Finance
What Is IRS Form 720?
Published: November 1, 2023
Learn about IRS Form 720 and its significance in finance. Understand the purpose, requirements, and potential benefits of filing this form with the IRS.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Purpose of IRS Form 720
- Who Needs to File IRS Form 720?
- Reporting Requirements for IRS Form 720
- Overview of IRS Form 720 Sections
- Part I: Excise Taxes on Specific Goods and Services
- Part II: Fuel Taxes
- Part III: Environmental Taxes
- Part IV: Communications and Air Transportation Taxes
- Part V: Health Insurance Policies
- Part VI: Payment and Signature Information
- Filing Deadlines for IRS Form 720
- Consequences of Non-Filing or Late Filing
- Conclusion
Introduction
When it comes to managing your finances, it’s important to stay on top of your tax obligations. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) is responsible for collecting taxes to fund vital government programs and services. As part of this process, the IRS has various forms that taxpayers need to complete, one of which is Form 720.
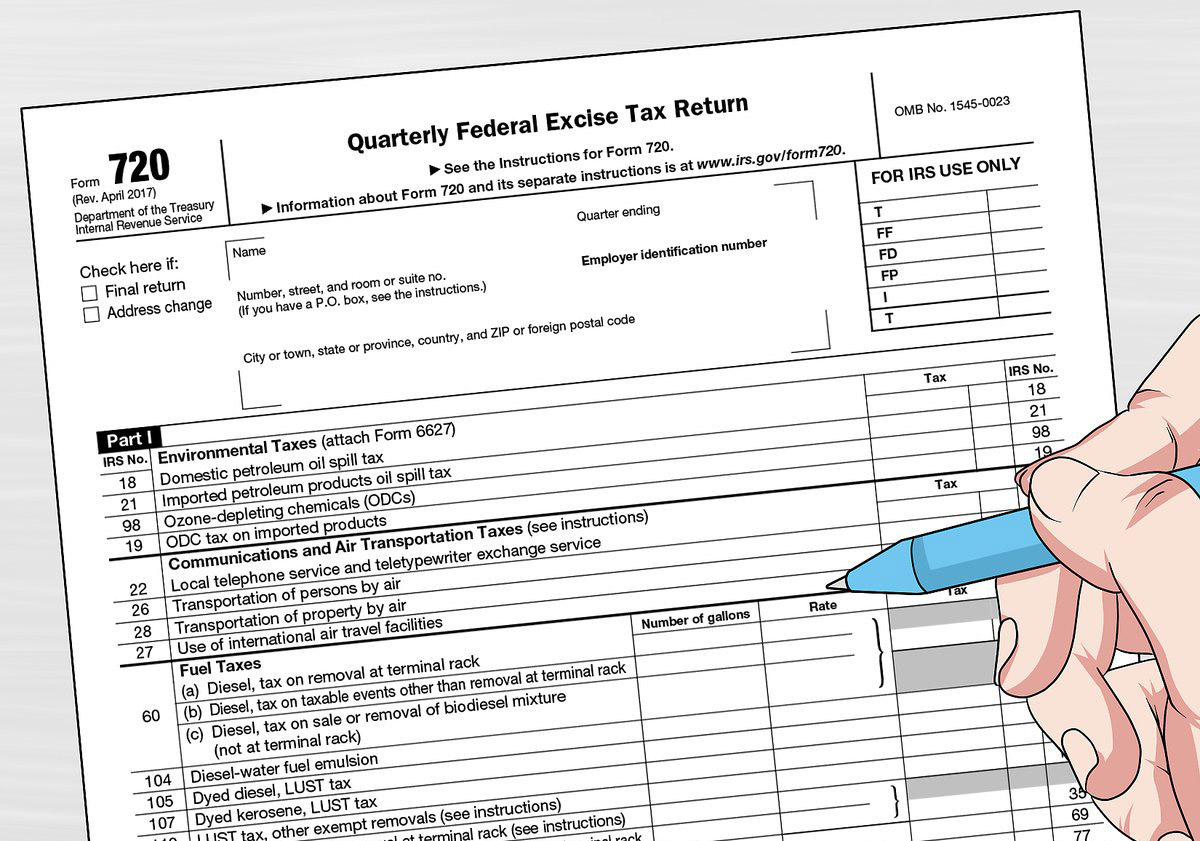
Form 720, also known as the Quarterly Federal Excise Tax Return, is used to report and pay excise taxes on a quarterly basis. These taxes are charged on specific goods, services, and activities, such as fuel, environmental activities, and health insurance policies. This form ensures that individuals and businesses meet their tax obligations and helps the IRS track and collect these excise taxes effectively.
Understanding Form 720 is crucial if you or your business falls into any of the categories that require its filing. In this article, we will delve into the purpose of Form 720, who needs to file it, the reporting requirements, the different sections of the form, and the consequences of non-filing or late filing.
Stay tuned as we guide you through the ins and outs of IRS Form 720, helping you navigate the complexities of tax compliance and ensuring you fulfill your financial responsibilities to the government.
Purpose of IRS Form 720
The primary purpose of IRS Form 720 is to report and pay various excise taxes to the IRS. Excise taxes are taxes incurred on the purchase or use of specific goods, services, or activities that have been deemed taxable by the government.
By requiring individuals and businesses to file Form 720, the IRS aims to ensure that all applicable excise taxes are properly reported and paid. This helps maintain tax compliance among taxpayers and prevents tax evasion or underpayment.
Additionally, Form 720 serves as a tool for the IRS to collect vital data and statistics on the consumption and usage of taxable goods and services. This information enables the IRS to monitor industry trends, analyze revenue streams, and make informed decisions regarding taxation policies.
Furthermore, Form 720 provides a clear record of excise tax payments, allowing taxpayers to maintain accurate financial records and easily reconcile their tax obligations. It acts as documentation for any potential audits or inquiries from the IRS.
It’s important to note that Form 720 is a quarterly filing, meaning it needs to be submitted four times a year. This frequency ensures that excise taxes are reported and paid in a timely manner, preventing any significant financial burdens from accumulating.
Overall, the purpose of IRS Form 720 is to facilitate the proper reporting and payment of excise taxes, maintain tax compliance, collect vital data and statistics, and provide a record of tax payments. By fulfilling this purpose, individuals and businesses can fulfill their financial obligations and contribute to the functioning of essential government programs and services.
Who Needs to File IRS Form 720?
Not all individuals and businesses are required to file IRS Form 720. The need to file this form depends on several factors, including the type of goods, services, or activities you engage in. Here are some categories of taxpayers who may need to file Form 720:
- Manufacturers and Producers: If you produce or manufacture goods that are subject to excise taxes, such as alcohol, tobacco, or firearms, you are generally required to file Form 720.
- Importers and Exporters: If you import goods into the United States that are subject to excise taxes, or if you export goods on which a refund of excise taxes has been claimed, you may need to file Form 720.
- Providers of Specific Services: Certain services are subject to excise taxes, such as indoor tanning services and air transportation. If you provide these services, you may be required to file Form 720.
- Operators of Facilities and Equipment: If you operate facilities or equipment that are subject to excise taxes, such as gasoline stations, you will likely need to file Form 720.
- Providers of Health Insurance Policies: Insurance companies and plan sponsors offering self-insured health coverage are required to file Form 720 to report and pay the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) fee.
It’s important to note that not all taxpayers within these categories are obligated to file Form 720. Specific exemptions, thresholds, and requirements may apply, so it’s crucial to consult the IRS instructions or seek guidance from a tax professional to determine your filing obligations.
Additionally, if you have no taxable liabilities for a particular quarter, you may not be required to file Form 720. However, it’s advisable to review the instructions and consult with a tax expert to ensure you are in compliance with the IRS regulations.
By understanding who needs to file IRS Form 720, you can determine if you fall within the scope of this reporting requirement and fulfill your tax obligations appropriately.
Reporting Requirements for IRS Form 720
When filing IRS Form 720, it’s essential to understand the reporting requirements to ensure accurate and compliant submission. Here are the key elements to consider:
- Filing Frequency: Form 720 is filed on a quarterly basis. The due dates for each quarter are April 30, July 31, October 31, and January 31 of the following year. It’s crucial to mark your calendar and submit the form and payment by the applicable deadline.
- Accurate Reporting: Ensure that all the information provided on Form 720 is accurate and complete. Double-check all calculations, identification details, and amounts before filing. Errors or omissions could lead to penalties or unwanted IRS scrutiny.
- Separate Reporting for Each Category: If you are subject to excise taxes in multiple categories, such as both fuel taxes and environmental taxes, you must report each category separately on the form. This ensures proper allocation of taxes and facilitates easier tracking for the IRS.
- Payment Information: Form 720 requires you to provide payment details for the excise taxes being reported. Ensure that you accurately report the amount due and include any additional information requested, such as contact information and payment method.
- Method of Filing: Form 720 can be filed electronically or by mail. Electronic filing is recommended as it is faster, more efficient, and reduces the risk of errors. The IRS provides an online portal for electronic filing, or you can use approved third-party software.
- Recordkeeping: It is important to maintain thorough and organized records of your Form 720 filings. Keep copies of filed forms, payment receipts, and any supporting documentation for at least three years. These records will be crucial in case of an audit or if you need to reference past filings.
It’s worth noting that the reporting requirements for Form 720 may vary depending on the specific section of the form related to your excise tax liability. Familiarize yourself with the instructions provided by the IRS for each section to ensure compliance.
By adhering to the reporting requirements for IRS Form 720, you can meet your tax obligations accurately and in a timely manner, reducing the risk of penalties or other compliance issues.
Overview of IRS Form 720 Sections
IRS Form 720 consists of several sections, each corresponding to different types of excise taxes. Understanding these sections will help you accurately report and pay the applicable taxes. Here’s an overview of the different sections of Form 720:
- Part I: Excise Taxes on Specific Goods and Services: This section covers a wide range of taxable goods and services, such as alcohol, tobacco, firearms, sports fishing equipment, and certain fuel-related activities. It requires detailed information on the type of goods or services, the quantities involved, and the corresponding excise tax liabilities.
- Part II: Fuel Taxes: This section focuses on excise taxes related to fuel, including gasoline, diesel fuel, and alternative fuels. It requires reporting on the amount of fuel sold or used, the applicable tax rates, and any credits or refunds claimed.
- Part III: Environmental Taxes: Here, you will report excise taxes related to environmental activities, such as ozone-depleting chemicals, petroleum spill taxes, and certain air transportation activities. This section requires specific information related to the taxable activity and the corresponding tax liabilities.
- Part IV: Communication and Air Transportation Taxes: This section covers excise taxes on communication services, such as telephone communication and air transportation. It requires reporting on the gross amounts of communication service receipts or air transportation charges, as well as any exemptions, adjustments, or refunds claimed.
- Part V: Health Insurance Policies: For insurance companies and plan sponsors offering self-insured health coverage, this section is used to report and pay the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) fee. It requires information on the average number of covered lives and the applicable fee amount.
- Part VI: Payment and Signature Information: The final section of Form 720 is where you provide the payment details for the total tax liability reported on the form. It also requires your signature to certify the accuracy of the information provided.
Each section of Form 720 has its own set of instructions and requirements, so it’s important to carefully review and understand the specific guidelines provided by the IRS. Make sure to accurately report the necessary information, perform any calculations correctly, and clearly indicate the amount due for each section.
By familiarizing yourself with the different sections of IRS Form 720, you can navigate the form more easily and ensure compliance with the reporting requirements for the applicable excise taxes.
Part I: Excise Taxes on Specific Goods and Services
Part I of IRS Form 720 focuses on excise taxes on specific goods and services. This section is expansive and covers a wide range of taxable items, ensuring that various industries and activities contribute to the federal excise tax revenue. Here’s an overview of the key areas covered in Part I:
- Alcohol: This category includes excise taxes on alcoholic beverages, such as beer, wine, and distilled spirits. The tax rates vary depending on the type and quantity of the product.
- Tobacco Products: Excise taxes on tobacco products, including cigarettes, cigars, and smokeless tobacco, are reported in this section. Different tax rates apply based on the type and weight of the product.
- Firearms: If you are involved in the manufacturing, importation, or sale of firearms, you will need to report the excise taxes associated with these transactions. This includes handguns, rifles, and shotguns.
- Sports Fishing Equipment: Excise taxes may be imposed on certain sporting fishing equipment, such as fishing rods, tackle boxes, and lures. These taxes contribute to the conservation of fish habitats and recreational fishing programs.
- Gas Guzzler Tax: This section pertains to the excise tax applied to vehicles that do not meet specific fuel efficiency requirements. It is aimed at discouraging the use of fuel-inefficient vehicles and promoting environmentally friendly alternatives.
- Air Transportation Taxes: Excise taxes imposed on air transportation services, including passenger ticket taxes, segment fees, and domestic and international flight segment taxes, are reported in this part of Form 720.
- Other Activities: Part I also includes excise taxes on various activities and goods, such as indoor tanning services, arrow shafts, recreational equipment, and certain use of highway motor vehicles.
When reporting excise taxes in Part I, you will need to provide detailed information about the items or services subject to taxation, such as the quantities involved and the corresponding tax liabilities. It’s important to carefully review the instructions provided by the IRS to accurately determine the applicable tax rates and calculation methods for each category.
By properly completing Part I of IRS Form 720, you can ensure that the excise taxes on specific goods and services are reported and paid in compliance with IRS regulations.
Part II: Fuel Taxes
Part II of IRS Form 720 is dedicated to reporting excise taxes related to fuel. It encompasses various types of fuel and ensures that taxes are collected on their sale or use. Here’s an overview of what is covered in Part II:
- Gasoline: Gasoline is one of the most commonly used fuels, and it is subject to federal excise taxes. When filing Form 720, you will report the quantity of gasoline sold or used during the quarter and calculate the applicable tax based on the current rate.
- Diesel Fuel: Similar to gasoline, diesel fuel is subject to federal excise taxes. Part II requires reporting the amount of diesel fuel sold or used and calculating the excise tax accordingly.
- Alternative Fuels: This category includes fuels such as ethanol, biodiesel, compressed natural gas (CNG), and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG). You must report the quantity of alternative fuels sold or used and calculate the corresponding tax liabilities.
- Aviation Fuels: Part II also covers excise taxes on aviation gasoline and kerosene used in commercial aviation. The tax rates may vary, so be sure to consult the IRS instructions to accurately determine the applicable tax rates and calculations for aviation fuels.
- Special Fuels: Certain types of fuel, such as fuel used in trains, vessels, and intercity buses, are categorized as special fuels. You are required to report the quantity of special fuels sold or used and calculate the respective excise taxes.
- Credits and Refunds: Form 720 also allows for the reporting of any credits or refunds to offset the excise tax liability on fuel. If you are eligible for any of these credits or refunds, you can provide the necessary information in this section.
When completing Part II of Form 720, it’s important to accurately report the quantities of fuel sold or used, calculate the corresponding tax liabilities, and apply any applicable credits or refunds. Refer to the IRS instructions and consult with a tax professional if needed to ensure compliance with the reporting requirements.
By properly reporting fuel taxes in Part II, you can fulfill your tax obligations and contribute to the funding of essential transportation infrastructure and programs.
Part III: Environmental Taxes
Part III of IRS Form 720 focuses on reporting excise taxes related to environmental activities. These taxes are imposed to address environmental concerns and promote sustainable practices. Here’s an overview of what is covered in Part III:
- Ozone-Depleting Chemicals: This section includes excise taxes on chemicals that are known to deplete the ozone layer. The tax rates vary based on the type and quantity of the chemicals.
- Petroleum Spill Taxes: Excise taxes are imposed on crude oil, petroleum products, and hazardous substances to support the Oil Spill Liability Trust Fund. Part III requires reporting the quantity of taxable substances and calculating the applicable tax liabilities.
- Air Transportation Activities: Certain air transportation activities, such as transporting persons or property by air and making aircraft available for hire, are subject to excise taxes. This includes taxes on domestic and international air transportation and fractional ownership of aircraft.
- Imported Coal: If you import coal into the United States, you may be required to report and pay excise taxes on its importation. This tax aims to address environmental concerns associated with coal consumption.
When completing Part III of Form 720, you will need to provide detailed information on the specific environmental activity or substance subject to excise taxes. This may include quantities, tax rates, and any applicable exemptions or credits.
It’s important to consult the IRS instructions to accurately determine the tax rates and calculations for each category in Part III. Pay close attention to any additional requirements or documentation needed to support your tax filings.
By properly reporting environmental taxes in Part III, you can fulfill your tax obligations and contribute to environmental programs and initiatives aimed at preserving our natural resources and promoting sustainable practices.
Part IV: Communications and Air Transportation Taxes
Part IV of IRS Form 720 is dedicated to reporting excise taxes related to communications services and air transportation. These taxes help fund vital infrastructure and services in the communication and aviation sectors. Here’s an overview of what is covered in Part IV:
- Communications Taxes: This section encompasses excise taxes on various communication services. It includes taxes on local and long-distance telephone services, voice over internet protocol (VoIP), and pre-paid phone cards. Reportable amounts include both taxable and nontaxable services, with specific guidelines provided by the IRS.
- Air Transportation Taxes: Excise taxes on air transportation services are also covered in Part IV. This includes taxes on the transportation of persons or property by air, as well as taxes on the fractional ownership of an aircraft. The tax rates and reporting requirements may differ based on domestic or international flights.
When completing Part IV of Form 720, it is essential to accurately report the gross amounts of communication service receipts and air transportation charges. Pay attention to any exemptions or adjustments that may apply to specific services, as well as the various tax rates for different types of communication and air transportation activities.
Consult the IRS instructions and seek guidance from a tax professional if needed to ensure compliance with the reporting requirements specific to each category in Part IV.
By properly reporting communications and air transportation taxes in Part IV, you can fulfill your tax obligations and contribute to the maintenance and improvement of communication infrastructure and air transportation services.
Part V: Health Insurance Policies
Part V of IRS Form 720 is dedicated to reporting and paying the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) fee for health insurance policies. This fee helps fund research initiatives and studies aimed at improving patient outcomes and healthcare quality. Here’s an overview of what is covered in Part V:
- Insurance Companies: Insurance companies that provide specified health insurance policies are required to report and pay the PCORI fee. These policies include medical, dental, and vision coverage.
- Self-Insured Health Plans: Plan sponsors offering self-insured health coverage are also responsible for reporting and paying the PCORI fee. This applies to employers who choose to self-fund their employee health benefit plans.
- Covered Lives: Part V requires reporting the average number of covered lives for each policy or plan subject to the PCORI fee. This includes both employees and their dependents who are covered under the policy or plan.
- Fee Calculation: The PCORI fee is calculated based on the number of covered lives, with specific rates set annually by the IRS. The fee is reported along with any adjustments, exemptions, or credits that may apply.
When completing Part V of Form 720, ensure that you accurately report the average number of covered lives for each applicable health insurance policy or self-insured health plan. Calculate the PCORI fee based on the current IRS rate, and report any adjustments or exemptions as necessary.
It’s important to consult the IRS instructions and seek guidance from a tax professional to ensure compliance with the reporting requirements and fee calculation for health insurance policies in Part V.
By properly reporting and paying the PCORI fee in Part V, you can fulfill your tax obligations and contribute to the funding of research initiatives aimed at improving patient-centered care and healthcare outcomes.
Part VI: Payment and Signature Information
Part VI of IRS Form 720 is the final section, where you will provide the payment and signature information for the form. It is essential to complete this section accurately to ensure the proper processing of your tax payment and submission. Here’s an overview of what is covered in Part VI:
- Payment Details: In this section, you will specify the total amount of tax liability that you owe for the taxable activities reported on Form 720. It includes the sum of the taxes reported in each part of the form, such as excise taxes, fuel taxes, and environmental taxes.
- Payment Methods: Form 720 allows you to choose various payment methods, such as electronic funds withdrawal (direct debit), EFTPS (Electronic Federal Tax Payment System), credit/debit card, or by check or money order.
- Signature: The form requires your signature to certify that the information provided is accurate and complete to the best of your knowledge. By signing the form, you acknowledge that you are authorized to submit it on behalf of the taxpayer, whether it’s yourself or the entity you represent.
When completing Part VI, double-check that the payment amount is correct and matches your tax liability. Ensure that you select the appropriate payment method and provide the required information, such as bank account details for electronic funds withdrawal or credit card information if applicable.
Finally, affix your signature in the designated area to confirm the accuracy of the information provided on the form. Keep in mind that by signing, you are legally attesting to the veracity of the information and assuming responsibility for its accuracy.
Before submitting Form 720, review the payment and signature details carefully to avoid any errors or omissions. Retain a copy of the filed form, as well as any payment confirmation or receipt, for your records.
By accurately completing Part VI of Form 720, you can ensure proper payment of your tax liability and provide the necessary verification of your submission.
Filing Deadlines for IRS Form 720
When it comes to IRS Form 720, it’s crucial to be aware of the filing deadlines to ensure timely submission and avoid penalties. The deadlines for filing Form 720 are based on a quarterly schedule. Here are the key dates to remember:
- 1st Quarter: The deadline for filing the 1st quarter Form 720 is April 30th. This includes excise taxes and other liabilities incurred during the months of January, February, and March.
- 2nd Quarter: The 2nd quarter Form 720 is due by July 31st. This covers the period from April to June.
- 3rd Quarter: The 3rd quarter filing deadline is October 31st. This encompasses excise taxes and liabilities accrued between July and September.
- 4th Quarter/Annual: The final quarter and annual Form 720 is due on January 31st of the following year. This is a comprehensive filing that includes any outstanding taxes from previous quarters and any additional annual obligations.
It’s important to mark these dates on your calendar and make sure to submit your Form 720 and associated payments by the respective deadlines. Late filing or non-filing can result in penalties and interest charges imposed by the IRS.
In addition to the filing deadlines, it’s advisable to start gathering the necessary information and completing the form well in advance. This allows ample time for review, calculation, and addressing any potential issues or questions that may arise.
Remember that the deadlines may vary slightly if the due date falls on a weekend or a federally recognized holiday. In such cases, the deadline typically shifts to the next business day.
By staying informed of the filing deadlines for IRS Form 720 and planning accordingly, you can ensure timely and compliant submission of your tax obligations.
Consequences of Non-Filing or Late Filing
Non-filing or late filing of IRS Form 720 can have several consequences, ranging from financial penalties to potential legal implications. It’s essential to understand these consequences to ensure compliance with the filing requirements. Here are the key consequences to be aware of:
- Penalties and Interest: Failing to file Form 720 or filing it after the deadline can result in penalties imposed by the IRS. The penalty amount varies based on the number of days the filing is late and the size of the tax liability. Additionally, interest may also be charged on any unpaid tax amount.
- Audit and Compliance Risk: Non-filing or late filing can increase the likelihood of being selected for an IRS audit. This can lead to additional scrutiny, inquiries, and potential legal consequences if discrepancies or inaccuracies are found in your tax filings.
- Loss of Refunds: Late filing may result in the loss of potential tax refunds you may be eligible for, especially if you have overpaid your excise taxes or are entitled to any credits or refunds.
- Failure to Meet Legal Obligations: Failing to meet your tax obligations, including timely filing of Form 720, can have legal implications. It can affect your legal standing, credibility, and ability to engage in certain business activities, particularly if your business relies on compliance with federal tax regulations.
- Reputational Damage: Non-compliance with tax filing requirements can damage your reputation and erode trust with customers, business partners, and other stakeholders. It’s essential to maintain a strong reputation for financial responsibility and compliance.
To avoid the consequences of non-filing or late filing, it’s important to stay organized, keep track of the filing deadlines, and ensure timely submission of Form 720. Utilize reminders, set up efficient record-keeping systems, and seek professional guidance if needed to ensure compliance with the IRS requirements.
If you have missed the filing deadline, it’s best to file as soon as possible to minimize the potential penalties and interest charges. The IRS generally encourages voluntary compliance, and acting promptly can help mitigate the consequences of non-filing or late filing.
By understanding the consequences of non-filing or late filing of IRS Form 720, you can take the necessary steps to meet your tax obligations on time, avoid penalties, and maintain compliance with tax regulations.
Conclusion
IRS Form 720, the Quarterly Federal Excise Tax Return, is an essential document for reporting and paying excise taxes on specific goods, services, and activities. Understanding the purpose, filing requirements, and deadlines associated with Form 720 is crucial for individuals and businesses in complying with their tax obligations and avoiding potential penalties.
Throughout this article, we have provided a comprehensive overview of IRS Form 720, covering its purpose and the various sections that encompass excise taxes on specific goods and services, fuel taxes, environmental taxes, communications and air transportation taxes, and health insurance policies.
We have also highlighted the importance of accurate reporting, the filing deadlines, and the potential consequences of non-filing or late filing, including financial penalties, audit risk, loss of refunds, and reputational damage.
To ensure compliance, it is essential to familiarize yourself with the IRS instructions, seek guidance from tax professionals if needed, and maintain thorough records of your tax filings and payments.
By staying informed, fulfilling your tax obligations, and timely submitting IRS Form 720, you can contribute to the functioning of vital government programs and services, while avoiding the consequences of non-compliance. It is always recommended to consult with qualified tax professionals for personalized advice and support to ensure accurate and compliant reporting.
Remember, proper compliance with tax regulations is not only a legal requirement but also an important aspect of maintaining financial stability and contributing to the overall well-being of society.