Home>Finance>How Does Increase In Accounts Receivable Affect Cash Flow


Finance
How Does Increase In Accounts Receivable Affect Cash Flow
Modified: February 21, 2024
Learn how an increase in accounts receivable affects cash flow in finance and discover the implications for your business.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to managing finances, one crucial aspect that businesses must pay close attention to is cash flow. Cash flow refers to the movement of funds in and out of a company, and it plays a vital role in the overall financial health and stability of an organization. Companies rely on cash flow to cover daily expenses, invest in growth opportunities, and meet financial obligations.
A key factor that can impact cash flow is accounts receivable. Accounts receivable are the amounts owed to a business by its customers for goods or services provided on credit. Essentially, it represents the sales that have been made but not yet collected in cash.
In this article, we will explore how an increase in accounts receivable can affect cash flow. We will delve into the definition of accounts receivable, provide an overview of the cash flow statement, discuss the impact of increasing accounts receivable on cash flow, highlight the factors that influence cash flow, and offer suggestions for effectively managing accounts receivable to maintain a healthy cash flow.
Definition of Accounts Receivable
Before we delve into the impact of accounts receivable on cash flow, let’s first define what accounts receivable actually means. Accounts receivable, also referred to as trade receivables, represents the money owed to a company by its customers for goods or services provided on credit.
When a business sells its products or services on credit, it allows customers to make purchases and defer payment to a later date. This creates an accounts receivable balance, which is recorded as an asset on the company’s balance sheet. It signifies the company’s right to collect the outstanding amounts from its customers.
Accounts receivable arise from normal business operations, indicating sales that have been made, but payment has not yet been received. It is a common practice for businesses to extend credit terms to their customers to encourage sales and build customer loyalty. However, managing accounts receivable effectively is crucial to ensure a healthy cash flow.
Typically, accounts receivable have a designated payment period, often referred to as the credit term. This period can vary depending on the business and industry standards. For instance, it could be 30 days, 60 days, or even 90 days. During this time, the customers are expected to make payment for the goods or services they have received.
Accounts receivable can include various types of transactions, such as sales of products, professional services rendered, or billable hours worked. It is important for businesses to keep track of their accounts receivable balance and ensure timely collection to maintain a steady cash flow.
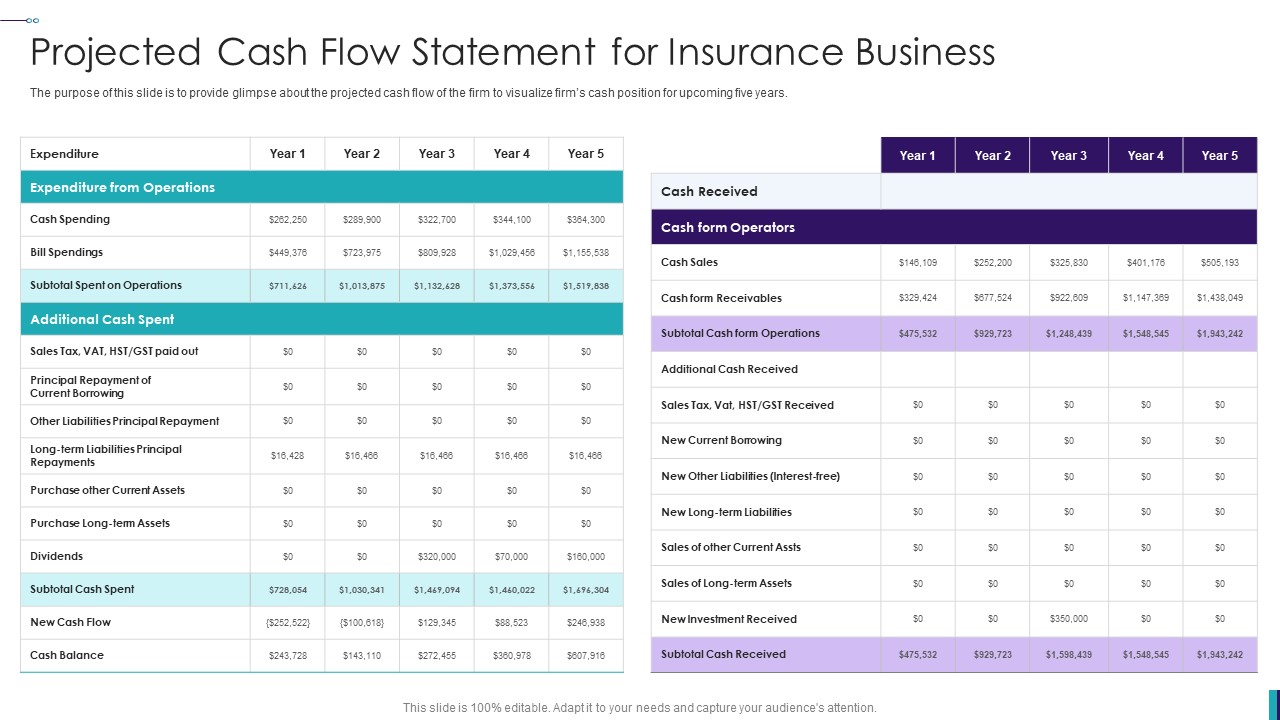
Cash Flow Statement Overview
In order to understand the impact of accounts receivable on cash flow, it is essential to have a basic understanding of the cash flow statement. The cash flow statement is a financial statement that provides information about the cash inflows and outflows of a business over a specified period of time.
The cash flow statement is divided into three main sections: operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities.
The operating activities section focuses on the cash flows generated from the company’s primary operations. It includes cash received from customers, cash paid to suppliers, payments for salaries and expenses, and other income or expenses directly related to the core business activities.
The investing activities section details the cash flows associated with the acquisition or disposal of long-term assets, such as property, plant, and equipment, as well as investments in other companies or securities. It includes cash inflows from the sale of assets and cash outflows for the purchase of assets or investments.
The financing activities section includes cash flows related to the company’s financing activities, such as borrowing or repaying loans, issuing or repurchasing shares, and paying dividends. It provides insights into how the company raises capital and manages its debt and equity.
The cash flow statement is important because it shows the net increase or decrease in cash during a specific period. It helps investors, creditors, and business owners assess the liquidity and financial viability of a company. It also provides valuable insights into the cash-generating ability of the business and its ability to meet its financial obligations.
Now that we have a basic understanding of the cash flow statement, let us explore how an increase in accounts receivable can impact the cash flow of a company.
Increase in Accounts Receivable
As mentioned earlier, accounts receivable represent the outstanding amounts owed to a company by its customers for goods or services provided on credit. An increase in accounts receivable occurs when the total amount owed by customers grows over a specific period of time.
There are several reasons why accounts receivable may increase. It could be due to an increase in credit sales, extended payment terms, or a delay in customer payments. This increase reflects the amount of sales made by the company that is yet to be converted into cash.
When accounts receivable increase, it indicates that the company has generated more revenue but hasn’t received the corresponding cash inflow. While this can be a positive sign of business growth, it also poses challenges for maintaining a healthy cash flow.
For instance, if a company sells products to customers on a 30-day payment term, an increase in accounts receivable means that cash will not be received immediately for those sales. The company will have to wait until the customers make their payments, potentially impacting its ability to cover immediate expenses or invest in new opportunities.
Moreover, an increase in accounts receivable can lead to a higher proportion of the company’s assets being tied up in outstanding customer payments. This can affect the company’s liquidity and ability to meet its short-term financial obligations.
It is important for businesses to closely monitor and manage their accounts receivable to prevent an excessive increase that could adversely impact cash flow. This involves implementing effective credit and collections policies, regular follow-ups on overdue payments, and proactive communication with customers to ensure timely payments.
Next, we’ll explore the impact that an increase in accounts receivable can have on cash flow.
Impact on Cash Flow
An increase in accounts receivable can have a significant impact on the cash flow of a business. It affects both the cash inflows and cash outflows, ultimately influencing the overall financial health and stability of the company.
On the cash inflows side, an increase in accounts receivable means that the company has provided goods or services to its customers, but the corresponding cash payments have not yet been received. This can lead to a delay in cash inflows, affecting the availability of funds to cover immediate expenses and financial obligations.
For example, if a company has a high accounts receivable balance and is waiting for customers to make their payments, it may not have sufficient cash on hand to pay its suppliers, employees, or other operational expenses. This can result in cash flow constraints and potentially lead to financial difficulties.
On the cash outflows side, the company still needs to make payments for various expenses, such as salaries, rent, utilities, and purchasing inventory or raw materials. These cash outflows can strain the available cash reserves, especially if accounts receivable continue to increase without accompanying cash inflows.
As a result, an increase in accounts receivable can lead to a negative cash flow cycle, where the company is using more cash to pay its expenses than it is receiving from its customers. This can create a cash flow shortfall and raise concerns about the company’s ability to meet its financial obligations and sustain its operations.
In addition to the immediate impact on cash flow, an increase in accounts receivable can also have long-term consequences. It can tie up valuable working capital that could be used to invest in growth opportunities, pay down debts, or buffer against economic downturns.
To mitigate the negative impact on cash flow, businesses need to implement effective strategies for managing their accounts receivable and ensure timely collection of outstanding payments. This includes establishing clear credit and collection policies, offering incentives for early payments, establishing strong customer relationships, and proactively addressing any payment delays or issues.
Next, we’ll explore the factors that influence cash flow and how they relate to accounts receivable.
Factors Influencing Cash Flow
Cash flow is influenced by various factors, and understanding these factors is crucial for managing accounts receivable effectively and maintaining a healthy cash flow. Here are some key factors that can impact cash flow:
- Sales Volume: The volume of sales directly affects cash flow. Higher sales can result in increased accounts receivable, while lower sales can lead to reduced cash inflows. It is important to strike a balance between generating sales and ensuring timely payment collection.
- Payment Terms: The credit terms offered to customers determine the timing of cash inflows. If longer payment terms are provided, it can delay the receipt of cash and negatively impact cash flow. Setting appropriate payment terms is crucial for managing accounts receivable and maintaining a steady cash flow.
- Customer Behavior: The payment behavior of customers can significantly impact cash flow. Delays in payment, defaulting on payments, or slow collections can strain the company’s cash flow. Building strong customer relationships and implementing effective collection strategies can help mitigate these risks.
- Credit Policy: The credit policy of a business determines who gets credit, how much credit is extended, and the terms associated with it. A well-defined credit policy helps in assessing the creditworthiness of customers and reducing the risk of non-payment or bad debts, ultimately impacting cash flow.
- Operating Expenses: The management of operating expenses is crucial for maintaining a healthy cash flow. If expenses are too high, they can consume a significant portion of the available cash, leaving little room for managing accounts receivable effectively. Keeping expenses in check and optimizing costs can contribute to a positive cash flow.
- Collections Process: Establishing an efficient collections process is essential for timely payment collection and improved cash flow. This involves sending timely invoices, following up on overdue payments, offering payment reminders, and implementing effective communication channels with customers.
By being mindful of these factors, businesses can take proactive steps to manage their accounts receivable and optimize cash flow. Effective cash flow management is essential for maintaining the financial stability and sustainability of a company.
Now let’s explore some strategies for effectively managing accounts receivable.
Managing Accounts Receivable
To maintain a healthy cash flow and effectively manage accounts receivable, businesses can implement several strategies. Here are some key practices to consider:
- Clear Credit Policies: Establish clear credit policies that outline the terms and conditions for granting credit to customers. This includes determining credit limits, payment terms, and any applicable interest or late payment fees. Clear policies help set expectations and reduce the risk of delinquencies or non-payment.
- Creditworthiness Assessment: Before extending credit to customers, conduct thorough creditworthiness assessments. This involves gathering information about the customer’s financial stability, credit history, and payment patterns. Assessing creditworthiness helps identify potential risks and make informed decisions about credit limits and payment terms.
- Timely Invoicing: Send out invoices promptly after delivering goods or providing services. Clearly state the details of the transaction, payment terms, and any discount incentives for early payment. Timely invoicing improves the chances of prompt payment and eliminates any confusion regarding payment obligations.
- Proactive Collections: Implement a proactive collections process to ensure timely and consistent payment collection. This includes sending reminders to customers as payment deadlines approach, following up on overdue invoices, and maintaining regular communication to resolve any payment issues. Promptly addressing outstanding payments helps reduce the risk of late or non-payments.
- Offering Incentives: Consider offering incentives for early payment to encourage customers to settle their accounts promptly. These incentives can include discounts, extended warranties, or other perks that provide value to the customer while improving cash flow for the business.
- Implementing Technology: Leverage technology solutions, such as accounting software and customer relationship management (CRM) systems, to streamline accounts receivable processes. Automating tasks like invoicing, payment reminders, and collections can improve efficiency, reduce errors, and enhance overall cash flow management.
- Building Strong Relationships: Cultivate strong relationships with customers by providing excellent customer service and maintaining open lines of communication. Good relationships can lead to better payment behavior, increased transparency, and cooperation during times of financial difficulty.
By implementing these practices, businesses can effectively manage their accounts receivable and maintain a healthy cash flow. This ensures the availability of funds to cover operational expenses, invest in growth opportunities, and meet financial obligations.
Now, let’s summarize what we’ve discussed so far.
Conclusion
Managing accounts receivable is vital for maintaining a healthy cash flow in any business. An increase in accounts receivable can have a significant impact on cash flow, as it represents sales that have been made but not yet collected in cash. It can lead to delayed cash inflows, strain available cash reserves, and hinder the ability to meet immediate financial obligations.
To mitigate the negative impact on cash flow, businesses should focus on implementing effective strategies. This includes establishing clear credit policies, assessing the creditworthiness of customers, invoicing promptly, implementing proactive collections processes, and leveraging technology solutions.
Additionally, factors such as sales volume, payment terms, customer behavior, credit policy, operating expenses, and collections processes can influence cash flow and should be carefully managed. By employing these strategies and considering these factors, businesses can optimize cash flow and maintain financial stability.
Managing and controlling accounts receivable is an ongoing process that requires regular monitoring, analysis, and adjustments. By maintaining a balance between generating sales and ensuring timely payment collection, businesses can sustain a healthy cash flow to support their operations, growth initiatives, and financial objectives.
In conclusion, understanding the impact of accounts receivable on cash flow and implementing effective management strategies is crucial for the long-term success and financial health of businesses.