Home>Finance>Preference Equity Redemption Cumulative Stock (PERCS) Definition


Finance
Preference Equity Redemption Cumulative Stock (PERCS) Definition
Published: January 10, 2024
Learn about Preference Equity Redemption Cumulative Stock (PERCS) and its definition in finance. Explore how PERCS can provide unique investment opportunities.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Understanding Preference Equity Redemption Cumulative Stock (PERCS)
If you’re familiar with the world of finance, you may have come across the term “Preference Equity Redemption Cumulative Stock” or PERCS. But what exactly does it mean? In this blog post, we’ll dive into the definition of PERCS and shed light on its significance in the financial market.
Key Takeaways:
- Preference Equity Redemption Cumulative Stock (PERCS) is a unique type of hybrid security that combines features of both debt and equity.
- PERCS offer investors the potential for both fixed income and equity returns, making them an attractive investment option.
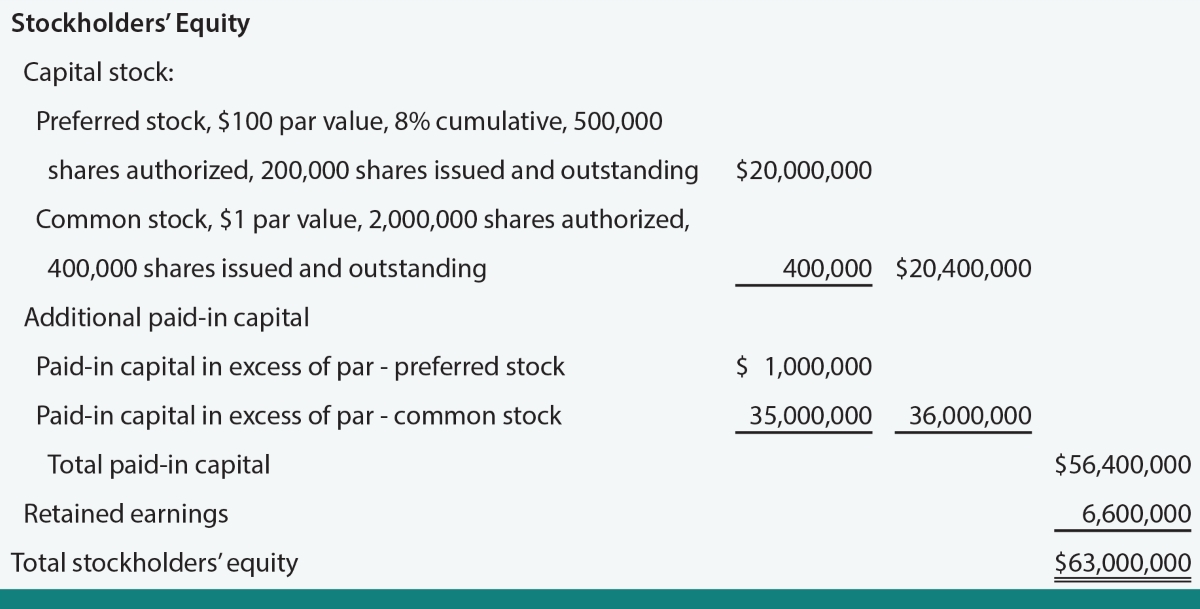
PERCS is a financial instrument that falls under the category of hybrid securities, which are a combination of debt and equity. What sets PERCS apart is its ability to provide investors with the potential for fixed income, similar to traditional debt securities, while also offering the opportunity for equity returns.
The term “Preference Equity” in PERCS refers to the fact that these securities have a preference or priority over common stockholders in terms of dividend payments and claims on the company’s assets in the event of liquidation. This preference gives PERCS holders a greater level of security compared to common shareholders.
Redemption is an important component of PERCS. These securities typically have a predetermined maturity date, at which point the issuing company has the option to redeem the shares at a specific price. If the shares are not redeemed, the investors may have the right to convert their PERCS into common stock. This feature provides investors with flexibility and potential for capital appreciation.
Cumulative is another characteristic of PERCS worth noting. It means that if the issuing company fails to pay a dividend on the PERCS, it accumulates and becomes payable in the future. This feature ensures that investors are not left empty-handed in case of a missed dividend payment.
So, why should investors consider PERCS? Here are two key takeaways:
- Income Potential: PERCS offer investors the opportunity to earn fixed income through regular dividend payments, making them suitable for those seeking a steady stream of income.
- Equity Upside: In addition to fixed income, PERCS also provide the potential for equity returns in the form of capital appreciation. This makes them an attractive option for investors looking to participate in the growth of the issuing company.
While PERCS may seem complex at first glance, they can be a valuable addition to an investor’s portfolio. It’s important to thoroughly research and understand the terms and conditions associated with each specific PERCS offering before making any investment decisions.
In conclusion, Preference Equity Redemption Cumulative Stock (PERCS) is a hybrid security that combines features of both debt and equity. With the potential for fixed income and equity returns, PERCS offer investors a unique investment opportunity. Consider including PERCS in your investment strategy to diversify your portfolio and potentially enhance your returns.