Finance
What Is A CIM In Investment Banking?
Modified: December 30, 2023
Learn about the role of a CIM in investment banking and its significance in the world of finance. Gain insights into the functions and responsibilities of a CIM.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
In the world of investment banking, financial documents play a crucial role in facilitating transactions and providing detailed information to potential buyers or investors. One such document is the Confidential Information Memorandum (CIM), which serves as an essential tool for investment bankers in their efforts to market and sell investment opportunities.
A CIM is a comprehensive document that outlines the key aspects of an investment opportunity, providing potential buyers with a detailed understanding of the company, its financials, and its growth potential. It is usually prepared by the investment banking team responsible for handling the deal, with the aim of attracting qualified investors and facilitating the due diligence process.
The CIM is considered a sacred document in the world of investment banking, as it contains sensitive and confidential information about the company being marketed. It is shared only with qualified buyers who have signed non-disclosure agreements and have been vetted by the investment banking team. This level of discretion ensures that sensitive information does not fall into the wrong hands and maintains the integrity of the deal.
The purpose of a CIM is to provide potential buyers with a comprehensive and accurate representation of the investment opportunity. It aims to provide detailed information about the company’s history, management team, market position, financial performance, growth prospects, and potential risks. It is essentially a marketing tool that showcases the company’s strengths and highlights why it is an attractive investment opportunity.
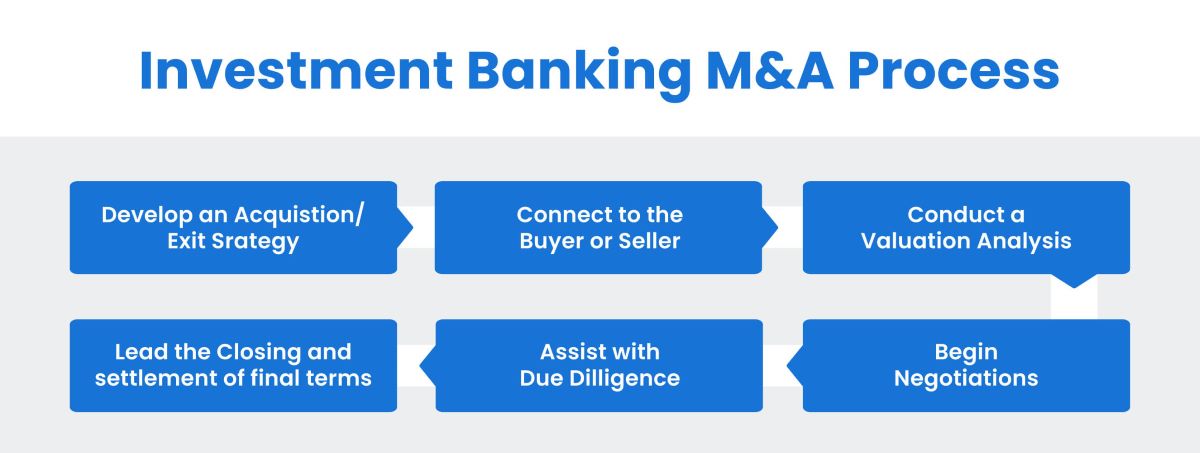
The components of a CIM typically include an executive summary, a description of the company and its industry, financial information, information about the management team, market analysis, and potential risks and opportunities. These components come together to create a holistic view of the company and allow potential buyers to assess the viability and potential return on investment.
In the next section, we will delve deeper into the structure of a CIM and explore the importance of this document in investment banking transactions.
Definition of CIM
A Confidential Information Memorandum (CIM), also known as an Investment Memorandum or an Offering Memorandum, is a comprehensive document that provides detailed information about an investment opportunity. It is a crucial tool in investment banking that is used to market and sell businesses, assets, or securities.
The CIM is prepared by the investment banking team working on a deal, with inputs from the company’s management and other stakeholders. It is designed to provide potential buyers or investors with a comprehensive understanding of the investment opportunity and guide them through the due diligence process.
The CIM is often referred to as confidential because it contains highly sensitive and proprietary information about the company, including financial statements, market analysis, intellectual property, and any other relevant information. Its distribution is limited to qualified buyers who have expressed an interest in the opportunity, and they are required to sign a non-disclosure agreement before receiving the document.
The purpose of a CIM is to provide potential investors with a thorough analysis of the investment opportunity and enable them to make informed decisions. It serves as a marketing tool that highlights the strengths of the company, showcases its growth potential, and addresses any potential risks that investors should be aware of. The goal is to attract credible and qualified investors who align with the strategic objectives of the company and are willing to invest the necessary capital.
In the CIM, the investment banking team presents a detailed description of the company’s background, including its history, management team, and key stakeholders. It also includes a thorough analysis of the industry in which the company operates, providing insights into market size, growth rates, and competitive landscape. Furthermore, the CIM presents the company’s financial performance, projecting future earnings and cash flows.
The CIM acts as a roadmap for potential investors, guiding them through the due diligence process and addressing any questions or concerns they may have. It is a critical document that sets the stage for negotiations and serves as the basis for further discussions and analysis.
In the next section, we will explore the purpose and components of a CIM in more detail to understand its significance in investment banking transactions.
Purpose of a CIM
The primary purpose of a Confidential Information Memorandum (CIM) in investment banking is to effectively market and promote an investment opportunity while providing potential buyers or investors with comprehensive information to support their decision-making process. The CIM serves as a vital tool for investment bankers in their efforts to attract qualified investors and facilitate the due diligence process.
1. Provide Detailed Information: The CIM aims to provide potential buyers with a detailed understanding of the investment opportunity. It contains crucial information about the company, including its background, management team, financial performance, growth prospects, and potential risks. By providing comprehensive information, a CIM allows potential investors to evaluate the opportunity in great detail and make informed investment decisions.
2. Highlight Key Investment Attributes: The CIM showcases the company’s unique selling points, competitive advantages, and growth potential. It emphasizes the strengths of the investment opportunity, such as a strong market position, innovative products or services, a robust customer base, or a talented management team. By highlighting these key attributes, the CIM aims to position the investment as an attractive and lucrative opportunity for potential buyers.
3. Facilitate Due Diligence: As potential investors conduct due diligence, the CIM serves as a reference document that provides a foundation of information. It helps streamline the due diligence process by collating important data and analysis in one document, saving time and effort for both the investment bankers and the potential buyers. The CIM acts as a starting point for deeper discussions and analysis, enabling potential investors to dig deeper into specific aspects of the investment opportunity.
4. Build Investor Confidence: The CIM plays a crucial role in building investor confidence. By providing detailed financial statements, market analysis, and growth projections, it gives potential buyers insight into the company’s financial health, growth potential, and future prospects. This transparency and detailed information instill confidence in potential investors, making them more inclined to move forward with the investment opportunity.
5. Attract Qualified Investors: A well-prepared CIM helps attract qualified investors who align with the strategic objectives of the company. By showcasing the company’s strengths, growth potential, and competitive advantages, the CIM attracts investors with relevant experience, industry knowledge, and access to necessary capital. This targeted approach ensures that the investment opportunity reaches the right audience, increasing the likelihood of a successful transaction.
In summary, the purpose of a CIM is to provide a comprehensive and detailed representation of an investment opportunity, attracting qualified investors while facilitating the due diligence process. It serves as a crucial marketing tool for investment bankers and lays the foundation for successful negotiations and transactions.
Components of a CIM
A Confidential Information Memorandum (CIM) is a comprehensive document that encompasses various components, each serving a specific purpose in providing potential buyers or investors with a comprehensive understanding of the investment opportunity. While the specific components may vary depending on the transaction and industry, the following are some common elements found in a CIM:
1. Executive Summary: The executive summary is a concise overview of the investment opportunity, highlighting key points such as the company’s mission, unique selling propositions, financial performance, and growth potential. It provides a snapshot of the opportunity and helps potential investors quickly grasp its value.
2. Company Description: This section provides an in-depth description of the company, including its history, corporate structure, legal status, and ownership. It also outlines the company’s products or services, target markets, and competitive advantages. This component allows potential investors to understand the company’s positioning and evaluate its potential for success.
3. Financial Information: The financial information section presents the company’s historical financial statements, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. It provides a comprehensive overview of the company’s financial performance, highlighting revenue growth, profitability, and key financial metrics. Projections for future financial performance may also be included to give potential investors insight into expected returns on investment.
4. Management Team: This component introduces the company’s management team, highlighting their qualifications, experience, and track record. It provides potential investors with confidence in the team’s ability to execute the business plan and steer the company towards success. Details about key management personnel, their roles, and their responsibilities are typically included in this section.
5. Market Analysis: The market analysis section assesses the industry dynamics, market size, growth trends, and competitive landscape. It provides potential investors with a clear understanding of the market in which the company operates and its potential for growth. This component also highlights any market trends or opportunities that could impact the investment’s viability.
6. Growth Opportunities and Risks: This section outlines the potential growth opportunities for the company, such as new markets, product expansion, or strategic partnerships. It also addresses potential risks and challenges that could impact the investment’s success, such as regulatory changes, industry disruptions, or competitive threats. This component provides a balanced view of the investment’s potential rewards and risks.
7. Appendices: The CIM may include appendices that provide additional information to support the investment opportunity. This could include legal documents, contracts, patents, customer testimonials, or market research reports. Appendices serve as supplementary material that potential investors can review for a more comprehensive understanding of the investment.
By including these components, a CIM provides potential investors with a holistic view of the investment opportunity, enabling them to make informed decisions. It covers essential aspects of the company, its financial performance, market analysis, and growth prospects, giving potential investors the necessary information to evaluate the viability of the investment and its potential for returns.
Structure of a CIM
The structure of a Confidential Information Memorandum (CIM) is carefully crafted to provide potential buyers or investors with a logical and organized presentation of the investment opportunity. While the specific structure may vary depending on the deal and industry, the following components are commonly included in a CIM:
1. Cover Page: The CIM begins with a cover page that typically includes the company’s name, logo, and the date of the document. It sets the tone for the document and provides a professional and cohesive visual presentation.
2. Table of Contents: The table of contents is a critical component of the CIM, as it provides a clear outline of the document’s contents. It allows potential investors to navigate through the document easily and locate specific sections of interest.
3. Executive Summary: The executive summary provides a concise overview of the investment opportunity, highlighting key points such as the company’s strengths, financial performance, growth potential, and unique selling propositions. It serves as a snapshot of the investment opportunity and aims to capture the attention of potential investors.
4. Company Overview: This section provides a comprehensive description of the company, including its history, mission, products or services, target markets, and competitive advantages. It provides potential investors with a thorough understanding of the company’s background and positioning in the market.
5. Financial Analysis: The financial analysis section presents detailed financial information about the company, including historical financial statements, key financial ratios, and projections. It enables potential investors to assess the company’s financial performance, profitability, cash flow, and potential return on investment.
6. Market Analysis: The market analysis section focuses on evaluating the industry in which the company operates. It includes an assessment of market size, growth trends, market share, competition, and potential opportunities. This component helps potential investors understand the market dynamics and determine the company’s competitive position.
7. Management Team: This section provides information about the company’s management team, including key executives and their qualifications, experience, and track record. It highlights the expertise and capabilities of the management team, reassuring potential investors about the company’s leadership and ability to execute its business strategy.
8. Growth Strategy: The growth strategy section outlines the company’s plans for future expansion and growth. It can include details about new markets, product development, strategic partnerships, or potential acquisitions. This component conveys the company’s vision for the future and its strategies for driving value and growth.
9. Risk Analysis: The risk analysis section identifies and addresses potential risks and challenges that may impact the investment. It includes factors such as regulatory changes, competitive threats, economic uncertainties, and operational risks. This component demonstrates transparency and helps potential investors assess the potential risks associated with the investment.
10. Appendices: The CIM may include appendices that provide supplementary information to support the investment opportunity. This can include legal documents, contracts, patents, customer testimonials, market research reports, or any other relevant documentation.
The structure of a CIM is designed to present a comprehensive and cohesive view of the investment opportunity. It enables potential investors to navigate through the document easily and find the information they need to evaluate the investment’s viability and potential returns.
Importance of CIM in Investment Banking
A Confidential Information Memorandum (CIM) plays a crucial role in investment banking transactions for several reasons. It serves as a powerful tool to attract potential buyers or investors, facilitate due diligence, and ultimately drive successful transactions. Here are some key reasons why the CIM is important in investment banking:
1. Marketing and Investor Attraction: A well-prepared CIM serves as a marketing tool to showcase the investment opportunity and attract qualified buyers or investors. It provides a comprehensive and compelling overview of the company, highlighting its strengths, growth potential, and unique selling points. By presenting an enticing investment narrative, the CIM helps generate interest among potential investors and compels them to further explore the opportunity.
2. Confidentiality and Information Control: The CIM ensures confidential handling of sensitive information about the company being marketed. By carefully controlling the distribution of this document, investment bankers can maintain confidentiality and protect the company’s proprietary information. It is shared only with qualified, pre-screened investors who have signed non-disclosure agreements, ensuring that the investment details remain secure.
3. Due Diligence Facilitation: The CIM serves as a foundation for due diligence, providing potential investors with essential information about the company’s operations, financials, market position, and growth prospects. It allows investors to delve deeper into the opportunity, ask relevant questions, and conduct further analysis. By providing a comprehensive overview, the CIM streamlines the due diligence process and ensures that potential investors have access to the required information.
4. Investor Decision Making: The CIM helps potential investors make informed investment decisions by providing them with a thorough understanding of the investment opportunity. It presents detailed financial statements, market analysis, growth projections, and potential risks. This comprehensive information allows investors to assess the potential returns and risks associated with the investment, enabling them to make informed choices aligned with their investment objectives.
5. Negotiation Tool: The CIM serves as a valuable negotiation tool during the deal-making process. It lays out the investment opportunity, allowing investment bankers and potential investors to have focused discussions and negotiations. The information in the CIM provides a common understanding between both parties, helping to align expectations and facilitate productive negotiations.
6. Documentation of Deal Details: The CIM acts as a comprehensive documentation of the investment opportunity, capturing all the relevant details in one place. This helps in maintaining a clear record of the transaction and ensures that all stakeholders have access to accurate and consistent information throughout the deal process. It also serves as a reference point for future discussions and analysis.
In summary, the CIM is of paramount importance in investment banking. It serves as a powerful marketing and due diligence tool, attracting potential investors, facilitating the assessment of the investment opportunity, and driving successful transactions. By presenting a comprehensive view of the investment, the CIM helps in making informed investment decisions and ensures the confidentiality and integrity of the deal process.
Differences between CIM and other investment banking documents
While the Confidential Information Memorandum (CIM) is a crucial document in investment banking, it is important to understand its unique characteristics and how it differs from other investment banking documents. Here are some key differences between the CIM and other commonly used documents in the industry:
1. CIM vs Pitch Deck: A pitch deck is a condensed presentation that provides an overview of the investment opportunity in a visually appealing and concise manner. It is usually used in initial meetings or presentations to generate interest and attract potential investors. In contrast, a CIM is a comprehensive document that contains detailed and in-depth information about the investment opportunity, providing a more thorough analysis for potential investors during the due diligence process.
2. CIM vs Teaser: A teaser, also known as an Executive Summary or a One-Pager, is a short document that provides a brief overview of the investment opportunity. It entices potential investors to express interest and sign a non-disclosure agreement to gain access to more detailed information, such as the CIM. While a teaser serves as a preliminary marketing tool, the CIM provides a more detailed analysis and comprehensive view of the investment opportunity.
3. CIM vs Business Plan: A business plan outlines a company’s business model, strategy, and financial projections. It is typically used by entrepreneurs or management teams to guide the internal operations of the company. In contrast, a CIM is prepared by investment bankers and is focused on marketing an investment opportunity to potential investors. The CIM provides a more comprehensive analysis of the company’s financials, market position, growth prospects, and potential risks, with the objective of attracting external investors.
4. CIM vs Term Sheet: A term sheet is a non-binding agreement that outlines the proposed terms and conditions of an investment or a transaction. It serves as a starting point for negotiations and helps align the expectations of both parties. The CIM, on the other hand, provides a thorough analysis of the investment opportunity, including financial performance, market analysis, and growth prospects. While a term sheet focuses on the terms of the deal, the CIM provides the necessary information to evaluate and assess the investment opportunity.
5. CIM vs Prospectus: A prospectus is a legal document that is typically prepared when a company decides to go public and issue securities to the general public. It provides detailed information about the company, including its history, business model, financials, and potential risks. The CIM, however, is prepared in the private market and is used to attract potential buyers or investors for a specific investment opportunity. The prospectus is a regulatory requirement for public offerings, while the CIM is a marketing document tailored to a specific investment opportunity.
In summary, while the CIM shares some similarities with other investment banking documents, such as providing information about an investment opportunity, it has distinct differences in terms of depth, focus, and audience. The CIM provides a comprehensive analysis of the investment opportunity to attract potential investors during the due diligence process, distinguishing it from other documents that serve different purposes in investment banking transactions.
Conclusion
The Confidential Information Memorandum (CIM) is a critical document in the world of investment banking. It serves as a comprehensive tool that enables investment bankers to market and sell investment opportunities to potential buyers or investors. The CIM provides detailed information about the company, its financials, market analysis, and growth prospects, allowing potential investors to make informed decisions and conduct due diligence.
The CIM’s importance in investment banking cannot be overstated. It serves as a marketing tool, attracting qualified investors by highlighting the key strengths and competitive advantages of the investment opportunity. It provides potential investors with the necessary information to evaluate the viability, potential returns, and risks associated with the investment.
Furthermore, the CIM facilitates the due diligence process by streamlining the access to information and serving as a reference document for further analysis and discussions. It helps build investor confidence, as it provides transparency and a clear understanding of the investment opportunity.
It is important to note that the CIM differs from other investment banking documents such as pitch decks, teasers, business plans, term sheets, and prospectuses. While these documents serve their own unique purposes, the CIM stands out for its comprehensive and detailed analysis of the investment opportunity.
In conclusion, the CIM plays a crucial role in investment banking by providing potential investors with a comprehensive understanding of the investment opportunity, attracting qualified buyers, and facilitating the due diligence process. It is a powerful tool for investment bankers to effectively market and sell investment opportunities, and its careful preparation is essential for a successful transaction. The CIM ensures confidentiality, enables in-depth analysis, and serves as a foundation for negotiations, making it an indispensable component in the investment banking landscape.