
Finance
What Is An Example Of A Banking Regulation?
Modified: December 30, 2023
Discover an example of a banking regulation in the field of finance and understand how it impacts the industry. Explore key policies and guidelines that shape the financial sector.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Banking regulation is an essential aspect of the financial system that ensures the stability, integrity, and transparency of banks and financial institutions. It entails a set of rules, guidelines, and regulations that govern the operations and conduct of banks, with the aim of protecting the interests of depositors, promoting financial stability, and preventing financial crises.
Regulators, such as central banks and regulatory authorities, play a crucial role in overseeing and enforcing these regulations to maintain the integrity of the banking industry. Banking regulations cover a wide range of areas, including capital requirements, risk management, consumer protection, anti-money laundering, and corporate governance.
In recent years, banking regulations have become even more important in the aftermath of the global financial crisis. The collapse of several major banks and the ensuing economic downturn highlighted the need for stronger regulatory oversight to prevent future crises and protect the financial system from excessive risk-taking.
This article will explore the definition of banking regulation, discuss its importance, and provide examples of various banking regulations that exist to safeguard the stability and trustworthiness of the banking industry.
Definition of Banking Regulation
Banking regulation refers to the set of laws, rules, and guidelines that govern the operations and conduct of banks and financial institutions. It is designed to maintain the stability and integrity of the banking system, protect the interests of depositors, and ensure fair practices in the financial industry.
These regulations are typically enforced by regulatory bodies such as central banks, financial regulatory authorities, and banking supervisory agencies. They establish a framework within which banks must operate, outlining the requirements and restrictions they must adhere to.
Banking regulations cover a wide range of areas, including capital adequacy, risk management, liquidity, lending practices, consumer protection, anti-money laundering, and corporate governance. They are shaped by a combination of international standards, national legislation, and regulatory frameworks specific to each country.
One of the primary goals of banking regulation is to maintain financial stability by monitoring and managing systemic risks. This involves setting capital adequacy requirements, which dictate the amount of capital banks must hold in relation to their risk exposure. Higher capital requirements help to protect banks from potential losses and enhance their ability to withstand economic shocks.
Consumer protection is another crucial aspect of banking regulation. It includes provisions to ensure fair and transparent treatment of customers, disclosure of product information, and mechanisms to resolve disputes. Additionally, regulations related to anti-money laundering and combating the financing of terrorism help safeguard the financial system from illicit activities.
Overall, banking regulation serves to foster trust, promote stability, and mitigate risks within the financial sector. By establishing a regulatory framework that governs the behavior and operations of banks, it aims to prevent excessive risk-taking, fraudulent activities, and systemic failures that can have far-reaching consequences for the economy and society as a whole.
Importance of Banking Regulation
Banking regulation plays a crucial role in safeguarding the stability and trustworthiness of the banking industry. Here are some key reasons why banking regulation is of utmost importance:
- Financial Stability: One of the primary goals of banking regulation is to maintain financial stability. By setting capital adequacy requirements and implementing risk management practices, regulators ensure that banks have sufficient buffers to withstand economic downturns. This helps prevent bank failures and the potential domino effect on the overall economy.
- Consumer Protection: Banking regulation includes provisions to protect consumers from unfair practices and ensure the transparency and reliability of financial products and services. It helps establish clear disclosure requirements, fair lending practices, and mechanisms to handle customer complaints and disputes.
- Prevention of Financial Crises: By monitoring and regulating the activities of banks, regulators can identify and mitigate emerging risks that may lead to financial crises. This includes monitoring excessive risk-taking, speculative lending practices, and ensuring banks maintain adequate liquidity levels to withstand periods of financial stress.
- Supervision and Oversight: Banking regulation establishes a framework for supervision and oversight of banks’ operations. It allows regulators to conduct regular assessments, inspections, and audits to ensure compliance with regulations and identify any potential weaknesses or vulnerabilities in banks’ risk management processes.
- Trust and Confidence: Robust banking regulation helps build trust and confidence in the banking system. It assures depositors and investors that their funds are protected, and banks are held to high standards of transparency and integrity. This trust is crucial for maintaining the flow of capital within the financial system.
Overall, banking regulation is essential for creating a stable and well-functioning banking sector. It mitigates risks, protects consumers, and ensures the integrity and soundness of financial institutions. By maintaining financial stability and promoting fair practices, banking regulation contributes to the overall health and resilience of the economy.
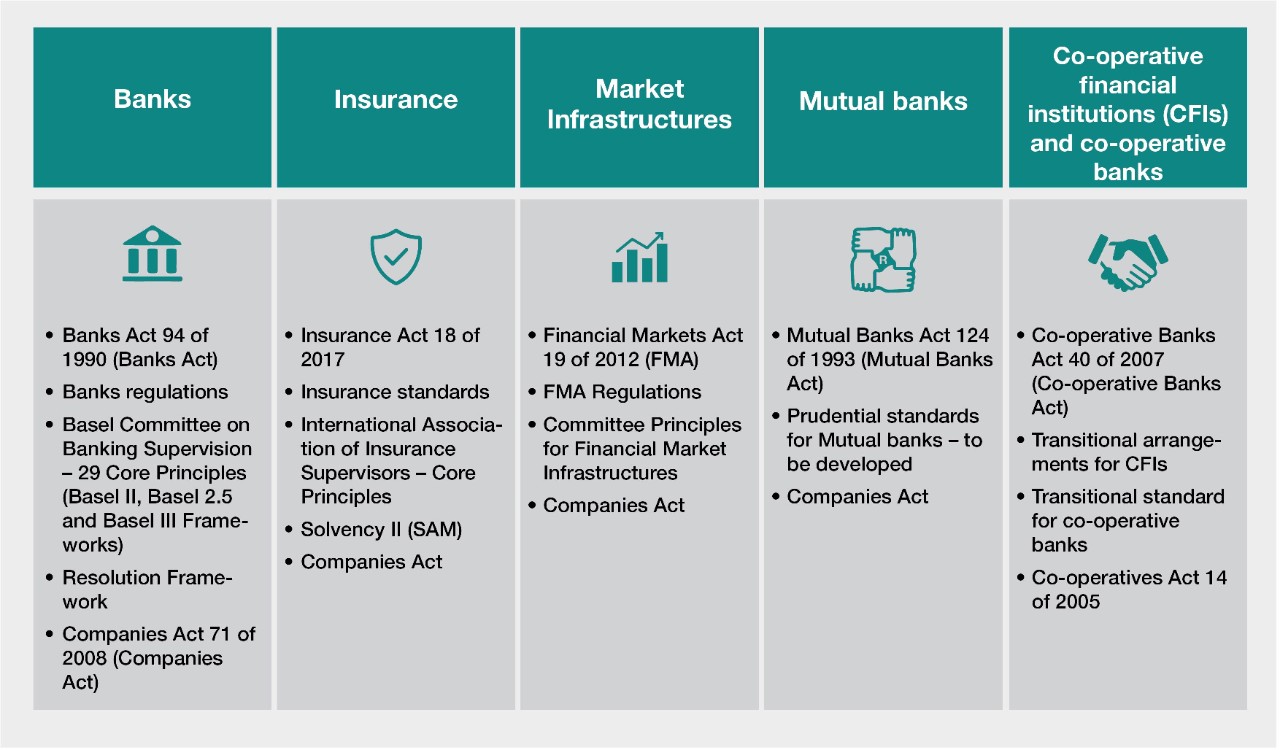
Examples of Banking Regulations
Banking regulations encompass a wide range of rules and guidelines that govern the operations and conduct of banks. Here are some examples of common banking regulations:
- Capital Requirements: Banks are generally required to maintain a minimum level of capital, known as capital adequacy requirements, to ensure they have sufficient funds to absorb losses. These requirements are set by regulatory authorities and are based on the risk profile of the bank’s assets.
- Liquidity Requirements: Banks are required to maintain a certain level of liquid assets to meet their short-term obligations. These requirements help ensure that banks have enough cash or assets that can be easily converted into cash to withstand short-term funding stresses.
- Prudential Standards: Regulators impose prudential standards on banks to ensure sound risk management practices. These standards cover areas such as risk assessment, risk controls, and risk reporting. They aim to prevent excessive risk-taking and promote responsible lending and investment practices.
- Consumer Protection: Banking regulations include provisions to protect consumers’ rights and ensure fair treatment. They may require banks to provide clear and transparent disclosures of fees, terms, and conditions associated with financial products and services. Regulations also govern areas such as fair lending practices, debt collection, and handling customer complaints.
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC): Regulations require banks to implement robust AML and KYC practices to prevent money laundering, terrorist financing, and other illicit activities. Banks are obligated to verify the identities of their customers, monitor transactions for suspicious activities, and report any suspicious transactions to the appropriate authorities.
- Corporate Governance: Regulations related to corporate governance aim to ensure effective oversight and accountability within banks. They may include requirements for independent board members, risk management committees, internal control mechanisms, and transparency in financial reporting.
It is worth noting that banking regulations vary across countries and jurisdictions. While there are commonalities in the regulatory frameworks, the specific requirements and implementation may differ. This is because regulations are developed to address specific financial system needs and account for the unique characteristics and risks in each jurisdiction.
Overall, banking regulations play a critical role in ensuring the stability, integrity, and fairness of the banking industry. They protect the interests of depositors, promote responsible lending practices, and contribute to the overall soundness and trustworthiness of financial institutions.
Conclusion
Banking regulation is pivotal in maintaining the stability, integrity, and transparency of the banking industry. The regulations are established to protect the interests of depositors, promote financial stability, and prevent financial crises.
Regulators, such as central banks and regulatory authorities, have a key role in overseeing and enforcing banking regulations. These regulations cover various aspects of banking operations, including capital requirements, risk management, consumer protection, anti-money laundering, and corporate governance.
The importance of banking regulation cannot be overstated. It ensures financial stability by mitigating systemic risks and preventing bank failures. It protects consumers from unfair practices and fosters trust and confidence in the banking system. It also helps prevent financial crises by monitoring and managing risks within the financial sector.
Examples of banking regulations include capital requirements, liquidity requirements, prudential standards, consumer protection measures, anti-money laundering and know your customer regulations, and corporate governance guidelines.
While banking regulations may differ across countries and jurisdictions, their ultimate goal remains the same: to maintain a well-functioning and reliable banking sector. Through effective regulation, banks and financial institutions are held accountable and operate within the boundaries of transparency and responsibility.
In conclusion, banking regulation is crucial for ensuring the stability, fairness, and trustworthiness of the banking industry. It is a vital component of the financial system that protects stakeholders, safeguards the economy, and promotes sustainable growth.














