Home>Finance>Correspondent Bank: Definition And How It Works


Finance
Correspondent Bank: Definition And How It Works
Published: November 3, 2023
Learn about correspondent banks and how they operate in the world of finance. Understand their role in facilitating international transactions and connecting financial institutions.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Understanding Correspondent Banks: What You Need to Know
When it comes to managing finances, there are numerous terms and concepts that can seem overwhelming. One such term is “correspondent bank.” If you’ve ever wondered what a correspondent bank is and how it functions, you’re in the right place. In this article, we’ll delve into the definition of a correspondent bank and shed light on its inner workings.
Key Takeaways:
- A correspondent bank acts as an intermediary between two financial institutions, facilitating various banking services and transactions.
- Correspondent banking relationships are vital for international trade and cross-border transactions.
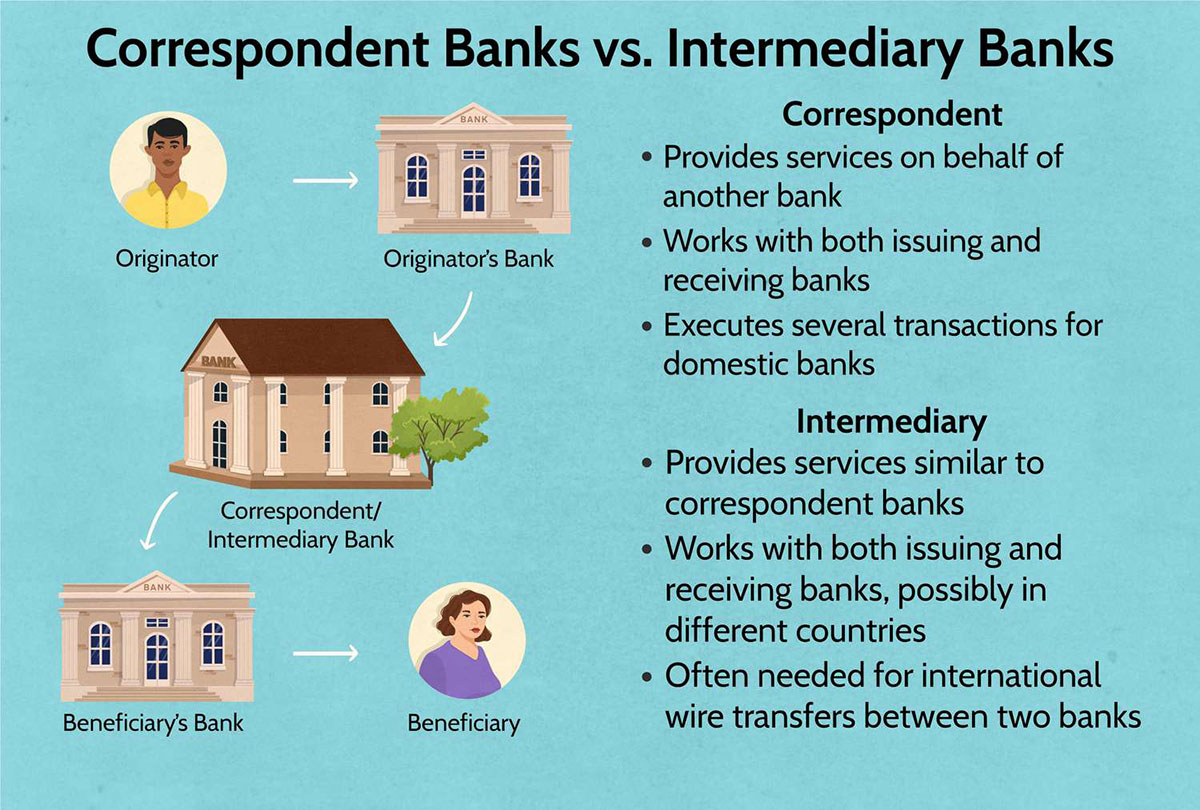
What is a Correspondent Bank?
A correspondent bank is a financial institution that provides services on behalf of another financial institution, typically in a different country or location. It acts as an intermediary to facilitate transactions and banking services between the two institutions. Correspondent banks play a crucial role in enabling global financial connectivity.
Financial institutions establish correspondent banking relationships to expand their market reach and provide more extensive banking services to their customers. By partnering with correspondent banks, they gain access to services such as international wire transfers, foreign exchange transactions, cash management, and trade financing.
How Does Correspondent Banking Work?
Let’s break down the process of correspondent banking into a few key steps:
- Establishing a Relationship: Financial institutions initiate a correspondent banking relationship by signing agreements and contracts. This lays the foundation for collaboration and outlines the terms and conditions of their partnership.
- Account Management: Correspondent banks hold accounts for their partner financial institutions to facilitate transactions. These accounts may be denominated in various currencies to support international trade.
- Payment Settlement: When a customer of the partner financial institution initiates a transaction, the funds are transferred to the correspondent bank’s account. The correspondent bank then processes the payment or wire transfer on behalf of the partner institution.
- Cash Management: Correspondent banks also provide cash management services, helping financial institutions manage their liquidity, optimize working capital, and mitigate risks.
- Trade Finance: For institutions engaged in international trade, correspondent banks offer trade financing solutions such as issuing letters of credit, providing guarantees, and facilitating trade settlements.
- Compliance and Anti-Money Laundering: Correspondent banks play a crucial role in ensuring compliance with international regulations and anti-money laundering procedures, enhancing the security and credibility of cross-border transactions.
The Importance of Correspondent Banking
Correspondent banking is instrumental in promoting international trade and fostering economic growth. It enables financial institutions to facilitate transactions across borders, access foreign markets, and provide comprehensive banking services to their customers.
For developing countries or regions with limited banking infrastructure, correspondent banking relationships play an even more critical role. They help bridge the gap between local financial institutions and the global banking network, facilitating cross-border remittances and access to international markets.
Conclusion
Correspondent banks act as linchpins of the global financial system, connecting financial institutions across borders and enabling seamless international transactions. By understanding the definition and inner workings of correspondent banks, individuals can gain a clearer picture of how the global financial ecosystem operates. Embracing the role of correspondent banks in facilitating international trade and financial connectivity can help foster economic growth and prosperity.