Home>Finance>Everything You Need To Know About Retained Earnings
Finance
Everything You Need To Know About Retained Earnings
Modified: September 6, 2023
Learn all about retained earnings and find out why they are as valuable as your net and gross income with our helpful guide.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
You might already be familiar with your net income and how to calculate it, but do you also know your retained earnings? It is important to know this aside from your revenue to evaluate your company’s financial health. With that being said, here is everything you need to know about retained earnings.
Definition Of Retained Earnings
Retained earnings or RE refers to the cumulative amount of net income left after dividends go to the shareholders. These leftover profits become part of the earnings from the beginning of the year. Businesses can generate earnings that are positive or negative, these are your profits or losses.

Photo by Steve Buissinne from Pixabay
Positive profits often go to shareholders or into the company for growth. It gives a lot of room for management or business owner/s to use the surplus money earned. The amount of money not paid to shareholders counts as retained earnings. These earnings also show whether the company can invest in itself and is genuinely profitable.
Where Do REs Come From
The balances in a company’s accounts form part of computing the net income at the end of an accounting year. These accounts range from revenues and gains to expenses and losses. Those account balances then go to the Retained Earnings account.
When the revenue and gain exceeds expenses and losses for the year, the company will have a positive net income. This causes an increase of balance in the Retained Earnings account.
If the company has fewer revenues and gains than the losses and expenses, the net loss will reduce the normal credit balance in the Retained Earnings account. There is also a decrease in the balance of the RE account when the company declares a cash dividend.
Retained Earnings Formula
The RE formula is as follows:
RE = Beginning Retained Earnings + (Net Income or Losses) – Cash Dividends – Stock Dividends
Beginning of Period Retained Earnings – At the end of every accounting year, REs act as the accumulated income from the previous year on the balance sheet. This includes the income of the current year minus the dividends paid to shareholders.
In the next accounting cycle, the RE ending balance from the prior period will now become the beginning of period retained earnings.
The RE balance is not always a positive number because it may reflect the greater net loss of the current period rather than that of the beginning balance. A large distribution of dividends exceeding the RE balance can cause it to go negative.
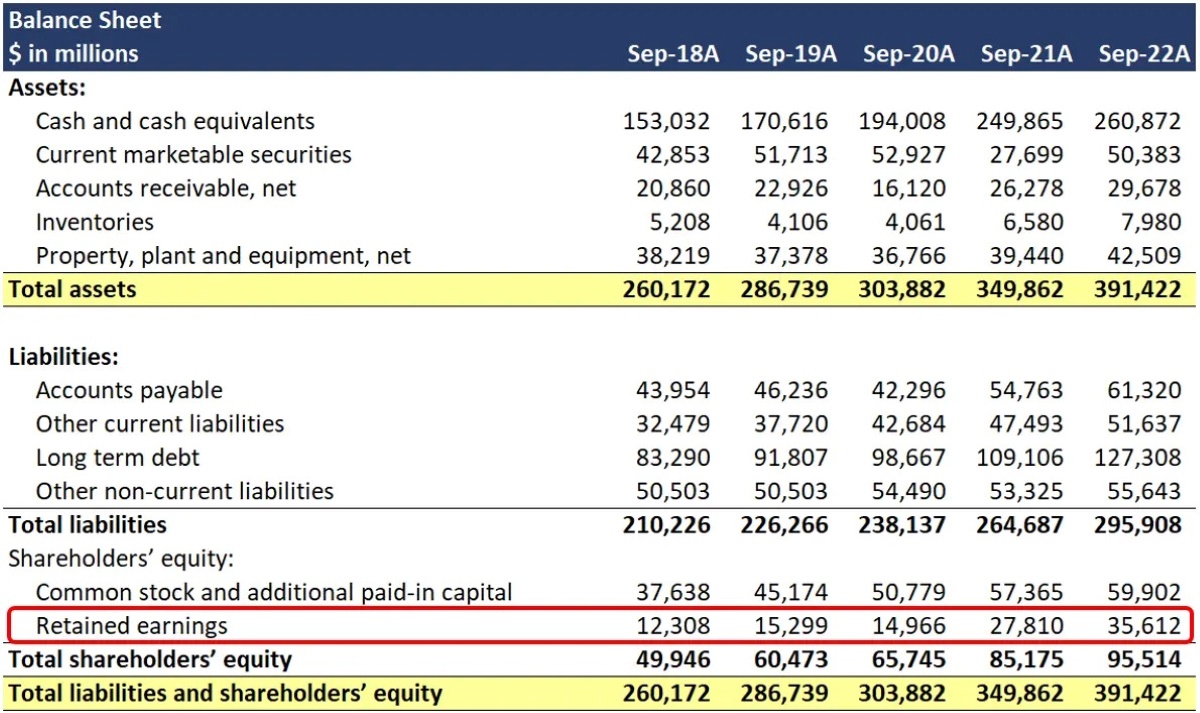
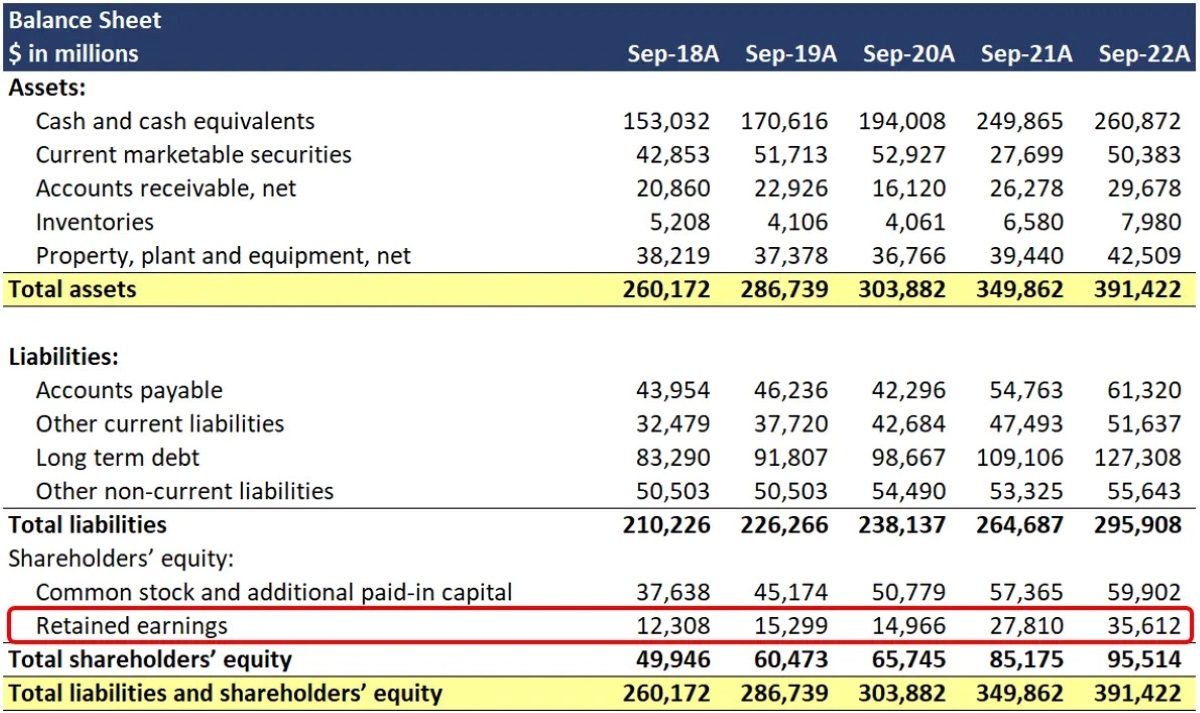
How To Calculate REs
Retained earnings go on the balance sheet of the company under the equity section of shareholders. You can also calculate it by taking the RE beginning balance, adding the current period’s net income or loss, and subtracting any dividends paid to shareholders.
For instance, let’s say a company has the following numbers for the current period:
A beginning retained earnings balance of $6000 when the reporting period began.
A net income of $3500 for the period.
And $1000 of dividends paid.
Thus, using the RE formula, the retained earnings at the end of the period is:
RE = Beginning Retained Earnings + (Net Income or Losses) – Cash Dividends – Stock Dividends
RE = $6000 + $3500 – $1000 = $8500
Impact Of Net Income On REs
Net income directly impacts the RE balance given any changes or movement. Such factors may include an increase or decrease in net earnings and incurrence of net loss. This will either pave the way to profitability or deficit of the business.
The same items that affect net income also affect retained earnings. The RE account can be negative due to cumulative net losses.
These items may include the cost of goods sold, depreciation, sales revenue, and other business operating expenses. Additionally, non-cash items also affect the account, such as impairments, write-downs, and stock-based compensation.
Impact Of Dividends On REs
Dividends can be distributed to shareholders in the form of cash or stock. Both forms can reduce the value of the business’ retained earnings. Cash payment of dividends represent a cash outflow and are considered in the cash account as net reductions. These reduce the asset value of the company on the balance sheet.
On the other hand, stock dividends do not require cash flow. The stock payment transfers a portion of the RE to common stock and additional paid-in capital accounts.
This allocation does not impact the size of the company’s balance sheet, but it decreases the value of stocks per share.
Purpose Of REs
Retained earnings serve as a useful link between the balance sheet and the income statement. Both statements are connected and recorded under the shareholders’ equity. The purpose of REs can be varied such as buying new equipment or put towards research and development that could promote the company’s growth.
REs can be re-invested into the company with the aim of achieving greater earnings in the future. If the company does not believe it can earn a sufficient return on investment, they will distribute those to shareholders as dividends.
The company can use and invest REs in these ways:
- full or partial distribution of income money among business owners in the form of dividends
- expansion of existing business operations, such as hiring more employees or increasing production capacity
- launching a new product or variant
- money can be used for any possible acquisition, partnership, or merger leading to improved business projects
- used for share buybacks
- repaying any outstanding loan or debt that the company may have

Photo by rawpixel from Pixabay
Difference Between Retained Earnings And Revenue
Revenue and retained earnings are both important indicators to see how a company is doing, but they also highlight different aspects.
Revenue refers to the total income or earnings generated by the company before deducting overhead costs and operating expenses. It sits at the top of the income statement and the top-line number to describe the financial performance of a company. Revenue is also referred to as gross sales in some industries.
Retained earnings are a part of the company’s profit that is retained, held, and saved for future use. They can be used as funds for expansion or paying dividends to shareholders. REs are related to net income, as it is the amount of income saved by the company over time.