
Finance
How To Forecast Balance Sheet
Modified: February 21, 2024
Learn how to accurately forecast your balance sheet in the field of finance with our step-by-step guide. Master the art of financial analysis and make informed decisions for your business.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Step 1: Gather Financial Data
- Step 2: Analyze Historical Trends
- Step 3: Identify Key Assumptions
- Step 4: Project Future Sales
- Step 5: Estimate Accounts Receivable
- Step 6: Forecast Inventory Levels
- Step 7: Calculate Accounts Payable
- Step 8: Determine Capital Expenditures
- Step 9: Forecast Debt and Interest Expense
- Step 10: Project Income Taxes
- Step 11: Assess Other Liabilities and Equity
- Step 12: Create Balance Sheet Projections
- Conclusion
Introduction
Forecasting the balance sheet is a crucial aspect of financial planning for any business. It provides insights into the company’s financial health, helps in identifying potential funding requirements, and aids in making informed business decisions. By projecting future assets, liabilities, and equity, a business can gain a better understanding of its financial position and plan for growth.
While forecasting a balance sheet may seem like a daunting task, it can be broken down into a series of manageable steps. This article will guide you through the process of forecasting a balance sheet, providing you with a framework to project key financial metrics and achieve accurate results.
In this article, we will outline a step-by-step approach to create a comprehensive balance sheet forecast. We will cover gathering financial data, analyzing historical trends, identifying key assumptions, estimating future sales, calculating accounts receivable, forecasting inventory levels, determining accounts payable, projecting capital expenditures, estimating debt and interest expenses, projecting income taxes, assessing other liabilities and equity, and creating the final balance sheet projection.
By following these steps, you will be able to develop a balance sheet forecast that will serve as a valuable tool for budgeting, financial planning, and decision-making. Let’s dive in and learn how to forecast a balance sheet effectively.
Step 1: Gather Financial Data
The first step in forecasting a balance sheet is to gather the necessary financial data. This data will serve as the foundation for your projections and ensure the accuracy of your forecast. Start by collecting financial statements, such as the income statement, cash flow statement, and previous balance sheets. These documents provide historical data and insights into the company’s past performance.
In addition to financial statements, gather other relevant information, such as sales data, customer contracts, supplier agreements, and industry reports. This data will help you understand the company’s current position, market trends, and potential risks and opportunities.
Once you have gathered all the necessary data, organize it in a systematic manner. Create spreadsheets or use financial software to input the financial statements and other relevant information. This will allow you to easily analyze the data and make accurate projections later in the process.
It is important to ensure that the financial data you gather is accurate and up-to-date. Double-check for any discrepancies or missing information, and reach out to the relevant departments or individuals to resolve any issues. Remember, the accuracy of your forecast relies heavily on the quality of the data you gather, so take the time to verify and validate it.
Gathering financial data is the foundational step in the balance sheet forecasting process. It provides you with a clear understanding of the historical performance of the company and sets the stage for analyzing trends and making projections in the following steps. By gathering accurate and comprehensive financial data, you are laying the groundwork for a reliable and insightful balance sheet forecast.
Step 2: Analyze Historical Trends
After gathering the necessary financial data, the next step in forecasting a balance sheet is to analyze historical trends. This analysis provides valuable insights into the company’s past performance and helps identify patterns or recurring trends that can be useful in projecting future financials.
Start by examining the historical balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements. Look for trends in key financial metrics such as revenue, expenses, assets, and liabilities. Identify any significant changes or fluctuations in these metrics over the past few years.
Pay close attention to ratios and relationships between different line items on the balance sheet. This analysis can provide insights into the company’s liquidity, leverage, and solvency. Financial ratios such as current ratio, debt-to-equity ratio, and return on assets can offer valuable information about the company’s financial health and performance.
In addition to financial ratios, consider external factors that may have influenced the company’s historical performance. This could include changes in market conditions, industry trends, competition, or regulatory factors. Understanding the external influences on the company’s financials will help you make more accurate projections for the future.
By analyzing historical trends, you can identify any seasonality or cyclical patterns that may exist in the company’s financials. For example, if sales tend to be higher during certain months or quarters, you can adjust your projections accordingly. Likewise, if there are any recurring expenses or liabilities, take them into account when forecasting future balance sheet items.
Through this analysis, you can gain a deeper understanding of the company’s financial performance and use it as a basis for your forecast. Historical trends provide valuable insights into the company’s strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement. By identifying and understanding these trends, you can make more informed projections for the future, ensuring a more accurate and reliable balance sheet forecast.
Step 3: Identify Key Assumptions
When forecasting a balance sheet, it is essential to identify and document the key assumptions that will drive your projections. These assumptions serve as the foundation for your forecast and help determine the accuracy and reliability of your final balance sheet.
Start by considering the macroeconomic factors that may impact your business. This could include factors such as interest rates, inflation rates, and GDP growth. Analyze the current economic climate and make reasonable assumptions about how these factors may evolve in the future. These assumptions will affect various aspects of your balance sheet, such as interest expense, purchasing power of assets and liabilities, and overall market conditions.
Next, consider the specific industry in which your business operates. Identify any industry-specific factors that may influence your financials. This could include industry growth rates, market competition, technological advancements, regulatory changes, or consumer behavior. Make assumptions about how these factors may impact your company’s financial performance in the future.
Take into account the company’s own internal factors that will impact the balance sheet. This includes assumptions about future sales growth rates, pricing strategies, cost structures, and operating efficiencies. Consider factors such as new product launches, expansion plans, or changes in distribution channels. These assumptions will directly impact your revenue, expenses, and overall financial position.
Lastly, think about other specific assumptions related to your balance sheet. For example, assume a target dividend payout ratio or a target equity-to-debt ratio. These assumptions will help determine the level of retained earnings and the overall capital structure of the company. Consider any potential changes to the company’s capital expenditure plans, such as investments in new assets or technology upgrades.
Identifying and documenting these key assumptions is vital for ensuring transparency and accuracy in your balance sheet forecast. It provides a clear framework for your projections and allows for more informed decision-making. Remember to revisit and reassess these assumptions periodically to ensure they align with the evolving business landscape.
Step 4: Project Future Sales
One of the fundamental elements in forecasting a balance sheet is projecting future sales. Sales projections serve as the starting point for estimating various revenue-related items on the balance sheet, such as accounts receivable and sales returns. By accurately forecasting future sales, you can provide a solid foundation for your overall balance sheet forecast.
To project future sales, start by analyzing historical sales data and identifying any trends or patterns. Consider factors such as seasonality, market conditions, and previous growth rates. This will provide insights into the company’s historical sales performance and help set a baseline for your projections.
Next, take into account any internal or external factors that may impact future sales. For example, if the company is launching new products or entering new markets, it could lead to increased sales. Conversely, if there are changes in customer preferences or increased competition, it may impact sales growth.
Consider industry trends and market forecasts to inform your sales projections. Conduct market research and analyze industry reports to understand the growth prospects and potential challenges in your industry. This information can help you make more accurate assumptions about future sales growth rates.
Additionally, take into account any sales initiatives or marketing strategies that the company plans to implement. Consider the effectiveness of these strategies and how they may impact sales growth. It is important to be realistic and fact-based when making assumptions about the success of these initiatives.
Once you have gathered all the necessary information, use it to develop a sales forecast. Base your projections on a combination of historical trends, industry analysis, and internal factors. Consider using different scenarios and sensitivity analysis to account for potential risks or uncertainties.
By projecting future sales accurately, you can provide a solid foundation for your overall balance sheet forecast. This step is crucial for estimating key items such as accounts receivable, which will influence the company’s liquidity and cash flow position. Understanding the drivers of sales growth and making informed projections will contribute to a more accurate and reliable balance sheet forecast.
Step 5: Estimate Accounts Receivable
In the process of forecasting a balance sheet, estimating accounts receivable is a critical step. Accounts receivable represents the amount of money owed to a company by its customers for goods or services delivered on credit. Estimating accounts receivable accurately is important for managing cash flow and understanding the company’s liquidity position.
Start by analyzing historical accounts receivable data. Look at past trends in accounts receivable turnover ratio, which measures how quickly the company collects its receivables. This ratio provides insights into the efficiency of the company’s credit and collection processes. Consider any seasonal or cyclical patterns in accounts receivable and adjust your projections accordingly.
Next, consider factors that may impact accounts receivable in the future. Evaluate the company’s credit policies and any changes that may affect the average collection period. Assess the creditworthiness of customers and the potential for bad debt losses. Consider any changes in payment terms or discounts offered to customers that may impact the timing of collections.
Take into account the projected changes in sales volume, as this will directly impact the level of accounts receivable. If sales are expected to increase, accounts receivable will likely increase as well. Consider the average collection period for similar customers and apply this to the projected sales to estimate future accounts receivable.
Additionally, review any outstanding invoices and assess the likelihood of collection. Identify any specific customers or accounts that may have a higher risk of defaulting on their payments. Consider any changes in the economic environment that may impact customers’ ability to pay.
To estimate accounts receivable, use a combination of historical data analysis, customer assessment, and sales projections. Consider different scenarios and sensitivity analysis to account for potential risks and uncertainties. Regularly review and update your estimates as new information becomes available.
Accurately estimating accounts receivable is crucial for managing cash flow and understanding the company’s working capital position. It provides insights into the company’s ability to collect on its credit sales and maintain healthy liquidity levels. By carefully considering historical trends, credit policies, sales projections, and customer assessments, you can generate a reliable and insightful estimate of accounts receivable for your balance sheet forecast.
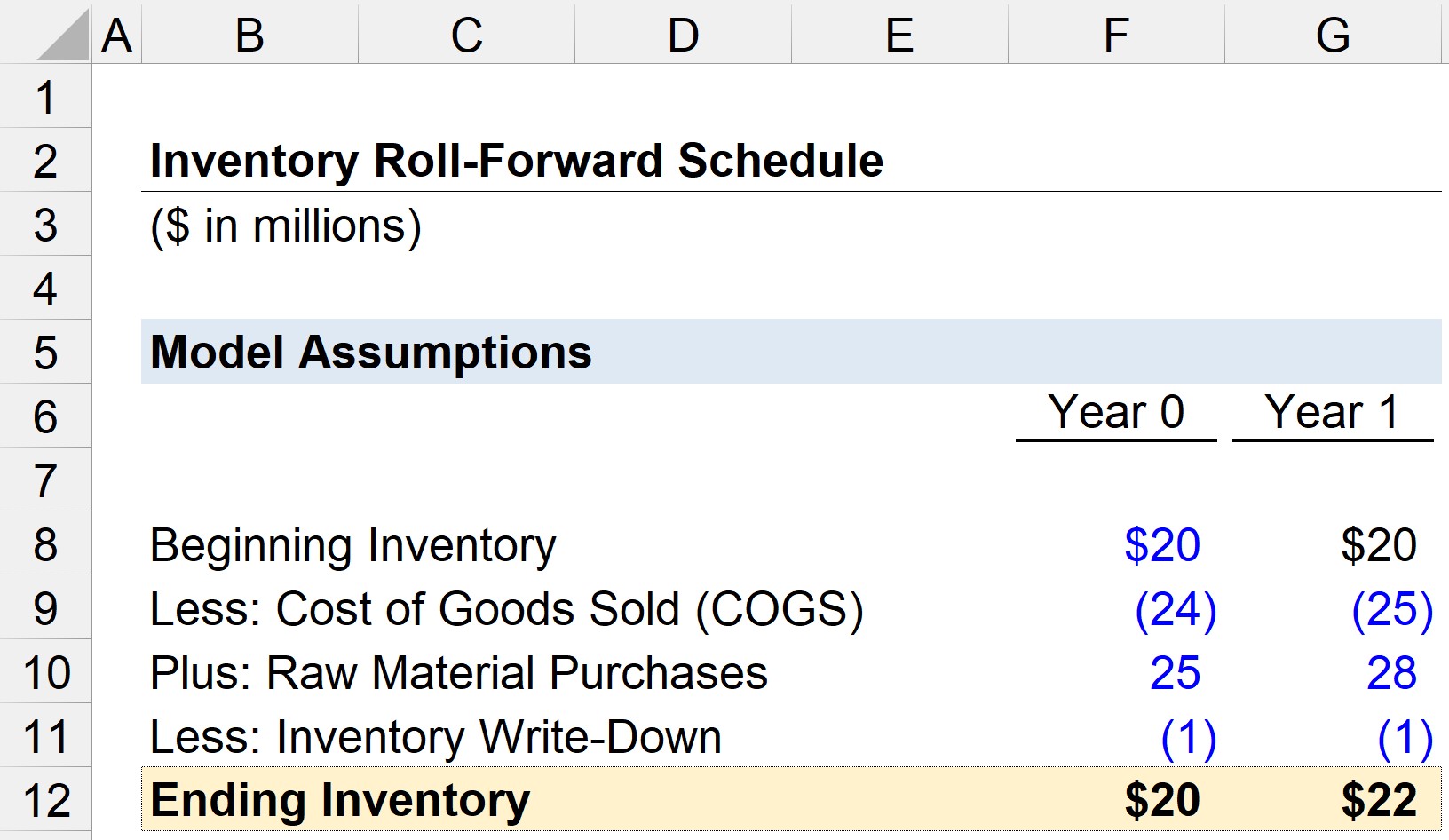
Step 6: Forecast Inventory Levels
Forecasting inventory levels is an essential step in the process of creating a balance sheet projection. Inventory represents the goods or raw materials a company holds for sale or for use in the production process. Accurate inventory forecasts are crucial for managing working capital, production planning, and meeting customer demand.
Start by analyzing historical inventory data to identify patterns and trends. Look at the inventory turnover ratio, which measures how quickly inventory is sold or used. Analyze any fluctuations in inventory levels based on seasonality or changes in sales volumes. Consider any obsolete or slow-moving inventory that may impact future inventory levels.
Next, consider factors that can influence inventory levels in the future. Evaluate the company’s sales forecast and production plans. If sales are expected to increase, inventory levels may need to be adjusted accordingly to meet customer demand. Assess any planned changes in production processes, changes in supplier lead times, or other factors that may impact the inventory holding period.
Additionally, evaluate industry trends and market conditions. Assess any potential supply chain disruptions or changes in customer preferences that may impact inventory levels. Consider any new product launches or changes in the company’s product mix that may influence inventory requirements.
Consider the company’s inventory management policies and practices. Evaluate the effectiveness of inventory control systems and any improvements that may be implemented to optimize inventory levels and reduce carrying costs. Assess any inventory write-offs or adjustments that may need to be made based on aging inventory or market conditions.
To forecast inventory levels, incorporate all of the above factors into your projections. Consider using forecasting techniques such as linear regression, moving averages, or industry benchmarks to refine your estimates. Regularly monitor and update your inventory forecasts as new information becomes available.
Accurate forecasting of inventory levels is crucial for managing working capital and meeting customer demands. It ensures that the company has the right amount of inventory on hand to satisfy customer needs while minimizing carrying costs and the risk of stockouts or excess inventory. By analyzing historical data, considering various factors and using appropriate forecasting techniques, you can generate reliable inventory projections for your balance sheet forecast.
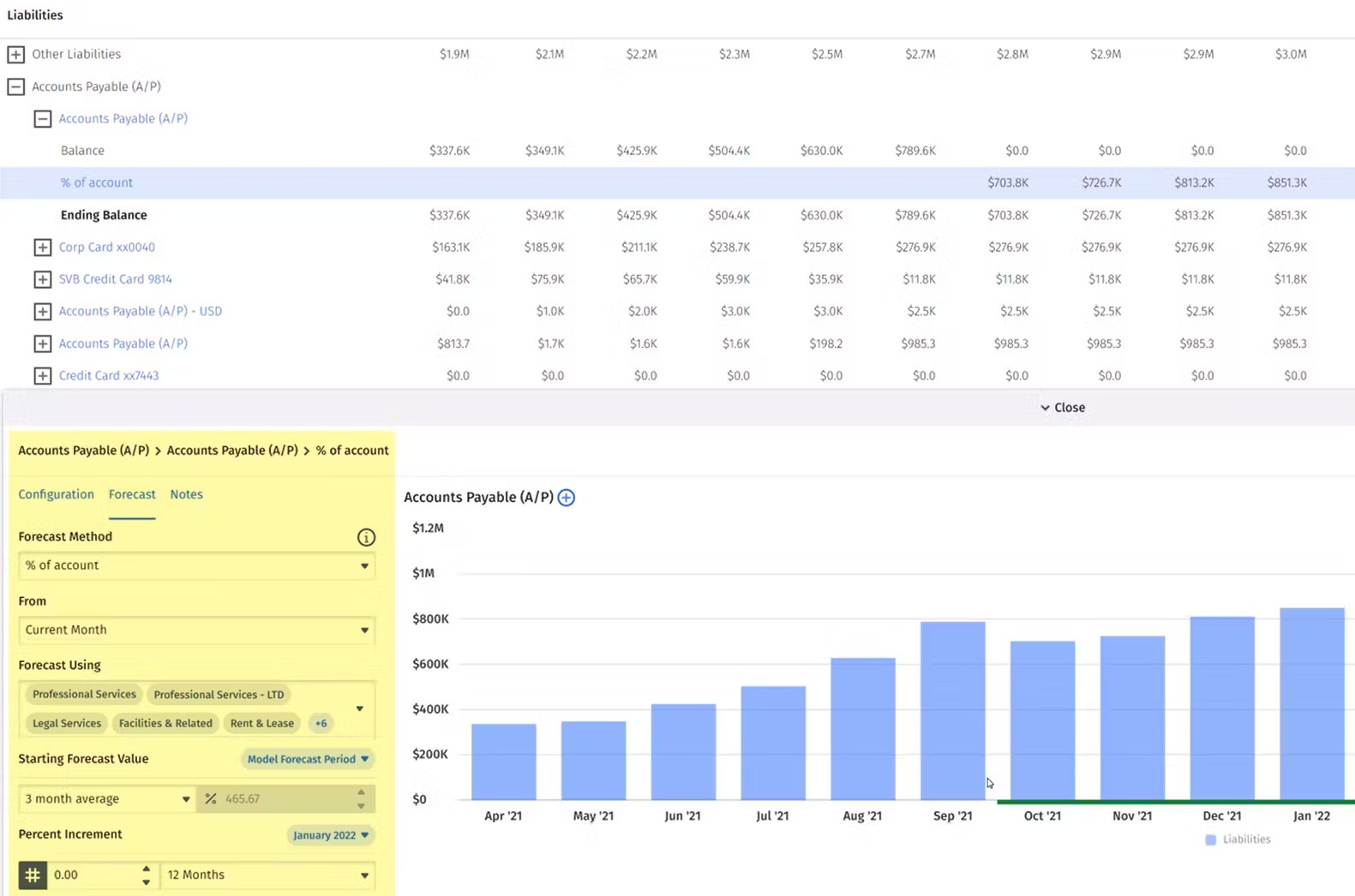
Step 7: Calculate Accounts Payable
In the process of forecasting a balance sheet, calculating accounts payable is a crucial step. Accounts payable represents the amount of money owed by a company to its suppliers for goods or services received but not yet paid for. Accurate estimation of accounts payable is important for managing cash flow and understanding the company’s liabilities.
Start by analyzing historical accounts payable data. Look at past trends in the accounts payable turnover ratio, which measures how quickly the company pays its suppliers. Assess any fluctuations in accounts payable based on changes in purchase volumes, payment terms, or changes in supplier relationships. Consider any seasonality or cyclical patterns in accounts payable and adjust your projections accordingly.
Next, consider factors that may impact accounts payable in the future. Evaluate any planned changes in purchasing strategies, supplier relationships, or terms and conditions of supplier contracts. Assess the company’s payment policies and any changes that may affect the average payment period.
Take into account the projected changes in purchase volumes. If sales are expected to increase, it is likely that purchases from suppliers will also increase, resulting in higher accounts payable. Consider the average payment period for similar suppliers and apply this to the projected purchases to estimate future accounts payable.
Additionally, consider any outstanding invoices from suppliers that have not yet been paid. Analyze any payment terms negotiated with suppliers and any discounts or incentives offered for early payments. Take into account any changes in the economic environment that may impact the company’s ability to meet payment obligations.
To calculate accounts payable, use a combination of historical data analysis, purchasing forecasts, and supplier payment terms. Consider different scenarios and sensitivity analysis to account for potential risks and uncertainties. Regularly review and update your projections as new information becomes available.
Accurately estimating accounts payable is vital for managing cash flow and understanding the company’s liabilities. It provides insights into the company’s payment obligations and its ability to meet those obligations. By carefully considering historical data, purchasing forecasts, and supplier payment terms, you can generate a reliable and insightful estimate of accounts payable for your balance sheet forecast.
Step 8: Determine Capital Expenditures
In the process of forecasting a balance sheet, determining capital expenditures is an important step. Capital expenditures, also known as CapEx, represent the investments made by a company in long-term assets, such as property, plant, and equipment (PP&E). Estimating capital expenditures accurately is crucial for understanding the company’s future asset base and cash flow commitments.
Start by reviewing historical capital expenditure data. Analyze past trends in CapEx and consider any significant investments made by the company in the past. Look for patterns or cycles in capital expenditures and assess the impact on the company’s assets and overall financial position.
Next, consider the company’s strategic plans and growth initiatives. Evaluate any planned expansions, acquisitions, or upgrades to existing assets. Assess the potential need for new technology or equipment to support business operations. Consider any investments needed to maintain regulatory compliance or adapt to changing industry standards.
Take into account any upcoming lease commitments or contractual obligations related to capital expenditures. Evaluate any lease agreements, loan agreements, or supplier contracts that may involve capital investments. Assess the timing and magnitude of these obligations and incorporate them into your forecast.
Consider the industry dynamics and market conditions. Evaluate any technological advancements or industry trends that may require capital investments in order to remain competitive. Analyze the capital expenditure practices of industry peers and competitors to gain insights into potential investment requirements.
Lastly, assess the company’s financial capacity and capital allocation strategy. Consider the company’s capital structure, debt levels, and available financial resources. Evaluate the company’s ability to secure financing for capital projects or the potential impact of funding constraints on capital expenditure plans.
To determine capital expenditures, integrate all the above factors into your projections. Make informed assumptions based on historical data, strategic plans, industry trends, and financial capacity. Regularly monitor and update your capital expenditure estimates as new information becomes available.
Determining capital expenditures accurately is crucial for understanding the company’s asset base, investment needs, and future cash flow commitments. It provides insights into the company’s growth plans and long-term asset requirements. By carefully considering historical data, strategic priorities, and industry trends, you can generate reliable and insightful estimates of capital expenditures for your balance sheet forecast.
Step 9: Forecast Debt and Interest Expense
When forecasting a balance sheet, it is important to accurately project debt levels and interest expenses. Debt represents the borrowed funds that a company owes to creditors, while interest expense is the cost of borrowing that includes interest payments on the debt. Estimating debt and interest expense is crucial for understanding the company’s financing obligations and their impact on its financial position.
Start by reviewing the company’s current debt levels and analyzing its debt repayment history. Look at outstanding loans, bonds, or other forms of borrowing and assess their maturity dates, interest rates, and repayment terms. Consider any significant changes in debt levels or refinancing activities that may impact the future debt obligations.
Next, evaluate the company’s financing plans and capital structure. Consider any planned debt issuances or debt repayments, as well as potential changes in the company’s debt-equity ratio. Assess the company’s creditworthiness and potential changes in interest rates that may impact borrowing costs.
Take into account any planned changes in interest rates or fluctuations in market interest rates. Analyze the company’s exposure to variable interest rates and assess any hedging mechanisms in place to mitigate interest rate risks. Consider any changes in the economic environment that may impact interest rates, such as fluctuations in inflation or central bank policies.
Consider the repayment schedules and interest rates on existing debt. Evaluate any provisions related to principal repayments, balloon payments, or debt covenants that may affect the timing and magnitude of debt repayments. Incorporate these provisions into your forecast to accurately estimate future debt levels and interest expense.
Additionally, consider any potential changes in credit rating or financial health that may impact the interest rates offered to the company. Assess the company’s ability to negotiate favorable borrowing terms and any costs associated with obtaining new financing.
To forecast debt and interest expense, integrate all of the above factors into your projections. Consider different scenarios and sensitivity analysis to account for potential risks and uncertainties. Regularly review and update your debt and interest expense estimates as new information becomes available.
Accurately forecasting debt and interest expense is important for understanding the company’s financing obligations and their impact on its financial position. It provides insights into the company’s debt management practices, funding requirements, and overall cost of borrowing. By carefully considering historical data, financing plans, interest rate trends, and debt repayment schedules, you can generate reliable and insightful estimates for your balance sheet forecast.
Step 10: Project Income Taxes
When forecasting a balance sheet, projecting income taxes is a crucial step to accurately estimate the company’s tax liabilities and their impact on its financial position. Income taxes represent the amount that a company owes to tax authorities based on its taxable income. Estimating income taxes helps in understanding the company’s tax obligations and planning for its tax liabilities.
Start by reviewing the company’s historical tax payments and analyzing any trends or patterns. Consider any changes in tax rates, tax laws, or tax incentives that may impact future tax liabilities. Assess the company’s tax planning strategies and any potential adjustments in tax calculations.
Next, consider the company’s projected taxable income. Evaluate the company’s sales forecast, expense projections, and other deductions or credits that may reduce taxable income. Consider any potential changes in the company’s operations or tax positions that may impact taxable income.
Take into account the tax jurisdiction in which the company operates. Assess the tax regulations and laws specific to the company’s industry and geographical locations. Analyze any potential changes in tax rules or tax rates that may affect the company’s tax liabilities.
Consider any tax planning strategies or tax incentives that the company may utilize to optimize its tax position. Assess the potential impact of tax deductions, credits, or tax holidays that may reduce the company’s tax liabilities. Take into account any potential changes in the company’s tax structure or tax planning initiatives.
Additionally, evaluate any tax-related contingencies or uncertainties that may impact future tax liabilities. Consider any ongoing tax audits, disputes, or potential changes in tax interpretations that may affect the company’s tax position. Assess the potential risks and consequences of these contingencies in estimating the company’s future tax liabilities.
To project income taxes, integrate all the above factors into your projections. Make informed assumptions based on historical data, sales forecasts, expense projections, and tax planning strategies. Regularly monitor and update your income tax estimates as new information becomes available.
Accurately projecting income taxes is crucial for understanding the company’s tax obligations and their impact on its financial position. It provides insights into the company’s tax planning strategies, potential tax liabilities, and overall tax position. By carefully considering historical data, future projections, and tax regulations, you can generate reliable and insightful estimates for your balance sheet forecast.
Step 11: Assess Other Liabilities and Equity
When forecasting a balance sheet, it is important to assess other liabilities and equity to accurately estimate the company’s financial obligations and equity position. Other liabilities encompass obligations that do not fall under traditional categories such as accounts payable or debt, while equity represents the ownership interest in the company. Assessing these components ensures a comprehensive understanding of the company’s financial position.
Start by reviewing the company’s current liabilities, excluding accounts payable and debt. Identify any outstanding obligations that may fall under the category of other liabilities. This may include items such as accrued expenses, deferred revenues, warranty provisions, or other contingent liabilities. Analyze historical data and trends in these categories to develop a baseline for your projections.
Next, consider any anticipated changes in other liabilities. Evaluate the company’s operations, strategic plans, and industry practices to identify potential future obligations. Anticipate any changes in warranty policies, employee benefit plans, legal settlements, or any other exposures that may give rise to additional liabilities.
Assess any changes in equity that may impact the balance sheet. Consider the issuance or repurchase of shares, stock dividends, or any other change in the company’s capital structure. Take into account any retained earnings or accumulated losses that may affect equity levels. Analyze the impact of recent or planned equity transactions on the company’s capital structure.
Consider any potential changes in shareholder equity due to changes in stock prices or changes in the fair value of financial instruments. Evaluate any reserves or stock-based compensation plans that may affect equity levels. Assess any changes in the company’s dividend policies or dividend declarations that may impact the distribution of equity to shareholders.
Lastly, assess any regulatory requirements or accounting standards that may impact other liabilities and equity. Stay updated on any changes in financial reporting standards that may impact the recognition or measurement of these items. Diligently address any disclosure requirements related to other liabilities and equity in your balance sheet forecast.
To assess other liabilities and equity, integrate all the above factors into your projections. Analyze historical data, industry practices, and anticipated changes to develop accurate estimates. Regularly review and update your projections as new information becomes available.
Assessing other liabilities and equity is crucial for accurately estimating the company’s financial obligations and equity position. It ensures a comprehensive understanding of the company’s financial health and its ability to meet its financial obligations. By carefully considering historical data, industry practices, and regulatory requirements, you can generate reliable and insightful estimates for your balance sheet forecast.
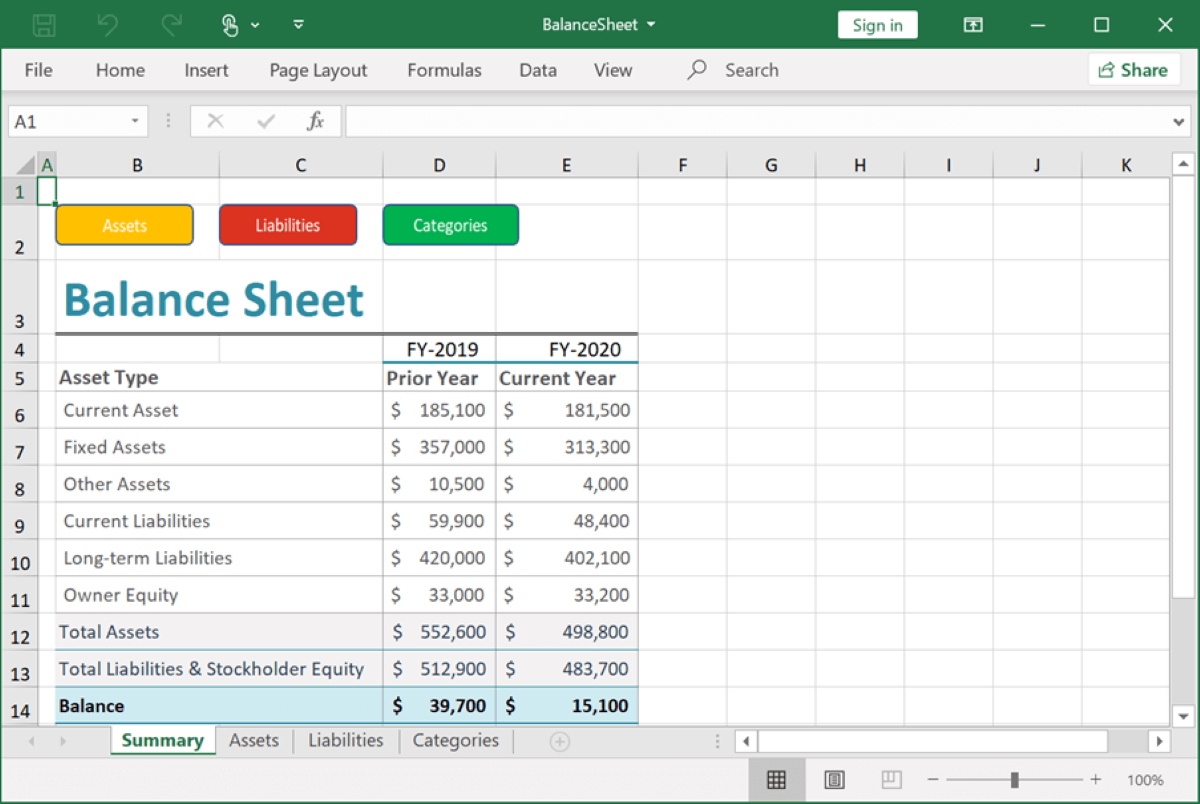
Step 12: Create Balance Sheet Projections
After completing the previous steps of gathering data, analyzing trends, estimating various components, and assessing liabilities and equity, it is time to create balance sheet projections. This final step brings together all the information and assumptions to forecast the company’s financial position accurately.
Start by utilizing the projected sales figures, accounts receivable, and inventory levels as inputs for the current assets section of the balance sheet. These components represent the cash conversion cycle and the company’s ability to convert sales into cash.
Next, incorporate the estimated accounts payable, debt levels, and interest expense into the current and long-term liabilities sections of the balance sheet. Consider the timing and magnitude of these obligations to ensure accurate representation of the company’s financing commitments.
Include the projected income taxes calculated in Step 10 as part of the tax liabilities in the current and long-term liabilities sections. Reflect any other liabilities identified in Step 11, such as accrued expenses, warranty provisions, or deferred revenues, accordingly.
For the equity section, account for any changes in equity resulting from share issuance, buybacks, dividends, or changes in fair value of financial instruments. Consider the retained earnings and accumulated losses to reflect the company’s earnings over time.
Ensure that the balance sheet balances by verifying that the total assets equal the total liabilities and equity. Make any necessary adjustments to align the figures and ensure accuracy in the balance sheet projections.
Regularly review and update the balance sheet projections as new information or changes in assumptions become available. Assess the impact of external factors such as market conditions, economic trends, or regulatory changes to refine your projections.
Creating balance sheet projections is a critical step in financial planning and decision-making. It provides a snapshot of the company’s financial health at a specific point in time and helps stakeholders understand the company’s assets, liabilities, and equity position. By incorporating all the necessary components and performing diligent analysis, you can generate reliable and informative balance sheet projections.
Conclusion
Forecasting a balance sheet is a complex yet essential task in financial planning. It allows businesses to gain insights into their financial health, anticipate funding requirements, and make informed decisions. By following the step-by-step approach outlined in this article, you can create accurate and reliable balance sheet projections.
Starting with gathering the necessary financial data, you lay the groundwork for the rest of the forecasting process. Analyzing historical trends provides insights into patterns and seasonality that can impact future financials. Identifying key assumptions helps make informed projections based on macroeconomic factors, industry trends, and internal strategies.
Estimating accounts receivable, inventory levels, and accounts payable provide visibility into the company’s working capital cycle and liquidity. Determining capital expenditures helps plan for investments in long-term assets, while projecting debt and interest expense allows for an understanding of financing commitments.
Forecasting income taxes ensures accurate estimation of tax liabilities, while assessing other liabilities and equity accounts for additional financial obligations and reflects the company’s ownership structure. Finally, by creating balance sheet projections, you bring together all the elements to paint a comprehensive picture of the company’s financial position.
Regularly review and update your projections as new information becomes available, and reassess your assumptions to adapt to changing market conditions. Remember, accuracy and reliability are essential in creating balance sheet projections that serve as valuable tools for financial planning and decision-making.
By effectively forecasting a balance sheet, you can gain a deeper understanding of your business’s financial position, make strategic financial decisions, and plan for future growth. Embrace the process, refine your forecasting skills, and leverage the power of balance sheet projections to drive your business forward.