
Finance
What Is Working Capital Management
Published: December 19, 2023
Learn the importance of working capital management in finance and how it impacts the financial stability and success of businesses.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Working Capital Management
- Components of Working Capital
- Importance of Working Capital Management
- Effective Working Capital Management Strategies
- Key Performance Indicators for Working Capital Management
- Challenges in Working Capital Management
- Benefits of Effective Working Capital Management
- Conclusion
Introduction
Working capital management is a crucial aspect of financial management for businesses of all sizes and industries. It involves managing a company’s short-term assets and liabilities to ensure its daily operations run smoothly and efficiently. The goal of working capital management is to maintain a balance between having enough liquidity to meet current obligations and optimizing the use of available resources.
Effective working capital management is essential for businesses to meet their short-term financial obligations, such as paying suppliers, managing inventory levels, and covering day-to-day operational expenses. It also plays a vital role in maintaining a stable cash flow, enhancing profitability, and sustaining growth.
Managing working capital requires careful planning and control over various components, including cash, inventory, accounts receivable, and accounts payable. It involves optimizing the levels of these components to mitigate risks associated with liquidity, return on investment, and operational efficiency.
In this article, we will explore the key components of working capital management, understand why it is important, and discuss effective strategies for managing working capital. We will also look at key performance indicators that can help evaluate the efficiency of working capital management and the challenges businesses often face in this area. Finally, we will highlight the benefits of implementing effective working capital management practices for long-term business success.
Definition of Working Capital Management
Working capital management refers to the process of monitoring and controlling a company’s current assets and liabilities to ensure the efficient use of resources and maintain sufficient liquidity to meet short-term obligations. It involves analyzing, planning, and managing the company’s cash flow, inventory, accounts receivable, and accounts payable.
Working capital is the capital required to fund a company’s day-to-day operations, including purchasing raw materials, paying wages, and covering other operational expenses. It is the difference between a company’s current assets and current liabilities.
Current assets include cash, short-term investments, accounts receivable, and inventory. These assets are expected to be converted into cash within a year or within the operating cycle of the business. On the other hand, current liabilities include accounts payable, accrued expenses, and short-term debt. These liabilities are typically due within a year or the operating cycle.
The primary objective of working capital management is to ensure that the company has enough liquidity to meet its short-term obligations while maximizing profitability and minimizing risks. It involves striking a balance between maintaining adequate cash flow for daily operations and avoiding excessive investment in non-productive assets.
Effective working capital management requires efficient cash flow forecasting, accurate inventory management, and careful monitoring of accounts receivable and accounts payable. It also involves optimizing working capital ratios, such as the current ratio and the quick ratio, to assess the company’s liquidity and financial health.
By managing working capital effectively, companies can improve cash flow, reduce borrowing costs, minimize the risk of stockouts or excess inventory, and enhance operational efficiency. It enables businesses to seize growth opportunities, navigate economic downturns, and build a solid foundation for long-term success.
Components of Working Capital
Working capital is comprised of several components that collectively determine a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations and maintain smooth operations. These components include:
- Cash: Cash is the most liquid asset and represents the amount of money available to the company at any given time. It includes cash on hand, cash in bank accounts, and highly liquid investments. Adequate cash reserves are crucial for meeting daily expenses, paying suppliers, and managing unforeseen expenses.
- Accounts Receivable: Accounts receivable refers to the money owed to a company by its customers for goods or services provided on credit. It represents the company’s outstanding invoices that are yet to be collected. Effective management of accounts receivable involves timely invoicing, credit assessments, collection efforts, and monitoring payment terms to minimize the risk of bad debts.
- Inventory: Inventory includes the goods and materials held by a company for production, sale, or use in its operations. Efficient inventory management is essential to balance the cost of carrying inventory with avoiding stockouts. It involves forecasting demand, optimizing order quantities, minimizing holding costs, and monitoring inventory turnover rates.
- Accounts Payable: Accounts payable represents the money owed by a company to its suppliers for goods or services purchased on credit. Managing accounts payable effectively involves negotiating favorable payment terms, taking advantage of early payment discounts, and ensuring timely payments to maintain good relationships with suppliers.
- Short-term Debt: Short-term debt consists of the company’s obligations to repay borrowed funds within a year. It can include bank loans, lines of credit, or short-term financing options. Prudent management of short-term debt involves proper planning, assessing the cost of borrowing, and ensuring that the repayment schedule aligns with the company’s cash flow.
Effective management of these working capital components is crucial for maintaining liquidity, maximizing profitability, and optimizing the use of available resources. It requires continuous monitoring, forecasting, and strategic decision-making to ensure the smooth functioning of a company’s day-to-day operations.
Importance of Working Capital Management
Working capital management is vital for the financial health and success of a company. It plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth functioning of day-to-day operations and maintaining a strong liquidity position. Here are some reasons why working capital management is important:
- Meet Short-term Obligations: Effective working capital management ensures that a company has enough liquidity to meet its short-term obligations, such as paying suppliers, wages, utility bills, and other operational expenses. It helps avoid disruptions in business operations and maintain a positive reputation with stakeholders.
- Optimize Cash Flow: By managing working capital efficiently, companies can enhance their cash flow and reduce the need for external financing. This allows them to allocate resources to growth initiatives, invest in new projects, and handle unforeseen expenses without relying heavily on borrowing.
- Manage Inventory Levels: Working capital management involves optimizing inventory levels to strike a balance between avoiding stockouts and minimizing holding costs. By effectively managing inventory, companies can reduce carrying costs, improve order fulfillment, and enhance customer satisfaction.
- Minimize Cost of Capital: Maintaining a healthy level of working capital reduces reliance on short-term borrowing and lowers the company’s cost of capital. This leads to improved profitability as less money is spent on interest payments, allowing more funds to be allocated to other productive uses.
- Improve Supplier Relationships: Sound working capital management involves timely payment to suppliers, which helps build strong relationships. By paying suppliers promptly, businesses can negotiate better terms, enjoy early payment discounts, and secure better pricing or credit terms in the future.
- Navigate Economic Downturns: In times of economic uncertainty or recession, companies with effective working capital management are better equipped to weather the storm. They can manage their cash flow, preserve liquidity, and make strategic decisions to sustain operations when revenues are impacted.
Overall, working capital management is essential for enhancing operational efficiency, maintaining financial stability, and supporting long-term growth. By effectively managing their working capital, companies can optimize their resources and position themselves for success in both favorable and challenging business environments.
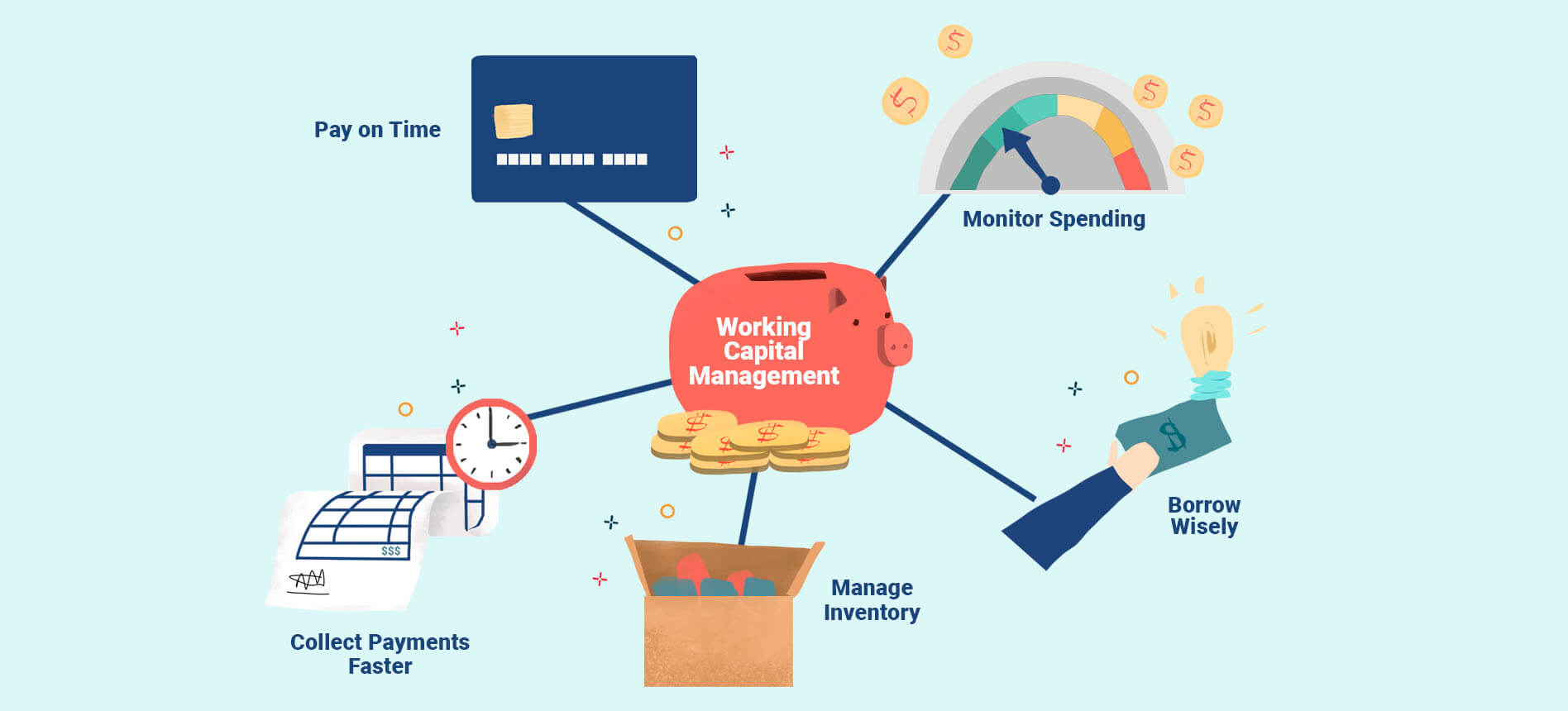
Effective Working Capital Management Strategies
Implementing effective working capital management strategies is essential to optimize the use of resources, maintain liquidity, and improve financial performance. Here are some key strategies that businesses can employ:
- Accurate Cash Flow Forecasting: Developing accurate cash flow forecasts allows businesses to anticipate fluctuations in cash inflows and outflows. By understanding their cash needs, companies can make informed decisions regarding managing expenses, prioritizing payments, and identifying opportunities to invest surplus funds.
- Tight Credit Control: Implementing efficient credit control practices is critical for managing accounts receivable. This involves conducting credit checks on customers, setting reasonable credit limits, and following up on overdue invoices promptly. By minimizing bad debts and improving collections, businesses can improve their cash flow and reduce the risk of financial instability.
- Optimized Inventory Management: Employing effective inventory management techniques helps strike the right balance between carrying costs and stockouts. This includes forecasting demand accurately, adopting just-in-time inventory systems, and conducting regular inventory audits to identify slow-moving or obsolete items. By optimizing inventory levels, businesses can minimize costs, improve cash flow, and enhance order fulfillment capabilities.
- Supplier Relationship Management: Building strong relationships with suppliers is crucial for negotiating favorable payment terms and securing discounts. This entails maintaining open lines of communication, fostering trust, and seeking opportunities for collaboration. By cultivating good relationships, companies can benefit from improved credit terms, faster delivery times, and cost savings.
- Efficient Accounts Payable Processes: Streamlining accounts payable processes helps businesses manage their outstanding debts effectively. This includes optimizing payment schedules, taking advantage of early payment discounts, and leveraging available payment technologies. By managing accounts payable efficiently, companies can maintain good relationships with suppliers, optimize cash flow, and avoid unnecessary late payment penalties.
- Working Capital Ratio Analysis: Regularly monitoring and analyzing key working capital ratios, such as the current ratio and the quick ratio, can provide valuable insights into a company’s financial health. These ratios enable businesses to assess their liquidity, identify areas where improvements can be made, and make data-driven decisions to optimize working capital management.
These strategies can be tailored to suit the specific needs and circumstances of each business. By implementing effective working capital management strategies, businesses can enhance their financial stability, improve cash flow, and position themselves for sustainable growth and success.
Key Performance Indicators for Working Capital Management
Tracking and measuring key performance indicators (KPIs) are vital in assessing the effectiveness of working capital management strategies. KPIs provide valuable insights into a company’s financial health, liquidity, and efficiency. Here are some key performance indicators for working capital management:
- Current Ratio: The current ratio is a widely-used liquidity indicator that measures a company’s ability to cover its short-term obligations. It is calculated by dividing current assets by current liabilities. A ratio of 2:1 or higher is generally considered healthy as it indicates that a company has sufficient current assets to cover its current liabilities.
- Quick Ratio: The quick ratio, also known as the acid-test ratio, is another important liquidity metric. It measures a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations using only its most liquid assets. It excludes inventory from current assets and is calculated by dividing quick assets (excluding inventory) by current liabilities. A ratio of 1:1 or higher is typically considered favorable.
- Days Sales Outstanding (DSO): DSO is a measure of the average number of days it takes for a company to collect payment from its customers. It indicates the efficiency of accounts receivable management. A lower DSO reflects a faster collection of receivables, which improves cash flow and reduces the risk of bad debts.
- Inventory Turnover Ratio: The inventory turnover ratio evaluates how efficiently a company manages its inventory. It calculates the number of times inventory is sold and replaced within a given period. A high turnover ratio generally indicates effective inventory management and better utilization of resources.
- Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio: The accounts payable turnover ratio measures how quickly a company pays its suppliers. It shows the efficiency of managing accounts payable and maintaining good relationships with vendors. A high turnover ratio suggests prompt payment and good credit standing.
These KPIs provide a snapshot of a company’s working capital management performance, allowing businesses to identify areas of improvement and make informed decisions. By regularly monitoring and analyzing these indicators, companies can identify trends, compare performance against industry benchmarks, and implement strategies to optimize their working capital management.
Challenges in Working Capital Management
While effective working capital management is crucial for the financial health of a company, it also poses several challenges that need to be addressed. Here are some common challenges in working capital management:
- Inventory Management: Balancing inventory levels to meet customer demand and avoid excess holding costs is a challenge. Overstocking can tie up valuable capital, while understocking may lead to lost sales. Accurate demand forecasting and implementing efficient inventory management systems can help mitigate this challenge.
- Collection of Accounts Receivable: Collecting payment from customers within the agreed credit period can be challenging, particularly if customers delay payments or become delinquent. Implementing strict credit policies, conducting credit checks, and having a robust collections process are essential to mitigate this challenge and optimize cash flow.
- Managing Accounts Payable: Balancing the need to maintain positive relationships with suppliers while ensuring timely payments can be challenging. Delayed payments may strain relationships, while early payments may impact cash flow. Implementing efficient accounts payable processes, negotiating favorable payment terms, and leveraging technology can help manage this challenge effectively.
- Working Capital Constraints: Limited access to working capital can hinder a company’s ability to fund operations, invest in growth, and meet short-term obligations. This challenge is particularly prevalent for small businesses or those with limited access to external financing. Exploring alternative financing options and establishing strong relationships with lenders or investors can help alleviate these constraints.
- Changing Business Environment: Businesses operate in a dynamic environment where economic conditions, market demands, and industry dynamics can change rapidly. Adapting working capital management strategies to accommodate these changes and mitigate potential risks requires agility, effective planning, and continuous monitoring.
- Overlooked Working Capital Components: In some cases, businesses may focus on improving one aspect of working capital management, such as accounts receivable or inventory, while neglecting other components. This can lead to imbalances and inefficiencies. Taking a holistic approach to working capital management and addressing all components is crucial for achieving optimal results.
Overcoming these challenges requires a strategic and proactive approach to working capital management. By identifying and addressing these challenges, businesses can enhance their liquidity, improve cash flow, and create a solid foundation for sustainable growth.
Benefits of Effective Working Capital Management
Implementing effective working capital management practices can yield several benefits for businesses. Here are some key advantages of efficiently managing working capital:
- Improved Cash Flow: Effective working capital management ensures that cash is readily available to cover short-term obligations. This leads to improved cash flow, which provides businesses with the flexibility to invest in growth opportunities, meet unexpected expenses, and reduce reliance on external financing.
- Better Liquidity: By maintaining the optimal level of liquidity, businesses can meet their financial obligations promptly. This enhances their credibility with suppliers, improves bargaining power, and allows them to take advantage of discounts and favorable credit terms.
- Reduced Borrowing Costs: By efficiently managing working capital, companies can minimize their reliance on external financing and reduce borrowing costs. This leads to savings in interest expense, improves profitability, and frees up capital for other business needs.
- Enhanced Profitability: Effective working capital management allows businesses to allocate resources efficiently, optimize cash flow, and reduce unnecessary costs. This helps improve profitability by maximizing revenue generation, controlling expenses, and ensuring efficient use of available resources.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Proper management of working capital components, such as inventory, accounts receivable, and accounts payable, leads to improved operational efficiency. Businesses can streamline processes, reduce waste, eliminate stockouts, and enhance order fulfillment, resulting in better customer satisfaction and retention.
- Greater Stability in the Face of Uncertainty: Effective working capital management provides businesses with a solid foundation to navigate economic downturns or unforeseen challenges. By having sufficient liquidity and the ability to adapt quickly, companies can weather financial crises and emerge stronger.
- Facilitates Business Growth: By optimizing working capital, businesses can access funds to finance growth initiatives, expand operations, and invest in new opportunities. Efficient working capital management ensures that resources are available to seize strategic opportunities without compromising the company’s financial health.
Overall, effective working capital management is crucial for the financial stability and long-term success of businesses. It improves cash flow, enhances liquidity, reduces borrowing costs, increases profitability, and enables businesses to operate with efficiency and resilience in a dynamic business environment.
Conclusion
Working capital management is a critical component of financial management for businesses. It involves the effective management and control of a company’s short-term assets and liabilities to ensure smooth operations and financial stability. By optimizing working capital, businesses can improve cash flow, enhance liquidity, reduce borrowing costs, and drive profitability.
The components of working capital, including cash, accounts receivable, inventory, and accounts payable, need to be carefully managed to strike a balance between maintaining sufficient liquidity and optimizing resource utilization. Employing effective strategies such as accurate cash flow forecasting, tight credit control, optimized inventory management, and maintaining positive supplier relationships can contribute to efficient working capital management.
Key performance indicators, including the current ratio, quick ratio, days sales outstanding, inventory turnover ratio, and accounts payable turnover ratio, provide insights into a company’s financial health and the effectiveness of working capital management efforts. Regular monitoring and analysis of these KPIs enable businesses to make informed decisions and drive continuous improvement.
While working capital management offers numerous benefits, businesses must also navigate challenges such as inventory management, collection of accounts receivable, managing accounts payable, working capital constraints, changing business environments, and overlooked working capital components. It requires proactive measures, adaptability, and holistic approaches to overcome these challenges and reap the rewards of efficient working capital management.
In conclusion, effective working capital management is vital for the financial stability, operational efficiency, and long-term success of businesses. By implementing sound strategies, monitoring key performance indicators, and addressing challenges proactively, businesses can enhance their cash flow, optimize resource utilization, and position themselves for growth and profitability in today’s competitive marketplace.