Finance
What Is Financial Risk Assessment
Modified: December 30, 2023
Learn how financial risk assessment is crucial for managing finance. Understand the key factors and strategies to mitigate risks in the dynamic world of finance.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
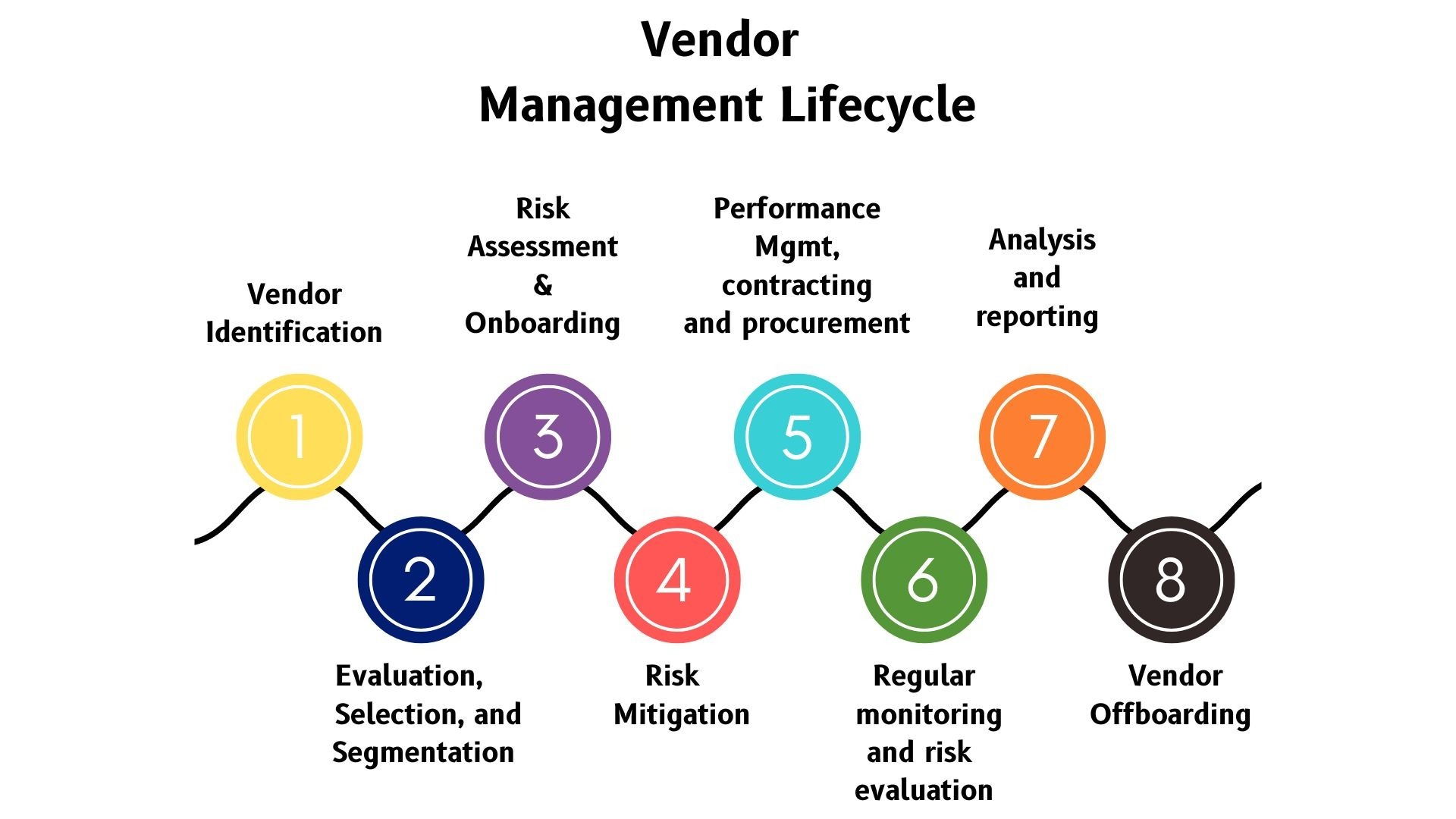
Financial risk assessment plays a crucial role in the field of finance by helping businesses and individuals understand and manage the risks associated with their financial activities. In simple terms, it involves the process of evaluating and analyzing potential risks that may affect financial performance and making informed decisions to mitigate those risks.
Financial risk assessment provides valuable insights into the potential impact of various factors on financial outcomes, allowing organizations to take proactive measures to protect their financial stability and maximize opportunities for growth. By assessing the risks involved, businesses can make well-informed decisions to protect their investments, secure funding, and optimize their overall financial strategies.
The key objective of financial risk assessment is to ascertain the likelihood and potential impact of various risks on an organization’s financial health. This involves identifying and evaluating potential risks, such as market volatility, interest rate fluctuations, credit risks, liquidity risks, operational risks, and legal and regulatory risks.
Financial risk assessment takes into account both quantitative and qualitative factors to provide a comprehensive evaluation of risk exposure. It involves analyzing financial statements, market trends, economic indicators, industry benchmarks, and assessing the overall financial health of the organization.
Furthermore, financial risk assessment is not limited to businesses alone. It is also essential for individuals in managing personal finances, investments, and retirement planning. By understanding and assessing potential risks, individuals can make informed decisions to protect their savings, investments, and achieve their long-term financial goals.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the definition of financial risk assessment, its importance in finance, the various factors considered in the assessment process, different methods used for assessing financial risk, common challenges faced, and best practices to follow for effective risk assessment.
Definition of Financial Risk Assessment
Financial risk assessment refers to the process of evaluating and analyzing potential risks that may impact the financial performance of an individual or organization. It involves identifying and quantifying various risks that can arise from internal and external factors and making informed decisions to mitigate those risks.
The goal of financial risk assessment is to assess the likelihood and potential consequences of risks, allowing individuals and organizations to take appropriate measures in order to protect their financial stability.
Financial risk can arise from various sources, including market volatility, economic factors, regulatory changes, technological advancements, credit risks, operational risks, and legal risks, among others. Each of these risks can have different impacts on an individual or organization, and financial risk assessment helps to understand and manage these risks effectively.
Financial risk assessment involves analyzing and evaluating various factors and indicators to determine the potential impact of risks. This includes conducting research, gathering data, and using quantitative and qualitative analysis techniques. It also involves assessing the financial health and stability of an individual or organization by analyzing financial statements, cash flow reports, market trends, economic indicators, and industry benchmarks.
By conducting a thorough financial risk assessment, individuals and organizations can gain a better understanding of the potential risks they face and develop strategies to mitigate those risks. This may involve implementing risk management policies, diversifying investments, hedging against market fluctuations, improving operational processes, or seeking insurance coverage.
Overall, financial risk assessment is an essential tool in the field of finance as it helps individuals and organizations make informed decisions to protect their financial interests, optimize investment strategies, and ensure long-term financial stability.
Importance of Financial Risk Assessment
Financial risk assessment is of paramount importance in the finance industry due to several key reasons. Let’s explore why it is crucial for individuals and organizations to conduct thorough financial risk assessments:
- Identification of Potential Risks: Financial risk assessment helps to identify and understand the various risks that can impact an individual’s or organization’s financial stability. By evaluating both internal and external factors, such as market volatility, economic changes, regulatory risks, industry trends, and operational risks, it becomes possible to identify potential threats early on.
- Protection of Financial Interests: Conducting financial risk assessments allows individuals and organizations to take proactive measures to protect their financial interests. By understanding the potential risks associated with investments, loans, or business operations, appropriate risk management strategies can be implemented to minimize potential losses and safeguard financial stability.
- Optimization of Investment Strategies: Financial risk assessments provide valuable insights into the potential risks and rewards of different investment opportunities. It helps individuals and organizations make informed decisions about where to allocate their financial resources by assessing the risk-return trade-off. By analyzing the potential risks associated with different investments, individuals can optimize their investment portfolios to achieve their long-term financial goals.
- Informed Decision Making: Financial risk assessments provide individuals and organizations with the necessary information to make informed decisions. By evaluating the potential risks and rewards of different financial opportunities, individuals can make well-informed choices about borrowing, investing, or expanding their business operations. This reduces the likelihood of making impulsive or uninformed decisions that may lead to financial losses.
- Compliance with Regulatory Requirements: Financial risk assessments are essential for ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. Many industries have specific regulations and guidelines related to risk management. By conducting thorough risk assessments, organizations can ensure that they are meeting the necessary compliance standards and avoiding potential legal and regulatory issues.
- Enhanced Financial Planning: Financial risk assessments provide critical information for effective financial planning. By understanding the potential risks, individuals and organizations can develop comprehensive financial plans that take into account various scenarios and mitigate potential risks. This aids in building a more stable and sustainable financial future.
Overall, financial risk assessment is essential for individuals and organizations to protect their financial interests, optimize investment strategies, make informed decisions, comply with regulations, and enhance overall financial planning. By identifying, evaluating, and managing potential risks, individuals and organizations can enhance their financial security and increase the likelihood of achieving their financial goals.
Factors Considered in Financial Risk Assessment
In financial risk assessment, various factors are taken into consideration to evaluate the potential risks that can impact the financial stability of individuals or organizations. These factors help paint a comprehensive picture of the risks involved and contribute to informed decision-making. Let’s explore some key factors that are typically considered in financial risk assessment:
- Market Volatility: Market volatility refers to the degree of price fluctuations in the financial markets. It is an important factor to consider as it can significantly impact investment returns and overall financial performance. Assessing market volatility helps individuals and organizations understand the potential risks associated with their investments and adjust their strategies accordingly.
- Economic Factors: Economic factors such as inflation rates, interest rates, GDP growth, and employment levels can have a substantial impact on financial stability. Economic downturns or recessions may pose higher risks to businesses and individuals, while favorable economic conditions may present growth opportunities. Evaluating economic factors provides insights into potential risks arising from macroeconomic changes.
- Industry and Competitive Risks: Each industry has its own set of risks and challenges. Assessing industry-specific risks helps individuals and organizations gauge the potential risks associated with their sector, such as technological advances, regulatory changes, or shifts in consumer preferences. Furthermore, studying competitive risks provides insights into the potential impact of competition on financial performance.
- Credit Risks: Credit risks arise when borrowers fail to fulfill their obligations to repay loans or debts. Evaluating credit risks involves assessing the creditworthiness of borrowers, including individuals or counterparties. This factor is particularly relevant for financial institutions or entities that have exposure to lending or credit activities.
- Operational Risks: Operational risks pertain to the potential losses arising from inadequate internal processes, systems failures, human error, or external events. These risks can impact an organization’s financial performance and reputation. Understanding and assessing operational risks helps individuals and organizations develop effective risk management strategies, enhance operational efficiency, and minimize potential losses.
- Legal and Regulatory Risks: Legal and regulatory risks refer to the potential risks arising from violations of laws, non-compliance with regulations, or legal disputes. These risks can result in significant financial penalties, reputational damage, and legal expenses. Assessing legal and regulatory risks ensures that individuals and organizations understand the potential legal implications of their actions and take appropriate measures to comply with applicable laws and regulations.
- Liquidity Risks: Liquidity risks arise when individuals or organizations face difficulties in accessing cash or selling assets quickly without significant loss. Evaluating liquidity risks helps individuals and organizations understand their ability to meet financial obligations and make necessary adjustments to maintain sufficient liquidity levels.
It is important to note that the factors considered in financial risk assessment can vary depending on the specific context and industry. By assessing these various factors, individuals and organizations can gain a comprehensive understanding of the potential risks they face and develop appropriate risk management strategies to mitigate those risks.
Methods of Financial Risk Assessment
Financial risk assessment involves the use of various methods and techniques to evaluate the potential risks faced by individuals or organizations. These methods enable a systematic and comprehensive analysis of the risk factors involved. Here are some commonly used methods of financial risk assessment:
- Quantitative Analysis: Quantitative analysis utilizes numerical data and statistical models to assess financial risks. This method involves analyzing historical data, financial statements, market trends, and economic indicators to calculate risk measures such as value at risk (VaR) and expected shortfall. Quantitative analysis provides a quantitative estimate of the potential losses that can be expected under different risk scenarios.
- Qualitative Analysis: Qualitative analysis involves a subjective assessment of risks based on non-quantifiable factors. This method relies on expert judgment, industry knowledge, and qualitative information to evaluate risks. Qualitative analysis is particularly useful for assessing risks that are difficult to quantify, such as reputational risks, regulatory risks, or strategic risks.
- Sensitivity Analysis: Sensitivity analysis measures the impact of changes in specific variables on financial outcomes. It involves testing the sensitivity of financial models to different scenarios or assumptions. By varying key factors, such as interest rates, exchange rates, or market prices, sensitivity analysis helps identify the impact of changes on financial performance and risk exposure.
- Scenario Analysis: Scenario analysis involves constructing various scenarios or hypothetical situations to assess the potential risks and outcomes. This method considers different combinations of factors that may occur in the future and evaluates their implications on financial performance. Scenario analysis helps individuals and organizations understand the potential range of outcomes and prepare contingency plans to mitigate risks.
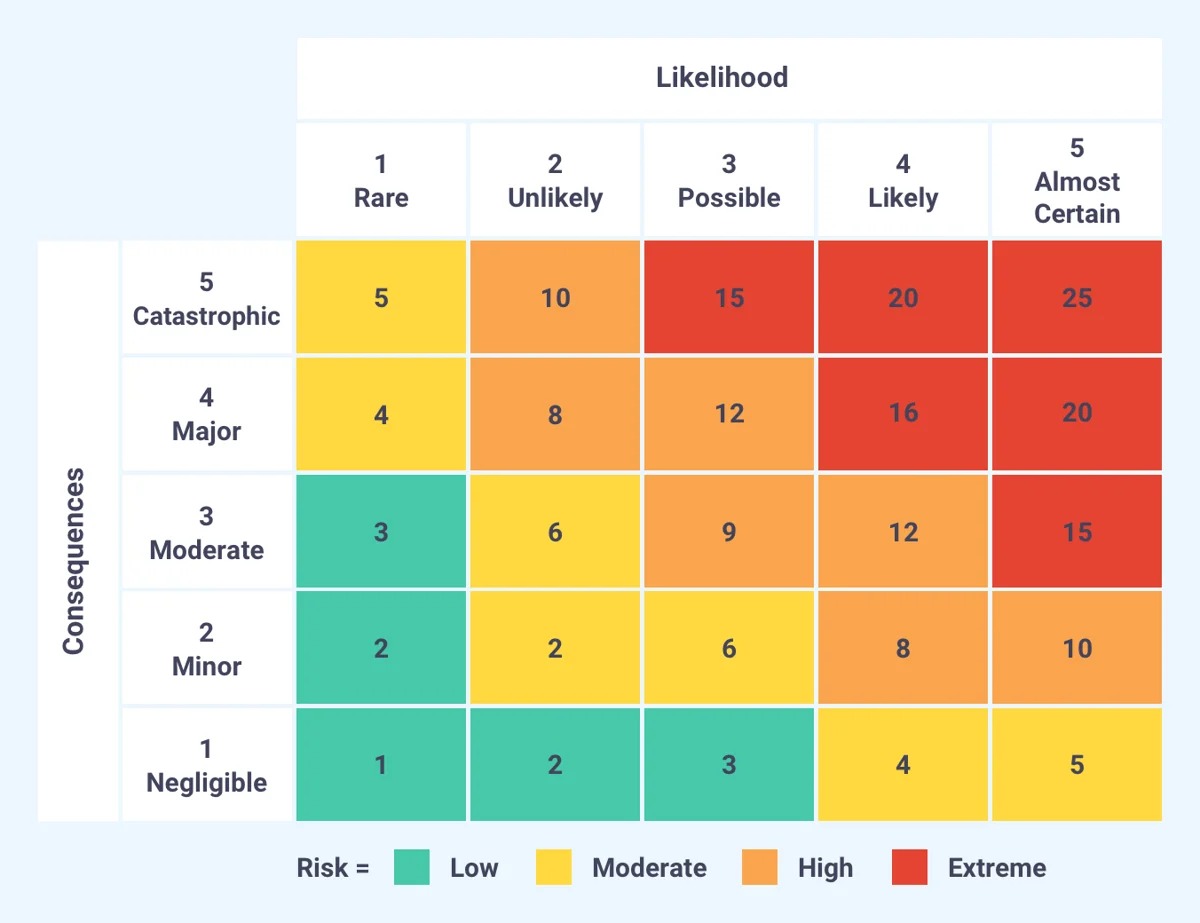
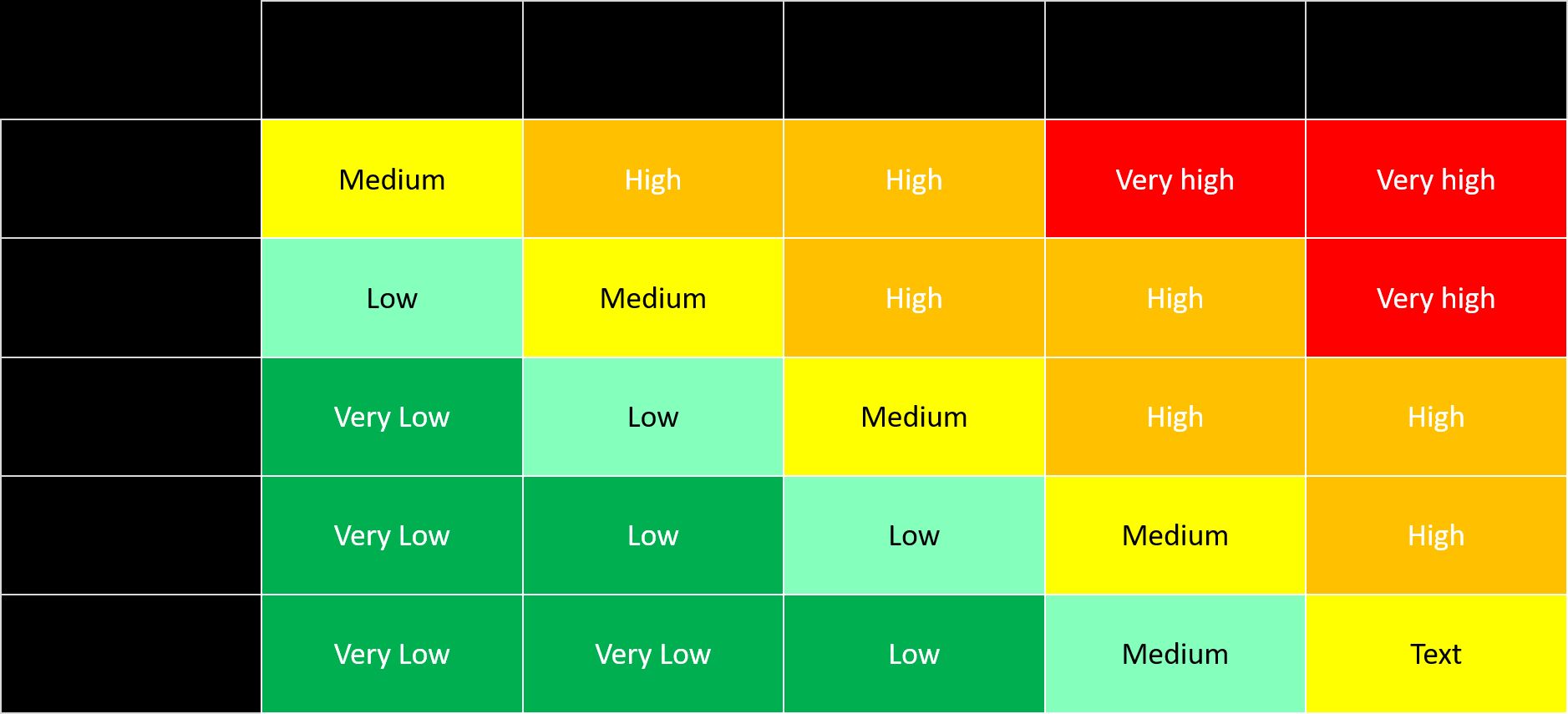
- Stress Testing: Stress testing involves subjecting a financial model or portfolio to extreme or adverse conditions to assess its resilience. It helps individuals and organizations understand the potential impact of severe market conditions, economic downturns, or specific events on their financial performance. Stress testing is particularly important for banks and financial institutions to ensure their capital adequacy and risk management capabilities.
- Risk Rating Systems: Risk rating systems assign quantitative or qualitative risk ratings to various financial assets, counterparties, or projects. These ratings help individuals and organizations prioritize their risk mitigation efforts and allocate resources effectively. Risk rating systems often incorporate a combination of objective criteria, industry benchmarks, and expert judgment.
It is important to note that the choice of method or combination of methods depends on the specific context, available data, and the nature of risks being assessed. A comprehensive risk assessment often utilizes multiple methods to capture both quantitative and qualitative aspects of financial risks.
By utilizing these methods of financial risk assessment, individuals and organizations can gain valuable insights into the potential risks they face and make informed decisions to mitigate those risks and protect their financial well-being.
Common Challenges in Financial Risk Assessment
Financial risk assessment is a complex process that involves analyzing various factors and uncertainties. While it provides valuable insights into potential risks, there are several common challenges that individuals and organizations may encounter during the assessment process. Understanding and addressing these challenges is crucial for effective risk management. Some of the common challenges in financial risk assessment include:
- Data Quality and Availability: The accuracy and availability of high-quality data are essential for conducting a robust risk assessment. However, obtaining reliable and comprehensive data can be challenging, especially when dealing with complex financial products, multiple data sources, or limited historical data. Incomplete or inaccurate data can lead to biased risk assessments and ineffective risk management strategies.
- Assumptions and Predictive Accuracy: Financial risk assessment often involves making assumptions and predictions about future events and market conditions. The accuracy of these assumptions and predictions heavily influences the reliability of risk assessments. However, predicting future events accurately is inherently challenging due to the ever-changing economic and market dynamics. Overreliance on faulty assumptions or inaccurate predictions can lead to faulty risk assessments.
- Interconnectedness of Risks: Risks in the financial system are often interconnected and can have cascading effects. Assessing individual risks in isolation may not capture the full extent of potential impact on overall financial stability. Understanding the interdependencies and correlations between different risks is crucial for a comprehensive risk assessment. Failure to consider these interconnections may result in underestimating the overall risk exposure.
- Limited Historical Data for Unprecedented Events: Financial risk assessment relies on historical data to make informed judgments about future risks. However, unprecedented events or Black Swan events, such as financial crises or pandemics, can challenge the use of historical data as a reliable predictor of future risks. Lack of historical data for such events may require alternative approaches, such as stress testing or scenario analysis, to assess potential risks accurately.
- Emerging and Complex Risks: Financial markets and the business environment continue to evolve, leading to the emergence of new and complex risks. These risks, such as cybersecurity threats, technological disruptions, or climate change-related risks, may not have well-established models or historical data for assessment. The dynamic nature of these risks requires continuous monitoring and adaptation of risk assessment methodologies.
- Subjectivity and Bias: Human judgment plays a critical role in financial risk assessment. However, subjective biases, cognitive errors, and conflicts of interest can influence risk assessments and lead to inaccurate or biased results. Assessors must strive for objectivity and ensure that risk assessment processes are transparent, consistent, and free from undue influence.
Overcoming these challenges requires a combination of robust data management practices, thorough analytical techniques, and continuous monitoring and adaptation of risk assessment methodologies. It is important to remain vigilant, update risk assessment frameworks regularly, and leverage the expertise of risk management professionals to effectively address these challenges and achieve reliable risk assessments.
Best Practices for Financial Risk Assessment
Financial risk assessment is a vital process for individuals and organizations to identify and manage potential risks to their financial stability. To ensure accurate and effective risk assessments, certain best practices should be followed. These practices help enhance the reliability of the assessment and enable informed decision-making. Here are some key best practices for financial risk assessment:
- Establish a Risk Management Framework: Develop a comprehensive risk management framework that outlines the objectives, scope, and methodologies for risk assessment. This framework should be aligned with the organization’s overall risk appetite and strategy, and it should clearly define roles and responsibilities for risk assessment and management.
- Gather Reliable and Comprehensive Data: Collect and analyze high-quality data from reliable sources. Ensure that the data is complete, accurate, and relevant to the risk assessment process. Utilize multiple data sources and consider both internal and external data to gain a holistic view of the risks involved.
- Utilize Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis: Employ a combination of quantitative and qualitative analysis techniques to assess risks. Quantitative analysis provides numerical insights, while qualitative analysis incorporates expert judgment and industry knowledge. The combination of both approaches enhances the accuracy and completeness of risk assessments.
- Regularly Review and Update Risk Models: Periodically review and update risk models and methodologies to reflect changes in the financial landscape and emerging risks. Stay abreast of new techniques, industry best practices, and regulatory requirements to ensure that risk assessments remain robust and relevant.
- Consider Scenarios and Stress Testing: Incorporate scenario analysis and stress testing into risk assessments to evaluate the impact of extreme or adverse events on financial outcomes. Develop plausible scenarios and conduct stress tests to assess the resilience of portfolios and risk management strategies under challenging conditions.
- Promote Risk Awareness and Education: Foster a risk-aware culture within the organization by providing training and education on risk management principles and practices. Increase risk awareness among employees and stakeholders to encourage active participation in risk assessment and mitigation efforts.
- Ensure Effective Communication and Reporting: Establish clear channels of communication for risk assessment findings and reports. Regularly communicate risk assessment results to stakeholders, including senior management, board members, and regulators. Present the information in a clear and concise manner to facilitate informed decision-making.
- Conduct Periodic Risk Assessments: Perform regular and periodic risk assessments to monitor the changing risk landscape. Conduct assessments at defined intervals or in response to significant events or changes in the business environment. This ensures that risk assessments remain up to date and enable timely risk mitigation strategies.
- Involve Multiple Perspectives: Encourage the involvement of diverse perspectives and expertise in the risk assessment process. Engage risk management professionals, subject matter experts, and stakeholders from different departments or areas of the organization. This allows for a comprehensive evaluation of risks and reduces potential biases.
- Continuously Monitor and Adapt: Monitor the effectiveness of risk assessment strategies and adjust them as needed. Stay vigilant to changes in the risk landscape and update risk management processes accordingly. Embrace a culture of continuous improvement to ensure that risk assessments remain accurate and effective.
By incorporating these best practices, individuals and organizations can conduct thorough and reliable financial risk assessments. This enables them to make well-informed decisions, implement effective risk management strategies, and safeguard their financial stability in an ever-changing business environment.
Conclusion
Financial risk assessment is a critical component of effective risk management in the field of finance. It enables individuals and organizations to identify, evaluate, and mitigate potential risks that can impact their financial stability. Through the comprehensive evaluation of various factors, including market volatility, economic conditions, credit risks, operational risks, and legal and regulatory risks, financial risk assessment helps individuals and organizations make informed decisions to protect their financial interests, optimize investment strategies, and ensure long-term financial stability.
Although financial risk assessment is a complex process, following best practices such as establishing a risk management framework, gathering reliable data, utilizing both quantitative and qualitative analysis, and regularly reviewing risk models can enhance the accuracy and reliability of risk assessments. Additionally, incorporating scenario analysis, stress testing, and effective communication helps stakeholders understand the potential risks and develop appropriate risk mitigation strategies.
While conducting financial risk assessments, it is important to recognize common challenges such as data quality, predictive accuracy, interconnectedness of risks, limited historical data, emerging risks, and subjective biases. Addressing these challenges by adopting robust data management practices, embracing new methodologies, and promoting risk awareness can lead to more effective risk assessments.
Financial risk assessment is not a one-time task but a continuous process that requires regular monitoring, updates, and adaptation to reflect changes in the business environment and emerging risks. By adhering to best practices and continuously evaluating and managing risks, individuals and organizations can enhance their risk management capabilities, protect assets, optimize financial strategies, and ultimately achieve long-term financial success.