Finance
Return On Retained Earnings (RORE) Definition
Published: January 20, 2024
Learn about the definition of Return on Retained Earnings (RORE) in finance and how it impacts financial performance. Explore its importance for business growth and profitability.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
The Importance of Return on Retained Earnings (RORE) in Finance
When it comes to managing your personal or business finances, one metric you should be familiar with is Return on Retained Earnings (RORE). But what exactly is RORE and why is it important? In this blog post, we will delve into the definition of RORE and its significance in the world of finance.
Key Takeaways:
- Return on Retained Earnings (RORE) measures the efficiency of a company in generating profits from its reinvested earnings.
- RORE is an important metric for investors and shareholders to evaluate the profitability and growth potential of a company.
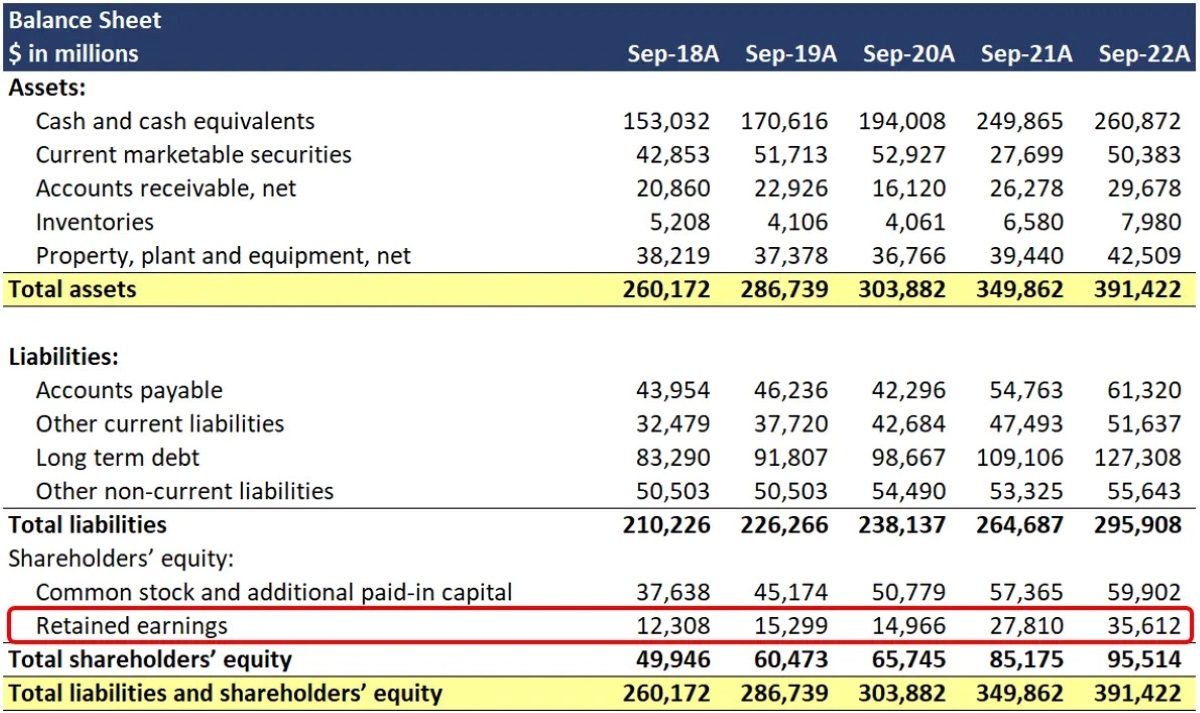
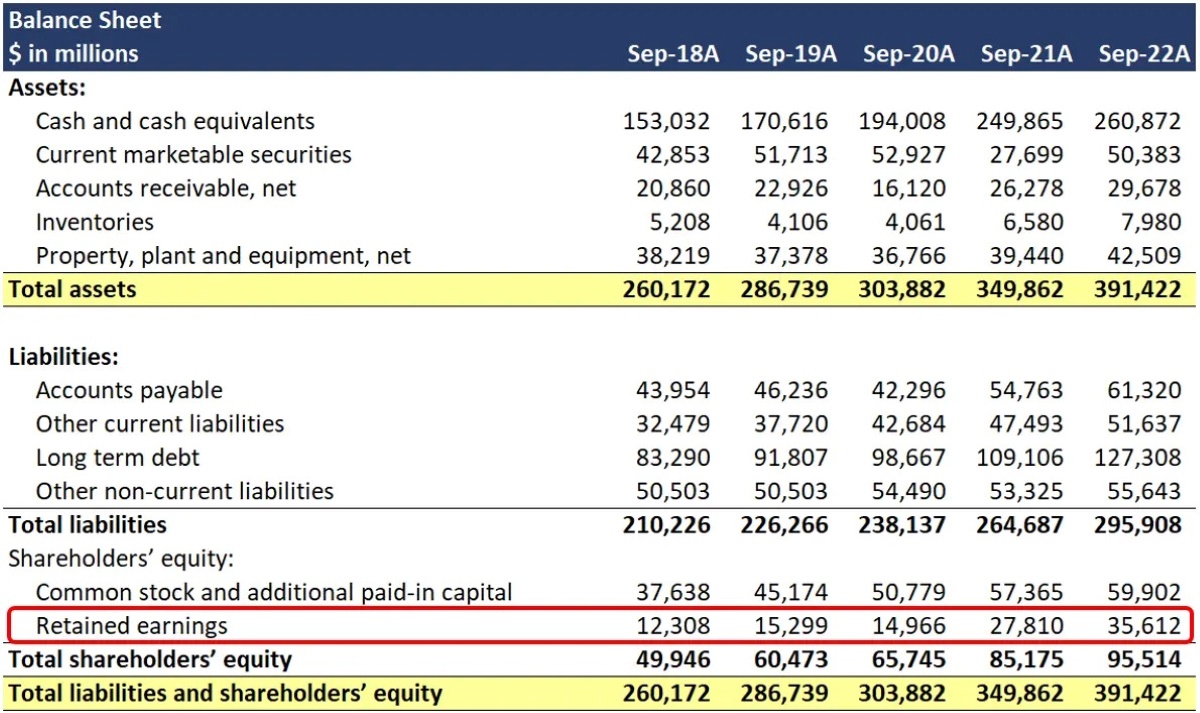
Return on Retained Earnings (RORE) is a financial ratio that assesses the profitability and effectiveness of reinvesting earnings within a company. It is calculated by dividing the net income earned from retained earnings by the average retained earnings over a specific period.
Why is RORE so important, you might ask?
Well, RORE provides valuable insights into how well a company is utilizing its retained earnings to generate additional profits. It helps investors and shareholders determine if the company is using its resources wisely and creating value. Additionally, a high RORE indicates that the company is effectively reinvesting its profits for future growth, making it an attractive investment option.
Here are a few key takeaways when considering RORE:
- RORE is a measure of profitability: By analyzing the RORE of a company, investors can evaluate its ability to generate profits from its retained earnings.
- RORE reflects growth potential: A higher RORE suggests that the company is reinvesting its earnings wisely, which can lead to future growth.
- Comparing RORE across companies: RORE allows investors to compare the financial performance and efficiency of different companies within the same industry.
Overall, understanding and monitoring RORE is crucial for effective financial management. It provides a clear picture of how well a company is utilizing its retained earnings and its potential for growth. Investors and shareholders can use RORE as a valuable tool in making informed decisions about their investments.
Next time you are evaluating a company’s financial performance, don’t forget to consider its Return on Retained Earnings!