates can incentivize borrowing, spur economic growth, and benefit corporate earnings.
Additionally, bond purchases by the Federal Reserve can have implications for inflation and deflationary pressures. Increased money supply from bond purchases can contribute to inflation, while the stimulation of economic activity can help prevent deflationary spirals.
The stock market is also influenced by the Federal Reserve’s bond purchases. Lower interest rates resulting from bond purchases can make stocks more attractive to investors, potentially boosting stock prices. However, other factors such as market sentiment and economic conditions also impact the stock market.
While the Federal Reserve’s bond purchases are aimed at supporting economic growth and stability, there are potential risks and concerns. These include the potential for inflation, distortions in asset prices, unintended consequences, international implications, market dependency, and the effectiveness of these actions.
Having a thorough understanding of the implications and consequences of the Federal Reserve’s bond purchases is crucial for investors, economists, and individuals alike. It allows for informed decision-making, helps navigate market dynamics, and better prepares for changes in the economic landscape.
As the Federal Reserve continues to manage monetary policy and adjust its bond purchasing activities, ongoing monitoring and analysis are key. By staying informed and aware of the broader implications, individuals can navigate the effects of the Federal Reserve’s bond purchases and make sound financial decisions.