
Finance
How To Make A Personal Balance Sheet
Published: December 27, 2023
Learn how to create a comprehensive personal balance sheet to track your finances and manage your wealth effectively. Master the art of finance with our step-by-step guide.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Managing personal finances is crucial for both short-term stability and long-term financial success. To effectively manage your finances, it is important to have a clear understanding of your assets, liabilities, and overall financial health. This is where a personal balance sheet can be extremely useful.
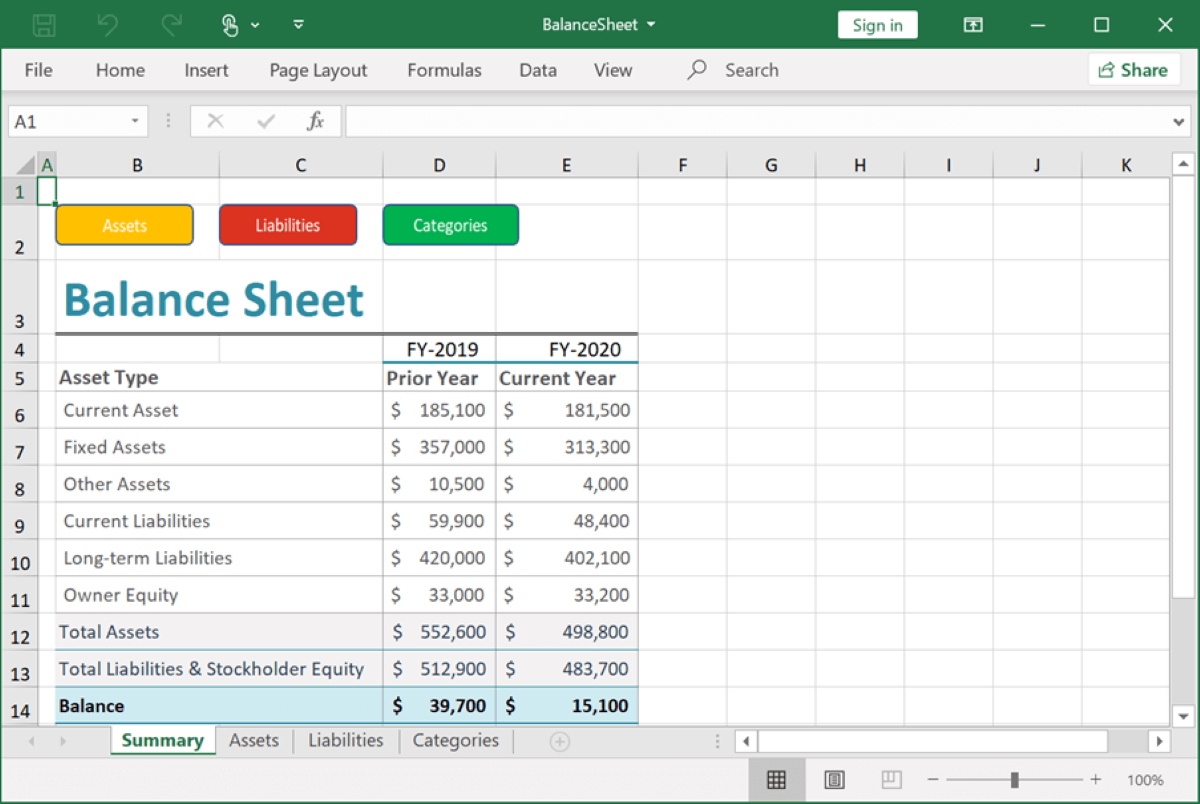
A personal balance sheet is a financial statement that provides a snapshot of an individual’s financial position at a specific point in time. It outlines all the assets, liabilities, and net worth of an individual. It is essentially a tool that helps you assess your financial strength and make informed decisions about your personal finances.
While personal balance sheets are commonly used in business and accounting, they are equally important for individuals. They can help you track your progress towards achieving financial goals, identify areas of improvement, and make better financial decisions.
In this article, we will explore the concept of a personal balance sheet in detail, its importance, and how you can create and analyze your own personal balance sheet. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of how to effectively manage your personal finances using this useful financial tool.
What is a Personal Balance Sheet?
A personal balance sheet is a financial statement that provides a summary of an individual’s financial position. It showcases the individual’s assets, liabilities, and net worth at a specific point in time. It is an essential tool for understanding your financial health and can help you make informed decisions about your personal finances.
Similar to a balance sheet used in businesses, a personal balance sheet follows the same fundamental principle of balancing assets and liabilities. It provides a snapshot of your financial situation by listing all the assets you own, such as cash, investments, real estate, vehicles, and personal possessions, as well as all your liabilities, such as credit card debt, mortgage, student loans, and other outstanding debts.
The difference between assets and liabilities is referred to as net worth or owner’s equity. Net worth represents your personal wealth and is calculated by subtracting your total liabilities from your total assets. A positive net worth indicates a financially healthy situation, while a negative net worth indicates debts outweighing assets.
A personal balance sheet helps you understand the following:
- Your current financial standing
- The total value of your assets
- The total amount of your liabilities
- Your net worth
By keeping an updated personal balance sheet, you can track changes in your financial situation over time, monitor your progress towards financial goals, and make well-informed decisions about your financial life.
It’s important to note that a personal balance sheet is not a budget or a spending plan. While a budget focuses on income, expenses, and cash flow, a balance sheet focuses on your overall financial position. Both tools complement each other and are necessary for a comprehensive financial plan.
In the next section, we will discuss the importance of maintaining a personal balance sheet and the benefits it can bring to your financial journey.
Importance of a Personal Balance Sheet
A personal balance sheet is a powerful tool that can greatly impact your financial wellbeing. Here are some key reasons why maintaining a personal balance sheet is important:
1. Financial Awareness: A personal balance sheet provides a clear snapshot of your financial situation. It helps you understand the current state of your assets, liabilities, and net worth. This awareness is essential for making informed decisions regarding your finances.
2. Goal Tracking: By regularly updating your personal balance sheet, you can track your progress towards your financial goals. It allows you to see how changes in your assets and liabilities impact your overall net worth. This visibility helps you stay on track and make necessary adjustments to achieve your financial objectives.
3. Debt Management: A personal balance sheet highlights your liabilities, including outstanding debts and obligations. By identifying and acknowledging your debts, you can develop strategies to manage and reduce them effectively. This can lead to improved financial stability and reduced financial stress over time.
4. Investment Decisions: Understanding your personal balance sheet can aid in making better investment decisions. By assessing your net worth and the distribution of your assets, you can determine if you have sufficient liquid assets for emergencies or if you’re overexposed to a single asset class. This information can guide you towards a well-diversified investment portfolio.
5. Financial Planning: A personal balance sheet is a valuable resource when creating a comprehensive financial plan. It provides a starting point for setting realistic goals, creating budgets, and establishing saving or retirement strategies. It acts as a foundation for organizing and managing your financial life.
6. Net Worth Evaluation: Your net worth is a key metric that reflects your overall financial health. Tracking your net worth over time helps you evaluate your progress, make adjustments, and assess your financial trajectory. It allows you to celebrate milestones and identify areas for improvement.
7. Financial Accountability: A personal balance sheet encourages financial accountability. By regularly updating and reviewing your financial position, you become more aware of your spending habits, debt management, and overall financial progress. This accountability can lead to better financial decision-making and ultimately more control over your financial future.
By understanding the importance of a personal balance sheet and utilizing it as a financial management tool, you can gain clarity, take control of your finances, and work towards a more secure and prosperous financial future.
Gathering Financial Information
Before you can create a personal balance sheet, it is important to gather all the necessary financial information. This includes collecting details about your assets, liabilities, and other relevant financial data. Here are the key steps to gather the required information:
1. Compile a List of Assets: Begin by making a comprehensive list of all your assets. This includes cash in bank accounts, investments such as stocks and bonds, retirement accounts, real estate properties, vehicles, valuable personal possessions like jewelry or artwork, and any other significant assets you own.
2. Determine the Value of Assets: Assign a monetary value to each asset on your list. For cash and bank accounts, use the current balance. For investments, use the market value. For real estate properties, you can use appraisals or recent sales prices of similar properties. For vehicles and personal possessions, estimate their fair market value.
3. Identify Your Liabilities: Next, identify and list all your liabilities. This includes mortgage loans, car loans, student loans, credit card debt, personal loans, and any other outstanding debts or financial obligations.
4. Determine the Outstanding Balance: For each liability, determine the outstanding balance or the amount you still owe. This can be obtained by reviewing loan statements or contacting your lenders. Make sure to include any accrued interest or fees as well.
5. Include Other Financial Information: In addition to assets and liabilities, gather other financial information that may be relevant to your personal balance sheet. This can include your income, expenses, and any significant financial transactions that occurred during the reporting period.
6. Organize and Update Regularly: It is important to organize your financial information and update it regularly. Keep track of your assets, liabilities, and financial records in a dedicated system or spreadsheet. This will ensure that your personal balance sheet remains accurate and up-to-date.
Gathering your financial information can be time-consuming, but it is a critical step in creating an accurate and informative personal balance sheet. By having a complete picture of your financial situation, you can gain valuable insights into your financial health and make more informed decisions about your finances.
Assets
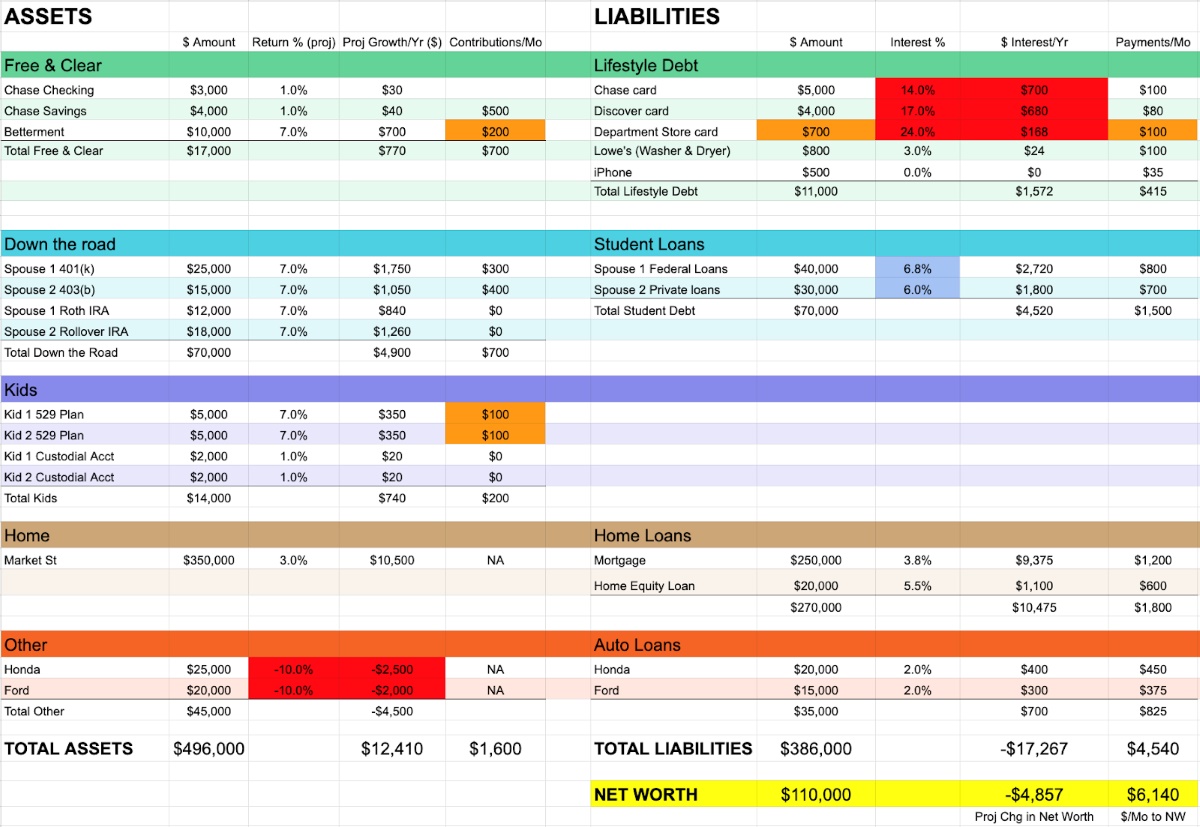
When creating a personal balance sheet, it is important to accurately identify and list your assets. Assets are the things you own that have a monetary value. They can be categorized into different types, each representing a different aspect of your financial worth. Here are the common types of assets you should consider:
1. Cash and Bank Accounts: This includes any cash you have on hand and the balances in your checking, savings, and money market accounts. These liquid assets are readily available for immediate use.
2. Investments: Investments refer to assets that can generate income or appreciate in value. They can include stocks, bonds, mutual funds, certificates of deposit (CDs), real estate investment trusts (REITs), and other securities or investment vehicles.
3. Retirement Accounts: This category includes any retirement savings you have, such as contributions to a 401(k), Individual Retirement Account (IRA), or a pension plan. These accounts are designed to provide you with income during your retirement years.
4. Real Estate: Real estate assets include properties you own, such as your primary residence, vacation homes, rental properties, or land. The value of real estate can fluctuate over time and may impact your net worth.
5. Vehicles: Include the market value of any vehicles you own, such as cars, motorcycles, boats, or recreational vehicles. It is important to use the fair market value when determining the worth of your vehicles.
6. Personal Possessions: Personal possessions include valuable items you own, such as jewelry, artwork, antiques, collectibles, and any other items with significant monetary worth.
7. Other Assets: Other assets may include business interests, valuable intellectual property, royalties, or any other assets that hold financial value for you.
It is important to assign a realistic monetary value to each asset when calculating your net worth. Consider current market conditions, appraisals, or expert evaluations to determine the fair value of your assets. Regularly update the values to reflect any changes that occur over time.
Remember, assets represent the resources you have available. By accurately identifying and listing your assets, you can better understand your financial position and assess your overall wealth. This information will be crucial when analyzing your personal balance sheet and making informed financial decisions.
Liabilities
When creating a personal balance sheet, it is important to identify and list your liabilities. Liabilities are the debts or financial obligations that you owe to others. They represent the amounts you owe and can provide insights into your financial obligations. Here are the common types of liabilities you should consider:
1. Mortgage Loans: If you have a mortgage on your primary residence or any other properties you own, include the outstanding balance. This is the amount you still owe on your mortgage loan.
2. Car Loans: If you have a loan for a vehicle, whether it’s a car, motorcycle, or any other vehicle, include the remaining balance of the loan.
3. Student Loans: Include the outstanding balance of any student loans that you have, whether they are federal loans, private loans, or both.
4. Credit Card Debt: List the total amount of credit card debt you owe. Include the balances on all your credit cards, including any accrued interest or fees.
5. Personal Loans: If you have taken out any personal loans from financial institutions or individuals, include the outstanding amount of those loans.
6. Other Debts: This category includes any other outstanding debts or financial obligations you may have, such as medical bills, tax debts, outstanding utility bills, or any other debts that need to be repaid.
It is important to note that liabilities represent your financial obligations and not all debt is necessarily bad. Responsible debt, such as a reasonable mortgage or student loans, can be considered an investment in your future. However, it is crucial to carefully manage your liabilities and ensure they remain within your means.
When updating your personal balance sheet, be sure to include the accurate outstanding balances of your liabilities. Regularly review this information and make efforts to pay down debts and reduce your financial obligations over time.
By accurately identifying and listing your liabilities, you can assess your overall financial obligations and understand how they impact your financial health. This information is essential for analyzing your personal balance sheet and making informed decisions to improve your financial well-being.
Net Worth
Net worth is a key metric derived from your personal balance sheet and represents your overall financial position. Calculating your net worth involves subtracting your total liabilities from your total assets. The resulting figure provides a snapshot of your wealth and can be a useful gauge of your financial health. Here’s how to calculate and interpret your net worth:
Calculating Net Worth: To calculate your net worth, add up the total value of all your assets from your personal balance sheet. Next, add up the total amount of your liabilities. Finally, subtract the total liabilities from your total assets to determine your net worth.
Interpreting Net Worth: A positive net worth indicates that your assets outweigh your liabilities. It suggests that you have built wealth over time and have financial resources to rely on. A negative net worth, on the other hand, indicates that your liabilities exceed your assets and suggests that you have more debt than assets.
While net worth is an important metric, it’s essential to interpret it in context. Factors such as age, income level, and financial goals can influence what is considered a “healthy” net worth. Additionally, your net worth can fluctuate over time due to changes in asset values, debt repayment, and other financial factors.
Monitoring your net worth over time can provide valuable insights into your financial progress. If your net worth is consistently increasing, it indicates positive wealth accumulation. If it is stagnant or decreasing, it may highlight the need to review your financial strategies and make necessary adjustments.
It’s important to note that while net worth is a significant indicator of financial health, it doesn’t paint the complete picture. Other factors such as cash flow, income stability, and debt management also play a role in overall financial well-being. Therefore, it’s crucial to consider net worth alongside other financial metrics to gain a holistic understanding of your financial situation.
Regularly calculating and tracking your net worth can help you set goals, evaluate progress, and make informed decisions about your finances. By understanding your net worth, you can work towards growing your wealth, reducing debt, and achieving long-term financial stability.
Analyzing Your Personal Balance Sheet
Once you have created your personal balance sheet by listing your assets, liabilities, and calculating your net worth, it’s time to analyze the information and gain insights into your financial situation. Here are some key aspects to consider when analyzing your personal balance sheet:
1. Assessing Financial Health: Start by evaluating your net worth. A positive net worth indicates that your assets outweigh your liabilities, which is a good sign of financial health. If your net worth is negative or lower than expected, it may indicate the need to focus on debt reduction or increasing your asset base.
2. Reviewing Asset Distribution: Examine the distribution of your assets across different categories. This analysis helps you ensure that your investments and holdings are appropriately diversified. It can also reveal areas where you may be overexposed or lacking in certain asset classes.
3. Evaluating Liabilities: Take a close look at your liabilities to understand the impact on your financial situation. Are there high-interest debts that need to be prioritized for repayment? Can you take steps to reduce your overall debt burden? This evaluation helps you identify opportunities to lower interest costs and improve cash flow.
4. Tracking Changes Over Time: Compare your current personal balance sheet with previous statements to monitor your progress. Look for positive changes in your net worth, asset values, and debt reduction. This analysis helps you gauge the effectiveness of your financial strategies and determine areas that require improvement.
5. Setting Financial Goals: Use your personal balance sheet to set realistic financial goals. Whether it’s increasing your net worth, paying off specific debts, or saving for a major purchase, having clear objectives helps guide your financial decisions and create a roadmap for achieving your desired outcomes.
6. Seeking Professional Advice: If analyzing your personal balance sheet feels overwhelming or if you have complex financial situations, consider consulting a financial advisor. They can provide valuable insights and help you develop strategies to optimize your financial position.
Remember, the purpose of analyzing your personal balance sheet is to gain a comprehensive understanding of your financial health and identify areas for improvement. Regular review and analysis of your personal balance sheet will help you make informed decisions, set financial goals, and work towards a more secure financial future.
Tips for Creating and Maintaining a Personal Balance Sheet
Creating and maintaining a personal balance sheet is a valuable practice in managing your personal finances. Here are some useful tips to consider when creating and maintaining your personal balance sheet:
1. Be diligent and consistent: Set a regular schedule, such as monthly or quarterly, to review and update your personal balance sheet. Regular maintenance will ensure that your financial information remains accurate and up-to-date.
2. Keep organized records: Maintain a system to organize your financial documents and records. Store important statements, receipts, and financial documents in a secure and easily accessible location. This will make it easier to gather the necessary information when updating your personal balance sheet.
3. Use online tools or spreadsheets: Utilize online personal finance tools or spreadsheets to simplify the process of creating and tracking your personal balance sheet. These tools can automatically calculate your net worth and generate reports, making it easier to analyze your financial position.
4. Include all relevant assets and liabilities: Make sure to account for all your assets, including cash, investments, real estate, vehicles, and personal possessions. Similarly, list all your liabilities, such as mortgage loans, student loans, credit card debts, and other outstanding loans or financial obligations. Leaving out any assets or liabilities can result in an incomplete and inaccurate representation of your financial health.
5. Regularly update asset values: Update the values of your assets based on current market conditions or appraisals. This will ensure that your balance sheet reflects the most accurate representation of your net worth.
6. Track changes in liabilities: Regularly review your liabilities and track changes in outstanding balances and interest rates. This information will help you understand the progress you are making in paying off debts and allow you to evaluate opportunities for refinancing or consolidating high-interest debts.
7. Compare against financial goals: Use your personal balance sheet to compare your current financial situation against your financial goals. Assess if you are on track to achieve those goals or if adjustments need to be made in your financial strategies.
8. Seek professional guidance: If you find the process challenging or if you need assistance in analyzing your personal balance sheet, consider consulting a financial advisor. They can provide valuable insights, offer personalized advice, and help you optimize your financial health.
Creating and maintaining a personal balance sheet is a proactive step towards managing your personal finances effectively. By implementing these tips, you can stay organized, gain a better understanding of your financial position, and make informed decisions to achieve your financial goals.
Conclusion
A personal balance sheet is a powerful tool that provides a comprehensive overview of your financial position. By listing your assets, liabilities, and calculating your net worth, you gain valuable insights into your financial health and can make informed decisions about your personal finances.
Creating and maintaining a personal balance sheet allows you to track your progress towards financial goals, evaluate your financial health, and identify areas for improvement. By regularly updating your balance sheet and analyzing the data, you can take control of your finances and work towards a more secure and prosperous financial future.
Remember to be diligent, consistent, and organized when creating and maintaining your personal balance sheet. Use online tools or spreadsheets to simplify the process and ensure accuracy. Include all relevant assets and liabilities, regularly update values, and track changes in liabilities over time.
By comparing your personal balance sheet against your financial goals, you can set realistic objectives and make the necessary adjustments to achieve them. Seek professional advice if needed, as financial advisors can provide valuable insights and recommendations tailored to your specific situation.
Overall, a personal balance sheet serves as a compass in navigating your financial journey. It helps you gain clarity, make informed decisions, and stay on track towards achieving your financial goals. Take the time to create and maintain your personal balance sheet, and reap the rewards of improved financial understanding and control.