
Finance
How To Roll Futures Contracts On TradeStation?
Published: December 24, 2023
Learn how to roll futures contracts on TradeStation to optimize your finance strategy. Enhance your trading skills with our comprehensive guide.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Futures Contracts
- Why Roll Futures Contracts?
- Preparing to Roll Futures Contracts on TradeStation
- Step 1: Analyzing Contract Data
- Step 2: Evaluating Roll Date
- Step 3: Identifying New Contract Month
- Step 4: Calculating Roll Yield
- Step 5: Placing the Roll Trade on TradeStation
- Conclusion
Introduction
In the world of finance, futures contracts offer a unique opportunity for investors to participate in the movement of various underlying assets, such as commodities, currencies, or stock indices. These contracts enable traders to speculate on price movements and hedge against potential risks.
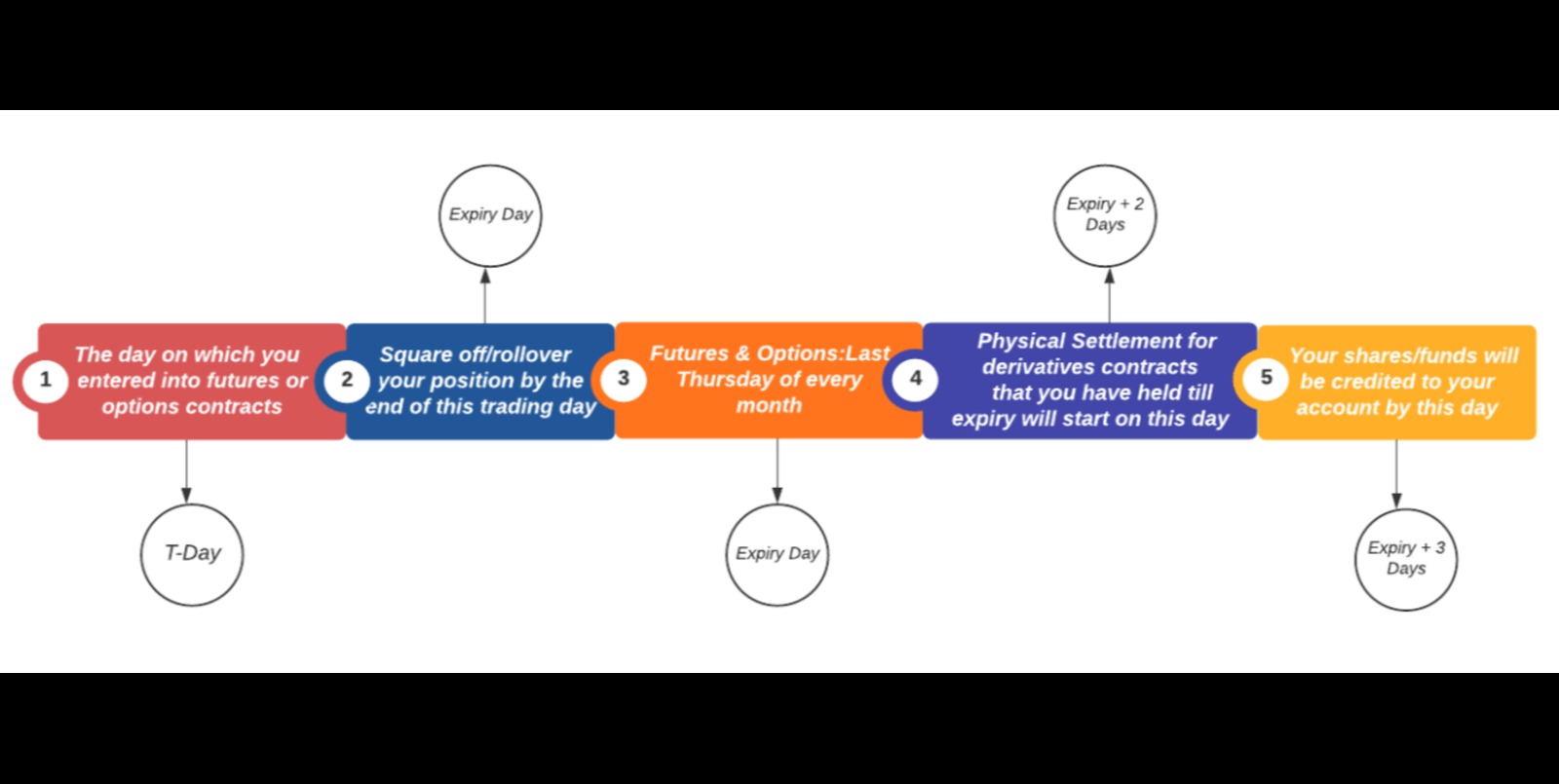
As a futures contract approaches its expiration date, traders need to roll over their positions to a new contract to ensure a smooth transition and continue their exposure to the underlying asset. This process, known as rolling futures contracts, involves closing the existing position and opening a new one with a longer expiration date.
TradeStation, a leading online brokerage platform, provides a seamless and efficient way for traders to roll their futures contracts. With its intuitive interface and advanced tools, TradeStation simplifies the process, allowing traders to manage their positions effectively.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of rolling futures contracts on TradeStation. We will explore the importance of rolling contracts, the steps to prepare for the roll, and how to execute the trade on the TradeStation platform.
Whether you are an experienced trader looking to enhance your trading strategies or a novice exploring the fascinating world of futures trading, understanding how to roll futures contracts on TradeStation is vital for effectively managing your positions and optimizing your investment returns.
Understanding Futures Contracts
Futures contracts are financial derivatives that enable traders to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price on a specific future date. These contracts are standardized agreements traded on regulated exchanges, such as the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) or the New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX).
Unlike options contracts, which provide the right but not the obligation to buy or sell an asset, futures contracts require both parties to fulfill the contract at the agreed-upon price and date. They are commonly used for hedging purposes by businesses that want to mitigate the risk of price fluctuations in commodities they rely on, such as oil, wheat, or gold.
Each futures contract specifies the quantity and quality of the underlying asset, the delivery month, and the settlement price. For example, in the case of crude oil futures, one contract typically represents 1,000 barrels of oil, with delivery dates occurring in specific months throughout the year.
Futures contracts are categorized into two types: long and short positions. A long position is initiated by a trader who believes the price of the underlying asset will rise, while a short position is taken by a trader who anticipates a decline in price.
Traders can profit from futures contracts by accurately predicting price movements. If the price of the asset increases, the trader who is long on the contract will gain, while the trader who is short will experience a loss. Conversely, if the price decreases, the short trader profits and the long trader suffers a loss.
It’s important to note that most futures contracts are not intended for physical delivery. Instead, traders typically close out their positions prior to expiration by executing an opposing trade. This allows them to realize their profits or losses and avoid the complexities involved in taking delivery of the physical asset.
Now that we have a basic understanding of futures contracts, let’s explore why rolling futures contracts is crucial for traders and investors.
Why Roll Futures Contracts?
Rolling futures contracts is an essential practice for traders and investors who hold positions in expiring contracts. Rather than allowing the contract to expire and facing potential disruptions or forced liquidation, rolling contracts allows for a seamless transition to a new contract with a later expiration date.
There are several key reasons why rolling futures contracts is important:
1. Continuity of Exposure: By rolling contracts, traders can maintain their exposure to the underlying asset. This is especially crucial for long-term investors who want to keep their investment intact without interruptions. Rolling contracts ensure that traders can capture the continued price movement of the asset without having to close out their positions.
2. Avoiding Forced Liquidation: When a futures contract nears expiration, the trader must either settle or sell the contract. If the trader fails to do so, they may face forced liquidation by the exchange. By actively rolling contracts, traders can avoid the hassle and potential losses associated with forced liquidation, maintaining control over their positions and strategies.
3. Managing Cost and Efficiency: Rolling contracts allows traders to manage the costs and efficiency of their trading strategies. By transitioning to a new contract, traders can adjust their position size, take advantage of changes in market conditions, and potentially reduce transaction costs. This flexibility and control contribute to more effective trading strategies and improved overall performance.
4. Managing Market Structure Changes: Over time, market dynamics and trading conditions can change. Rolling futures contracts allows traders to adapt to these changes and stay current with the most liquid and actively traded contracts. This is particularly important for traders who rely on market depth and liquidity to execute their trading strategies effectively.
5. Handling Expiration-Related Challenges: As a futures contract approaches expiration, it may experience reduced liquidity and increased volatility. Rolling contracts allows traders to avoid these challenges and take advantage of smoother trading conditions in the new contract. By transitioning to a longer-dated contract, traders can mitigate potential risks associated with the expiration process.
Overall, rolling futures contracts is crucial for maintaining continuity, managing costs and efficiency, adapting to market changes, and avoiding expiration-related challenges. TradeStation provides a user-friendly platform that streamlines the process of rolling contracts, empowering traders to effectively manage their positions and optimize their trading strategies.
Preparing to Roll Futures Contracts on TradeStation
Before rolling futures contracts on TradeStation, it is important to thoroughly prepare and analyze key factors to ensure a smooth and successful transition. Here are some steps to take when preparing to roll futures contracts:
1. Analyzing Contract Data: Begin by reviewing the contract specifications and important details of the expiring contract. This includes the contract symbol, expiration date, contract size, tick size, and margin requirements. Make sure to gather all the necessary information to accurately identify the expiring contract and its corresponding new contract.
2. Evaluating Roll Date: Determine the appropriate roll date based on the liquidity and trading volume of the current and new contracts. Ideally, the roll should be executed when there is sufficient liquidity in both contracts to ensure smooth order execution. TradeStation provides real-time market data and advanced tools to help traders identify the optimal roll date.
3. Identifying New Contract Month: Once the roll date is established, identify the new contract month that aligns with your trading strategy and objectives. Consider factors such as the liquidity of the new contract and its pricing dynamics. Traders may choose to roll to the next month or select a further future expiration based on their trading preferences.
4. Calculating Roll Yield: Roll yield refers to the potential gain or loss incurred during the process of rolling futures contracts. It is influenced by the price difference between the expiring contract and the new contract. Traders should carefully calculate the roll yield to assess the impact on their positions and decide whether rolling is advantageous or not. TradeStation provides pricing information and tools to assist with roll yield calculations.
5. Placing the Roll Trade on TradeStation: Once all the necessary analysis and preparations are complete, it’s time to execute the roll trade on TradeStation. Traders can use the platform’s order entry tools to initiate the trade and seamlessly transition from the expiring contract to the new contract. Ensure that you enter the correct quantity and contract specifications to avoid any unintended errors.
By following these steps and leveraging the features and tools offered by TradeStation, traders can effectively prepare for rolling futures contracts. This enables them to smoothly transition their positions, adapt to changing market dynamics, and maintain control over their trading strategies. TradeStation’s user-friendly platform and comprehensive market data make the process efficient and accessible for traders of all experience levels.
Step 1: Analyzing Contract Data
When preparing to roll futures contracts on TradeStation, it is crucial to start by thoroughly analyzing the contract data of the expiring contract. This analysis will help you identify the key details necessary for a successful roll. Here are the important factors to consider during this step:
Contract Specifications: Begin by reviewing the contract specifications of the expiring contract. This includes information such as the contract symbol, expiration date, contract size, tick size, and margin requirements. Understanding these specifications is essential for accurately identifying and trading the correct contracts on TradeStation.
Expiration Date: Take note of the expiration date of the current contract. This information is crucial as it helps determine the appropriate timing for the roll. Traders typically aim to initiate the roll a few days before the expiration date to ensure a smooth transition to the new contract. By being aware of the expiration date, you can plan and execute your roll strategy accordingly.
Volume and Open Interest: Examine the volume and open interest of the expiring contract. Volume refers to the total number of contracts traded during a specific period, while open interest represents the total number of outstanding contracts. Analyzing volume and open interest provides valuable insights into the liquidity and popularity of the contract. Higher liquidity often results in better order execution and tighter bid-ask spreads.
Price Dynamics: Evaluate the price dynamics of the expiring contract in relation to the underlying asset. Observe the price movements and fluctuations, as well as any patterns or trends that may be present. Understanding the historical price behavior can help you determine the optimal roll date and evaluate the potential impact on your positions when transitioning to the new contract.
Market Depth: Assess the market depth of the expiring contract, which refers to the quantity of buy and sell orders at different price levels. Deep market depth indicates high liquidity and the ability to easily enter and exit trades with minimal slippage. It is important to consider market depth when deciding the appropriate time to roll the contract.
TradeStation Tools: Utilize the various tools and features provided by TradeStation to analyze contract data effectively. TradeStation offers real-time market data, customizable charts, and technical indicators that can assist in analyzing volume, open interest, price movements, and market depth. These tools can enhance your decision-making process and help you make informed choices when rolling futures contracts.
Taking the time to analyze the contract data of the expiring contract is a crucial first step in preparing to roll futures contracts on TradeStation. By understanding the contract specifications, expiration date, volume and open interest, price dynamics, and market depth, you can make informed decisions and set yourself up for a smooth and successful roll to the new contract.
Step 2: Evaluating Roll Date
When rolling futures contracts on TradeStation, the timing of the roll is critical. Evaluating the roll date is an important step in the preparation process, as it determines when you should transition from the expiring contract to the new contract. Consider the following factors when evaluating the roll date:
Liquidity: Assess the liquidity of both the expiring and new contracts. Liquidity refers to the ease with which a contract can be bought or sold without significantly impacting its price. A higher liquidity ensures smoother order execution and tighter bid-ask spreads. Choose a roll date when there is sufficient liquidity in both contracts, allowing for a seamless transition without potential disruptions.
Trading Volume: Analyze the trading volume of the expiring and new contracts. Volume indicates the number of contracts traded during a specific period. Higher trading volume suggests greater market participation and increased liquidity. Look for a roll date when both contracts have adequate trading volume to ensure efficient order execution and minimize potential slippage.
Market Impact: Consider the potential market impact of rolling futures contracts. When a large number of traders roll their positions, it can lead to increased price volatility and trading activity. Monitor the market closely and choose a roll date when you anticipate minimal market impact to avoid unfavorable price movements during the roll.
Contract Transition: Evaluate the transition process between the expiring and new contracts. Some contracts have a specified roll date, while others require a manual selection. Identify the specific guidelines provided by TradeStation for rolling contracts and ensure you understand the process. Plan ahead to avoid any confusion or challenges when transitioning from the expiring to the new contract.
News and Market Events: Take into account any upcoming news releases or significant market events that could potentially impact the price of the contract or the underlying asset. News events can lead to increased volatility and unpredictable market conditions. Evaluate the current market environment and consider whether it is favorable to roll contracts during periods of potential market turbulence.
TradeStation Analytics: Leverage the analytical tools provided by TradeStation to evaluate the ideal roll date. The platform offers real-time market data, historical charts, and technical indicators that can help you assess liquidity, volume, and market trends. Utilize these tools to identify optimal roll dates based on your specific trading strategy and objectives.
By carefully evaluating the roll date, taking into account factors such as liquidity, trading volume, market impact, contract transition process, news and market events, and TradeStation analytics, you can make an informed decision on when to roll futures contracts. Selecting the right roll date plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth transition and mitigating potential risks during the roll process.
Step 3: Identifying New Contract Month
After analyzing the contract data and evaluating the roll date, the next step in rolling futures contracts on TradeStation is to identify the new contract month. When the expiration date of the current contract approaches, traders need to transition their positions to a longer-dated contract to maintain exposure to the underlying asset. Here’s how you can identify the new contract month:
1. Expiration of Current Contract: Determine the expiration date of the current contract. This information is crucial as it helps identify the timeframe within which you need to roll to the new contract. Take note of the specific date to ensure you select a suitable new contract month.
2. Available Contract Months: Check the available contract months for the underlying asset you are trading. Different futures contracts have varying monthly expirations. For example, some contracts may have monthly expirations, while others may have quarterly expirations. Identify the available contract months to choose the one that aligns with your trading strategy.
3. Liquidity of the New Contract: Evaluate the liquidity of the new contract month. Liquidity ensures that there are enough buyers and sellers in the market, allowing for efficient order execution and tight bid-ask spreads. Choose a new contract that offers sufficient liquidity to ensure smooth trading and minimize slippage.
4. Rollover Volume: Consider the volume and open interest in the new contract month. Rollover volume refers to the total number of contracts being rolled from the expiring contract to the new contract. Higher rollover volume suggests increased market participation and can indicate a smoother transition. Look for a new contract month with significant rollover volume to ensure a seamless shift in positions.
5. Price Spread: Examine the price spread between the current contract and the new contract month. Price spread refers to the price difference between the two contracts. A narrower price spread indicates a smoother transition, while a wider spread may result in potential profit or loss due to the price difference. Consider the price spread and evaluate its impact on your trading strategy before selecting the new contract month.
6. Trading Objectives: Align the new contract month with your trading objectives and strategy. Consider factors such as the duration of your desired position, market conditions, and trading goals. For example, if you are a long-term investor, selecting a new contract with a later expiration date may be more suitable. If you prefer shorter-term trading, a closer expiration date may be preferred.
7. Research and Analysis: Conduct thorough research and analysis on the new contract month. Review historical price movements, market trends, and any relevant news or events that may affect the new contract. This information will help you gain insights into the potential performance of the new contract and make an informed decision.
By following these steps and considering factors such as the expiration date, available contract months, liquidity, rollover volume, price spread, trading objectives, and conducting thorough research and analysis, you can successfully identify the new contract month during the process of rolling futures contracts on TradeStation. Choosing the right new contract is essential for maintaining continuous exposure to the underlying asset and aligning your trading strategy with market dynamics.
Step 4: Calculating Roll Yield
Calculating the roll yield is a crucial step in the process of rolling futures contracts on TradeStation. Roll yield refers to the potential gain or loss incurred during the transition from the expiring contract to the new contract. It is influenced by the price difference between the two contracts. To calculate the roll yield, follow these steps:
1. Determine Contract Price Differential: Calculate the difference in prices between the expiring contract and the new contract. This can be done by comparing the prices of both contracts at the time of the roll. The price differential represents the potential gain or loss that may occur during the transition.
2. Consider Transaction Costs: Take into account any transaction costs associated with rolling futures contracts. These costs may include exchange fees, brokerage fees, or other expenses involved in executing the roll trade. Subtract these costs from the potential gain or add them to the potential loss to obtain a more accurate calculation of the roll yield.
3. Evaluate Carry Costs: Carry costs refer to the costs of holding a position in the new contract over time. These costs can include interest charges or storage costs, depending on the underlying asset. Assess the carry costs associated with the new contract and factor them into the calculation of the roll yield. Subtract these costs from the potential gain or add them to the potential loss.
4. Analyze Market Conditions: Consider the prevailing market conditions and the impact they may have on the roll yield calculation. Volatile markets can lead to wider price differentials and higher transaction costs, potentially affecting the roll yield. Take fluctuations in supply and demand, political events, or economic factors into account when assessing the potential gain or loss during the roll.
5. Evaluate Impact on Trading Strategy: Analyze the calculated roll yield in relation to your overall trading strategy and objectives. Determine whether the roll yield is favorable or unfavorable, and assess how it aligns with your intended trading outcomes. This evaluation will help you make informed decisions when executing the roll trade.
6. Utilize TradeStation Analysis Tools: Leverage the analysis tools provided by TradeStation to aid in calculating the roll yield. TradeStation offers real-time market data, historical charts, and technical indicators that can assist with pricing analysis and cost assessment. These tools can enhance the accuracy of your calculations and provide valuable insights into the potential roll yield.
By following these steps and considering factors such as the contract price differential, transaction costs, carry costs, market conditions, and trading strategy impact, you can effectively calculate the roll yield. This calculation allows you to assess the potential gain or loss involved in transitioning from the expiring contract to the new contract, aiding in your decision-making process when rolling futures contracts on TradeStation.
Step 5: Placing the Roll Trade on TradeStation
After analyzing the contract data, evaluating the roll date, identifying the new contract month, and calculating the roll yield, the next step in rolling futures contracts on TradeStation is to place the roll trade. TradeStation provides a user-friendly platform that simplifies the process of executing the roll trade. Here’s how to place the roll trade on TradeStation:
1. Log into your TradeStation account: Access the TradeStation platform using your username and password. Ensure that you have access to real-time market data and trading functionalities before proceeding with the roll trade.
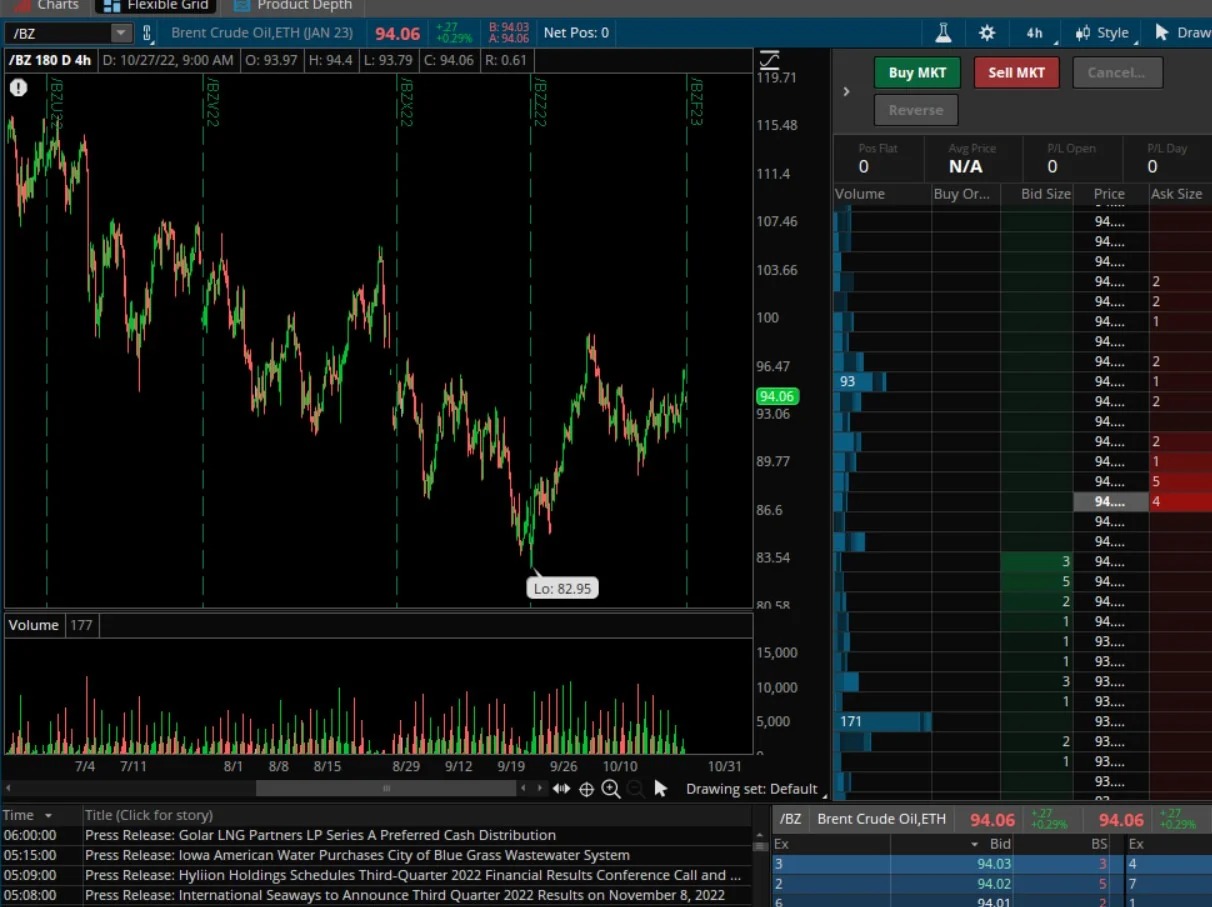
2. Navigate to the Order Entry window: Locate the Order Entry window on the TradeStation platform. This window allows you to input the necessary details to execute the roll trade.
3. Select the current contract: In the Order Entry window, choose the current contract that you want to roll from. Input the contract symbol or select it from the available options provided by TradeStation.
4. Specify the new contract: Input the details of the new contract that you want to roll into. This includes the contract symbol, expiration month, and any other required specifications. Ensure that you select the correct contract to roll into, as specified during the analysis phase.
5. Enter the position size: Specify the position size for the roll trade. Determine the quantity or number of contracts you want to roll from the current contract to the new contract. Double-check the position size to avoid any unintended errors.
6. Choose the order type: Select the appropriate order type for the roll trade. This can be a market order, limit order, or other available order types. Consider factors such as order execution speed, price limit, and market conditions when choosing the order type.
7. Set any stop-loss or take-profit levels: If desired, set stop-loss or take-profit levels for the roll trade. These levels help manage risk and protect your position in case of adverse price movements. Specify the desired levels based on your risk tolerance and trading strategy.
8. Review and confirm the order: Review all the details of the roll trade, including the current contract, new contract, position size, order type, and any specified stop-loss or take-profit levels. Double-check that all the information is correct before confirming the order.
9. Execute the roll trade: Once you are satisfied with the details, confirm the order to execute the roll trade. TradeStation will process your order and transition your position from the current contract to the new contract. Monitor the execution process and verify that the trade has been executed successfully.
10. Monitor and manage your position: After executing the roll trade, monitor your new position in the new contract on TradeStation. Keep track of market conditions, price movements, and any relevant news or events that may affect your trading strategy. Make adjustments as necessary to optimize your position and manage risk effectively.
By following these steps and leveraging the intuitive platform provided by TradeStation, you can easily place the roll trade and transition your futures contract positions from the expiring contract to the new contract. Ensure that you are familiar with executing trades on TradeStation and double-check all details before confirming the order to mitigate any potential errors.
Conclusion
Rolling futures contracts on TradeStation is an essential process for traders and investors to maintain continuous exposure to the underlying asset. By understanding the contract data, evaluating the roll date, identifying the new contract month, calculating the roll yield, and placing the roll trade, traders can effectively manage their positions and optimize their trading strategies.
TradeStation provides a user-friendly platform that streamlines the process of rolling futures contracts. With access to real-time market data, advanced analytics tools, and intuitive order entry functionalities, TradeStation empowers traders to make informed decisions and execute the roll trade seamlessly.
Understanding the importance of rolling futures contracts is crucial for traders. It ensures continuity of exposure, helps avoid forced liquidation, manages costs and efficiencies, adapts to market structure changes, and handles expiration-related challenges. By actively rolling contracts, traders can maintain control over their positions and adapt to market dynamics.
Throughout the rolling process, it is important to analyze contract data, evaluate the roll date, identify the new contract month, calculate the roll yield, and consider market conditions and trading objectives. Thorough preparation and research enable traders to make educated decisions about the optimal time to roll contracts.
When executing the roll trade on TradeStation, traders should log into their accounts, navigate to the Order Entry window, select the current and new contracts, specify the position size, choose the appropriate order type, set stop-loss or take-profit levels if desired, review and confirm the order, and monitor and manage the new position accordingly.
In conclusion, TradeStation offers a seamless and efficient platform for rolling futures contracts. By following the steps and utilizing the tools provided, traders can successfully navigate the roll process and adapt their positions to suit their specific trading needs. Rolling futures contracts on TradeStation empowers traders to optimize their strategies, manage risk, and make the most of opportunities in the ever-evolving futures market.