Finance
What Is Insurance And Risk Management
Published: November 21, 2023
Learn about insurance and risk management in the field of finance to protect your assets and manage potential financial risks. Find out how to minimize losses and maximize financial stability.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Insurance and Risk Management
- Importance of Insurance and Risk Management
- Components of Insurance and Risk Management
- Types of Insurance
- Roles and Responsibilities of Insurance Companies
- Risk Identification and Assessment
- Risk Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
- Claims Management
- Emerging Trends in Insurance and Risk Management
- Conclusion
Introduction
Insurance and risk management are two interconnected concepts that play a crucial role in our lives, both personally and financially. In a world full of uncertainties, where unexpected events can have significant impact, insurance provides a safety net and peace of mind. It helps individuals, businesses, and organizations protect themselves against potential financial losses and mitigate risks.
Risk management, on the other hand, is the process of identifying, assessing, and responding to risks by implementing strategies to minimize or prevent potential losses. It involves analyzing potential risks, evaluating their impact and likelihood, and developing risk mitigation plans.
Together, insurance and risk management form a comprehensive framework that helps individuals, businesses, and the economy as a whole to navigate uncertain situations and safeguard their assets and financial stability.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the world of insurance and risk management, exploring their definitions, importance, components, and various types of insurance. We will also discuss the roles and responsibilities of insurance companies, strategies for risk identification and assessment, risk prevention and mitigation techniques, claims management, and emerging trends in the field.
So, whether you are an individual looking to protect your personal assets, a business owner aiming to safeguard your company’s financial stability, or simply interested in understanding the world of insurance and risk management, this article will provide you with valuable insights and practical knowledge to navigate the complexities of this vital field.
Definition of Insurance and Risk Management
Insurance can be defined as a contract between an individual or an entity and an insurance company, where the individual or entity, known as the policyholder, pays a premium in exchange for financial protection against potential losses. In simple terms, insurance transfers the risk of financial loss from the policyholder to the insurance company.
Risk management, on the other hand, refers to the systematic process of identifying, assessing, and responding to risks to minimize or prevent potential losses. It involves analyzing potential risks, evaluating their impact and likelihood, and implementing strategies to mitigate risks.
Insurance and risk management go hand in hand. Insurance is one of the key tools used in risk management to cope with and transfer potential risks. It serves as a means of managing and reducing the financial impact of unexpected events.
Insurance serves as a form of protection against specific risks. By paying regular premiums, individuals or organizations can obtain coverage for various risks such as property damage, liability, medical expenses, and more. When an insured event occurs, the policyholder files a claim with the insurance company, and if the claim is valid, the insurance company provides financial compensation to cover the losses.
Risk management, on the other hand, involves a broader approach to identifying and managing risks. It encompasses proactive measures to minimize the likelihood of risks occurring and their potential impact. Risk management strategies may include implementing safety protocols, diversifying investments, creating contingency plans, and utilizing insurance as a means of transfer.
Insurance and risk management are essential in all aspects of life – from personal to business. They provide individuals and organizations with the necessary tools to navigate uncertainties and protect their financial well-being. Whether it is insuring a home, a car, a business, or even one’s health, insurance and risk management play a crucial role in minimizing the financial impact of unexpected events.
Understanding the definitions of insurance and risk management is fundamental to appreciate their significance and the comprehensive approach they bring to mitigating potential risks and safeguarding against financial losses.
Importance of Insurance and Risk Management
Insurance and risk management are of paramount importance in today’s world, offering a multitude of benefits and advantages. Let’s explore why they are crucial for individuals, businesses, and society as a whole:
Financial Protection: One of the primary reasons for insurance and risk management is to provide financial protection against unexpected events. Life is full of uncertainties, and unforeseen circumstances such as accidents, natural disasters, or illnesses can lead to significant financial losses. Insurance acts as a safety net, covering these unforeseen costs and helping individuals and businesses recover from such setbacks.
Security and Peace of Mind: Knowing that you are protected in the event of a loss can bring peace of mind and a sense of security. Insurance provides a sense of comfort, allowing individuals and organizations to focus on their daily activities and long-term goals without constantly worrying about unforeseen risks and financial consequences.
Encourages Risk Taking: Insurance and risk management encourage individuals and businesses to take calculated risks. When risks are properly managed and insured, individuals and organizations are more inclined to explore new opportunities, invest in growth, and pursue innovation. Insurance provides a safety net that allows for calculated risk-taking, fostering entrepreneurship and economic development.
Legal Compliance: In many cases, insurance is a legal requirement. For instance, car insurance is mandatory in most countries to protect drivers and third parties in the event of accidents. Similarly, businesses often need to have various types of insurance, such as workers’ compensation and liability insurance, to comply with legal and regulatory requirements. Failure to have appropriate insurance coverage may result in legal penalties or even business closure.
Business Stability and Continuity: Insurance and risk management are essential for business continuity. In the face of unexpected events such as fire, theft, or natural disasters, insurance provides financial support to rebuild, repair, or replace assets. This allows businesses to recover quickly and resume operations, minimizing financial losses and maintaining stability.
Protects Personal and Business Assets: Insurance ensures that personal and business assets are protected against potential risks. Whether it is your home, car, equipment, or inventory, insurance provides coverage for damages and losses. This protection allows individuals and businesses to maintain their financial stability and avoid significant financial setbacks that may take years to recover from.
Social Welfare and Economic Stability: Insurance plays a vital role in societal welfare and economic stability. In the event of a widespread disaster, such as a natural calamity or a pandemic, insurance helps distribute the financial burden by compensating affected individuals and businesses. This not only aids in the recovery process but also contributes to maintaining overall economic stability.
In summary, insurance and risk management are of utmost importance for individuals, businesses, and society as a whole. They provide financial protection, security, and peace of mind, encourage entrepreneurship and innovation, promote legal compliance, ensure business stability and continuity, protect assets, and contribute to overall social welfare and economic stability. Investing in insurance and implementing effective risk management strategies is a wise decision that can have long-lasting positive effects.
Components of Insurance and Risk Management
Insurance and risk management involve several interconnected components that work together to provide comprehensive coverage and minimize potential risks. Let’s explore the essential components of insurance and risk management:
1. Insurance Policies: Insurance policies are contracts that outline the terms and conditions of coverage provided by an insurance company. They specify the scope of coverage, premium amounts, deductibles, limits, and exclusions. Policyholders select the type of insurance policies they need based on the specific risks they want to protect against.
2. Premiums: Premiums are the payments made by policyholders to the insurance company in exchange for insurance coverage. The amount of premiums is determined based on factors such as the type of insurance, the level of coverage, the insured’s risk profile, and the history of claims.
3. Deductibles: A deductible is the amount that a policyholder must pay out of pocket before the insurance coverage kicks in. Higher deductibles generally lead to lower premiums, as they shift a portion of the risk to the policyholders.
4. Limits: Insurance policies often come with limits, which specify the maximum amount that the insurance company will pay in the event of a claim. These limits can be per occurrence or aggregate limits, depending on the type of coverage.
5. Risk Assessment: Risk assessment involves identifying and evaluating potential risks. This process helps insurance companies and individuals understand the likelihood and potential impact of different risks. It allows for better decision-making regarding the type and level of insurance coverage needed.
6. Risk Prevention and Mitigation Measures: Risk prevention and mitigation strategies aim to minimize the likelihood and impact of potential risks. This may involve implementing safety protocols, conducting regular inspections and maintenance, investing in security systems, and creating contingency plans.
7. Claims Processing: Claims processing is the procedure followed when a policyholder reports a loss covered by the insurance policy. It involves submitting necessary documentation, such as proof of loss or damages, to the insurance company. The insurance company then assesses the claim and, if approved, provides compensation to the policyholder.
8. Underwriting: Underwriting is the process by which insurance companies evaluate the risks associated with potential policyholders. It involves assessing the applicant’s risk profile, including factors such as age, health, occupation, and claims history, to determine the cost of premiums and eligibility for coverage.
9. Reinsurance: Reinsurance is a mechanism used by insurance companies to transfer a portion of their risk to other insurance companies. Reinsurance helps insurers manage large or catastrophic losses by sharing the risk with other parties, maintaining stability, and ensuring that they can meet their financial obligations in the event of significant claims.
10. Policyholder Education: Educating policyholders on insurance coverage, policy terms, and risk management practices is an essential component of insurance and risk management. It helps individuals and businesses make informed decisions about the type and level of coverage needed and empowers them to effectively manage their risks.
By understanding and implementing these components, individuals and organizations can benefit from comprehensive insurance coverage and effective risk management practices. This not only provides financial protection but also promotes proactive risk prevention and ensures long-term stability and resilience.
Types of Insurance
Insurance comes in various forms, each designed to offer protection against specific risks. Here are some common types of insurance:
1. Life Insurance: Life insurance provides financial protection to the beneficiaries of the policyholder in the event of their death. It can help cover funeral expenses, settle outstanding debts, replace lost income, and provide for the future financial needs of dependents.
2. Health Insurance: Health insurance covers medical expenses and provides financial protection against the high costs of healthcare. It can include coverage for doctor visits, hospital stays, prescription medications, and preventive care. Health insurance may be provided by employers, government programs, or obtained individually.
3. Property Insurance: Property insurance protects physical assets such as homes, buildings, and their contents against damages or loss due to events like fire, theft, or natural disasters. It can also provide liability coverage in case someone gets injured on the property.
4. Auto Insurance: Auto insurance covers damages to vehicles and liability for injuries to others in the event of an accident. It typically includes coverage for physical damage, liability, and medical expenses related to automobile accidents.
5. Liability Insurance: Liability insurance offers protection against claims or lawsuits filed against individuals or businesses in the event that they cause harm or damage to others. It covers legal expenses and compensation payments to the affected parties.
6. Homeowners Insurance: Homeowners insurance provides coverage for homes and their contents, protecting against damages or losses due to fire, theft, vandalism, or certain natural disasters. It also offers liability coverage in case someone gets injured on the property.
7. Business Insurance: Business insurance is tailored to protect businesses against various risks. It may include coverage for property damage, liability claims, business interruption, professional errors, and employee-related issues.
8. Disability Insurance: Disability insurance provides income replacement in the event that an individual becomes disabled and is unable to work. It can help cover daily living expenses and medical costs during the disability period.
9. Travel Insurance: Travel insurance offers coverage for potential risks associated with traveling, such as trip cancellation or interruption, medical emergencies, lost luggage, or travel accidents. It provides financial protection and assistance while traveling.
10. Pet Insurance: Pet insurance covers veterinary expenses for pets, ensuring that they receive necessary medical care without the burden of high costs. It may cover accidents, illnesses, surgeries, and preventive care.
These are just a few examples of the types of insurance available. It is important to assess individual needs and risks to determine the appropriate types and levels of coverage required. Insurance provides peace of mind, financial security, and protection against unexpected events, allowing individuals and businesses to navigate uncertainties with confidence.
Roles and Responsibilities of Insurance Companies
Insurance companies play a vital role in the insurance and risk management ecosystem. Their primary responsibility is to provide individuals and businesses with financial protection and assist them in managing risks. Let’s explore the key roles and responsibilities of insurance companies:
1. Risk Assessment and Underwriting: Insurance companies assess the risks associated with potential policyholders through the underwriting process. They evaluate the applicant’s risk profile, including factors such as age, health, occupation, and claims history, to determine the cost of premiums and eligibility for coverage.
2. Policy Offerings and Customization: Insurance companies develop and offer a wide range of insurance policies that cater to different risks and needs. They provide policyholders with options to customize coverage based on their specific requirements.
3. Premium Calculation and Collection: Insurance companies determine the cost of insurance coverage by calculating premiums. Premiums take into account factors such as the risk level, coverage amount, deductibles, and policyholder’s history. The insurance company is responsible for collecting premiums from policyholders.
4. Policyholder Servicing: Insurance companies provide customer support and assistance to policyholders throughout the policy lifecycle. They handle inquiries, assist with policy changes, and address any concerns or issues that policyholders may have.
5. Claims Processing and Settlement: When a policyholder experiences a covered loss, insurance companies are responsible for processing and settling claims. This involves reviewing the claim, assessing the extent of the covered loss, and providing compensation to the policyholder within the policy’s terms and coverage limits.
6. Risk Management and Loss Control: Insurance companies are proactive in promoting risk management and loss control practices. They may provide resources, guidance, and recommendations to policyholders on minimizing and managing risks effectively. This may include safety protocols, risk prevention strategies, and loss control measures.
7. Reinsurance and Risk Transfer: Insurance companies manage their own risk exposure by transferring a portion of the risk to other insurance companies through reinsurance agreements. This helps insurance companies maintain stability, ensure financial solvency, and handle large or catastrophic losses.
8. Regulatory Compliance: Insurance companies must adhere to legal and regulatory requirements in the jurisdictions in which they operate. They must comply with licensing, financial reporting, consumer protection, and ethical standards to ensure proper conduct and fair treatment of policyholders.
9. Financial Management and Solvency: Insurance companies have a responsibility to manage their financial resources prudently. They must ensure sufficient reserves and capital to meet their ongoing obligations and settle claims promptly. Sound financial management practices are crucial to maintaining the trust and confidence of policyholders.
10. Innovation and Adaptation: Insurance companies strive to innovate and adapt to changing customer needs and emerging risks. They continuously evaluate market trends, technological advancements, and societal changes to develop new products, improve processes, and provide enhanced insurance solutions.
Insurance companies play a crucial role in providing financial protection, managing risks, and promoting stability in our society. Their responsibilities extend beyond selling insurance policies to actively managing risks, supporting policyholders, and ensuring their financial solvency. By fulfilling these roles and responsibilities, insurance companies contribute to the overall well-being and resilience of individuals, businesses, and the economy as a whole.
Risk Identification and Assessment
Risk identification and assessment are fundamental steps in the process of effective risk management. By identifying and evaluating risks, individuals and organizations can make informed decisions on how to mitigate or manage them. Let’s explore the key aspects of risk identification and assessment:
1. Identifying Risks: The first step in risk management is to identify potential risks. This involves a systematic process of identifying all possible events or circumstances that could negatively impact an individual or organization. Risks can arise from various sources, such as natural disasters, accidents, financial uncertainties, regulatory changes, or technological disruptions.
2. Internal and External Factors: Risks can originate from internal factors within an organization, such as operational inefficiencies, human errors, or inadequate security measures. External risks, on the other hand, are factors beyond an organization’s control, such as macroeconomic conditions, geopolitical events, or industry-specific challenges.
3. Risk Register: A risk register is a tool used to record and document identified risks. It serves as a central repository of information, providing a comprehensive overview of potential risks, their likelihood, potential impact, and recommended actions for mitigation or management.
4. Risk Analysis: Once risks are identified, they need to be analyzed to determine their significance and potential impact. This involves assessing the likelihood of occurrence and the potential consequences of each risk. Qualitative and quantitative techniques can be used to evaluate risks, such as probability analysis, impact assessment, and risk scoring.
5. Risk Prioritization: After analyzing the identified risks, it is essential to prioritize them based on their severity and potential impact. This helps allocate appropriate resources and prioritize risk mitigation efforts. Risks that pose higher probability and significant potential impact are given higher priority for mitigation or management.
6. Risk Mitigation Strategies: Once risks are identified and prioritized, organizations can develop risk mitigation strategies. These strategies aim to reduce the likelihood of occurrence or minimize the impact of identified risks. Risk mitigation strategies may include implementing safety protocols, diversifying investments, creating redundancies, adopting technology solutions, or purchasing insurance coverage.
7. Risk Monitoring and Review: Risk management is an ongoing process that requires regular monitoring and review. Organizations should establish mechanisms to track and update the identified risks, assess their effectiveness of mitigation strategies, and make adjustments as necessary. Continuous monitoring helps identify new risks, reassess existing risks, and adapt risk management approaches to changing circumstances.
8. Risk Communication: Effective risk management involves clear and transparent communication of identified risks to stakeholders, both internal and external. This ensures that all relevant parties are aware of potential risks and understand the organization’s approach to mitigating them. Open communication fosters a risk-aware culture and encourages proactive risk management practices.
9. Technological Advances in Risk Assessment: With the advent of advanced technology, organizations now have access to various tools and software systems that can aid in risk identification and assessment. These technologies can help automate data collection, enhance risk analysis models, and provide real-time risk monitoring and reporting capabilities.
10. Expert Consultation: In some cases, organizations may seek external expertise to identify and assess risks more effectively. Risk management consultants or specialized professionals can provide valuable insights, experience, and knowledge to help organizations identify and understand their risks more comprehensively.
By systematically identifying and assessing risks, individuals and organizations can take proactive measures to minimize the impact of potential risks. Risk identification and assessment are critical steps in the overall risk management process and serve as a foundation for effective decision-making and strategic planning.
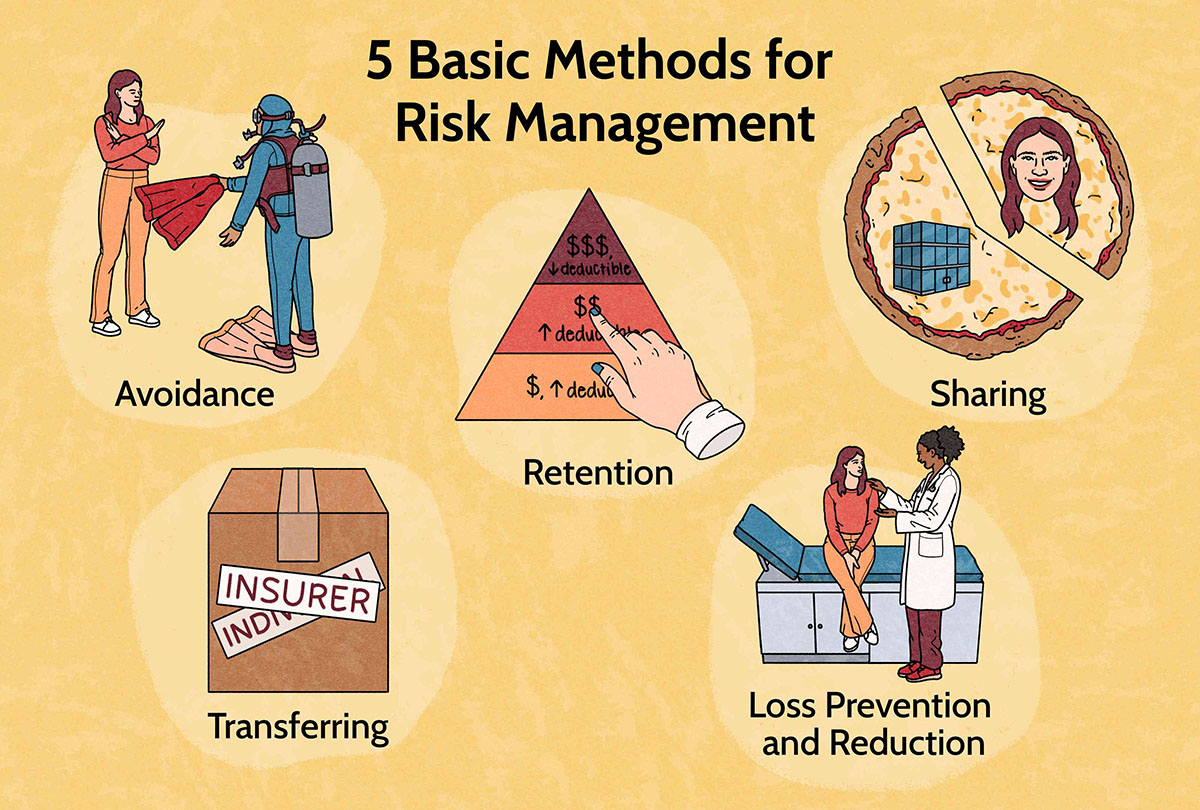
Risk Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
Risk prevention and mitigation strategies are essential components of effective risk management. These strategies aim to minimize the likelihood of risks occurring and reduce the potential impact on individuals or organizations. By implementing preventive measures and proactive actions, individuals and organizations can better protect themselves against potential risks. Let’s explore some common risk prevention and mitigation strategies:
1. Safety Protocols and Training: Implementing and enforcing safety protocols is crucial in preventing accidents and injuries. This may include providing appropriate training to employees, conducting regular safety inspections, and promoting a culture of safety awareness in the workplace.
2. Security Measures: Implementing robust security measures helps minimize the risk of theft, vandalism, or unauthorized access. This may include installing security systems, video surveillance, access control measures, and cybersecurity protocols to protect sensitive data and information.
3. Business Continuity Planning: Developing a comprehensive business continuity plan helps ensure that operations can continue in the face of unforeseen events. This involves identifying critical processes, creating contingency plans, and establishing alternative work arrangements to minimize disruptions in case of emergencies or disasters.
4. Diversification: Diversifying investments and business activities can help spread risk and minimize the impact of potential losses. By allocating resources across different sectors, geographical locations, or asset classes, individuals and businesses can reduce their exposure to the risks associated with a single investment or activity.
5. Insurance Coverage: Insurance is a vital risk mitigation strategy that transfers the financial burden of potential losses to an insurance company. By purchasing appropriate insurance coverage, individuals and organizations can protect themselves against various risks, such as property damage, liability, professional errors, or business interruption.
6. Contractual Risks Transfer: Transferring certain risks through contracts and agreements can help mitigate potential liabilities. This involves including indemnification clauses, waivers, and limitation of liability provisions in contracts to shift the responsibility for specific risks to other parties.
7. Regular Maintenance and Inspections: Conducting regular maintenance and inspections helps identify potential risks or issues before they escalate. This includes routine checks on equipment, infrastructure, and systems to ensure they are in proper working condition and comply with safety standards.
8. Emergency Response Planning: Developing comprehensive emergency response plans helps mitigate the impact of unexpected events. This includes establishing protocols for evacuations, communication, and coordination with emergency responders. Regular drills and training sessions can help ensure preparedness and effective response in crisis situations.
9. Business Process Optimization: Optimizing business processes can help identify and address potential risks and vulnerabilities. By streamlining workflows, improving internal controls, and utilizing technology, organizations can reduce opportunities for errors, fraud, or operational inefficiencies.
10. Continuous Risk Monitoring and Evaluation: Risk management is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and evaluation. Regularly analyzing and reassessing risks allows organizations to adapt and adjust risk management strategies in response to changing circumstances, emerging risks, or new opportunities.
It is important to note that risk prevention and mitigation strategies should be tailored to the specific needs and risks of each individual or organization. A comprehensive approach that combines multiple strategies and proactive measures provides the best protection and resilience against potential risks. By implementing these strategies, individuals and organizations can reduce the likelihood and impact of risks, safeguard their assets, and ensure long-term stability and success.
Claims Management
Claims management is a critical aspect of the insurance process that involves the handling and settlement of claims made by policyholders. Effective claims management ensures timely and fair compensation for losses covered by insurance policies. Let’s explore the key components and best practices of claims management:
1. Claims Processing: The claims process begins when a policyholder experiences a covered loss and submits a claim to the insurance company. The insurer verifies the claim, assesses the extent of the loss, and determines the coverage and compensation amount according to the policy terms. Efficient claims processing involves prompt acknowledgement, thorough investigation, and fair evaluation of the claim.
2. Transparent Communication: Transparent communication is crucial throughout the claims management process. Insurance companies should keep policyholders informed about the progress of their claim, provide clear explanations of claim decisions, and promptly respond to any inquiries or concerns. Open and regular communication helps build trust and ensures a positive claims experience.
3. Documentation and Evidence: Valid claims require supporting documentation and evidence. Policyholders should provide the necessary documents, such as police reports, medical records, or repair estimates, to substantiate their claim. Insurance companies, in turn, should clearly communicate the required documentation and guide policyholders on what is needed to process their claim.
4. Efficient Claims Handling: Timely and efficient claims handling is essential. Insurance companies should set realistic timeframes for claim processing, strive to meet those timelines, and keep policyholders informed of any delays. Utilizing technology and automated systems can help streamline claims handling and reduce processing times.
5. Fair Claims Evaluation: Insurance companies must conduct fair evaluations of claims to determine the extent of coverage and compensation amount. Claims should be assessed based on the policy terms and conditions, applicable deductibles, and coverage limits. Objective and accurate evaluation ensures policyholders receive the appropriate compensation for their covered losses.
6. Fraud Detection and Prevention: Claims management involves diligent efforts to detect and prevent fraud. Insurance companies employ specialized tools, data analysis techniques, and investigation teams to identify potentially fraudulent claims. Early detection of fraudulent activities helps protect legitimate policyholders and maintain the integrity of the insurance system.
7. Effective Claims Settlement: Upon completion of the claims evaluation, insurance companies should promptly process the settlement and disburse the compensation to policyholders. The settlement should be fair, based on the policy coverage, and reflect the actual losses suffered by the policyholder. Timely and accurate settlement ensures that policyholders can recover from their losses and restore their financial position.
8. Dispute Resolution: In cases where there are disagreements or disputes regarding claim settlements, insurance companies should have a structured and fair dispute resolution process. This process may involve arbitration, mediation, or other means of alternative dispute resolution to arrive at a mutually acceptable resolution for both parties.
9. Continuous Improvement: Insurance companies should consistently evaluate their claims management processes and seek ways to improve efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction. Feedback from policyholders and regular analysis of claims data can help identify areas for improvement and drive enhancements in claims handling practices.
10. Customer Support and Satisfaction: Providing exceptional customer support is essential throughout the claims management process. Insurance companies should strive to exceed policyholders’ expectations, address their concerns, and ensure their satisfaction. Positive claims experiences foster customer loyalty and strengthen the relationship between policyholders and insurers.
Efficient and fair claims management is crucial for maintaining policyholder trust and ensuring the successful functioning of the insurance industry. By following best practices in claims handling, insurance companies can demonstrate their commitment to policyholder satisfaction, enhance their reputation, and uphold the principles of integrity and reliability in the insurance market.
Emerging Trends in Insurance and Risk Management
The insurance and risk management industry is constantly evolving to address new challenges and incorporate advancements in technology and societal changes. Here are some emerging trends shaping the landscape of insurance and risk management:
1. Data Analytics and Artificial Intelligence (AI): The utilization of data analytics and AI is revolutionizing the insurance industry. Insurers can gather and analyze vast amounts of data to identify trends, assess risks, and personalize insurance coverage. AI algorithms can automate underwriting processes, claims management, and risk assessments, increasing efficiency and accuracy.
2. Internet of Things (IoT): The IoT is being leveraged to gather real-time data from connected devices, enabling insurers to offer usage-based insurance policies and more accurately assess risks. From telematics devices in vehicles to wearable devices collecting health data, the IoT helps insurers understand customer behavior and develop tailored coverage options.
3. Cyber Insurance: With the rise in cyber threats, there is a growing demand for cyber insurance coverage. Insurers are developing specialized policies to address the financial impact of data breaches, cyber-attacks, and other cyber risks. Cyber insurance helps businesses protect themselves against potential losses due to cyber incidents and assists in managing the aftermath of such events.
4. Climate Change and Natural Catastrophe Insurance: The increasing frequency and severity of natural disasters have led to a surge in demand for climate change and natural catastrophe insurance coverage. Insurers are developing specialized policies to address the financial implications of climate-related events, such as hurricanes, floods, wildfires, and extreme weather conditions.
5. Parametric Insurance: Parametric insurance is an innovative approach that pays out a predetermined amount based on the occurrence of a predefined trigger event. For example, instead of indemnifying actual damages, a parametric insurance policy may pay out a predetermined sum if a specific metric, such as wind speed or rainfall levels, exceeds a certain threshold. This type of insurance speeds up claims processing and provides quicker payouts.
6. Peer-to-Peer Insurance: Peer-to-peer (P2P) insurance utilizes technology platforms to connect individuals directly with one another to share risk. P2P insurance allows groups of like-minded individuals to pool their premiums and provide coverage to one another. It promotes transparency, shared responsibility, and lower costs by eliminating traditional intermediaries.
7. Ecosystem Partnerships: Insurers are increasingly collaborating with other industry sectors to create ecosystem partnerships. These alliances bring together insurers, technology companies, health providers, and more to offer integrated solutions and services. By combining resources and expertise, insurers can provide a holistic approach to risk management and enhance the customer experience.
8. Microinsurance and Parametric Coverage for Developing Markets: Microinsurance aims to provide affordable insurance coverage to individuals and businesses in low-income or developing markets. Parametric insurance is particularly useful in these markets, as it simplifies claims settlement and caters to the unique challenges faced in these regions. These specialized insurance products help extend financial protection to underserved populations.
9. Ethics and ESG Considerations: Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors are increasingly being considered in insurance and risk management practices. Insurers are incorporating ethical considerations into their underwriting and investment strategies. This includes assessing and promoting sustainable practices, corporate social responsibility, and good governance principles.
10. Cybersecurity Risk Assessment and Services: Given the rising threats of cyber-attacks, insurers are expanding their services to include cybersecurity risk assessment and mitigation. They offer tools and services to help policyholders identify vulnerabilities, implement security measures, and respond effectively to cyber incidents.
These emerging trends in insurance and risk management illustrate the industry’s constant evolution and adaptation. By embracing these trends, insurers and risk managers can better address the changing needs of individuals, businesses, and society as a whole. As technology advances and risks evolve, staying at the forefront of these trends is crucial for successfully navigating the dynamic landscape of insurance and risk management.
Conclusion
Insurance and risk management are integral aspects of our lives, providing financial protection, stability, and peace of mind in the face of uncertainties. Understanding the definitions, importance, and components of insurance and risk management is crucial for individuals, businesses, and society as a whole.
Insurance serves as a safety net, transferring potential financial losses from individuals and organizations to insurance companies. It covers various risks, including life, health, property, liability, and more. Risk management, on the other hand, involves identifying, assessing, and responding to risks through preventive measures, mitigation strategies, and effective claims management.
The roles and responsibilities of insurance companies encompass risk assessment, underwriting, policy offerings, claims processing, and ensuring financial stability. They play a vital role in providing individuals and businesses with the necessary coverage and assistance to manage risks.
Identifying and assessing risks are essential steps in effective risk management. It enables individuals and organizations to make informed decisions, develop risk prevention and mitigation strategies, and optimize their operations for long-term success.
By leveraging emerging trends such as data analytics, AI, IoT, and specialized insurance coverage, the insurance industry continues to evolve. These trends facilitate personalized coverage, efficient claims management, and better risk assessment practices to adapt to the changing needs of customers.
In conclusion, insurance and risk management are crucial in safeguarding individuals, businesses, and society against potential financial losses and uncertainties. By understanding the concepts, embracing best practices, and keeping up with the emerging trends, individuals and organizations can effectively navigate risks, protect their assets, and ensure financial stability. Insurance and risk management provide the necessary foundation for growth, resilience, and a secure future in an unpredictable world.