
Finance
4-Part Test: What Qualifies For R&D Tax Credit
Published: January 4, 2024
Learn if your finance activities qualify for the R&D tax credit with our 4-part test. Maximize your tax savings and boost your bottom line.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Part 1: Overview of R&D Tax Credit
- Part 2: The 4-Part Test
- 1 Substantially All Test
- 2 Process of Experimentation
- 3 Technological in Nature
- 4 Elimination of Uncertainty
- Part 3: Qualifying Activities and Expenses
- 1 Research Expenses
- 2 Wages
- 3 Supply Expenses
- 4 Contract Research Expenses
- 5 Basic Research Payments
- Part 4: Documentation and Reporting
- 1 Record-keeping Requirements
- 2 Proper Documentation
- 3 Filing for the R&D Tax Credit
- Conclusion
Introduction
Welcome to the world of R&D Tax Credit! In today’s competitive business landscape, companies of all sizes are constantly striving to innovate and stay ahead of the curve. To encourage and support research and development activities, governments around the world have implemented tax incentives, such as the R&D Tax Credit.
The R&D Tax Credit is a powerful tool that helps businesses offset some of the costs associated with qualifying research and development activities. By taking advantage of this credit, companies can not only drive innovation but also improve their bottom line by reducing their tax liability.
However, understanding and navigating the intricacies of the R&D Tax Credit can be daunting. That’s where this four-part article series comes in. In this series, we will take a deep dive into the qualification criteria, eligible expenses, and documentation requirements for the R&D Tax Credit.
Whether you are a business owner, accountant, or tax professional, this series will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of what qualifies for the R&D Tax Credit and how you can maximize its benefits.
Let’s get started with Part 1, where we will provide an overview of the R&D Tax Credit and its significance for businesses.
Part 1: Overview of R&D Tax Credit
The R&D Tax Credit is a tax incentive provided by governments to encourage companies to invest in research and development activities. It is designed to reward businesses that are actively striving to advance technology, improve processes, and drive innovation. By reducing the tax burden associated with R&D expenses, governments aim to spur economic growth and stimulate technological progress in various industries.
The R&D Tax Credit is available in countries such as the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, Australia, and many others. Each country has its own specific eligibility criteria and guidelines, but the underlying goal is the same – to support and incentivize research and development.
One of the key benefits of the R&D Tax Credit is that it allows businesses to recoup a portion of their qualified R&D expenses. These expenses can include wages paid to employees involved in R&D activities, costs of materials and supplies used in R&D, overhead expenses directly associated with R&D, and even certain contract research expenses.
It’s important to note that the R&D Tax Credit is not limited to technology or science-based industries. It is applicable to a wide range of sectors, including manufacturing, software development, engineering, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and more. Whether you are developing new products, improving existing processes, or conducting innovative research, you may be eligible for the R&D Tax Credit.
By taking advantage of the R&D Tax Credit, companies can not only reduce their tax liability but also reinvest the savings into further research and development. This creates a cycle of innovation, fostering growth and competitiveness in the marketplace.
In the next part of our series, we will delve into the four-part test that businesses must satisfy in order to qualify for the R&D Tax Credit. Understanding these requirements is crucial for maximizing your eligibility and ensuring compliance with the tax laws. Let’s explore this in Part 2: The 4-Part Test.
Part 2: The 4-Part Test
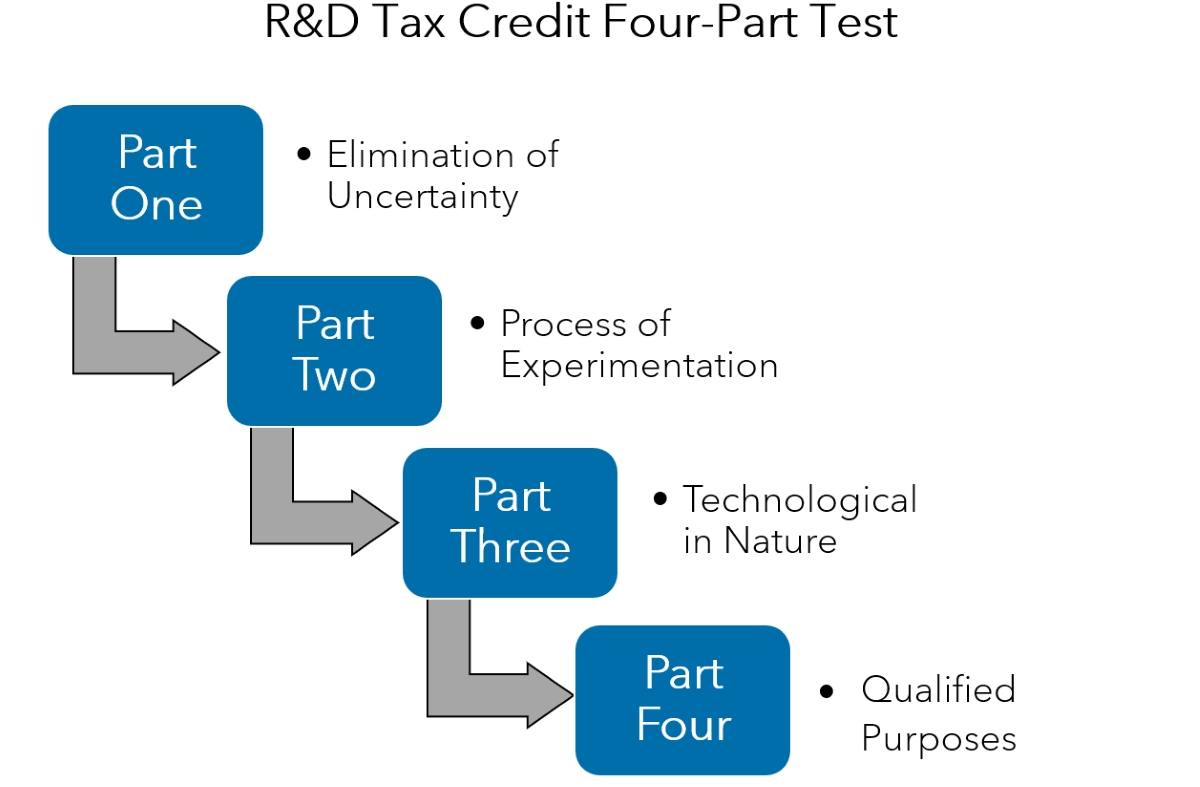
The 4-Part Test is a set of criteria that businesses must meet to qualify for the R&D Tax Credit. These criteria are designed to determine the eligibility of research and development activities and ensure that they meet the necessary requirements for claiming the credit. Let’s dive into each part of the test:
2.1 Substantially All Test
The first part of the test, known as the “Substantially All” test, requires that the research activities undertaken by the business be intended to discover information that is technological in nature and that the activities must constitute a process of experimentation.
In simpler terms, this means that the majority of the business’s research efforts must be focused on developing new or improved technologies, products, or processes that involve a systematic approach to testing and evaluation. Under this part of the test, routine data collection or ordinary product testing would not qualify for the R&D Tax Credit.
2.2 Process of Experimentation
The second part of the test is the “Process of Experimentation.” This criterion requires that the business engage in a systematic process of trial and error, evaluating different alternatives, and gathering empirical evidence to resolve technical uncertainties. The experimentation must rely on principles of engineering, physical, biological, or computer sciences.
Essentially, this part of the test ensures that the research activities involve a scientific or technical method to overcome technological challenges and uncertainties. It emphasizes the importance of experimenting and iterating to achieve a desired outcome.
2.3 Technological in Nature
The third part of the test requires that the research activities be “Technological in Nature.” This means that the research must fundamentally rely on principles of engineering, physical, biological, or computer sciences.
Whether it’s developing new software, creating innovative medical devices, or improving manufacturing processes, the research activities must have a technological basis. This part of the test ensures that the R&D Tax Credit is targeted towards activities that drive technological advancement and innovation.
2.4 Elimination of Uncertainty
The final part of the test is the “Elimination of Uncertainty” criterion. This criterion requires that the research activities aim to eliminate uncertainty regarding the development or improvement of a product, process, or technology.
Uncertainty refers to situations where the business is uncertain about the capability or method for achieving a desired outcome, or about the appropriateness of the design for a particular purpose. The research activities must involve a systematic approach to resolving these uncertainties through the process of experimentation.
By meeting the requirements of the 4-Part Test, businesses can demonstrate that their research activities are eligible for the R&D Tax Credit. In the next part of our series, we will explore the specific qualifying activities and expenses that can be claimed under this credit. Stay tuned for Part 3: Qualifying Activities and Expenses.
1 Substantially All Test
The Substantially All Test is the first part of the 4-Part Test that businesses must satisfy to qualify for the R&D Tax Credit. This test assesses whether the research activities undertaken by the business meet the criteria of being technological in nature and constituting a process of experimentation.
To pass the Substantially All Test, the research activities must be primarily focused on discovering information that is technological in nature. This means that the activities must involve the development of new or improved products, processes, or software that require technical knowledge and expertise.
Additionally, the research activities must constitute a process of experimentation. This involves developing and testing hypotheses, evaluating different alternatives, and systematically gathering data to resolve technical uncertainties. The process of experimentation must be systematic and well-documented, demonstrating a structured approach to problem-solving and innovation.
It’s important to note that routine data collection or ordinary product testing does not qualify as eligible research activities for the R&D Tax Credit. The activities must go beyond routine or commonly known practices and involve a level of technical risk and experimentation.
A key consideration when applying the Substantially All Test is the degree of emphasis and resources dedicated to qualified research activities. While there is no specific threshold, it is generally expected that a significant portion of the company’s research efforts should be allocated towards the development or improvement of technology-driven products or processes.
Ultimately, the Substantially All Test aims to identify and reward businesses that invest substantial time, effort, and resources into research and development that drives technological advancements. By meeting this test, companies can demonstrate their eligibility for the R&D Tax Credit and access the financial benefits associated with it.
In the next part of our series, we will delve into the second part of the 4-Part Test: the Process of Experimentation. This criterion assesses the systematic approach businesses take to trial and error, evaluation of alternatives, and gathering empirical evidence to resolve technical uncertainties. Stay tuned for Part 2.2: Process of Experimentation.
2 Process of Experimentation
The second part of the 4-Part Test for the R&D Tax Credit is the “Process of Experimentation.” This criterion assesses the systematic approach businesses take to trial and error, evaluation of alternatives, and gathering empirical evidence to resolve technical uncertainties.
The Process of Experimentation involves conducting research activities that rely on principles of engineering, physical, biological, or computer sciences. It requires businesses to engage in a structured and iterative process that allows for testing different hypotheses and exploring various alternatives to achieve the desired outcome.
To meet this criterion, businesses must document their process of experimentation. This documentation should outline the steps taken to identify the technical uncertainties, define objectives, develop and test hypotheses, evaluate alternatives, and analyze the results. It should also include information about the methodologies, tools, and technologies used in the experimentation process.
The research activities should go beyond routine and commonly known practices. They should involve a level of technical risk and the possibility of failure. This means that the business is pushing boundaries, exploring new approaches or technologies, and taking calculated risks to overcome technical challenges.
Importantly, the Process of Experimentation does not require that a successful outcome is achieved. Even if the experimentation does not yield the desired result, as long as it meets the systematic approach to testing and evaluation, it can still be considered eligible for the R&D Tax Credit.
Examples of activities that can demonstrate the Process of Experimentation include prototyping, testing different materials or components, conducting simulation studies, developing and refining algorithms or software code, and running controlled experiments to validate hypotheses.
By fulfilling the Process of Experimentation criterion, businesses can demonstrate that they are actively seeking technological advancements and innovative solutions. This showcases their commitment to pushing boundaries, solving technical challenges, and driving progress in their respective industries.
In our next installment, we will explore the third part of the 4-Part Test: Technological in Nature. This criterion ensures that the research activities are based on principles of engineering, physical, biological, or computer sciences. Stay tuned for Part 2.3: Technological in Nature.
3 Technological in Nature
The third part of the 4-Part Test for the R&D Tax Credit is the “Technological in Nature” criterion. This criterion ensures that the research activities being carried out by a business have a technological basis and rely on principles of engineering, physical, biological, or computer sciences.
To meet this criterion, the research activities must be grounded in a scientific or technical discipline. They should involve the application of scientific knowledge and methodologies to develop or improve products, processes, or software. Whether it’s creating new algorithms, developing innovative medical devices, or enhancing manufacturing techniques, the research must demonstrate the integration of technological principles.
The Technological in Nature criterion recognizes that technological advancements are critical drivers of innovation and economic growth. It ensures that the R&D Tax Credit is targeted towards activities that contribute to improving and advancing technology.
It’s important to note that research activities that focus solely on market research, social sciences, humanities, or general business operations do not satisfy the Technological in Nature criterion. The primary focus should be on the application of technical or scientific principles to solve technical challenges and drive technological advancements.
Examples of research activities that fulfill the Technological in Nature criterion include developing new software algorithms, designing and testing prototypes, conducting scientific experiments, creating innovative materials, or exploring new technologies to improve product performance.
When documenting research activities, businesses should emphasize the technical aspects of the work and highlight the scientific or engineering principles applied. Providing detailed explanations of how the research aligns with technological principles and contributes to advancing technology will strengthen the case for meeting the Technological in Nature criterion.
By meeting this criterion, businesses can demonstrate that their research activities meet the necessary technological standards and are eligible for the R&D Tax Credit. In the next part of our series, we will explore the fourth and final part of the 4-Part Test: the Elimination of Uncertainty. Stay tuned for Part 2.4: Elimination of Uncertainty.
4 Elimination of Uncertainty
The final part of the 4-Part Test for the R&D Tax Credit is the “Elimination of Uncertainty” criterion. This criterion requires that the research activities aim to resolve technical uncertainties regarding the development or improvement of a product, process, or technology.
Uncertainty refers to situations where the business is uncertain about the capability or method for achieving a particular outcome, or about the appropriateness of the design for a specific purpose. The research activities under this criterion should be focused on addressing and resolving these uncertainties through a systematic approach.
The Elimination of Uncertainty criterion encourages businesses to undertake research and development activities that involve a degree of technical risk and require innovative solutions to overcome challenges. It recognizes that uncertainty is inherent in the pursuit of technological advancements and rewards businesses for successfully resolving these uncertainties.
It’s important to note that the research activities should be aimed at eliminating uncertainties that are technical in nature. This means that the uncertainties should be related to the development, improvement, or application of technological knowledge. Uncertainties regarding market demand, consumer behavior, or economic factors typically do not meet the requirements of this criterion.
When documenting research activities, it is crucial to outline the specific uncertainties that were addressed and describe how the experimentation process helped in resolving them. This can include detailing the hypotheses tested, the data gathered, and the analysis performed to mitigate or eliminate the uncertainties.
Examples of uncertainties that can be addressed through research and development activities include the feasibility of a new technology, the performance of a product under certain conditions, the scalability of a manufacturing process, or the compatibility of different components or systems.
By demonstrating the Elimination of Uncertainty in their research activities, businesses can showcase their commitment to overcoming technical challenges and driving innovation. This criterion ensures that the R&D Tax Credit is rewarded to companies that actively engage in research and development efforts with the goal of resolving technical uncertainties.
In the next part of our series, we will shift focus to the specific qualifying activities and expenses that can be claimed under the R&D Tax Credit. Stay tuned for Part 3: Qualifying Activities and Expenses.
Part 3: Qualifying Activities and Expenses
In Part 3 of our series on the R&D Tax Credit, we will explore the specific activities and expenses that qualify for this tax incentive. These qualifying elements play a crucial role in determining the eligibility and the amount of the credit that a business can claim.
3.1 Research Expenses
Research expenses include direct costs incurred in carrying out qualified research activities. These can include expenses related to materials and supplies, equipment, facilities, and even certain contract research expenses. It’s important to note that the expenses must be directly attributable to the research activities and reasonable in amount.
3.2 Wages
Wages paid to employees involved in qualified research activities can also be considered as qualifying expenses. This can include wages for employees directly conducting research, as well as wages for employees providing direct support, supervision, or assistance to the researchers. Both regular and overtime wages can be included in this category.
3.3 Supply Expenses
Supply expenses encompass the cost of materials and supplies that are used or consumed in the research activities. This can include items like chemicals, lab equipment, testing materials, prototypes, and any other necessary supplies. These expenses need to be directly related to the qualified research activities.
3.4 Contract Research Expenses
Contract research expenses refer to the costs incurred for research conducted by third-party contractors or outside vendors who are engaged by the business to perform qualified research activities. The expenses related to these contracts can be included as qualifying expenses, under certain conditions.
3.5 Basic Research Payments
Basic research payments made to qualified organizations, such as universities or scientific institutes, for the performance of fundamental research are also considered as qualifying expenses. These payments should be made for research conducted with the primary purpose of gaining knowledge or understanding of underlying principles, without any specific commercial application in mind.
It’s important to note that while these expenses qualify for the R&D Tax Credit, documentation and substantiation of these costs are crucial. Proper record-keeping and documentation of the expenses incurred and their direct correlation to qualified research activities are critical for successfully claiming the credit.
To efficiently claim the R&D Tax Credit, it’s recommended that businesses work closely with their accountants or tax professionals who have expertise in this area. They can help identify all eligible activities and expenses and ensure accurate documentation and reporting.
In the next part of our series, we will dive into the requirements and best practices for documentation and reporting when claiming the R&D Tax Credit. Stay tuned for Part 4: Documentation and Reporting.
1 Research Expenses
In order to qualify for the R&D Tax Credit, businesses can include certain research expenses as part of their eligible costs. These research expenses encompass the direct costs that are incurred in carrying out qualified research activities.
Research expenses can include a wide range of expenditures that are directly associated with the research and development efforts. These expenses must be directly attributable to the research activities and reasonable in amount. Here are some key components of research expenses:
Materials and Supplies:
This includes the costs associated with the materials and supplies that are used or consumed in the research activities. This can include items such as chemicals, lab equipment, testing materials, prototypes, and any other necessary supplies. It’s essential that these expenses are directly linked to the qualified research activities being conducted.
Equipment:
Research expenses can also include the costs of acquiring or leasing equipment that is specifically used for the research activities. This can include specialized machinery, computer hardware, software, or any other equipment that is essential for the undertaking of the research efforts.
Facilities:
When research activities require dedicated spaces or facilities, the expenses related to these locations may also be considered as part of the research expenses. This can include rental or lease payments for research labs, manufacturing facilities, or any other space utilized exclusively for the research and development initiatives.
Contract Research Expenses:
Businesses may also engage third-party contractors or outside vendors to perform certain qualified research activities on their behalf. The expenses related to these contract research arrangements, such as payments made to the contractors, can also be considered as research expenses.
It’s important to note that these research expenses must be properly documented and substantiated. Businesses should maintain detailed records and documentation that clearly demonstrate the direct correlation of these expenses to the qualified research activities being conducted. This documentation will be crucial when claiming the R&D Tax Credit and substantiating the eligible costs.
Working closely with an accountant or tax professional with expertise in the R&D Tax Credit can greatly assist in accurately identifying and documenting the eligible research expenses. They can guide businesses through the complexities of the credit and provide guidance on what expenses can be included to maximize the tax benefits.
In the next section, we will delve into another vital aspect of claiming the R&D Tax Credit: the wages paid to employees involved in the qualified research activities. Stay tuned for Section 3.2: Wages.
2 Wages
One of the key components of qualifying expenses for the R&D Tax Credit is the wages paid to employees involved in the qualified research activities. These wages can include both the compensation for employees directly engaged in the research efforts, as well as the wages for employees providing direct support, supervision, or assistance to those directly involved in the research work.
For the wages to qualify as a research expense, they must meet certain criteria:
Directly Involved in Research:
The wages of employees who are directly engaged in the qualified research activities can be considered as eligible expenses. These employees are typically involved in conducting the research, performing experiments, analyzing data, and developing prototypes. Their work directly contributes to the advancement of technological knowledge and the resolution of technical uncertainties.
Providing Support and Assistance:
In addition to employees directly involved in research, the wages of individuals providing direct support, supervision, or assistance to the research personnel can also be included. These employees may not be engaged in the hands-on research work but play a crucial role in facilitating and supporting the research efforts. Examples include project managers, team leaders, technical support staff, and administrative personnel involved in overseeing and coordinating the research activities.
Included Wages:
When calculating the wages for the R&D Tax Credit, businesses can include both regular and overtime wages paid to eligible employees during the time they were directly engaged in qualified research activities. This can include salaries, wages, commissions, and bonuses that are directly allocated to the research efforts. However, it’s important to note that fringe benefits and stock options are not eligible wages for the R&D Tax Credit.
Proper documentation and record-keeping are essential to substantiate the wages claimed for the R&D Tax Credit. Businesses should maintain accurate records that clearly establish the connection between the wages paid and the specific research activities being conducted. This documentation will play a crucial role in demonstrating the eligibility for the credit and supporting the claimed amounts.
Working with an accountant or tax professional experienced in the R&D Tax Credit can be invaluable in properly identifying and documenting the eligible wages. They can help ensure compliance with the regulations and assist in maximizing the tax benefits associated with the credit.
In the next section, we will discuss another important element of qualifying expenses for the R&D Tax Credit: supply expenses. Stay tuned for Section 3.3: Supply Expenses.
3 Supply Expenses
When it comes to qualifying expenses for the R&D Tax Credit, supply expenses play a significant role. These expenses encompass the costs incurred for the purchase of materials and supplies directly related to the research and development (R&D) activities.
Supply expenses can include a wide range of items and materials used in the course of the R&D process. Here are some key points to understand:
Materials and Consumables:
These expenses cover the costs of raw materials, components, chemicals, and other similar items that are essential for the research work. They encompass any physical materials that are used or consumed during the R&D process. Examples include metals, plastics, circuit boards, reagents, solvents, electronic components, and other specialized materials.
Testing and Prototyping:
Supply expenses also include the costs associated with creating prototypes and conducting testing during the R&D process. This can include the purchase of prototype components or materials, specialized testing equipment or software, and any other supplies needed for testing and validation purposes.
Specialized Tools and Instrumentation:
Supply expenses may include the costs of acquiring or leasing specialized tools, equipment, or instrumentation that are used exclusively for the R&D activities. These can be tools or instruments that are specifically required for the research work and not available as general-use equipment within the business.
Software and Licenses:
In cases where software is essential for the R&D activities, the expenses related to acquiring or licensing the software can also be included. This can include specialized software tools, simulation software, data analysis software, or any other software necessary for the research work.
It is important to note that for supply expenses to qualify, they must be directly tied to the qualified research activities. Documentation and proper record-keeping are crucial to substantiate the supply expenses claimed for the R&D Tax Credit. Businesses should maintain accurate records, including purchase invoices, receipts, and documentation illustrating the use of these supplies in the R&D process. This documentation will help support the eligibility of these expenses when claiming the credit.
Consulting with an experienced accountant or tax professional knowledgeable in the R&D Tax Credit can be highly beneficial. They can help identify eligible supply expenses, ensure compliance with documentation requirements, and assist in maximizing the benefits associated with the credit.
In the next section, we will explore another component of qualifying expenses for the R&D Tax Credit: contract research expenses. Stay tuned for Section 3.4: Contract Research Expenses.
4 Contract Research Expenses
Contract research expenses are an important category of qualifying expenses for the R&D Tax Credit. These expenses refer to the costs incurred when a business engages third-party contractors or outside vendors to conduct research on its behalf.
Contract research can be a valuable resource for businesses that lack the internal capabilities or expertise to carry out certain aspects of their research and development (R&D) activities. By outsourcing research tasks to specialized contractors, companies can still benefit from the expertise and technical knowledge required to advance their projects.
Here are key points to understand about contract research expenses:
Eligibility Criteria:
To be considered for the R&D Tax Credit, contract research expenses must meet certain requirements. The research conducted by the third-party contractor must qualify as eligible research activities under the guidelines set forth by the tax authority. It must also directly relate to the business’s specific project or objective.
Qualifying Expenses:
The expenses incurred for contract research can include direct costs associated with the research activities performed by the contractor. This can encompass payments made to the contractor for their services, as well as any other costs directly related to the outsourced research work.
Documentation:
Proper documentation is crucial when claiming contract research expenses for the R&D Tax Credit. Businesses should maintain records that clearly establish the nature and purpose of the contracted research, detailing the specific activities carried out, the payments made to the contractor, and any other relevant supporting documentation. This documentation will help substantiate the eligibility of the contract research expenses.
Contractual Agreements:
It is important to have clear contractual agreements in place when engaging third-party contractors for research purposes. These agreements should outline the scope of work, deliverables, timeline, payment terms, and ownership of intellectual property. Having well-drafted contracts can provide further support for the eligibility of the contract research expenses when claiming the R&D Tax Credit.
It’s worth noting that in some tax jurisdictions, there may be additional requirements or limitations on claiming contract research expenses. Consulting with an experienced accountant or tax professional who is knowledgeable in the R&D Tax Credit regulations specific to the jurisdiction can help ensure compliance with all requirements and maximize the benefits associated with the credit.
In the next section, we will discuss another aspect of qualifying expenses for the R&D Tax Credit: basic research payments made to qualified organizations. Stay tuned for Section 3.5: Basic Research Payments.
5 Basic Research Payments
Qualifying expenses for the R&D Tax Credit also include basic research payments made to qualified organizations. Basic research refers to scientific or academic research conducted with the primary purpose of gaining knowledge or understanding of underlying principles, without any specific commercial application in mind. These payments made to qualified organizations contribute to the advancement of scientific knowledge and can be considered as eligible expenses for the credit.
Here are key points to understand about basic research payments:
Eligible Organizations:
Payments made to qualified organizations, such as universities, scientific institutes, or government research agencies, for the performance of basic research can be included as qualifying expenses. These organizations typically have a focus on fundamental research and contribute to the overall advancement of scientific understanding.
Research Agreements:
To support the eligibility of basic research payments, it’s important to have formal research agreements or contracts in place with the qualified organizations. These agreements should outline the scope of the research, the funds allocated, the objectives, and any other relevant terms and conditions. Having well-documented research agreements helps substantiate the eligibility of the payments when claiming the R&D Tax Credit.
Direct Payment:
Basic research payments must be made directly to the qualified organizations conducting the research. The payments should be for the purpose of supporting the basic research efforts and not for specific development projects or commercial purposes.
Documentation:
Proper documentation is crucial for basic research payments. Businesses should maintain records that clearly establish the nature of the research being conducted, the specific organizations receiving the payments, and the purpose of the payments. This documentation helps substantiate the eligibility of the payments when claiming the R&D Tax Credit.
It’s important to consult with an experienced accountant or tax professional familiar with the regulations and requirements of the R&D Tax Credit in the specific jurisdiction. They can provide guidance on the eligibility criteria and documentation best practices for basic research payments, ensuring compliance with all the necessary guidelines.
In the next section, we will explore the importance of proper documentation and reporting when claiming the R&D Tax Credit. Stay tuned for Part 4: Documentation and Reporting.
Part 4: Documentation and Reporting
In Part 4 of our series on the R&D Tax Credit, we will discuss the importance of proper documentation and reporting when claiming the credit. As with any tax incentive, maintaining accurate records and providing comprehensive documentation is crucial to substantiate eligibility and support the claimed amount.
4.1 Record-keeping Requirements:
Businesses claiming the R&D Tax Credit must comply with record-keeping requirements as outlined by the tax authorities. This includes maintaining documentation that supports the eligibility of the research activities and expenses claimed for the credit. Relevant records should span the entire duration of the research and development projects and should be kept for a sufficient period of time as specified by local tax regulations.
4.2 Proper Documentation:
In order to substantiate the claimed activities and expenses, businesses should maintain proper documentation that clearly demonstrates the connection between the research efforts and the requirements for the R&D Tax Credit. This may include project plans, technical designs, research notes, experimental data, testing protocols, and any other relevant documentation that showcases the systematic approach to research and development.
4.3 Filing for the R&D Tax Credit:
When it comes to reporting the R&D Tax Credit, businesses need to ensure accurate and timely filing. This involves completing the necessary tax forms, such as Form 6765 in the United States, and providing the required documentation and supporting evidence for the claimed activities and expenses. It’s important to follow the specific guidelines and deadlines set by the tax authorities to avoid any potential issues or delays in claiming the credit.
Working closely with an experienced accountant or tax professional is highly advised when navigating the documentation and reporting requirements for the R&D Tax Credit. They can provide guidance on the specific documentation needed, help ensure compliance with the regulations, and maximize the benefits associated with the credit.
By maintaining proper documentation and adhering to the reporting guidelines, businesses can successfully claim the R&D Tax Credit and leverage the financial rewards associated with driving innovation and advancing technology.
With this, we conclude our four-part series on the R&D Tax Credit. By understanding the qualification criteria, eligible expenses, and documentation requirements, businesses can position themselves to take full advantage of this valuable tax incentive. Remember, staying informed and working with knowledgeable professionals is key to optimizing the benefits of the R&D Tax Credit.
1 Record-keeping Requirements
When it comes to claiming the R&D Tax Credit, one of the crucial aspects that businesses must consider is record-keeping. Properly maintaining and organizing relevant documentation is essential to substantiate the eligibility of the research activities and expenses claimed for the credit. Maintaining accurate records not only helps support the claimed amount, but also ensures compliance with the requirements set by the tax authorities.
Here are key points to understand about the record-keeping requirements for the R&D Tax Credit:
Documentation:
Businesses should maintain comprehensive documentation that demonstrates the connection between the research activities and the requirements for the R&D Tax Credit. This documentation should provide clear evidence of the systematic approach to research and development, including project plans, technical designs, research notes, experimental data, testing protocols, and any other relevant materials.
Timeliness:
It’s important to maintain records in a timely manner, ensuring that they are contemporaneous with the research activities. Records should be consistently updated and maintained throughout the duration of the project. Delays in record-keeping could result in gaps or inaccuracies that may raise concerns during an audit or review process.
Duration:
The duration for which records should be retained varies depending on the jurisdiction. It is important to review and comply with the specific regulations and guidelines outlined by the tax authorities in the respective jurisdiction. In many cases, businesses are required to retain records for a specified period of time, typically several years, after the filing of the tax return that claims the R&D Tax Credit.
Substantiate Claimed Amounts:
Accurate and detailed records can help substantiate the claimed amounts for qualified research expenses, wages, supply costs, contract research payments, and other eligible expenditures. These records provide evidence of the expenditures incurred and the activities performed, reinforcing the eligibility and the documentation required for claiming the credit.
By maintaining proper records and adhering to record-keeping requirements, businesses can demonstrate their compliance and support the legitimacy of the claimed R&D Tax Credit. Working closely with an experienced accountant or tax professional is highly recommended to ensure adherence to the specific regulations and guidelines set by the tax authorities.
Proper record-keeping not only facilitates the claiming process but also plays a critical role in providing transparency and accountability to regulatory authorities. It is an essential component for businesses seeking to maximize the benefits of the R&D Tax Credit while maintaining compliance with the applicable tax laws.
Remember, accurate and comprehensive records are key when it comes to claiming the R&D Tax Credit, and they can significantly contribute to the success of the overall tax strategy for a business.
2 Proper Documentation
When it comes to claiming the R&D Tax Credit, proper documentation is essential to substantiate the eligibility of the research activities and expenses. Accurate and comprehensive documentation not only supports the claimed amount but also helps demonstrate compliance with the requirements set by the tax authorities. It provides a clear record of the systematic approach to research and development and strengthens the case for claiming the credit.
Here are key points to understand about proper documentation for the R&D Tax Credit:
Documenting Research Activities:
Businesses should maintain thorough documentation that outlines the nature and scope of the research activities being conducted. This includes project plans, technical designs, research notes, experiment records, testing protocols, and any other relevant materials that illustrate the systematic and scientific approach undertaken during the research and development process.
Linking Expenses to Research Activities:
Clear documentation is needed to establish a direct link between the claimed research expenses and the eligible research activities. This includes records of materials and supply purchases, invoices, receipts, and any other documentation that demonstrates the connection between the expenses incurred and the specific research efforts undertaken.
Record of Employee Involvement:
It’s crucial to document the role of employees in the research activities. This includes maintaining records of employee time logs, project assignments, and any other supporting documentation that verifies their active involvement and contribution to the eligible research efforts.
Contracts and Agreements:
For any contracted research efforts, businesses should keep copies of the research agreements, scope of work, deliverables, payment information, and any other relevant contractual documentation. These documents help substantiate the eligibility of contract research expenses and establish the nature and purpose of the research conducted by external parties.
Internal Controls and Policies:
Implementing internal controls and policies can assist in maintaining proper documentation. This involves establishing processes for record-keeping, ensuring consistency in documenting research activities and expenses, and having protocols in place to securely store and manage the documentation for the required period of time.
Working closely with an experienced accountant or tax professional is highly recommended to ensure compliance with proper documentation practices for the R&D Tax Credit. They can provide guidance on the specific documentation needs, assist in organizing the necessary records, and align the documentation with the requirements set by the tax authorities.
Remember, proper documentation is crucial for substantiating the eligibility of the claimed activities and expenses, supporting compliance, and maximizing the benefits of the R&D Tax Credit. Accurate and comprehensive documentation strengthens the credibility of the claimed credits and ensures a smooth claiming process.
3 Filing for the R&D Tax Credit
When it comes to the R&D Tax Credit, proper documentation and accurate reporting are essential for successfully claiming the credit. Filing for the R&D Tax Credit involves completing the necessary tax forms and providing the required documentation and evidence to support the claimed activities and expenses. Here’s what you need to know about filing for the R&D Tax Credit:
Completing Tax Forms:
Businesses must complete the appropriate tax forms specified by the tax authorities in their jurisdiction to claim the R&D Tax Credit. In the United States, for example, Form 6765 is used to calculate and claim the credit. It’s important to accurately fill out the required information, including details about the research activities, qualified expenses, and other relevant documentation as specified in the form.
Documentation and Supporting Evidence:
During the filing process, businesses must provide proper documentation and supporting evidence for the claimed activities and expenses. This includes the documentation discussed in previous sections, such as project plans, research records, expense receipts, employee involvement documentation, and contractual agreements. The documentation serves as proof of the eligibility of research activities and qualified expenses.
Submission and Deadlines:
Businesses must adhere to the specified filing deadlines set by the tax authorities. It’s crucial to submit the R&D Tax Credit claim within the designated timeframe. Late filings may lead to penalties or the loss of the opportunity to claim the credit for that particular tax year. Therefore, it’s essential to carefully review and understand the deadlines to ensure timely submission. Working with an experienced accountant or tax professional can help facilitate compliance with the filing requirements.
Audit and Review Procedures:
The tax authorities may audit or review the R&D Tax Credit claim to ensure compliance with the regulations and substantiation of the claimed activities and expenses. During these processes, the authorities may request additional documentation or conduct interviews to verify the eligibility and accuracy of the claimed credit. Proper documentation and record-keeping practices will help facilitate the audit or review process, ensuring a smoother experience and minimizing any potential issues.
Professional Assistance:
Given the complexities of claiming the R&D Tax Credit, it’s highly recommended to work with an experienced accountant or tax professional who specializes in this area. They can guide businesses through the filing process, ensure compliance with the requirements, and maximize the benefits associated with the credit.
By following proper filing procedures, maintaining accurate documentation, and working with knowledgeable professionals, businesses can effectively navigate the filing process for the R&D Tax Credit, supporting their claim and optimizing the financial benefits of the credit.
With this, we conclude our comprehensive series on the R&D Tax Credit. Armed with a strong understanding of the qualification criteria, eligible expenses, and documentation requirements, businesses can confidently pursue and successfully claim this valuable tax incentive.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the R&D Tax Credit is a powerful incentive that encourages businesses to invest in research and development activities to drive innovation and technological advancement. It provides financial benefits by offsetting a portion of the costs associated with qualified research expenses and employee wages.
Understanding the qualification criteria, including the 4-Part Test, is crucial for businesses to determine their eligibility for the credit. The Substantially All Test, Process of Experimentation, Technological in Nature, and Elimination of Uncertainty criteria help ensure that the research activities meet the necessary requirements.
Expenses such as research expenses, wages, supply costs, contract research payments, and basic research payments can be considered as qualifying expenses for the R&D Tax Credit. Proper documentation and record-keeping are essential to substantiate these expenses and support the claimed credit amounts.
Filing for the R&D Tax Credit requires accurate reporting and timely submission of the necessary tax forms, along with providing proper documentation and supporting evidence. Adhering to the guidelines and deadlines set by the tax authorities is crucial to successfully claim the credit.
Working closely with an experienced accountant or tax professional who specializes in the R&D Tax Credit can greatly assist businesses in understanding and navigating the intricacies of the credit. They can help identify eligible activities and expenses, ensure compliance with the documentation and filing requirements, and maximize the benefits associated with the credit.
By leveraging the R&D Tax Credit, businesses can not only drive innovation and technological advancements but also improve their bottom line by reducing their tax liability. It is a valuable incentive that rewards companies for their dedication to research and development, fostering growth, competitiveness, and economic progress across various industries.
We hope this comprehensive series has provided businesses, accountants, and tax professionals with a deep understanding of the R&D Tax Credit. Armed with this knowledge, businesses can confidently pursue and capitalize on this tax incentive to support their research and development efforts.