Finance
How Does Group Life Insurance Work?
Published: October 14, 2023
Learn how group life insurance works and how it can provide financial security for you and your loved ones. Find out why it's a smart financial decision.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Group Life Insurance
- How Group Life Insurance Works
- Advantages of Group Life Insurance
- Disadvantages of Group Life Insurance
- Eligibility and Enrollment Process
- Coverage and Benefits
- Premiums and Cost-sharing
- Claim Process and Payouts
- Employer Responsibilities
- Employee Responsibilities
- Considerations when Choosing Group Life Insurance
- Conclusion
Introduction
Group life insurance is a valuable employee benefit that provides financial protection to a group of individuals, typically employees of a company or members of an organization. This type of insurance is offered by employers to their employees as part of a comprehensive benefits package, and it is often provided at a lower cost compared to individual life insurance policies. Group life insurance allows employees to secure life insurance coverage without the need for medical exams or individual underwriting.
Group life insurance functions as a contract between the employer and the insurance provider, where the employer acts as the policyholder and the employees are the insured individuals. In the unfortunate event of the death of an insured employee, the insurance company pays a predetermined amount, known as the death benefit, to the designated beneficiaries. This benefit ensures that the financial needs of the employee’s family are met, providing them with a measure of stability during a difficult time.
One of the key advantages of group life insurance is its affordability. Since the coverage is provided to a large number of individuals as a group, the risk is spread out, resulting in lower premium costs for each participant. This makes it a cost-effective option for both employers and employees, as it provides essential financial protection at a reduced cost.
Additionally, group life insurance typically does not require a medical examination or individual underwriting. This means that even individuals with pre-existing health conditions can obtain coverage, as the insurer assesses the risk based on the overall health of the group rather than individual health profiles. This can be highly advantageous for employees who may have difficulty obtaining affordable coverage on their own due to medical issues.
In the following sections, we will explore how group life insurance works, the advantages and disadvantages of this type of coverage, the eligibility and enrollment process, coverage and benefits, premiums and cost-sharing, the claim process and payouts, as well as the responsibilities of both employers and employees. By understanding the intricacies of group life insurance, individuals can make informed decisions that best suit their financial needs and provide security and peace of mind for their loved ones.
Definition of Group Life Insurance
Group life insurance is a type of life insurance that provides coverage to a group of individuals who share a common affiliation, such as employees of a company or members of an organization. It is a benefits package offered by employers to their employees, offering financial protection in the event of an employee’s death.
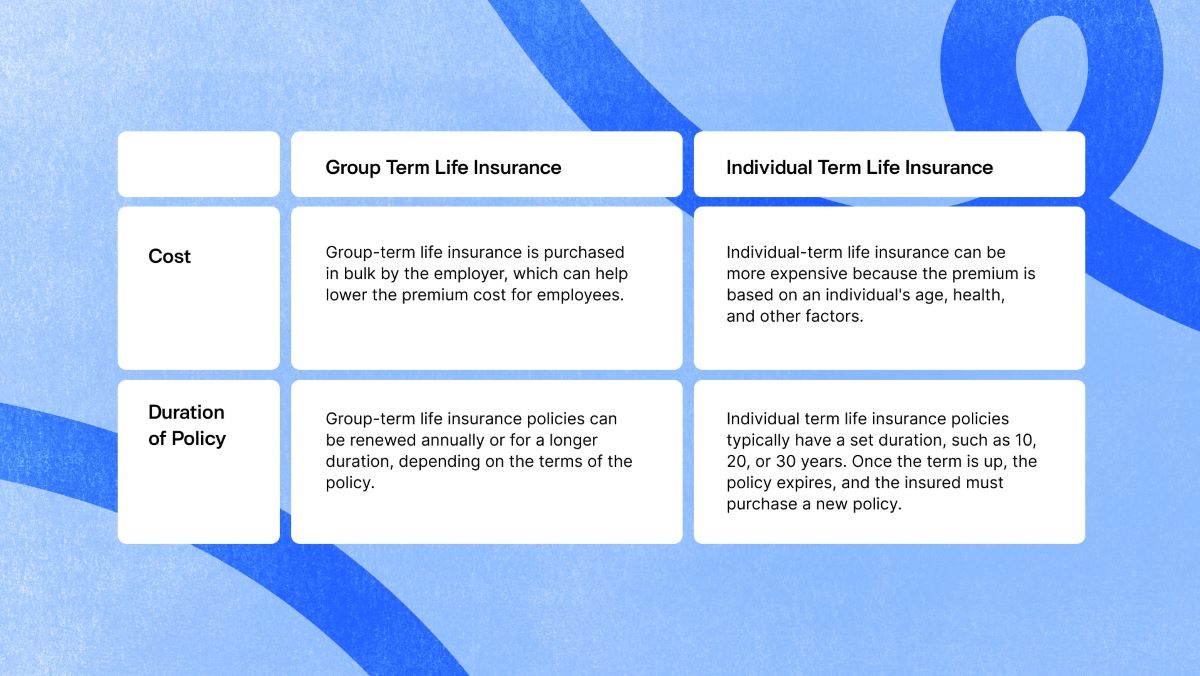
This type of insurance is different from individual life insurance, where an individual purchases and pays for their own policy. In group life insurance, the employer acts as the policyholder and pays the premiums on behalf of the employees. The coverage is typically provided at a low or no-cost basis to the employees, making it an attractive employee benefit.
The coverage amount for group life insurance is usually a multiple of an employee’s salary, such as one or two times their annual salary. However, the actual coverage amount can vary depending on the specific policy and the employer’s chosen level of coverage. This death benefit is payable to the designated beneficiary or beneficiaries of the insured employee.
In most cases, group life insurance provides term life coverage, meaning it is in effect for a specified period of time, typically as long as the individual remains employed by the company or organization. However, some policies may also include options for conversion to individual policies or for coverage to continue after an employee leaves the company or upon retirement.
It’s important to note that group life insurance only provides coverage for death due to natural causes, accidents, or illness. It does not typically cover deaths resulting from suicide, war, or other exclusions outlined in the policy. Additionally, group life insurance does not accumulate cash value or serve as an investment vehicle like some types of individual life insurance policies.
Overall, group life insurance serves as a valuable and cost-effective employee benefit that offers essential financial protection for employees and their families. It provides peace of mind by ensuring that loved ones are taken care of in the event of an employee’s untimely demise.
How Group Life Insurance Works
Group life insurance works by providing financial protection to a group of individuals under a single policy. Here is an overview of how group life insurance works:
- Employer selects a policy: The first step is for the employer to choose a group life insurance policy from an insurance provider. The employer determines the amount of coverage, the terms of the policy, and the eligibility criteria for employees to participate.
- Employee eligibility: Once the policy is in place, the employer determines which employees are eligible to participate in the group life insurance program. Eligibility criteria may include factors such as length of employment, job status, or minimum hours worked.
- Automatic enrollment or opt-in: Depending on the employer’s policy, employees may be automatically enrolled in the group life insurance program or given the option to opt-in voluntarily. Automatic enrollment ensures that all eligible employees have coverage, while opt-in allows employees to make an active choice regarding their participation.
- Premium payment: The employer, as the policyholder, pays the premiums for the group life insurance coverage. The premiums are generally more affordable compared to individual life insurance policies, as the risk is spread out among a larger group of individuals.
- Coverage period: Group life insurance policies typically provide coverage as long as the employee remains with the company or organization. If an employee leaves the company or retires, they may have the option to convert their group life insurance policy to an individual policy or obtain coverage through another means.
- Coverage amount: The death benefit, or coverage amount, is typically based on a multiple of the employee’s salary. The exact amount may vary depending on the policy and the employer’s chosen level of coverage. This benefit is paid to the designated beneficiary or beneficiaries named by the employee.
- Death benefit payment: In the unfortunate event of an employee’s death, the designated beneficiaries must file a claim with the insurance company. Once the claim is verified, the insurance company will pay out the death benefit to the beneficiaries according to the terms of the policy.
It’s important to note that group life insurance coverage is not portable, meaning it does not stay with the employee if they leave the company. However, some policies may offer conversion options or the ability to continue the coverage on an individual basis, often at a higher cost.
Overall, group life insurance provides employees with an important safety net, offering financial protection in the event of their untimely death. It is a valuable employee benefit that provides peace of mind to both employees and their loved ones.
Advantages of Group Life Insurance
Group life insurance offers several advantages for both employers and employees. Here are some of the key advantages of group life insurance:
- Financial protection for employees: Group life insurance provides essential financial protection for employees and their families in the event of the employee’s death. The death benefit helps to ensure that the employee’s loved ones are taken care of financially, including covering expenses such as funeral costs, outstanding debts, and ongoing living expenses.
- Lower cost: Group life insurance is generally more affordable compared to individual life insurance policies. The cost is spread out among a large group of individuals, reducing the premium amount paid by each participant. This makes it an attractive employee benefit, as employees can obtain coverage at a lower cost than if they were to purchase an individual policy.
- No medical exam or individual underwriting: Group life insurance typically does not require a medical examination or individual underwriting. This means that employees with pre-existing health conditions can still obtain coverage, as the insurer assesses the risk based on the overall health of the group. This eliminates the need for individuals to undergo medical tests or answer detailed health questions for the purpose of obtaining coverage.
- Automatic enrollment: Many group life insurance programs offer automatic enrollment, meaning that eligible employees are automatically enrolled in the coverage without needing to take any action. This ensures that all eligible employees have access to life insurance protection and reduces the chance of employees missing out on this valuable benefit.
- Convenience: Group life insurance is typically managed by the employer on behalf of the employees. This means that the administrative tasks, such as premium payments and policy maintenance, are handled by the employer or the insurance provider. Employees can enjoy the convenience of having their life insurance needs taken care of without needing to set up and manage an individual policy.
Overall, group life insurance offers affordable and accessible coverage for employees, providing them with peace of mind and financial protection for their loved ones. It is a valuable benefit that demonstrates an employer’s commitment to the well-being of their employees and can contribute to a positive and supportive work environment.
Disadvantages of Group Life Insurance
While group life insurance offers numerous advantages, it is important to be aware of the potential disadvantages as well. Here are some of the key disadvantages of group life insurance:
- Limited coverage options: Group life insurance policies often provide a predetermined amount of coverage based on an employee’s salary. This may not be sufficient for individuals with unique financial needs or those who require a higher level of coverage. Employees may find themselves underinsured if their personal circumstances require more extensive life insurance protection.
- Lack of customization: Group life insurance policies are standardized to fit the needs of a large group of employees. Therefore, there is limited flexibility for customization to cater to individual preferences or circumstances. The coverage and terms of the policy are determined by the employer or the insurance provider, which may not align perfectly with every employee’s specific needs.
- Portability limitations: Group life insurance coverage is typically tied to employment. If an employee leaves the company or changes jobs, they will no longer have access to the group life insurance policy. This lack of portability can leave employees without coverage during transitional periods, leading to potential gaps in their life insurance protection.
- Insufficient coverage after retirement: For retirees, group life insurance coverage may end or become significantly reduced. This leaves retirees without the same level of financial protection as they had during their working years. It is important for individuals approaching retirement to evaluate their life insurance needs and consider alternative options to ensure continued coverage.
- Limited beneficiary choice: Group life insurance policies may limit the number of beneficiaries or have restrictions on who can be named as beneficiaries. This can be problematic for individuals who wish to designate specific individuals or entities as beneficiaries, particularly in complex family or financial situations.
It is important for employees to carefully assess their individual circumstances and evaluate whether group life insurance coverage adequately meets their needs. In some cases, individuals may choose to supplement group coverage with additional individual policies to ensure sufficient coverage and tailored protection.
Employees should also review the terms and conditions of the group life insurance policy to fully understand the scope of coverage, any limitations or exclusions, and the process for filing a claim. Being informed and proactive will ensure that individuals have the appropriate coverage to protect their loved ones in the event of their untimely death.
Eligibility and Enrollment Process
The eligibility and enrollment process for group life insurance varies depending on the employer and the specific policy. Here is an overview of how eligibility and enrollment typically work:
- Eligibility criteria: The employer sets the criteria for employees to be eligible for group life insurance coverage. This may include factors such as length of employment, job status (full-time or part-time), or minimum hours worked per week. Employers may also set a waiting period before employees become eligible for coverage, such as 30, 60, or 90 days of employment.
- Automatic enrollment: Some employers may have an automatic enrollment process, where eligible employees are automatically enrolled in the group life insurance program without needing to take any action. This ensures that all eligible employees have access to coverage and reduces the likelihood of employees missing out on this valuable benefit.
- Voluntary enrollment: Other employers may require employees to opt-in or enroll voluntarily to participate in the group life insurance program. Employees will need to complete an enrollment form, provide necessary information, and indicate their desire to join the program.
- Enrollment periods: Employers typically have designated enrollment periods during which employees can enroll or make changes to their group life insurance coverage. These enrollment periods may occur annually or at specific times throughout the year. It is important for employees to be aware of these enrollment periods and take action within the specified timeframe.
- Beneficiary designation: As part of the enrollment process, employees will be required to designate their beneficiaries – the individuals or entities who will receive the death benefit in the event of their passing. Employees can typically name primary and contingent (secondary) beneficiaries. It is important to update beneficiary designations whenever there are changes in personal circumstances, such as marriage, divorce, or the birth of a child.
During the enrollment process, employees may be provided with information about the coverage amount, premium costs, and any optional features or riders available with the group life insurance policy. It is important for employees to review this information and evaluate their personal needs to ensure they are making informed decisions related to their life insurance coverage.
If an employee initially declines group life insurance coverage but later decides to enroll at a later date, they may be subject to the employer’s “late entrant” rules, which may involve providing evidence of insurability or limitations on coverage amounts.
It is crucial for employees to carefully review and understand the terms of the group life insurance policy, including any limitations, exclusions, and the process for filing a claim. By being proactive and informed throughout the eligibility and enrollment process, employees can ensure they have the appropriate coverage to protect their loved ones in the event of their passing.
Coverage and Benefits
Group life insurance provides employees with valuable coverage and benefits in the event of their death. Here is an overview of the coverage and benefits typically offered:
- Death benefit: The primary benefit of group life insurance is the death benefit, which is the amount paid out to the designated beneficiaries upon the death of the insured employee. The death benefit is usually a multiple of the employee’s annual salary, such as one or two times their salary. However, the actual amount can vary depending on the specific policy and the employer’s chosen level of coverage.
- Terminal illness benefit: Some group life insurance policies may also include a terminal illness benefit. This benefit allows employees to access a portion of their death benefit if they are diagnosed with a terminal illness and have a life expectancy of less than 12 months. The terminal illness benefit can provide financial assistance to cope with medical expenses or fulfill end-of-life wishes.
- Accidental death and dismemberment: Group life insurance policies may also provide an additional benefit known as accidental death and dismemberment (AD&D) coverage. AD&D coverage pays out a benefit if the insured employee suffers a loss of life or a specified loss of limbs or faculties as a direct result of an accident. This additional coverage can provide extra financial protection for accidental injuries or fatalities.
- Conversion options: In some cases, group life insurance policies may offer conversion options. These options allow employees to convert their group life insurance coverage to an individual policy if they leave the company or retire. This can be beneficial as it allows individuals to maintain life insurance coverage beyond their employment tenure. However, conversion options may have time limits and may involve higher premium costs.
- Additional riders or benefits: Employers may have the option to add additional riders or benefits to the group life insurance policy. Common riders include accelerated death benefits, which provide access to a portion of the death benefit if the insured employee experiences a terminal illness or long-term care need. Employers should review the available riders and their costs to determine if they are suitable for their employees’ needs.
It’s important for employees to review the details of their group life insurance coverage to understand the specific benefits provided, any exclusions or limitations, and the process for filing a claim. By having a clear understanding of the coverage and benefits, employees can ensure their loved ones are adequately protected financially in the event of their passing.
Lastly, employees may also have the option to supplement their group life insurance coverage with individual life insurance policies to further enhance their overall life insurance protection. This can provide greater customization and flexibility to meet unique financial needs and circumstances.
Premiums and Cost-sharing
Group life insurance premiums and cost-sharing arrangements vary depending on the employer and the specific policy. Here is an overview of how premiums and cost-sharing are typically managed in group life insurance:
- Employer-paid premiums: In most cases, the employer is responsible for paying the premiums for the group life insurance coverage. The cost of the premiums is often subsidized by the employer as part of the employee benefits package. This means that employees do not directly contribute financially to the premiums.
- Cost-sharing arrangements: There are instances where employees may be required to share the cost of the group life insurance premiums. In such cases, the employer and the employee may split the premium payment, with the employer covering a portion and the employee contributing through payroll deductions or direct payments.
- Group rating: Insurance companies often use a process called group rating to determine the premium amounts for group life insurance coverage. Group rating involves assessing the overall risk of the entire group to determine the premium rates. Factors that influence group rating include the age, gender, and overall health profile of the group members.
- Age-banded premiums: Age-banded premiums are common in group life insurance, where the premium rates increase as employees move into higher age brackets. This means that older employees may have higher premium costs compared to younger employees. The age bands are typically set at five-year intervals.
- Tax implications: It is important to note that the premiums paid by employers for group life insurance coverage are generally tax-deductible for the business. Additionally, the death benefit received by the designated beneficiaries is typically tax-free for the recipients.
Overall, the cost of group life insurance is typically lower compared to individual life insurance policies due to the risk being spread out among a large group of individuals. The ability to obtain coverage without undergoing a medical examination or individual underwriting also contributes to the affordability of group life insurance.
Employees should review the details of their group life insurance policy to understand the premiums and any cost-sharing arrangements. It is also important to inquire about any potential premium increases over time or changes to the coverage and how such changes may impact the cost-sharing arrangement.
Additionally, employees should consider the affordability of the coverage and evaluate whether it is sufficient for their individual needs. In some cases, individuals may decide to supplement their group life insurance coverage with individual policies to ensure they have adequate protection.
It is crucial for employees to have a clear understanding of the premium costs and any cost-sharing involved to make informed decisions about their group life insurance coverage and to ensure the financial protection of their loved ones in the event of their passing.
Claim Process and Payouts
The claim process and payouts in group life insurance involve several steps to ensure that the designated beneficiaries receive the death benefit in a timely manner. Here is an overview of how the claim process and payouts typically work:
- Notify the insurance company: In the event of the insured employee’s death, the designated beneficiaries or a representative should notify the insurance company as soon as possible. The insurance company will provide guidance on the required documents and forms needed to initiate the claim process.
- Submit the necessary documentation: The designated beneficiaries will be required to fill out and submit the necessary claim forms, which may include a death claim form, a certified copy of the death certificate, and any additional documentation required by the insurance company. It is important to gather all the required documents and provide accurate information to avoid delays in the claim process.
- Review and verification: The insurance company will review the claim and verify the information provided. This may involve contacting the employer or other parties involved to validate the insured employee’s coverage and ensure all necessary documentation has been submitted.
- Investigation (if necessary): In some cases, the insurance company may need to conduct an investigation to determine the cause of death or any other relevant factors. This may be required if the death occurs within a specified period after the coverage begins or if there are questions surrounding the circumstances of the employee’s death.
- Payout of the death benefit: Once the claim is approved and all necessary verifications have been completed, the insurance company will initiate the payout of the death benefit to the designated beneficiaries. The payment is typically made in a lump sum, although some policies may offer structured payout options.
The time it takes to receive the death benefit may vary depending on factors such as the complexity of the claim, the completeness of the documentation, and any required investigations. However, insurance companies strive to process claims in a timely manner to provide the much-needed financial support to the beneficiaries during a difficult time.
It is essential for the insured employee to keep the designated beneficiaries updated on the group life insurance coverage and provide them with the necessary information to facilitate the claim process. Additionally, beneficiaries should promptly notify the appropriate parties in the event of the employee’s death to initiate the claim process as soon as possible.
By understanding the claim process and ensuring that all required documentation is promptly submitted, the designated beneficiaries can receive the death benefit and access the financial support they need to navigate the challenges that arise from the loss of a loved one.
Employer Responsibilities
Employers play a crucial role in the administration and management of group life insurance for their employees. Here are some of the key responsibilities that employers typically have regarding group life insurance:
- Plan selection: Employers are responsible for selecting and implementing a suitable group life insurance plan for their employees. This involves evaluating different policy options, coverage amounts, and premium costs to ensure they align with the needs and budget of the business and its workforce.
- Communication and education: Employers should effectively communicate and educate employees about the group life insurance coverage provided. This includes providing detailed information about the coverage amounts, benefits, beneficiaries, and any additional features or riders. Employers should also ensure that employees understand the enrollment process and any applicable premium costs or cost-sharing arrangements.
- Premium payment: As the policyholder, employers are responsible for paying the premiums for the group life insurance coverage. This may involve making regular payments to the insurance provider in a timely manner to maintain the coverage for all eligible employees. Employers should establish efficient systems and processes to manage premium payments and ensure they remain up to date.
- Enrollment and eligibility management: Employers are responsible for managing the eligibility and enrollment process for group life insurance. This includes determining employee eligibility criteria, enrolling eligible employees into the coverage, and providing necessary enrollment forms and documentation. Employers should also update employee records as changes in employment status occur, such as new hires or terminations.
- Beneficiary updates: Employers should facilitate and coordinate the process of updating designated beneficiaries for group life insurance policies. This involves providing employees with the necessary forms and instructions to designate or change beneficiaries. Employers should also ensure that beneficiary designations are updated promptly when employees experience life events, such as marriage, divorce, or the birth of a child.
- Claims assistance: Employers should assist employees and their designated beneficiaries in navigating the claim process when an employee passes away. This includes providing the necessary information and forms, facilitating communication with the insurance company, and offering support during a difficult time. Employers should be knowledgeable about the claim process and guide employees and beneficiaries through the necessary steps.
- Policy review and renewal: Employers should periodically review their group life insurance policy to ensure it continues to meet the needs of the business and its employees. This may involve assessing the coverage amounts, evaluating premium costs, and considering any changes or enhancements to the policy. Employers should also manage the policy renewal process and negotiate with the insurance provider to secure favorable terms and rates.
By fulfilling these responsibilities, employers demonstrate their commitment to the well-being of their employees and their families. Effective management and administration of group life insurance can provide financial protection, peace of mind, and a sense of security for employees during their employment tenure.
Employee Responsibilities
While employers take on many responsibilities related to group life insurance, employees also have important roles to play in managing their coverage. Here are some key employee responsibilities regarding group life insurance:
- Understanding the coverage: Employees should take the time to understand the details of their group life insurance coverage, including the coverage amount, beneficiaries, and any additional benefits or riders. This will ensure that employees are aware of the financial protection they have and can plan accordingly.
- Enrollment and eligibility: Employees are responsible for familiarizing themselves with the enrollment process and eligibility criteria for group life insurance. This includes reviewing the eligibility requirements set by the employer and taking the necessary steps to enroll during the designated enrollment periods or opting in if required.
- Beneficiary designation: It is important for employees to designate their beneficiaries for the group life insurance policy. Employees should review and update their beneficiary designations as needed, ensuring that the designated beneficiaries reflect their current wishes and any changes in personal circumstances.
- Reviewing and updating information: Employees should review the accuracy of their personal information related to group life insurance, such as their name, date of birth, and contact details. Any changes or updates should be promptly provided to the employer to ensure accurate administration of the coverage.
- Managing life changes: Employees should proactively communicate any life changes that may impact their group life insurance coverage. This includes events such as marriage, divorce, the birth or adoption of a child, or changes in employment status. These changes may require updating beneficiary designations, adjusting coverage amounts, or reassessing the need for additional individual life insurance policies.
- Understanding the claims process: Employees should familiarize themselves with the claims process for group life insurance and communicate this information to their designated beneficiaries. This includes knowing how to initiate a claim, what documentation is required, and contacting the employer or the insurance company promptly in the event of the insured employee’s passing.
- Keeping beneficiaries informed: Employees should ensure that their designated beneficiaries are aware of their group life insurance coverage. This includes providing them with important information, such as the name and contact details of the employer, the insurance company, and any necessary documentation or forms required to initiate a claim.
By fulfilling their responsibilities, employees can actively manage their group life insurance coverage, ensure the accuracy of their information, and make informed decisions to protect their loved ones in the event of their passing. Being proactive and communicative will facilitate a smoother administration of the group life insurance policy and provide the intended financial support to the designated beneficiaries at the appropriate time.
Considerations when Choosing Group Life Insurance
When selecting group life insurance, there are several key considerations that employees should take into account to ensure they choose the right coverage for their needs. Here are some important factors to consider:
- Coverage amount: Evaluate the coverage amount offered by the group life insurance policy. Consider your financial obligations, such as outstanding debts, mortgage or rent payments, and the needs of your dependents. Ensure that the coverage amount is sufficient to provide for your loved ones in the event of your passing.
- Additional benefits and riders: Explore any additional benefits or riders offered with the group life insurance policy. These may include features such as accelerated death benefits, which allow you to access a portion of the death benefit if diagnosed with a terminal illness, or accidental death and dismemberment coverage. Assess whether these additional benefits align with your specific needs and provide value for your situation.
- Portability: Consider the portability options of the group life insurance policy. Determine if the coverage can be continued or converted to an individual policy if you leave the company or retire. Portability can provide flexibility and continuity of coverage during transitions in employment or retirement.
- Cost-sharing arrangements: Understand any cost-sharing arrangements associated with the group life insurance coverage. Determine if there are any premium expenses that you need to contribute towards and evaluate the affordability of the coverage based on your financial situation.
- Enrollment process: Familiarize yourself with the enrollment process and any eligibility requirements set by the employer. Determine if enrollment is automatic or if you need to opt-in voluntarily. Be aware of any enrollment periods and take prompt action to ensure you are enrolled in the group life insurance program.
- Insurance provider: Evaluate the reputation and financial stability of the insurance provider offering the group life insurance policy. Research their track record in claim processing and their ability to meet their financial obligations to policyholders. Consider seeking out reviews or recommendations to gain insights into the provider’s reliability and customer service.
- Employee support: Assess the level of employee support provided by the employer in managing the group life insurance coverage. Consider the employer’s understanding of the policy, the availability of assistance during the enrollment process and ongoing maintenance of the coverage, and their knowledge of the claim process. Adequate employee support can be crucial in navigating the complexities of group life insurance.
Ultimately, the decision to choose group life insurance requires careful consideration of the coverage, benefits, cost-sharing, and portability options. It is crucial to assess your individual needs, review the available options, and consult with insurance professionals or financial advisors, if necessary, to make an informed decision. By selecting the right group life insurance policy, you can provide essential financial protection for your loved ones and have peace of mind knowing that their needs will be taken care of in the event of your passing.
Conclusion
Group life insurance is a valuable employee benefit that offers financial protection to a group of individuals, typically employees of a company or members of an organization. It provides essential coverage in the event of an employee’s untimely death, ensuring that their loved ones are taken care of financially during a difficult time. The advantages of group life insurance, such as its affordability, no medical exams or individual underwriting requirements, and convenience, make it an attractive option for both employers and employees.
However, it is important to consider the disadvantages of group life insurance as well, including limited customization, lack of portability, and limitations on coverage options. Employees should carefully review their coverage, understand the policy terms, and assess whether additional individual policies may be needed to supplement their group coverage.
Both employers and employees have important responsibilities when it comes to group life insurance. Employers must select an appropriate policy, communicate the details to employees, facilitate the enrollment process, and provide support for the claims process. Employees must understand their coverage, enroll when eligible, designate beneficiaries, and stay proactive in managing their coverage throughout their employment tenure.
When choosing group life insurance, employees should consider factors such as coverage amount, additional benefits and riders, portability options, cost-sharing arrangements, and the reputation of the insurance provider. By making informed decisions and considering individual needs, employees can select the right group life insurance coverage to meet their financial protection requirements.
In conclusion, group life insurance is an important tool in providing financial security to employees and their families. It offers peace of mind and a safety net in times of tragedy. By understanding the intricacies of group life insurance, employees can make informed choices that ensure the well-being of their loved ones and provide financial stability during challenging times.