Finance
What Is FIG Investment Banking?
Modified: December 30, 2023
Learn all about FIG investment banking and how it plays a crucial role in the finance industry. Explore the various services, functions, and opportunities it offers.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Overview of FIG Investment Banking
- Key Functions and Responsibilities of FIG Investment Bankers
- Skills and Qualifications Required for FIG Investment Banking
- Areas and Sectors Covered in FIG Investment Banking
- Typical Deals and Transactions in FIG Investment Banking
- Career Prospects and Opportunities in FIG Investment Banking
- Challenges and Risks in FIG Investment Banking
- Conclusion
Introduction
Welcome to the world of FIG investment banking! If you’re interested in finance and have a passion for helping businesses in the financial services industry, then FIG investment banking might just be the perfect career path for you. FIG, which stands for Financial Institutions Group, is a specialized sector within investment banking that focuses on advising and providing financial solutions to banks, insurance companies, asset management firms, and other financial institutions.
FIG investment bankers play a crucial role in facilitating mergers and acquisitions, capital raising, restructuring, and strategic advisory services for their clients in the financial services industry. They are experts in understanding the unique dynamics and regulatory requirements of this sector, which enables them to provide tailored financial solutions that meet the specific needs of their clients.
In recent years, the FIG sector has gained significant importance and prominence due to the growing complexity and globalization of the financial services industry. As the industry continues to evolve and adapt to new market trends and regulations, the demand for skilled FIG investment banking professionals has never been higher.
In this article, we will explore the world of FIG investment banking in more detail, including its key functions, responsibilities, and the skills and qualifications required to succeed in this field. We will also delve into the different sectors covered by FIG investment banking and highlight some of the typical deals and transactions that FIG bankers work on. Additionally, we’ll discuss the career prospects and opportunities available in FIG investment banking, as well as the challenges and risks that professionals in this field may face.
If you’re eager to learn more about the exciting world of FIG investment banking, let’s dive in and explore this dynamic and fast-paced sector together.
Overview of FIG Investment Banking
FIG investment banking is a specialized area within the broader field of investment banking that focuses on providing financial services and advice to clients in the financial institutions sector. This sector includes banks, insurance companies, asset management firms, and other financial institutions.
The objective of FIG investment banking is to help these financial institutions achieve their strategic goals and navigate the complex and ever-changing landscape of the financial services industry. FIG investment bankers work closely with their clients to provide a wide range of services, including mergers and acquisitions, capital raising, debt and equity offerings, restructuring, and strategic advisory.
One of the key roles of FIG investment bankers is to analyze the financial health and performance of their clients and identify opportunities for growth and improvement. They use their industry expertise and knowledge of regulatory frameworks to assess risks and develop tailored financial solutions that align with their clients’ objectives.
FIG investment bankers also play a crucial role in facilitating mergers and acquisitions within the financial institutions sector. They help clients evaluate potential targets, conduct due diligence, negotiate deal terms, and provide advice on integration strategies. This requires a deep understanding of the specific challenges and considerations unique to the financial services industry, such as regulatory compliance, customer relationships, and risk management.
Moreover, FIG investment bankers assist financial institutions with capital raising activities, whether it’s through debt or equity offerings. They assess market conditions, analyze the optimal capital structure, and guide their clients through the process of raising funds. This can involve preparing investor presentations, coordinating roadshows, and negotiating with potential investors to secure the best terms.
Strategic advisory services are another important aspect of FIG investment banking. FIG bankers provide guidance and recommendations to their clients on various strategic initiatives, such as expansion into new markets, diversification of product offerings, or improving operational efficiency. They act as trusted advisors, helping financial institutions make informed decisions that will enhance their competitive position and drive long-term success.
In summary, FIG investment banking is a specialized field that focuses on providing financial services and advice to clients in the financial institutions sector. FIG investment bankers play a crucial role in facilitating mergers and acquisitions, capital raising, restructuring, and strategic advisory services for their clients. Their expertise and knowledge of the financial services industry enable them to develop tailored solutions that align with their clients’ objectives.
Key Functions and Responsibilities of FIG Investment Bankers
FIG investment bankers have a wide range of functions and responsibilities that revolve around providing financial solutions and strategic advice to clients in the financial institutions sector. Let’s explore some of the key functions and responsibilities of FIG investment bankers:
- Financial Analysis: FIG investment bankers conduct in-depth financial analysis of their clients’ businesses. They analyze financial statements, assess profitability, evaluate risk exposures, and identify areas for improvement. This analysis helps them understand the financial health of their clients and enables them to develop tailored financial solutions.
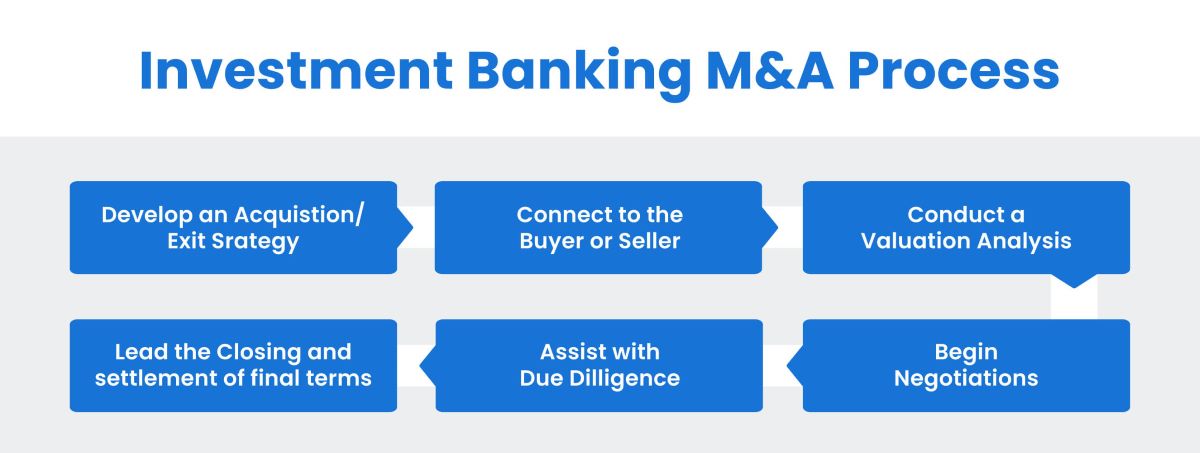
- Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A): FIG investment bankers play a crucial role in facilitating mergers, acquisitions, and divestitures within the financial institutions sector. They assist clients in identifying potential targets, conducting due diligence, structuring deals, negotiating terms, and advising on integration strategies.
- Capital Raising: FIG investment bankers help financial institutions raise capital through equity and debt offerings. They evaluate market conditions, determine optimal capital structures, and assist clients in preparing investor presentations. They also help coordinate roadshows and facilitate negotiations with potential investors.
- Strategic Advisory: FIG investment bankers provide strategic advice to their clients in areas such as market expansion, product diversification, and operational efficiency. They analyze market trends, competitive dynamics, and regulatory developments to help financial institutions make informed decisions and achieve their strategic objectives.
- Regulatory Compliance: FIG investment bankers have a deep understanding of the regulatory frameworks and compliance requirements specific to the financial services industry. They help their clients navigate complex regulatory environments and ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
- Relationship Management: FIG investment bankers develop and maintain strong relationships with their clients. They act as trusted advisors, providing ongoing support and building long-term partnerships. They keep clients informed about market trends, industry developments, and opportunities for growth.
- Deal Execution: FIG investment bankers oversee the execution of transactions, ensuring that all regulatory and legal requirements are met. They coordinate with internal teams and external stakeholders to complete deals within specified timelines.
- Market Research: FIG investment bankers conduct extensive market research to stay updated on industry trends, competitive landscape, and emerging opportunities. This research helps them provide valuable insights and strategic guidance to their clients.
These functions and responsibilities highlight the diverse and multifaceted nature of FIG investment banking. Effective FIG investment bankers possess a combination of financial acumen, industry knowledge, analytical skills, and relationship-building abilities to meet the complex demands of this role.
Skills and Qualifications Required for FIG Investment Banking
Working in FIG investment banking requires a unique set of skills and qualifications due to the specialized nature of the financial institutions sector. Here are some of the key skills and qualifications that are typically required for a successful career in FIG investment banking:
- Financial Expertise: A strong foundation in finance is essential for FIG investment bankers. They should have a solid understanding of financial concepts, accounting principles, and industry-specific metrics. Proficiency in financial modeling, valuation techniques, and financial statement analysis is crucial.
- Industry Knowledge: In-depth knowledge of the financial institutions sector is vital to understanding the unique challenges, trends, and regulatory frameworks within the industry. FIG investment bankers should stay updated on industry developments, market dynamics, and emerging trends that may impact their clients.
- Analytical Skills: FIG investment bankers must possess excellent analytical capabilities. They need to analyze complex financial data, assess risk exposures, and evaluate the financial performance of their clients. Strong quantitative and problem-solving skills are essential for identifying opportunities, assessing feasibility, and making informed decisions.
- Communication and Presentation Skills: Effective communication and presentation skills are critical for FIG investment bankers. They need to articulate complex financial concepts to clients, colleagues, and stakeholders in a clear and concise manner. The ability to prepare compelling presentations and deliver persuasive pitches is vital for building relationships and securing deals.
- Negotiation Skills: FIG investment bankers often find themselves in negotiations with clients, potential investors, and other parties involved in transactions. Strong negotiation skills are necessary to secure favorable terms for their clients and reach mutually beneficial agreements.
- Attention to Detail: Accuracy and attention to detail are paramount in FIG investment banking. Meticulously reviewing financial documents, contracts, and regulatory frameworks is crucial to ensure compliance and avoid potential risks. Small errors can have significant consequences, so a keen eye for detail is essential.
- Teamwork and Collaboration: FIG investment bankers work in teams and collaborate with colleagues, clients, and external advisors. The ability to work effectively in a team, delegate tasks, and leverage collective expertise is crucial for success in this field.
- Education and Qualifications: A bachelor’s degree in finance, economics, business, or a related field is typically required for FIG investment banking roles. Many firms also prefer candidates with an MBA or advanced degree. Additionally, obtaining professional certifications such as Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) or Financial Risk Manager (FRM) can enhance credibility and marketability in the field.
While these skills and qualifications are essential for FIG investment banking, it’s important to note that continuous learning, adaptability, and a passion for the financial services industry are equally important. Staying abreast of industry trends, developing new skills, and cultivating a deep understanding of the changing dynamics within the financial institutions sector will contribute to long-term success in FIG investment banking.
Areas and Sectors Covered in FIG Investment Banking
FIG investment banking encompasses a wide range of areas and sectors within the financial services industry. Let’s delve into some of the key areas and sectors covered by FIG investment banking:
- Banks: One of the primary areas covered by FIG investment banking is the banking sector. This includes commercial banks, investment banks, regional banks, and other financial institutions that provide banking services. FIG investment bankers assist these institutions in various financial transactions, including mergers and acquisitions, capital raising, and advisory services.
- Insurance Companies: Another significant sector within FIG investment banking is the insurance industry. FIG investment bankers provide financial solutions to insurance companies, including reinsurance transactions, capital optimization, and strategic advisory. They help insurance companies navigate regulatory challenges, evaluate growth opportunities, and structure deals.
- Asset Management Firms: FIG investment banking also covers the asset management sector, including investment firms, private equity firms, and mutual fund companies. FIG investment bankers assist these firms in raising capital, structuring deals, and providing strategic advice. They help asset management firms in acquiring or divesting businesses, evaluating investment opportunities, and optimizing their capital structures.
- Payment and Fintech Companies: With the rapid growth of the digital economy, FIG investment banking now extends to payment companies and fintech startups. FIG investment bankers provide financial advisory services, assist with capital raising, and support mergers and acquisitions in this dynamic sector. They help these companies navigate the complex regulatory landscape and position themselves for growth.
- Specialty Finance: FIG investment banking covers specialty finance companies that provide non-traditional financial services. This includes sectors such as consumer finance, commercial lending, factoring, leasing, and other niche segments. FIG investment bankers support specialty finance companies in raising capital, structuring transactions, and optimizing their business models.
- Regulatory and Compliance: FIG investment banking professionals also work closely with regulatory bodies and provide expertise in compliance matters. They assist financial institutions in navigating regulatory requirements, implementing risk management frameworks, and ensuring compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
- Emerging Markets: The FIG investment banking sector also covers emerging markets, where financial institutions are experiencing rapid growth and evolution. FIG investment bankers provide strategic advice and financial solutions to navigate the unique challenges and opportunities present in these markets.
These are just a few examples of the areas and sectors covered in FIG investment banking. The field is dynamic and continually evolving as the financial services industry progresses. FIG investment bankers need to stay updated on industry trends and developments to provide the best possible financial solutions and advisory services to their clients.
Typical Deals and Transactions in FIG Investment Banking
FIG investment banking involves a wide range of deals and transactions within the financial institutions sector. The following are some typical deals and transactions that FIG investment bankers often work on:
- Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A): FIG investment bankers play a crucial role in facilitating mergers, acquisitions, and divestitures within the financial institutions sector. They assist in identifying potential targets, conducting due diligence, valuing businesses, structuring deals, and negotiating terms. M&A transactions in FIG investment banking can involve banks acquiring other banks, insurance companies acquiring smaller competitors, or asset management firms merging with complementary businesses.
- Capital Raising: FIG investment bankers help financial institutions raise capital through various means. This can involve debt and equity offerings, including initial public offerings (IPOs), secondary offerings, convertible bonds, or debt issuances. FIG investment bankers evaluate market conditions, assess optimal capital structures, prepare investor presentations, and facilitate negotiations with potential investors.
- Restructuring and Recapitalization: In times of financial distress or strategic change, FIG investment bankers assist financial institutions with restructuring and recapitalization efforts. They develop strategies to improve capital positions, optimize balance sheets, and reposition businesses for long-term success. This may involve negotiating debt restructurings, raising new capital, or divesting non-core assets.
- Strategic Advisory: FIG investment bankers provide strategic advice to financial institutions on a wide range of initiatives. They assist in market expansion, diversification of product offerings, operational efficiency improvements, and regulatory compliance. Strategic advisory services can also include evaluating potential partnerships or joint ventures with other financial institutions.
- Valuations: FIG investment bankers are often involved in valuations of financial institutions. They conduct detailed analysis and use various valuation methodologies to determine the worth of banking, insurance, or asset management businesses. Valuations are essential for mergers and acquisitions, capital raising, or internal decision-making by financial institutions.
- Regulatory Compliance: FIG investment bankers help financial institutions navigate complex regulatory environments and ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations. This can involve conducting compliance audits, implementing risk management frameworks, and advising on regulatory requirements related to capital adequacy, anti-money laundering, data protection, and consumer protection.
- FinTech Partnerships: With the rise of financial technology (FinTech), FIG investment bankers assist traditional financial institutions in establishing partnerships or collaborations with FinTech companies. They identify strategic opportunities for financial institutions to leverage technology, enhance customer experiences, and improve operational efficiency.
These are just a few examples of the typical deals and transactions in FIG investment banking. Each transaction requires a deep understanding of the financial institutions sector, regulatory frameworks, and the specific needs and goals of the clients involved. FIG investment bankers play a vital role in guiding their clients through these complex transactions and helping them achieve their strategic objectives.
Career Prospects and Opportunities in FIG Investment Banking
FIG investment banking offers a wide range of rewarding career prospects and opportunities for individuals interested in the financial services industry. The demand for skilled FIG investment bankers continues to grow as the industry becomes increasingly complex and globalized. Here are some of the career prospects and opportunities in FIG investment banking:
- Professional Growth: FIG investment banking provides ample opportunities for professional growth and advancement. Starting as an Analyst or Associate, individuals can progress to more senior positions such as Vice President, Director, and Managing Director. With experience and a track record of success, there are opportunities to lead deal teams, manage client relationships, and contribute to the overall strategic direction of the firm.
- Specialization: FIG investment banking allows individuals to specialize within the financial institutions sector. Professionals can develop expertise in specific areas such as banking, insurance, asset management, or fintech. This specialization enhances marketability, deepens industry knowledge, and opens doors to more senior and specialized roles within FIG investment banking.
- Global Exposure: FIG investment banking offers the opportunity to work on deals and transactions with global implications. Financial institutions operate in an interconnected world, and FIG investment bankers often collaborate with international teams, advise multinational clients, and execute cross-border transactions. This global exposure provides a broader perspective and opens doors to potential international assignments or opportunities in different financial centers.
- Client Interaction: FIG investment bankers have the opportunity to build strong relationships with clients in the financial institutions sector. Working closely with senior executives and management teams, FIG investment bankers become trusted advisors, providing tailored financial solutions to help clients achieve their strategic objectives. These client interactions foster professional growth, networking opportunities, and the chance to make a lasting impact on clients’ businesses.
- Dynamic and Challenging Environment: FIG investment banking operates in a fast-paced and dynamic environment. Financial institutions face evolving market trends, regulatory changes, and technological advancements. FIG investment bankers must stay at the forefront of these developments, constantly adapting to new challenges and opportunities. This dynamic nature of the work keeps professionals engaged, continuously learning, and developing new skills.
- Entrepreneurial Opportunities: FIG investment banking provides an entrepreneurial environment for driven individuals. There are opportunities to originate deals, build new client relationships, and explore niche areas within the financial institutions sector. FIG investment bankers who can identify market trends, develop innovative solutions, and build a strong network can create their own opportunities and have a significant impact on the industry.
Overall, FIG investment banking offers a diverse and rewarding career path for individuals interested in the financial services industry. It provides opportunities for professional growth, specialization, global exposure, client interaction, and the chance to thrive in a dynamic and challenging environment. As the financial institutions sector continues to evolve, skilled FIG investment bankers will continue to be in high demand, making it an attractive field for ambitious individuals seeking rewarding and fulfilling careers.
Challenges and Risks in FIG Investment Banking
While FIG investment banking offers numerous opportunities, it also presents its fair share of challenges and risks. It’s crucial for professionals in this field to be aware of these challenges and effectively manage the associated risks. Here are some of the key challenges and risks in FIG investment banking:
- Regulatory Complexity: The financial institutions sector is heavily regulated, and regulatory frameworks are constantly evolving. FIG investment bankers must stay updated on regulatory changes and ensure compliance with applicable laws. Failing to navigate the complex regulatory landscape can lead to reputational damage, legal consequences, and financial penalties.
- Market Volatility: The financial services industry is subject to market volatility, which can impact deal activity and financing conditions. FIG investment bankers need to navigate uncertain market conditions, evaluate risks, and adjust transaction structures accordingly. Market fluctuations can result in deals falling through, delays in capital raising, or challenges in valuing financial institutions accurately.
- Competition: FIG investment banking is a highly competitive field. Firms compete for deals, clients, and talent. Standing out in a crowded market requires differentiated expertise, strong relationships, and impeccable execution. The competition can lead to fee pressures, longer deal processes, and the need to consistently deliver exceptional results to secure and retain clients.
- Complex Deal Structures: Deals within the financial institutions sector can be intricate, involving multiple parties, complex regulatory considerations, and unique valuation methodologies. FIG investment bankers must possess excellent technical skills to understand and execute complex deal structures. These complexities can increase the risk of errors, delays, and challenges in due diligence and integration processes.
- Managing Client Expectations: Financial institution clients have high expectations and unique requirements. FIG investment bankers need to effectively manage client expectations, ensuring clear communication, alignment of objectives, and delivering on promises. Meeting client expectations while navigating regulatory complexities and market conditions can be challenging.
- Operational and Cyber Risks: Financial institutions are exposed to various operational and cyber risks. FIG investment bankers need to be mindful of these risks and ensure proper due diligence processes, robust risk management frameworks, and cybersecurity measures are in place. Failure to address operational and cyber risks can result in financial losses, reputational damage, and regulatory scrutiny.
- Work-Life Balance: FIG investment banking is known for its demanding nature, often requiring long hours, tight deadlines, and intense workloads. Achieving work-life balance can be challenging, and professionals in this field must be prepared for periods of high stress and prolonged hours. Managing work-life balance can be crucial for long-term career sustainability and personal well-being.
It’s important for FIG investment banking professionals to be proactive in addressing these challenges and managing associated risks. By staying informed, adapting to market conditions, cultivating strong relationships with clients, and maintaining a focus on compliance and risk management, professionals in this field can navigate the challenges and mitigate potential risks to achieve success.
Conclusion
FIG investment banking offers a dynamic and challenging career path for individuals interested in the financial services industry. As a specialized sector within investment banking, FIG investment banking focuses on providing financial solutions and advisory services to clients in the financial institutions sector.
In this article, we explored the key aspects of FIG investment banking, including its functions, responsibilities, and the skills and qualifications required to succeed. We also discussed the areas and sectors covered in FIG investment banking, typical deals and transactions, and the career prospects and opportunities available in this field.
While FIG investment banking provides numerous opportunities, it also comes with its own set of challenges and risks. Professionals in this field must navigate the complex regulatory environment, manage market volatility, and address competition. They must also be equipped to handle complex deal structures, manage client expectations, and address operational and cyber risks.
Despite the challenges, FIG investment banking offers abundant rewards and the potential for professional growth. It allows individuals to specialize within the financial institutions sector, develop strong client relationships, and gain exposure to global markets. The field is characterized by its dynamic nature, requiring continuous learning, adaptability, and a focus on generating innovative solutions for clients.
In conclusion, FIG investment banking is an exciting and ever-evolving field within the financial services industry. With the right skills, qualifications, and mindset, professionals can make a significant impact in helping financial institutions achieve their strategic objectives and contribute to the growth and stability of the industry as a whole.