Home>Finance>How To Calculate Book Value Per Share From Balance Sheet


Finance
How To Calculate Book Value Per Share From Balance Sheet
Modified: December 30, 2023
Learn how to calculate book value per share in finance using the balance sheet. Discover valuable insights for evaluating a company's worth.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on how to calculate book value per share from a balance sheet. Understanding the concept of book value per share is essential for investors and financial analysts seeking to evaluate the value and financial health of a company. By calculating this figure, one can gain insight into the worth of each share of stock and make informed investment decisions.
Book value per share is a measure of the net worth of a company and represents the value of each share if the company were to be liquidated and all assets were sold and liabilities paid off. It provides a snapshot of the company’s financial position at a specific point in time and helps investors determine whether the stock is trading at a discount or premium to its intrinsic value. In conjunction with other financial ratios and metrics, book value per share can aid in assessing the overall financial health and stability of a company.
Understanding how to calculate book value per share requires a sound understanding of the components of a balance sheet, as this is where the necessary information is derived. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the components of a balance sheet, explore the calculation of book value per share, analyze its interpretation, and discuss the limitations of using this measure.
Whether you are a seasoned investor or just starting your journey in the world of finance, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to calculate and interpret book value per share with confidence. So, let’s dive in and explore this fundamental concept together!
Definition of Book Value per Share
Book value per share is a financial metric that calculates the per-share value of a company based on its balance sheet. It represents the net worth of a company and provides insight into the value that each share of stock holds.
To understand book value per share, let’s break down the components:
- Book Value: Book value, also known as net asset value, is the total value of a company’s assets minus its liabilities. It represents the residual value that would be left if all debts were paid off and assets were liquidated.
- Shares Outstanding: This refers to the total number of shares that a company has issued and is currently held by shareholders.
The formula to calculate book value per share is:
Book Value per Share = (Total Shareholder’s Equity – Preferred Stock) / Shares Outstanding
It is important to note that book value per share is a historical measure and does not take into account factors such as future earnings potential or market sentiment. It provides a tangible value based on the company’s financial position at a specific point in time.
Book value per share is particularly important for value investors who focus on buying stocks that are trading at a discount to their intrinsic value. By comparing a stock’s current market price to its book value per share, investors can gauge whether the stock is undervalued or overvalued.
Now that we have a clear understanding of the concept of book value per share, let’s move on to the next section and explore the different components of a balance sheet.
Understanding the Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is one of the three fundamental financial statements, along with the income statement and cash flow statement. It provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position by presenting its assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity at a specific point in time.
Let’s explore the key components of a balance sheet:
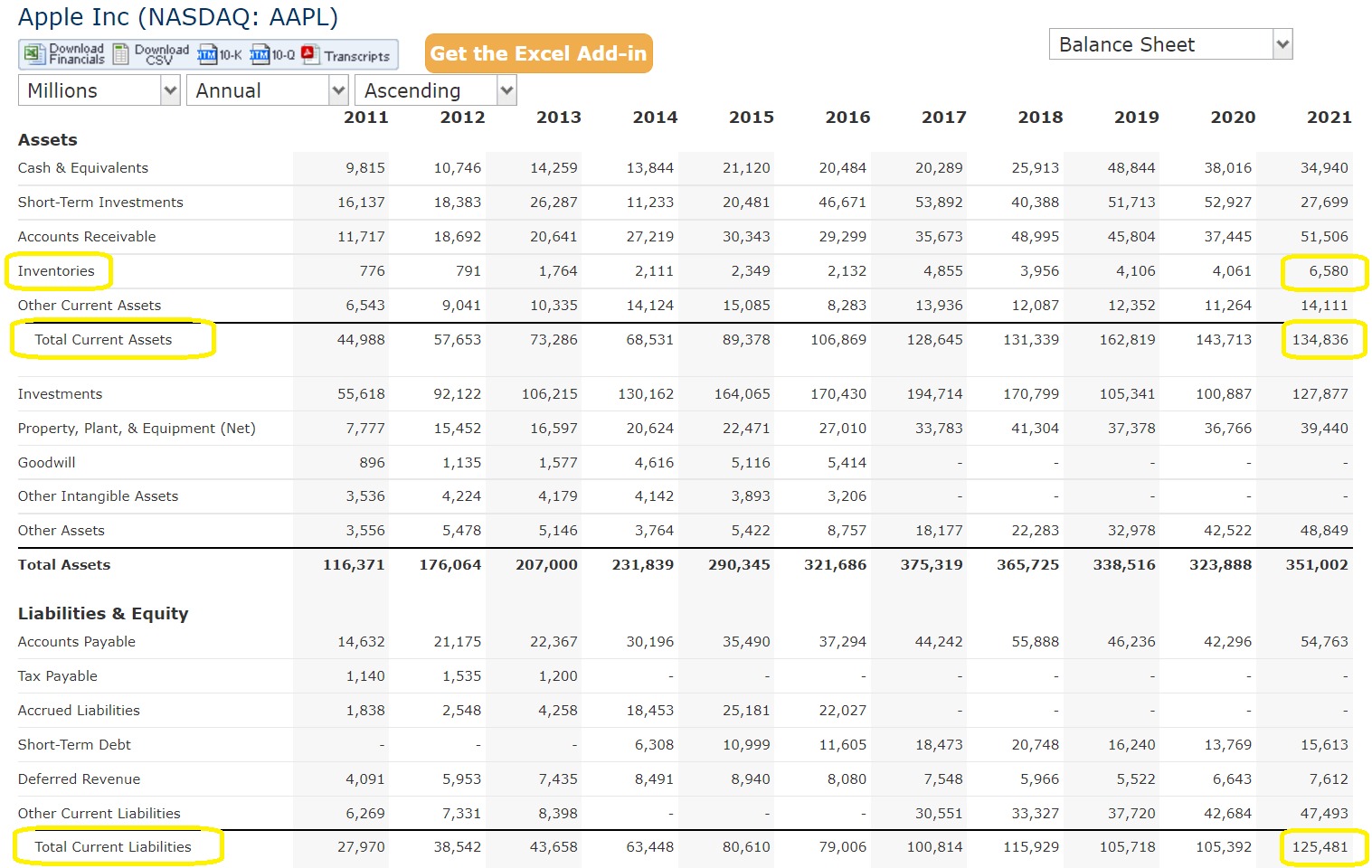
- Assets: Assets are the resources owned by a company that have economic value. They can be classified into two categories: current assets and non-current assets. Current assets include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, and short-term investments. Non-current assets, also known as long-term assets, include property, plant, and equipment, intangible assets, and long-term investments.
- Liabilities: Liabilities are the obligations or debts that a company owes to external parties. Similar to assets, liabilities can be categorized as current liabilities and non-current liabilities. Current liabilities include accounts payable, short-term loans, and accrued expenses. Non-current liabilities, also known as long-term liabilities, include long-term debt and deferred taxes.
- Shareholders’ Equity: Shareholders’ equity, also referred to as net worth or owner’s equity, represents the residual interest in the assets of a company after deducting liabilities. It includes common stock, additional paid-in capital, retained earnings, and any other components of equity.
The balance sheet follows the fundamental accounting equation:
Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders’ Equity
This equation highlights the dual nature of the balance sheet, where the total value of a company’s assets must be equal to the sum of its liabilities and shareholders’ equity.
By examining the components of a balance sheet, investors can gain insight into a company’s financial health, liquidity, and solvency. The balance sheet provides crucial information for calculating book value per share, as it includes the necessary figures to determine the net worth of the company.
Now that we have a solid understanding of the balance sheet, let’s move on to the next section and learn how to calculate book value per share.
Calculation of Book Value per Share
Calculating book value per share involves using information from the balance sheet to determine the net worth of a company on a per-share basis. The formula for calculating book value per share is:
Book Value per Share = (Total Shareholder’s Equity – Preferred Stock) / Shares Outstanding
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the calculation:
- Obtain the balance sheet of the company in question. The balance sheet should include the total shareholder’s equity and the number of shares outstanding.
- If the balance sheet includes preferred stock, subtract the value of the preferred stock from the total shareholder’s equity. This is because preferred stockholders have a higher claim on assets compared to common stockholders.
- Divide the adjusted shareholder’s equity by the number of shares outstanding. This will give you the book value per share.
Let’s take a hypothetical example to illustrate the calculation. Suppose Company XYZ has a total shareholder’s equity of $10 million and 1 million shares outstanding. The balance sheet does not mention any preferred stock:
Book Value per Share = $10,000,000 / 1,000,000 = $10
In this example, the book value per share for Company XYZ is $10.
It’s important to note that book value per share is a historical measure and is based on the balance sheet values at a specific point in time. As a result, it may not reflect the current market value or future earnings potential of the company.
In addition to calculating book value per share for an individual company, investors can also calculate it for a portfolio of stocks by aggregating the book value per share of each holding. This can provide insights into the overall value and performance of the portfolio.
Now that we know how to calculate book value per share, let’s move on to the next section and analyze its interpretation.
Analysis and Interpretation of Book Value per Share
Book value per share is a valuable metric for investors and analysts as it provides insight into the intrinsic value of a company’s shares. Here are some key points to consider when analyzing and interpreting book value per share:
Comparison to Market Price: Comparing the book value per share to the market price can give an indication of whether a stock is overvalued or undervalued. If the market price is higher than the book value per share, it suggests that investors have priced in expectations of future growth and profitability. Conversely, if the market price is lower than the book value per share, it may indicate that the stock is undervalued and potentially a good investment opportunity.
Trend Analysis: Analyzing the trend of book value per share over time can reveal the company’s ability to generate value for shareholders. If the book value per share is consistently increasing, it suggests that the company is effectively utilizing its assets and generating profits. Conversely, a decreasing trend may indicate financial challenges or poor management decisions.
Comparison to Peers: Comparing the book value per share of a company to its industry peers can provide insights into its relative financial strength. If a company has a higher book value per share compared to its peers, it may indicate better financial stability and a stronger balance sheet.
Tracking Changes: Examining the changes in book value per share over time can highlight important events or factors affecting the company’s financial position. For example, issuing additional shares, acquiring or divesting assets, or borrowing significant amounts of debt can all impact the book value per share. Understanding the reasons behind these changes can aid in making informed investment decisions.
It’s important to note that book value per share is just one piece of the puzzle when evaluating a company’s investment potential. It should be used in conjunction with other financial ratios and metrics, such as earnings per share, price-to-earnings ratio, and return on equity, to gain a comprehensive understanding of a company’s financial health and valuation.
Lastly, it’s crucial to consider the industry and specific circumstances of the company. Some industries, such as technology or healthcare, may place more emphasis on future earnings potential rather than book value per share. Furthermore, companies with significant intangible assets, like intellectual property, may have a higher market value beyond their book value per share.
By considering these factors and conducting thorough analysis, investors can make more informed decisions about the value and growth potential of the company’s shares.
Now that we have analyzed the interpretation of book value per share, let’s move on to discuss the limitations of this calculation method.
Limitations of Book Value per Share Calculation
While book value per share is a useful metric for evaluating a company’s worth, it is important to be aware of its limitations. Here are some key limitations to consider:
Intangible Assets: Book value per share does not take into account the value of intangible assets, such as brand value, intellectual property, or patents. These assets can be valuable contributors to a company’s overall worth but are not reflected in the balance sheet and therefore not considered in the book value per share calculation.
Market Value: Book value per share represents the historical accounting value of a company’s assets and does not necessarily reflect their current market value. Factors such as supply and demand, market sentiment, and investor expectations can significantly influence the market price of a stock, causing it to deviate from its book value per share.
Growth Potential: Book value per share does not account for a company’s growth potential or its ability to generate future profits. Companies with high growth potential, innovative business models, or strong competitive advantages may have a higher market value than their book value per share would suggest.
Depreciation and Amortization: The balance sheet reflects the historical cost of assets, which may differ significantly from their current market value. The book value per share calculation does not consider the impact of depreciation and amortization, which can result in an understatement of the company’s actual worth.
Debt Obligations: Book value per share does not factor in a company’s debt obligations. A company with a high level of debt may have a lower book value per share, even if it possesses valuable assets. Understanding the company’s debt structure and its impact on the overall financial position is essential for a comprehensive analysis.
Industry Differences: Different industries have varying levels of reliance on tangible assets. For example, manufacturing companies typically have higher book values due to their significant investments in plants and equipment, while technology companies may have fewer tangible assets but higher market valuations based on their intellectual property or customer base.
It is crucial to consider these limitations in conjunction with other financial metrics and qualitative factors when assessing a company’s value and investment potential. Book value per share should be used as a tool in a broader analysis, in combination with factors such as earnings, cash flow, industry dynamics, and the competitive landscape.
Now that we have explored the limitations, let’s conclude the article.
Conclusion
Understanding how to calculate and interpret book value per share is essential for investors and financial analysts. This metric provides valuable insights into a company’s net worth on a per-share basis, allowing for comparisons to market price and evaluations of its financial health.
By utilizing the formula for book value per share and analyzing its interpretation, investors can gain a better understanding of a company’s intrinsic value. Comparing book value per share to the market price can help identify potential investment opportunities. Looking at trends, comparing to industry peers, and tracking changes in book value per share over time further enhances the analysis.
However, it’s important to recognize the limitations of book value per share. Factors such as intangible assets, market value, growth potential, depreciation, and debt obligations can affect a company’s overall worth, which may not be fully reflected in its book value per share.
Therefore, it’s crucial to consider book value per share alongside other financial ratios, qualitative factors, and industry dynamics to make well-informed investment decisions.
In conclusion, book value per share provides a valuable starting point for evaluating a company’s worth and assessing its financial position. By using this metric, investors can gain insights into the underlying value of a company’s shares, aiding in the identification of potential investment opportunities and the understanding of a company’s financial health.
We hope this comprehensive guide has provided you with a better understanding of book value per share and its significance in the world of finance. As always, conducting thorough research and analysis is vital when making investment decisions, and book value per share is just one tool in your toolbox.
Now go forth and apply your knowledge to navigate the intricate world of finance with confidence!