
Finance
Who Can Sell Surety Bonds
Published: October 12, 2023
Looking to sell surety bonds? Finance professionals with expertise in the industry can help you. Maximize your profits with our assistance.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Surety Bonds
- Purpose of Surety Bonds
- Types of Surety Bonds
- Roles and Responsibilities of Surety Bond Sellers
- Licensing and Requirements for Surety Bond Sellers
- Surety Bond Seller Options
- Benefits of Using a Surety Bond Seller
- Risks and Concerns when Choosing a Surety Bond Seller
- Conclusion
Introduction
Welcome to the world of surety bonds! If you’re unfamiliar with this term, you may be wondering who can sell surety bonds and what exactly they are. In this article, we will delve into the world of surety bonds and explore the role of surety bond sellers.
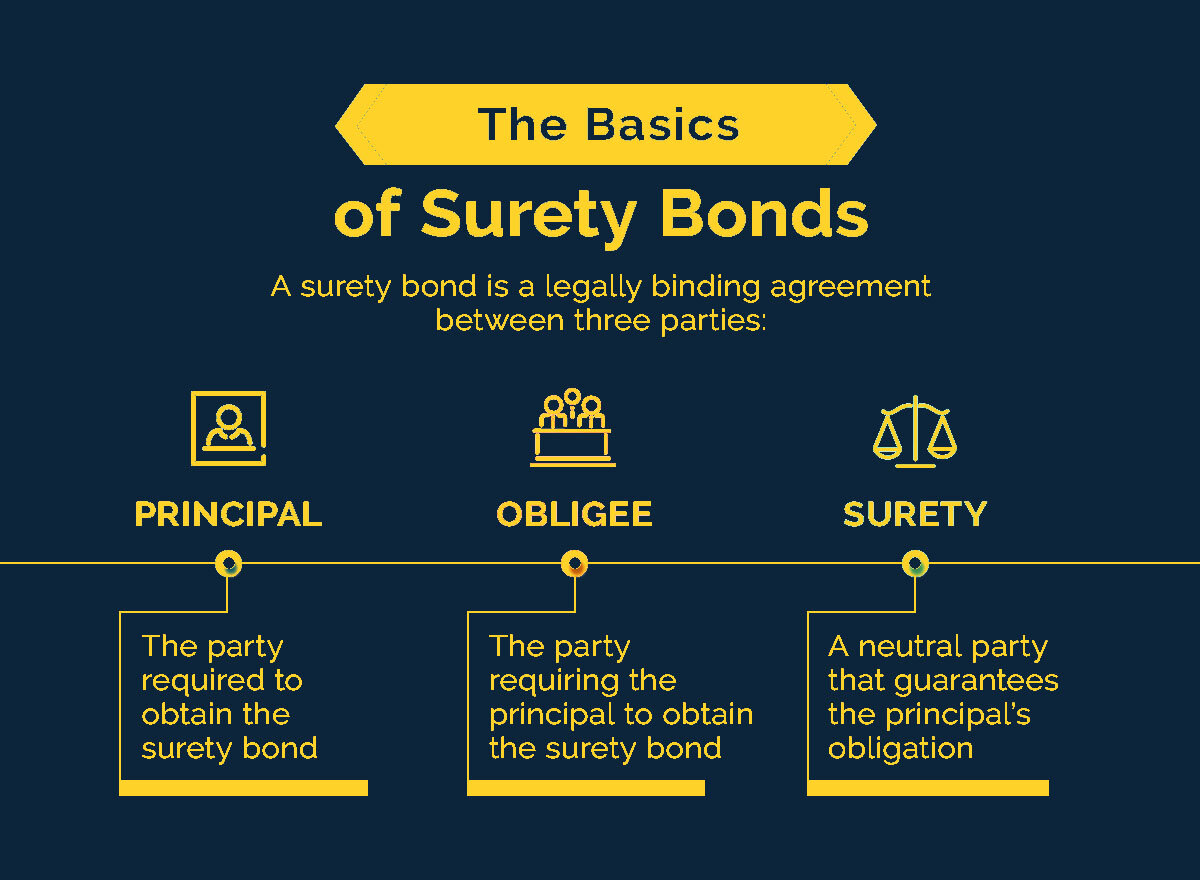
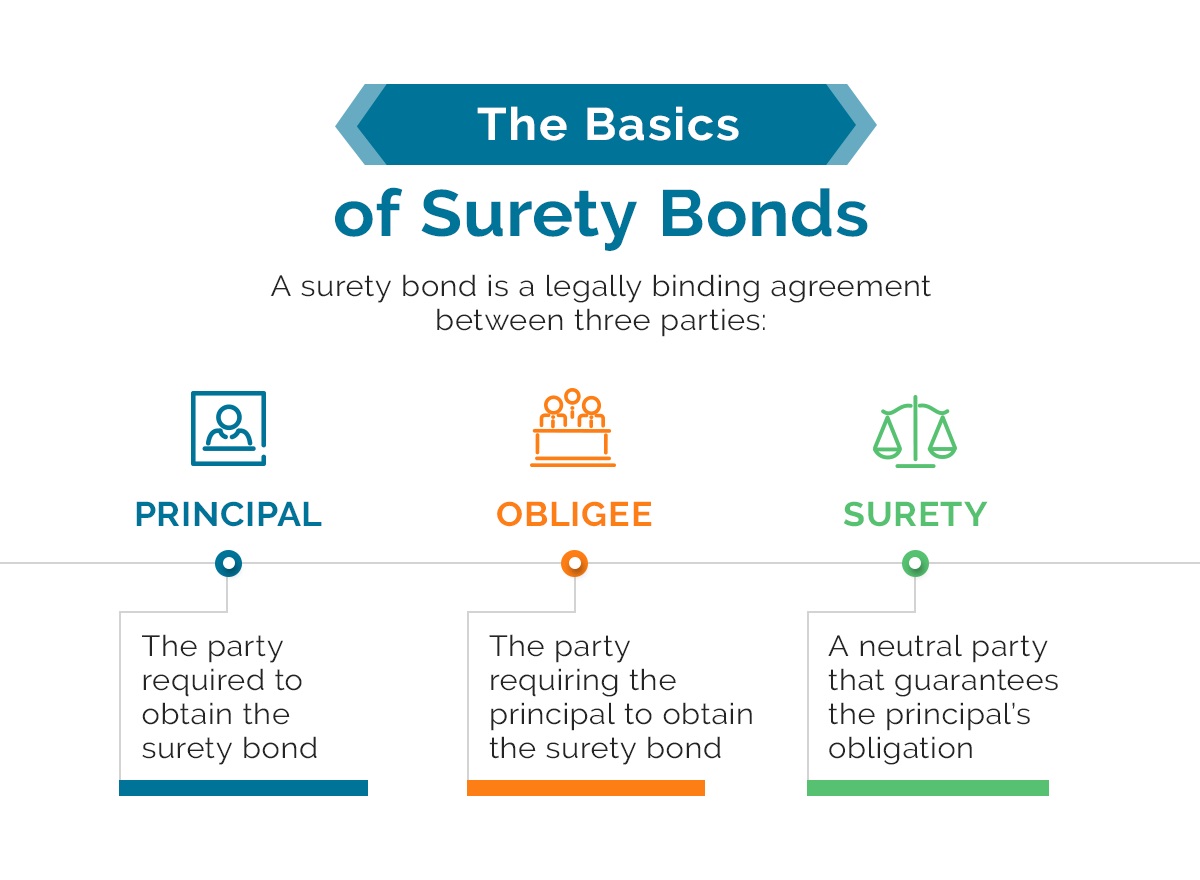
Surety bonds play a vital role in various industries, providing a layer of financial protection and assurance to parties involved in a contract or agreement. They are a type of legally binding contract that involves three parties—the principal, the obligee, and the surety bond seller.
The principal, often a business or individual, is the party that purchases the bond to guarantee their performance or fulfillment of obligations. The obligee, on the other hand, is the party that requires the bond as a form of protection. Finally, the surety bond seller acts as the intermediary, ensuring that the principal fulfills their obligations as outlined in the bond.
Now that we have a basic understanding of surety bonds, let’s explore the types of surety bonds that are commonly sold and the various roles and responsibilities of surety bond sellers.
Definition of Surety Bonds
Surety bonds are a type of contract that provide financial protection and assurance to parties involved in a contractual agreement. These bonds serve as a guarantee that one party, known as the principal, will fulfill their obligations as outlined in the bond. In the event that the principal fails to fulfill their responsibilities, the surety bond provides a source of compensation to the other party, known as the obligee.
The surety bond is a legally binding agreement that involves three parties—the principal, the obligee, and the surety bond seller. The principal is the party purchasing the bond in order to provide assurance of their performance or fulfillment of obligations. The obligee is the party who requires the bond as a form of protection in case the principal fails to meet their obligations. The surety bond seller, also known as a surety company or surety agency, is the entity that issues the bond and guarantees the performance of the principal.
It’s important to note that surety bonds are different from traditional insurance policies. While both involve risk management, surety bonds specifically focus on guaranteeing contractual obligations. Surety bonds are often required by government agencies, regulatory bodies, or private parties as a condition of entering into a contract or conducting certain business activities.
There are various types of surety bonds designed for different industries and purposes. These can include contract bonds, license and permit bonds, court bonds, and fidelity bonds, among others. Each type of surety bond serves a specific function and provides protection to parties involved in contractual agreements.
In summary, surety bonds are legally binding contracts that provide financial protection and assurance to parties in a contractual agreement. They guarantee the performance of the principal and provide compensation to the obligee in the event of a breach of contract. Surety bond sellers play a crucial role in issuing and facilitating these bonds, ensuring that contractual obligations are met and that parties are protected.
Purpose of Surety Bonds
Surety bonds serve several important purposes for parties involved in contractual agreements. Let’s explore the key purposes of surety bonds:
- Financial Protection: One of the primary purposes of surety bonds is to provide financial protection to the obligee. In the event that the principal fails to fulfill their obligations as outlined in the bond, the surety bond ensures that the obligee receives compensation for any resulting losses or damages.
- Risk Mitigation: Surety bonds help mitigate risks for both the principal and the obligee. For the obligee, the bond provides assurance that they will be compensated if the principal fails to fulfill their obligations. Meanwhile, for the principal, the bond allows them to establish credibility and trust with the obligee, increasing their chances of securing contracts or conducting business activities.
- Legal Compliance: Many industries and governmental bodies require surety bonds as a form of legal compliance. For example, construction companies often need to obtain contract bonds to bid on and engage in public projects. These bonds ensure that the contractor will fulfill their contractual obligations and comply with regulations throughout the project.
- Quality Assurance: Surety bonds also serve as a form of quality assurance for the obligee. By requiring the principal to obtain a bond, the obligee can have confidence that the principal has undergone a rigorous screening process by the surety bond seller. This helps ensure that only qualified and reliable individuals or businesses are involved in the contractual agreement.
- Consumer Protection: In certain industries, surety bonds are directly related to consumer protection. For example, in the insurance industry, insurance agents are often required to have a surety bond to protect clients from any fraudulent or wrongful actions. This provides peace of mind to consumers and helps maintain the integrity of the industry.
Overall, the purpose of surety bonds is to provide financial protection, mitigate risks, ensure legal compliance, maintain quality standards, and protect consumers. These bonds play a crucial role in various industries by establishing trust, responsibility, and accountability among parties involved in contractual agreements.
Types of Surety Bonds
There are several types of surety bonds, each serving a specific purpose in different industries and contractual agreements. Let’s explore some of the common types of surety bonds:
- Contract Bonds: Contract bonds are commonly used in the construction industry. They include bid bonds, performance bonds, and payment bonds. Bid bonds provide assurance to project owners that the contractor will enter into a contract if awarded the bid. Performance bonds guarantee that the contractor will complete the project as specified, and payment bonds ensure that subcontractors and suppliers will be paid for their work and materials.
- License and Permit Bonds: License and permit bonds are required by government agencies to ensure that individuals or businesses comply with regulations. These bonds are often necessary for professionals in industries such as construction, plumbing, electricians, and car dealerships. They provide assurance that the licensee will operate in accordance with established rules and regulations.
- Court Bonds: Court bonds come into play in legal proceedings. They include appeal bonds, guardian bonds, executor bonds, and injunction bonds, among others. These bonds ensure that individuals assigned certain roles within the legal system—such as guardians or executors—fulfill their responsibilities correctly and ethically.
- Fidelity Bonds: Fidelity bonds protect businesses against employee dishonesty or fraudulent acts. They provide compensation to the employer for financial losses incurred due to theft, embezzlement, or other illegal acts committed by employees.
- Public Official Bonds: Public official bonds are required for individuals holding public office positions. These bonds serve as protection against any wrongdoing or negligence committed by the official during their term in office.
These are just a few examples of the various types of surety bonds available. Each type of bond has its own specific purpose and is tailored to meet the unique needs of different industries and contractual agreements.
It’s important to consult with a knowledgeable surety bond seller to determine the specific type of bond required for your particular situation. By understanding the different types of surety bonds, you can ensure that you have the right form of financial protection and compliance for your industry and contractual obligations.
Roles and Responsibilities of Surety Bond Sellers
Surety bond sellers, also known as surety companies or surety agencies, play a crucial role in the process of issuing and managing surety bonds. Let’s take a closer look at the roles and responsibilities they fulfill:
- Evaluating Risk: One of the primary responsibilities of a surety bond seller is to assess the risk associated with providing a bond to a particular principal. This involves evaluating the financial stability, reputation, and track record of the principal. By conducting thorough risk assessments, the surety bond seller can determine the likelihood of the principal fulfilling their obligations and mitigate the risk of financial loss for the obligee.
- Issuing Bonds: Surety bond sellers have the authority to issue bonds to principals who meet the criteria and requirements set by the bond seller. In this role, they prepare, execute, and deliver the surety bond to the principal. The bond serves as a legally binding document that outlines the terms, conditions, and obligations of the principal.
- Managing Bond Claims: In the event of a default or failure by the principal to fulfill their obligations, the surety bond seller becomes responsible for managing bond claims. This includes investigating the claim, determining its validity, and ensuring appropriate compensation is provided to the obligee, up to the limits stated in the bond.
- Building Relationships: Surety bond sellers strive to build strong relationships with both principals and obligees. They act as intermediaries, establishing trust, and facilitating smooth communication between the two parties. By developing long-term relationships, bond sellers can provide ongoing support and guidance throughout the lifecycle of the bond.
- Monitoring Compliance: Surety bond sellers have a vested interest in ensuring that principals comply with the terms and conditions of the bond. They may conduct periodic reviews and inspections to verify that the principal is fulfilling their obligations as outlined in the bond. This helps mitigate risk and ensures that the bond remains valid and enforceable.
- Keeping Up with Regulations: Surety bond sellers stay up to date with industry regulations and changes in legal requirements. They ensure that the bonds they issue comply with current laws and regulations. This knowledge allows them to provide accurate and reliable guidance to both principals and obligees regarding the specific requirements for their industry and contractual agreements.
Overall, surety bond sellers play a critical role in the surety bond process. They evaluate risk, issue bonds, manage claims, cultivate relationships, monitor compliance, and stay informed about industry regulations. Their expertise and services provide assurance to principals and obligees, facilitating trust, financial protection, and compliance in contractual agreements.
Licensing and Requirements for Surety Bond Sellers
Surety bond sellers, also known as surety companies or surety agencies, are required to fulfill certain licensing and regulatory requirements in order to operate legally and provide their services. Let’s explore the licensing and requirements for surety bond sellers:
- Licensing: Surety bond sellers are typically required to obtain a license from the relevant regulatory authority in the jurisdiction where they operate. The licensing process involves meeting specific criteria, such as demonstrating financial stability, maintaining a certain level of capitalization, and providing proof of expertise in the field of surety bonding.
- Insurance Licenses: In addition to a surety bond seller license, many jurisdictions also require surety bond sellers to hold insurance licenses. This ensures that the bond seller is knowledgeable about insurance regulations and capable of handling the financial transactions and obligations associated with providing surety bonds.
- Financial Strength: Surety bond sellers are expected to demonstrate financial strength and stability. This includes maintaining sufficient assets, having a healthy financial track record, and fulfilling financial reporting requirements. These measures are in place to protect the interests of the principals and obligees involved in the surety bond agreements.
- Insurance Coverage: Surety bond sellers often need to maintain appropriate insurance coverage to protect against potential liabilities and claims. This coverage can include errors and omissions insurance, professional liability insurance, and general liability insurance. This requirement ensures that the bond seller is adequately protected and capable of fulfilling their responsibilities in the event of claims or disputes.
- Continuing Education: Many jurisdictions have continuing education requirements for surety bond sellers to ensure that they stay up to date with industry knowledge, regulatory changes, and best practices. These requirements may involve completing specific courses, attending seminars, or acquiring a certain number of educational credits within a specified timeframe.
- Compliance and Ethics: Surety bond sellers are expected to operate in accordance with ethical standards and industry best practices. They must adhere to strict compliance guidelines and maintain integrity in their interactions with principals, obligees, and other stakeholders. Ethical conduct and compliance with legal and regulatory requirements are essential for establishing trust and reliability in the field of surety bonding.
It’s important to note that licensing and requirements for surety bond sellers may vary from jurisdiction to jurisdiction. It’s recommended to consult the appropriate regulatory authority or an expert in the field to ensure compliance with the specific requirements in the desired operational area.
By adhering to licensing and regulatory requirements, surety bond sellers can provide their services with credibility and professionalism, safeguarding the interests of both principals and obligees in the surety bond agreements.
Surety Bond Seller Options
When it comes to choosing a surety bond seller, there are several options available for individuals and businesses in need of bonding services. Let’s explore some of the common surety bond seller options:
- Direct Surety Companies: Direct surety companies are entities that issue surety bonds directly to principals. They have their underwriting departments to evaluate risks and determine bond eligibility. Working with a direct surety company allows for a direct relationship between the principal and the underwriting team, potentially streamlining the bonding process.
- Surety Bond Agencies: Surety bond agencies act as intermediaries between principals and surety companies. These agencies have established relationships with multiple surety companies and can help streamline the bonding process by matching the specific needs of the principal with the most suitable surety company. They provide guidance, support, and expertise to principals throughout the bonding process.
- Insurance Brokers: Insurance brokers may also offer surety bond services as part of their broader range of insurance offerings. While they primarily focus on insurance, they can assist with obtaining surety bonds through their network of surety companies. Insurance brokers can provide a comprehensive approach and help businesses assess their overall risk management needs, including surety bonding.
- Online Surety Marketplaces: With advancements in technology, online surety marketplaces have emerged as platforms connecting principals with surety bond providers. These platforms offer a digital solution for obtaining surety bonds, allowing principals to compare quotes, select the most suitable bond provider, and complete the bonding process online. Online surety marketplaces can offer convenience and efficiency for those seeking surety bond services.
- Financial Institutions: Some financial institutions, such as banks and credit unions, may offer surety bond services as part of their commercial offerings. These institutions leverage their financial expertise and customer relationships to provide surety bonds to their clients. Working with a financial institution for surety bonding may offer the benefit of convenience, especially for businesses that already have existing relationships with these institutions.
It’s important to evaluate your specific needs and preferences when choosing a surety bond seller. Consider factors such as the complexity of your bonding requirements, the level of expertise and support needed, and the convenience and efficiency of the service provided by the seller.
Consulting with a knowledgeable surety bond professional can help you navigate the various options available and make an informed decision based on your specific bonding needs.
Benefits of Using a Surety Bond Seller
Utilizing the services of a surety bond seller offers numerous advantages for individuals and businesses in need of surety bonds. Let’s explore some of the key benefits of using a surety bond seller:
- Expertise and Guidance: Surety bond sellers are professionals with deep knowledge and understanding of the surety bond industry. They can provide expert guidance and advise principals on the most appropriate type of bond for their specific needs. Their expertise ensures that principals obtain the right bond and understand their obligations.
- Access to Multiple Surety Companies: Surety bond sellers often have established relationships with multiple surety companies. This gives principals access to a broader range of options and allows them to obtain competitive rates and terms for their bonds. Sellers can match principals with the most suitable surety company based on factors such as bond requirements, industry expertise, and financial stability.
- Streamlined Bonding Process: Working with a surety bond seller can streamline the bonding process. Sellers have a deep understanding of the underwriting process and the documentation required for bond issuance. They can facilitate the application process, gather necessary information, and ensure that all requirements are met, saving principals time and effort.
- Financial Protection and Risk Mitigation: Surety bonds provide a layer of financial protection for obligees. By using a surety bond seller, principals can demonstrate their commitment to fulfilling their obligations, which enhances their reputation and credibility. The bond seller also assesses the principal’s financial stability, mitigating the risk for the obligee and offering assurance of compensation in case of default.
- Industry Expertise: Surety bond sellers often specialize in serving specific industries. They have in-depth knowledge of the unique bonding requirements and regulations within these industries. This expertise allows them to provide tailored solutions and better meet the bonding needs of principals in those industries.
- Continued Support: Surety bond sellers offer ongoing support throughout the life of the bond. They assist principals in managing bond-related issues, such as making updates or changes to the bond, addressing claims, or renewing bonds. The seller acts as a reliable resource and point of contact for any questions or concerns that arise during the bond term.
Using a surety bond seller provides numerous benefits, including expertise and guidance, access to multiple surety companies, a streamlined bonding process, financial protection, industry-specific knowledge, and ongoing support. By leveraging the services of a surety bond seller, principals can navigate the complexities of surety bonding more effectively and obtain the necessary bonds with confidence and ease.
Risks and Concerns when Choosing a Surety Bond Seller
While utilizing the services of a surety bond seller offers numerous benefits, it’s important to be aware of potential risks and concerns that may arise when choosing a surety bond seller. Here are some factors to consider:
- Reputation and Reliability: It’s crucial to research and assess the reputation and reliability of the surety bond seller. Look for a seller with a history of providing quality service and honoring their commitments. Check customer reviews, testimonials, and ratings to get a sense of their track record.
- Financial Stability: Consider the financial stability of the surety bond seller. Ensure that they have the necessary financial strength to meet potential claims and obligations. You can evaluate their financial stability by reviewing their financial statements and credit ratings.
- Licensing and Credentials: Verify that the surety bond seller holds the required licensing and credentials to operate legally in your jurisdiction. Check if they are licensed by the appropriate regulatory authority and inquire about any certifications or professional affiliations they may have.
- Transparency and Communication: Look for a surety bond seller who demonstrates transparency and clear communication throughout the bonding process. They should be able to explain the terms, conditions, and obligations of the bond clearly. Prompt and effective communication is essential in ensuring a smooth and successful bonding experience.
- Exclusivity: Some surety bond sellers may be exclusive to specific industries or geographic regions. Ensure that the seller you choose has experience and expertise in serving your industry or location, as this will help ensure that they can meet your specific bonding needs and comply with regulatory requirements.
- Claims Handling: It’s important to understand the claims handling process of the surety bond seller. Inquire about their procedures and policies for handling claims and their track record in providing timely and fair compensation to obligees. A reputable bond seller should have a proven track record of efficiently managing claims.
Take the time to thoroughly research and evaluate potential surety bond sellers before making a decision. By addressing these risks and concerns, you can minimize the likelihood of encountering issues or complications during the bonding process.
Consult with professionals in the industry, such as attorneys or financial advisors, to ensure that you are making an informed decision and selecting a surety bond seller that best fits your specific needs and requirements.
Conclusion
Surety bonds play a vital role in providing financial protection and assurance to parties involved in contractual agreements. When seeking a surety bond, it’s important to understand who can sell surety bonds and the various considerations involved in choosing a surety bond seller.
Surety bond sellers, such as surety companies, agencies, insurance brokers, online marketplaces, and financial institutions, offer expertise, guidance, and access to multiple surety companies. They streamline the bonding process, provide financial protection, and offer ongoing support throughout the life of the bond.
Nonetheless, it’s crucial to be aware of potential risks and concerns when selecting a surety bond seller. Factors such as reputation, financial stability, licensing, transparency, and claims handling should be carefully considered to ensure a positive and successful bonding experience.
By conducting thorough research, evaluating potential sellers, and seeking input from professionals in the industry, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions and select a surety bond seller that best fits their specific needs and requirements.
Remember, surety bonds are essential for establishing trust, compliance, and financial security in contractual agreements. By choosing the right surety bond seller, you can confidently proceed with your projects, business activities, or legal obligations, knowing that you have the necessary financial protection and support.