Home>Finance>How To Calculate Dividends From The Income Statement


Finance
How To Calculate Dividends From The Income Statement
Published: January 2, 2024
Learn how to calculate dividends from the income statement in finance. Understand the importance of this financial metric for investors and make informed decisions.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of dividends! Dividends are the distribution of a company’s earnings to its shareholders, and they serve as a reward for investors and a way for companies to share their profits. If you’re interested in understanding how dividends are calculated from the income statement, you’ve come to the right place.
Dividends are an integral part of investing, whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out. They provide a steady stream of income and can significantly contribute to the overall returns of your investment portfolio. However, it’s important to have a clear understanding of how dividends are calculated to make informed investment decisions.
In this article, we will break down the process of calculating dividends from the income statement, step by step. We will explore the key components of the income statement and how they relate to dividends. By the end of this article, you will have the knowledge to confidently calculate dividends and make better decisions regarding your investment strategy.
Whether you’re an individual investor seeking regular income or a financial analyst analyzing the dividend payout ratio for a company, understanding how to calculate dividends is essential. So, let’s dive into the world of dividends and discover the steps involved in calculating them from the income statement.
Understanding Dividends
Before we delve into the technicalities of calculating dividends from the income statement, let’s first establish a solid understanding of what dividends are and why they are important.
Dividends represent a portion of a company’s profits that are distributed to its shareholders. They are typically paid out in cash, although some companies may choose to issue dividends in the form of additional shares of stock or other assets. Dividends serve as a way for companies to reward their shareholders for their investment and generate shareholder loyalty.
Investors often view dividends as a source of passive income. By investing in dividend-paying stocks, individuals can receive regular cash payments, providing a stable income stream. Dividends can be particularly attractive for long-term investors who are seeking to generate income and increase the value of their investment portfolios.
When considering dividends, it’s important to understand that not all companies pay dividends. Growth-oriented companies, especially those in emerging industries, may choose to reinvest their profits back into the business instead of distributing them to shareholders. These companies typically prioritize expansion and development over providing immediate returns to investors.
Dividends are not only beneficial for individual investors but can also influence the overall market. The announcement of dividend payments can impact stock prices, as investors often react positively to companies with a track record of consistent and increasing dividend payments. Dividends can also signal the financial health and stability of a company, attracting potential investors and instilling confidence in existing shareholders.
Now that we have a solid understanding of dividends and their significance let’s move on to the step-by-step process of calculating dividends from the income statement.
Step 1: Obtain the Income Statement
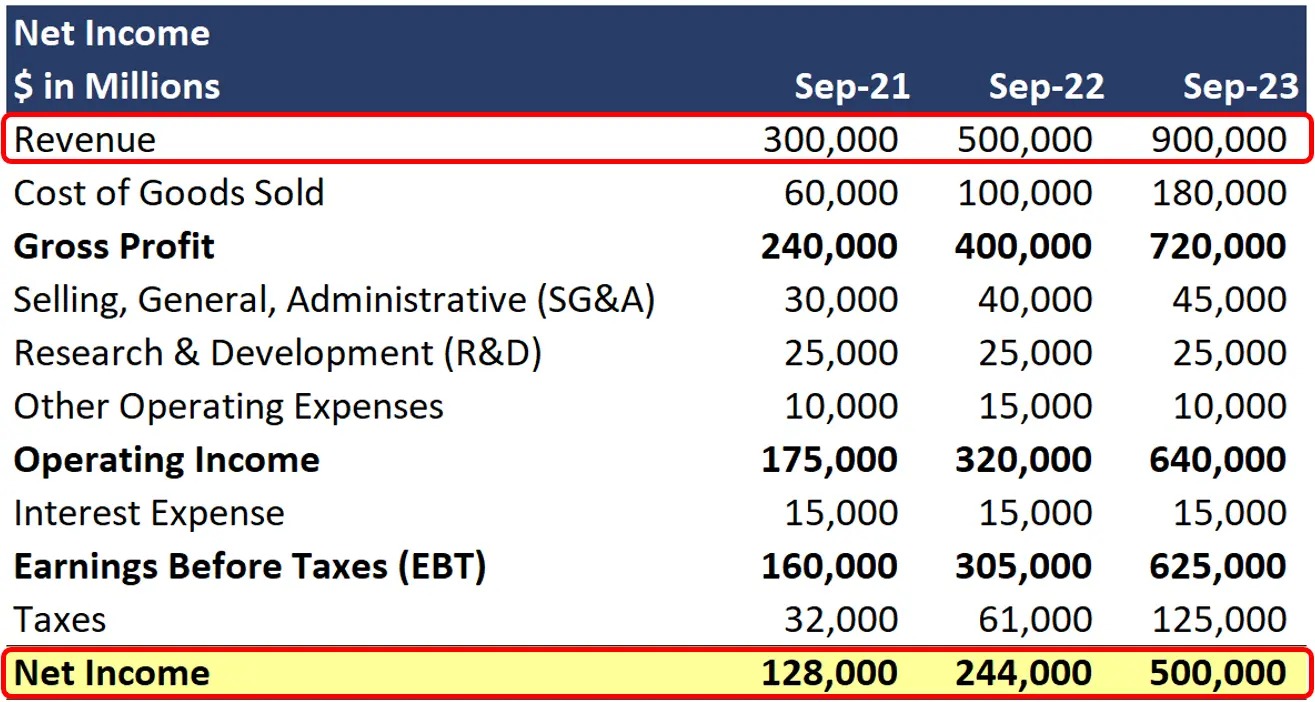
The first step in calculating dividends from the income statement is to obtain a copy of the company’s income statement. The income statement, also known as the profit and loss statement, provides a summary of the company’s revenues, expenses, and net income for a specific period.
You can typically find the income statement in a company’s annual report or quarterly financial statements, which are accessible through the company’s investor relations website or financial news portals. If you’re unable to locate the income statement, you can reach out to the company’s investor relations department for assistance.
The income statement consists of various line items, such as revenues, cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and taxes, all of which contribute to determining the company’s net income. Net income is a crucial component in calculating dividends.
Once you have obtained the income statement, you can move on to the next step.
Key points to remember:
- The income statement provides a summary of the company’s revenues, expenses, and net income for a specific period.
- You can find the income statement in the company’s annual report or quarterly financial statements.
- Net income is an essential component in calculating dividends.
Step 2: Identify the Net Income
Once you have obtained the income statement, the next step in calculating dividends is to identify the net income. Net income is the company’s total revenue minus all expenses and taxes. It represents the profit that the company has generated during a specific period, such as a quarter or a year.
On the income statement, you will typically find the net income listed as a separate line item towards the bottom. It may be labeled as “Net Income,” “Net Profit,” or “Earnings After Tax.” This figure reflects the company’s profitability and serves as a crucial component in determining the dividends that will be distributed to shareholders.
It’s important to note that net income is calculated after accounting for various expenses, such as operating expenses, cost of goods sold, depreciation, and taxes. These deductions are necessary to accurately reflect the company’s profitability and the amount available for distribution to shareholders.
Net income is typically presented as an absolute dollar amount or as earnings per share (EPS), which is the net income divided by the number of outstanding shares of the company. Earnings per share is an important metric frequently used to assess a company’s financial performance and growth potential.
By identifying the net income from the income statement, you have now established the foundation for calculating dividends. In the next step, we will determine the dividend payout ratio to understand how much of the net income is distributed to shareholders.
Key points to remember:
- Net income is calculated by subtracting expenses and taxes from the company’s total revenue.
- It represents the company’s profit during a specific period.
- The net income is usually listed as a separate line item on the income statement.
- Net income can be presented as an absolute amount or as earnings per share.
Step 3: Determine the Dividend Payout Ratio
After identifying the net income, the next step in calculating dividends is to determine the dividend payout ratio. The dividend payout ratio is a financial metric that indicates the percentage of a company’s earnings paid out to shareholders in the form of dividends. It represents the portion of net income that the company chooses to distribute to its shareholders.
To calculate the dividend payout ratio, divide the amount of dividends paid by the net income. The formula for the dividend payout ratio is:
Dividend Payout Ratio = Dividends Paid / Net Income
The dividend payout ratio is expressed as a percentage. For example, if a company has a net income of $1,000,000 and pays out $200,000 in dividends, the dividend payout ratio would be 20%.
The dividend payout ratio provides insights into a company’s dividend policy and financial health. A higher dividend payout ratio indicates that a larger portion of the company’s profits is being distributed to shareholders. It may be a positive sign for income-seeking investors, as it suggests a commitment to regular dividend payments.
However, a high dividend payout ratio may also indicate that the company is not reinvesting enough in its growth and expansion. On the other hand, a lower dividend payout ratio suggests that the company is retaining a significant portion of its earnings for future investments and strategic initiatives.
It’s important to note that the dividend payout ratio can vary across industries and among companies within the same sector. Some mature companies in stable industries may have higher dividend payout ratios, while younger growth-focused companies may have lower ratios as they prioritize reinvesting profits back into the business.
By determining the dividend payout ratio, you can gain a better understanding of how much of the company’s net income is allocated towards dividends. In the next step, we will use this ratio to calculate the actual dividend amount.
Key points to remember:
- The dividend payout ratio is the percentage of net income paid out as dividends.
- It is calculated by dividing dividends paid by net income.
- A higher dividend payout ratio indicates a greater portion of profits being distributed to shareholders.
- The ratio can vary across industries and companies.
Step 4: Calculate Dividends
Once you have determined the dividend payout ratio, you can move on to the final step of calculating dividends. In this step, you will use the dividend payout ratio and the net income to calculate the actual dividend amount that will be distributed to shareholders.
To calculate dividends, multiply the net income by the dividend payout ratio. The formula for calculating dividends is:
Dividends = Net Income * Dividend Payout Ratio
For example, if a company has a net income of $2,000,000 and a dividend payout ratio of 40%, the calculation would be:
Dividends = $2,000,000 * 0.40 = $800,000
In this example, the company would distribute $800,000 in dividends to its shareholders.
It’s important to note that the calculated dividend amount represents the total dividends to be distributed. This amount can be further divided among the individual shareholders based on their ownership stakes or the company’s dividend policy.
Dividends can be distributed on a regular basis, such as quarterly or annually, or as a one-time special dividend. The frequency of dividend payments and the exact amount are determined by the company’s board of directors, who consider various factors, including financial performance, cash flow, growth plans, and shareholder expectations.
Calculating dividends allows investors to estimate the potential income they can expect to receive from their investments. It is important to keep in mind that dividends are not guaranteed and can fluctuate based on the company’s financial performance and economic conditions.
Key points to remember:
- Dividends are calculated by multiplying net income by the dividend payout ratio.
- The dividend payout ratio represents the percentage of net income allocated for dividends.
- The calculated dividend amount is the total dividends to be distributed.
- Dividends can be distributed on a regular or one-time basis.
- Dividend amounts are determined by the company’s board of directors.
Example Calculation
To further illustrate the process of calculating dividends from the income statement, let’s consider an example.
Suppose XYZ Company has an income statement for the year 2021. The company’s net income for the year is $1,500,000. XYZ Company has a dividend payout ratio of 30%, indicating that it distributes 30% of its net income as dividends.
Using the formula mentioned earlier, we can calculate the dividends:
Dividends = Net Income * Dividend Payout Ratio
Dividends = $1,500,000 * 0.30 = $450,000
In this example, XYZ Company would distribute $450,000 in dividends to its shareholders for the year 2021.
It’s important to note that this is a simplified example and does not take into consideration other factors that may affect the dividend calculation, such as outstanding shares or any adjustments for preferred stock dividends. Additionally, companies may have different dividend policies that can influence the actual dividend amount.
Calculating dividends provides investors with valuable insights into the potential income they can expect from their investments in dividend-paying stocks. It also allows investors to compare companies in the same industry and evaluate their dividend policies.
Keep in mind that this example is for illustrative purposes only. When analyzing a real company’s dividends, it is essential to consider the specific details provided in the company’s financial statements and consult with a financial professional if needed.
Key points to remember:
- An example calculation helps illustrate the process of calculating dividends.
- Consider a company with a net income of $1,500,000 and a dividend payout ratio of 30%.
- Using the formula, we calculate dividends as $450,000 for the year.
- Remember that real-life calculations may involve additional factors and considerations.
Conclusion
Calculating dividends from the income statement is a fundamental process that allows investors and financial analysts to understand how much of a company’s earnings are distributed to shareholders. By following the step-by-step procedure outlined in this article, you can confidently calculate dividends and make informed investment decisions.
Understanding dividends and their calculation is crucial for investors seeking regular income from their investments. Dividends not only provide a steady stream of cash flow but also serve as a way to participate in the success and profitability of a company.
Remember, the process of calculating dividends begins with obtaining the income statement, identifying the net income, determining the dividend payout ratio, and finally calculating the actual dividend amount. It’s important to consider variations in dividend policies across different companies and industries.
While dividends can be an appealing aspect of investing, it’s important to conduct thorough research and analysis before making any investment decisions. Consider factors such as the company’s financial health, dividend history, growth prospects, and overall market conditions.
Additionally, keep in mind that dividends are not guaranteed and can fluctuate based on various factors. Companies may choose to increase, decrease, or even suspend dividend payments, depending on their financial performance and strategic priorities.
By understanding how to calculate dividends, you can evaluate the income potential and financial stability of companies in your investment portfolio. Remember to stay updated with the latest financial statements and consult with a financial advisor for personalized investment advice.
Now that you have the knowledge and tools to calculate dividends from the income statement, you can confidently analyze dividend-paying companies and make informed investment decisions.
Additional Resources
Want to dive deeper into the world of dividends and financial analysis? Here are some additional resources that can further enhance your understanding and help you make well-informed investment decisions:
- Investopedia: An online resource for financial education, Investopedia offers a comprehensive guide on dividends, including definitions, calculations, and strategies for dividend investing. Visit www.investopedia.com to explore their dividend-related content.
- Financial Statements: Understanding financial statements is essential for calculating dividends. Consider exploring resources that provide in-depth explanations on income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements to develop a holistic understanding of a company’s financial health.
- Company Investor Relations Websites: Visit the investor relations section of individual company websites to access their annual reports, financial statements, and dividend policies. This will help you gain insights into specific companies and their dividend-related information.
- Financial News Portals: Stay updated with the latest financial news through reputable financial news portals such as Bloomberg, CNBC, or Reuters. These sources often provide coverage on dividend announcements, changes in dividend policies, and market trends related to dividends.
- Books on Dividend Investing: Explore books that focus on dividend investing strategies and case studies. Some popular titles include “The Little Book of Big Dividends” by Charles B. Carlson and “The Ultimate Dividend Playbook” by Josh Peters.
These additional resources will expand your knowledge base on dividends and equip you with the tools to analyze companies and make sound investment decisions. Remember, continuous learning and research are key to successful investing.