
Finance
What Are The Cons Of Debt Consolidation
Published: March 6, 2024
Learn about the potential drawbacks of debt consolidation and how it may impact your financial situation. Understand the risks involved in consolidating your debts.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
**
Introduction
**
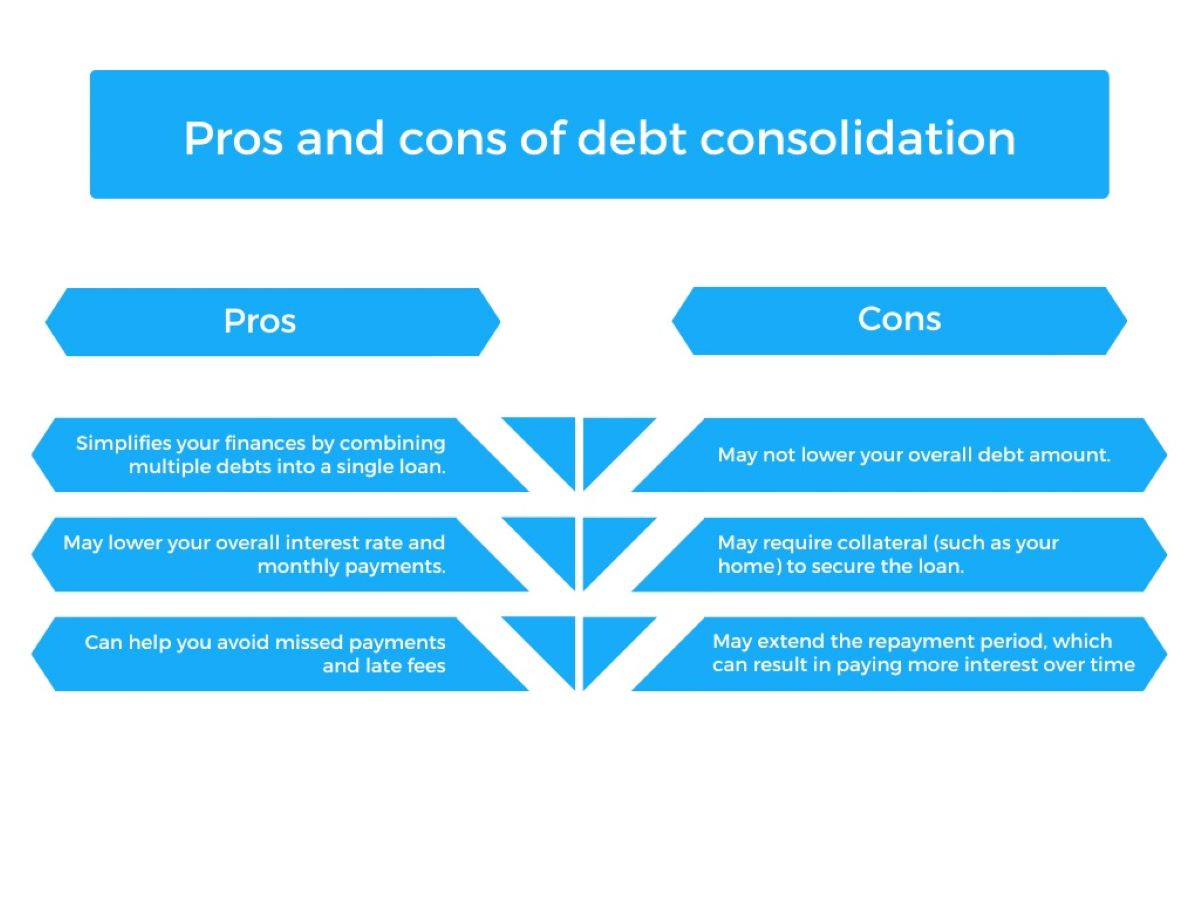
Debt consolidation is often touted as a financial panacea, a seemingly magical solution to the burden of multiple debts. It involves combining various high-interest debts into a single, more manageable payment, typically through a debt consolidation loan or a balance transfer credit card. While this approach offers potential benefits, it's essential to recognize that there are also drawbacks to consider. Understanding the cons of debt consolidation is crucial for individuals seeking to make informed decisions about their financial well-being.
By exploring the potential downsides of debt consolidation, individuals can weigh the pros and cons to determine the most suitable path for their unique circumstances. In this article, we will delve into the various disadvantages associated with debt consolidation, shedding light on aspects that are often overlooked in the allure of a simplified repayment structure. From the impact on credit scores to the risk of accumulating new debt, we will navigate through the complexities of debt consolidation to provide a comprehensive understanding of its potential drawbacks. Let's embark on this insightful journey to uncover the cons of debt consolidation and empower individuals to make informed financial decisions.
Impact on Credit Score
One of the significant concerns associated with debt consolidation is its potential impact on an individual’s credit score. When consolidating debts, especially through a new loan or credit card, there are several factors that can influence credit scores negatively. Firstly, the process often involves a hard inquiry on the individual’s credit report, which can cause a temporary dip in the credit score. Additionally, if the existing debts are closed after consolidation, it can affect the length of credit history and the credit utilization ratio, both of which are crucial components of credit scoring models.
Furthermore, if the debt consolidation loan or credit card carries a high balance relative to the credit limit, it can elevate the credit utilization ratio, which may lead to a decrease in the credit score. Moreover, if the individual continues to carry balances on the paid-off accounts, it can further impact the credit utilization ratio negatively. Understanding these potential repercussions is vital for individuals considering debt consolidation, as it allows them to anticipate and mitigate the adverse effects on their credit scores.
It’s important to note that while debt consolidation can initially cause a slight decline in credit scores, it may lead to long-term improvements if managed responsibly. By making timely payments and reducing overall debt, individuals can gradually enhance their credit profiles. However, the initial impact on credit scores remains a crucial consideration for those evaluating the feasibility of debt consolidation.
Potential for Increased Interest
While debt consolidation aims to simplify repayment and potentially reduce interest rates, there is a notable risk of encountering increased interest costs, particularly if the consolidation involves unsecured debts. In some cases, individuals may secure a debt consolidation loan with a lower monthly payment, but a longer repayment term. Although this can provide immediate relief by easing the monthly financial burden, it may result in significantly higher interest payments over the extended life of the loan.
Moreover, if the new consolidation loan carries a higher interest rate than the average rate of the existing debts, individuals may find themselves paying more in interest over time. This scenario can arise if the individual’s creditworthiness has declined since obtaining the original debts, leading to less favorable terms for the consolidation loan. It’s crucial for individuals to carefully assess the potential interest rates and fees associated with debt consolidation, ensuring that they will not incur greater financial costs in the long run.
Additionally, for those considering balance transfer credit cards as a form of debt consolidation, it’s essential to scrutinize the introductory and ongoing interest rates. While promotional periods may offer low or 0% interest rates, these can escalate significantly once the promotional period expires, potentially surpassing the interest rates of the original debts. Failing to account for these fluctuations can result in unexpected and burdensome interest expenses.
Understanding the potential for increased interest costs is paramount in evaluating the feasibility of debt consolidation. By carefully reviewing the terms, interest rates, and total repayment amounts, individuals can make informed decisions that align with their long-term financial well-being.
Risk of Losing Collateral
When considering debt consolidation, particularly through secured loans or home equity lines of credit (HELOC), individuals face the potential risk of losing collateral tied to the new financing. Secured loans require borrowers to pledge assets, such as their home or vehicle, as collateral to secure the loan. While this arrangement often enables individuals to obtain lower interest rates and higher loan amounts, it also exposes them to the inherent risk of losing the pledged assets if they default on the consolidated loan.
If unforeseen financial challenges arise, leading to an inability to meet the repayment obligations, the lender may initiate foreclosure or repossession proceedings to recoup the outstanding debt by claiming the pledged collateral. This can have devastating consequences, resulting in the loss of a home, vehicle, or other valuable assets that were used to secure the consolidation loan. The potential for such dire outcomes underscores the critical importance of carefully assessing the risks associated with secured debt consolidation.
Furthermore, the risk of losing collateral amplifies the stakes of debt consolidation, especially for individuals who may already be grappling with financial instability. It’s imperative for individuals to thoroughly evaluate their financial circumstances and the potential consequences of default before leveraging collateral to consolidate debts. Additionally, exploring alternative consolidation options that do not jeopardize valuable assets can provide a sense of security and mitigate the risk of substantial loss in the event of financial hardship.
By acknowledging the risk of losing collateral in the context of debt consolidation, individuals can make informed decisions that align with their risk tolerance and overall financial well-being. Understanding the potential ramifications of secured loans empowers individuals to navigate the consolidation landscape prudently and safeguard their valuable assets.
Extended Repayment Periods
Debt consolidation often involves the extension of repayment periods, which can present both advantages and drawbacks for individuals seeking to manage their debts more effectively. While lengthening the repayment term can reduce the immediate financial strain by lowering monthly payments, it also entails prolonged indebtedness and increased overall interest costs.
Individuals opting for debt consolidation may secure loans with extended repayment periods, spanning several years beyond the original debt timelines. While this can provide breathing room and alleviate immediate financial pressures, it can also result in significantly higher total interest payments over the extended life of the loan. Moreover, the prospect of being in debt for an extended duration can impede individuals’ financial freedom and delay their ability to achieve long-term financial goals, such as homeownership, retirement savings, or investment endeavors.
Furthermore, the extended repayment periods associated with debt consolidation can lead to a psychological burden, as individuals may feel trapped in a prolonged cycle of debt repayment. This can impact their overall well-being and financial outlook, contributing to stress and anxiety associated with protracted indebtedness.
It’s essential for individuals considering debt consolidation to carefully evaluate the trade-offs associated with extended repayment periods. While the immediate relief from reduced monthly payments may seem appealing, it’s crucial to assess the long-term implications of prolonged indebtedness and increased interest costs. Exploring alternative strategies to manage debts, such as accelerated repayment plans or targeted debt reduction methods, can offer a more balanced approach that aligns with individuals’ financial objectives.
By recognizing the potential drawbacks of extended repayment periods in the context of debt consolidation, individuals can make informed decisions that prioritize their long-term financial well-being. Evaluating the trade-offs and considering alternative approaches empowers individuals to navigate debt consolidation prudently and pursue a path that aligns with their financial goals.
Temptation to Accumulate New Debt
One often overlooked drawback of debt consolidation is the temptation it poses for individuals to accumulate new debt. Upon consolidating their existing debts, individuals may experience a sense of financial relief and newfound access to available credit, which can inadvertently lead to additional spending and the incurrence of fresh debts. This phenomenon can be attributed to a psychological shift, where individuals perceive the consolidation as an opportunity to reset their financial standing and may consequently engage in discretionary spending or take on new financial obligations.
Moreover, the closure of paid-off accounts after debt consolidation can create a false sense of available credit, as the credit limits of the original accounts are no longer factored into the individual’s outstanding balances. This perceived availability of credit may prompt individuals to utilize their newly freed-up credit lines, potentially leading to the accumulation of new debts alongside the consolidated loan or credit card balances.
Furthermore, if individuals fail to address the root causes of their initial debt accumulation, such as overspending or financial mismanagement, the cycle of debt accumulation may persist despite the consolidation efforts. Without implementing fundamental changes in their financial behaviors and practices, individuals may find themselves in a recurring pattern of debt accumulation, undermining the intended benefits of debt consolidation.
Recognizing the temptation to accumulate new debt following consolidation is crucial for individuals seeking to regain financial stability. By acknowledging this potential pitfall, individuals can take proactive measures to fortify their financial discipline and resist the allure of unnecessary spending or additional borrowing. Establishing a comprehensive budget, cultivating prudent spending habits, and building emergency savings can serve as effective safeguards against succumbing to the temptation of accumulating new debt post-consolidation.
By understanding and addressing the potential temptation to accumulate new debt, individuals can leverage debt consolidation as a springboard to sustainable financial health, steering clear of the pitfalls that may hinder their journey toward lasting financial stability.
Conclusion
Debt consolidation presents a compelling opportunity for individuals to streamline their financial obligations and regain control over their monetary well-being. However, it is essential to approach this strategy with a discerning eye, recognizing the potential drawbacks that can impact one’s overall financial landscape.
Understanding the impact of debt consolidation on credit scores, the potential for increased interest costs, the risk of losing collateral, extended repayment periods, and the temptation to accumulate new debt is paramount for individuals contemplating this financial undertaking. While debt consolidation offers the allure of simplified payments and potential interest savings, the associated cons demand careful consideration to ensure that the chosen path aligns with long-term financial objectives.
By acknowledging the potential downsides of debt consolidation, individuals can make informed decisions that encompass a holistic understanding of their financial circumstances. It is crucial to weigh the immediate benefits against the long-term implications, fostering a balanced approach that prioritizes sustainable financial health and prudent debt management.
Ultimately, the decision to pursue debt consolidation should be underpinned by a comprehensive assessment of the individual’s financial goals, risk tolerance, and the potential impact on their overall financial well-being. By navigating the complexities of debt consolidation with astuteness and foresight, individuals can leverage this strategy as a catalyst for enduring financial stability and empowerment.














