Home>Finance>Universal Banking: Definition, Functions, Regulation


Finance
Universal Banking: Definition, Functions, Regulation
Published: February 13, 2024
Learn the definition, functions, and regulation of universal banking in finance. Explore the role of financial institutions in offering a wide range of services under one roof.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Universal Banking: Definition, Functions, Regulation
Finance is a vast and complex field, comprising various sectors that serve different purposes. One such sector is universal banking, which plays a crucial role in the global financial system. In this blog post, we will explore the definition, functions, and regulation of universal banking.
Key Takeaways:
- Universal banks offer a wide range of financial services, including commercial banking, investment banking, and asset management.
- Regulators enforce strict guidelines and regulations to ensure the safety, transparency, and stability of universal banks.
So, what exactly is universal banking? Simply put, it is a banking model that allows financial institutions to provide a comprehensive range of services under one roof. Universal banks go beyond traditional commercial banking activities and embrace various financial functions such as investment banking, insurance, and asset management. This integration of diverse services enables universal banks to cater to the diverse financial needs of individuals, businesses, and even governments.
Universal banks offer a wide array of financial products and services, including but not limited to:
- Accepting deposits and offering checking and savings accounts.
- Extending loans and credit facilities to individuals and businesses.
- Facilitating trade financing and international transactions.
- Providing investment advisory and portfolio management services.
- Underwriting securities and facilitating capital market transactions.
- Offering insurance products and services to mitigate risks.
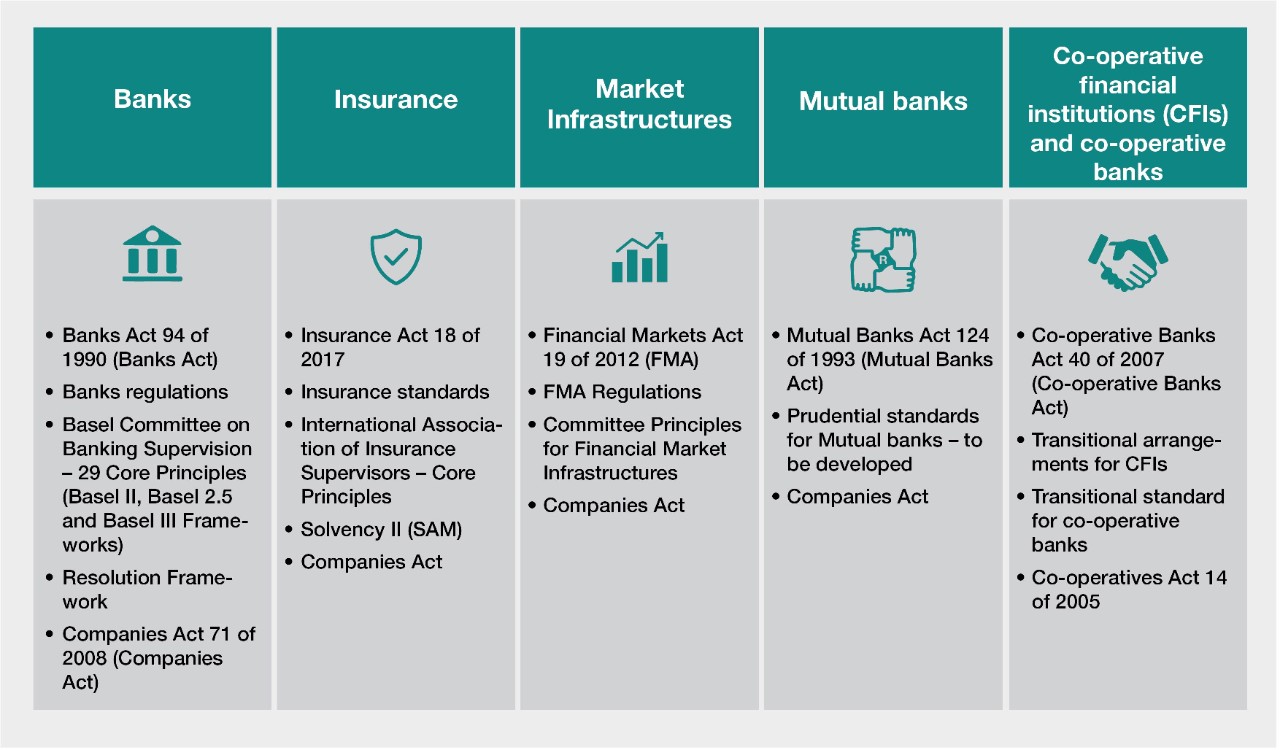
Now that we understand the functions of universal banks, let’s dive into the regulations governing this sector. Given the wide range of services offered, universal banks are subject to stringent regulations imposed by financial authorities and regulatory bodies. These regulations aim to maintain the stability, transparency, and integrity of the financial system.
Regulatory authorities keep a close eye on universal banks and ensure compliance with guidelines that cover aspects such as:
- Capital adequacy requirements to ensure that banks have sufficient funds to cover potential losses.
- Liquidity regulations to guarantee the availability of funds to meet customer demands and maintain stability.
- Risk management protocols to manage and mitigate potential risks associated with various financial activities.
- Consumer protection measures to safeguard the interests of customers and ensure fair practices.
- Anti-money laundering and anti-terrorism financing controls to combat financial crimes.
The goal of these regulations is to strike a balance between allowing universal banks to provide diverse services and safeguarding the interests of customers and the overall financial system. Regulators play a crucial role in monitoring and enforcing compliance with these regulations, ensuring the safety and soundness of universal banks.
In conclusion, universal banking is a multi-faceted sector within the broader financial industry, offering a wide range of services to individuals, businesses, and governments. The functions and regulations surrounding universal banking ensure the stability, transparency, and integrity of the financial system. By understanding the definition and significance of universal banking, individuals can make informed decisions about their financial needs and also comprehend the robust regulatory framework that governs this sector.