Finance
What Is A Financial Risk Manager
Modified: December 30, 2023
Learn about the role and responsibilities of a Financial Risk Manager. Stay ahead in the field of finance by understanding and managing various financial risks.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Financial Risk Manager
- Roles and Responsibilities of a Financial Risk Manager
- Importance of Financial Risk Management
- Skills Required to be a Financial Risk Manager
- Steps to Become a Financial Risk Manager
- Career Opportunities for Financial Risk Managers
- Challenges Faced by Financial Risk Managers
- Conclusion
Introduction
When it comes to managing financial risks, it’s crucial for businesses and organizations to have professionals who specialize in this area. This is where a Financial Risk Manager (FRM) comes into play. A Financial Risk Manager is a highly skilled individual who is responsible for identifying, assessing, and minimizing potential risks that can impact an organization’s financial stability.
The role of a Financial Risk Manager is becoming increasingly important in today’s complex and volatile financial landscape. With the ever-changing global economy and the increasing complexity of financial instruments, organizations need experts who can navigate through these challenges and make informed decisions to protect their assets.
A Financial Risk Manager is not only responsible for analyzing and managing financial risks, but they also play a crucial role in developing risk management strategies to ensure the organization’s long-term financial success. They work closely with various departments within an organization, including finance, accounting, and operations, to identify potential risks and implement risk mitigation measures.
Financial Risk Managers are highly sought after by banks, insurance companies, investment firms, and other financial institutions. Their expertise is essential in ensuring the stability and growth of these organizations, especially in the face of economic uncertainties.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the world of Financial Risk Managers. We will discuss the definition of a Financial Risk Manager, their roles and responsibilities, the importance of financial risk management, the skills required to be successful in this role, steps to become a Financial Risk Manager, career opportunities, and the challenges they face in their daily work.
Definition of Financial Risk Manager
A Financial Risk Manager is a professional who specializes in identifying, analyzing, and managing potential risks that can affect the financial health and stability of an organization. They are responsible for assessing the potential impact of risks on the organization’s financial performance and recommending strategies to mitigate these risks.
Financial Risk Managers work in a variety of industries, including banking, insurance, investment management, and consulting firms. They have a deep understanding of financial markets, instruments, and regulatory frameworks. They are knowledgeable about different types of risks, such as market risk, credit risk, liquidity risk, operational risk, and regulatory risk.
One of the primary responsibilities of a Financial Risk Manager is to assess the overall risk profile of an organization. This involves conducting risk assessments and stress tests to identify potential vulnerabilities and areas of concern. Based on their analysis, they develop risk management strategies and policies to minimize the impact of these risks.
Financial Risk Managers also play a crucial role in monitoring and reporting on the organization’s risk exposure. They regularly analyze financial data, market trends, and other relevant information to ensure that risk management strategies are effective and up to date. They also provide recommendations for adjustments and improvements to risk management processes and policies.
The role of a Financial Risk Manager requires strong analytical and problem-solving skills. They must have the ability to analyze complex financial data and make informed decisions based on their findings. They need to stay updated on industry trends, regulations, and best practices to effectively manage risks in a dynamic financial environment.
In summary, a Financial Risk Manager is a specialized professional who helps organizations identify, assess, and manage financial risks. They play a critical role in ensuring the financial stability and success of an organization by implementing effective risk management strategies.
Roles and Responsibilities of a Financial Risk Manager
A Financial Risk Manager has a wide range of roles and responsibilities that are essential to ensuring the financial stability and success of an organization. Let’s explore some of the key responsibilities of a Financial Risk Manager:
- Identifying and assessing financial risks: One of the primary responsibilities of a Financial Risk Manager is to identify and assess potential financial risks that may impact the organization. This involves analyzing market trends, economic indicators, financial statements, and other relevant data to identify vulnerabilities and potential threats.
- Developing risk management strategies: Financial Risk Managers are responsible for developing risk management strategies and policies to mitigate the identified risks. They work closely with senior management and other stakeholders to define risk tolerance levels, establish risk mitigation measures, and implement effective risk control frameworks.
- Monitoring and evaluating risk exposure: Financial Risk Managers continuously monitor and evaluate the organization’s risk exposure. They analyze financial data, market conditions, and other relevant factors to assess the effectiveness of risk management strategies. This includes conducting stress tests, scenario analyses, and other quantitative and qualitative assessments to determine the impact of various risks on the organization’s financial performance.
- Implementing risk mitigation measures: Once risks are identified and evaluated, Financial Risk Managers play a key role in implementing risk mitigation measures. They collaborate with different departments within the organization to develop and implement control frameworks, policies, and procedures to minimize risks. This may involve establishing risk limits, developing hedging strategies, and implementing internal controls.
- Ensuring regulatory compliance: Financial Risk Managers are responsible for ensuring that the organization complies with relevant financial regulations and industry standards. They stay updated on changing regulatory requirements and work closely with compliance officers to ensure that the organization’s risk management practices align with regulatory guidelines.
- Reporting and communication: Financial Risk Managers provide regular reports and updates to senior management and other stakeholders regarding the organization’s risk profile. They communicate complex risk-related information in a clear and concise manner, highlighting key risks, mitigation strategies, and any emerging risks that require attention. Their reports serve as a basis for informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Overall, the roles and responsibilities of a Financial Risk Manager require a strong understanding of financial markets, risk management principles, and analytical skills. They play a critical role in safeguarding the financial health of an organization by identifying, assessing, and managing potential risks.
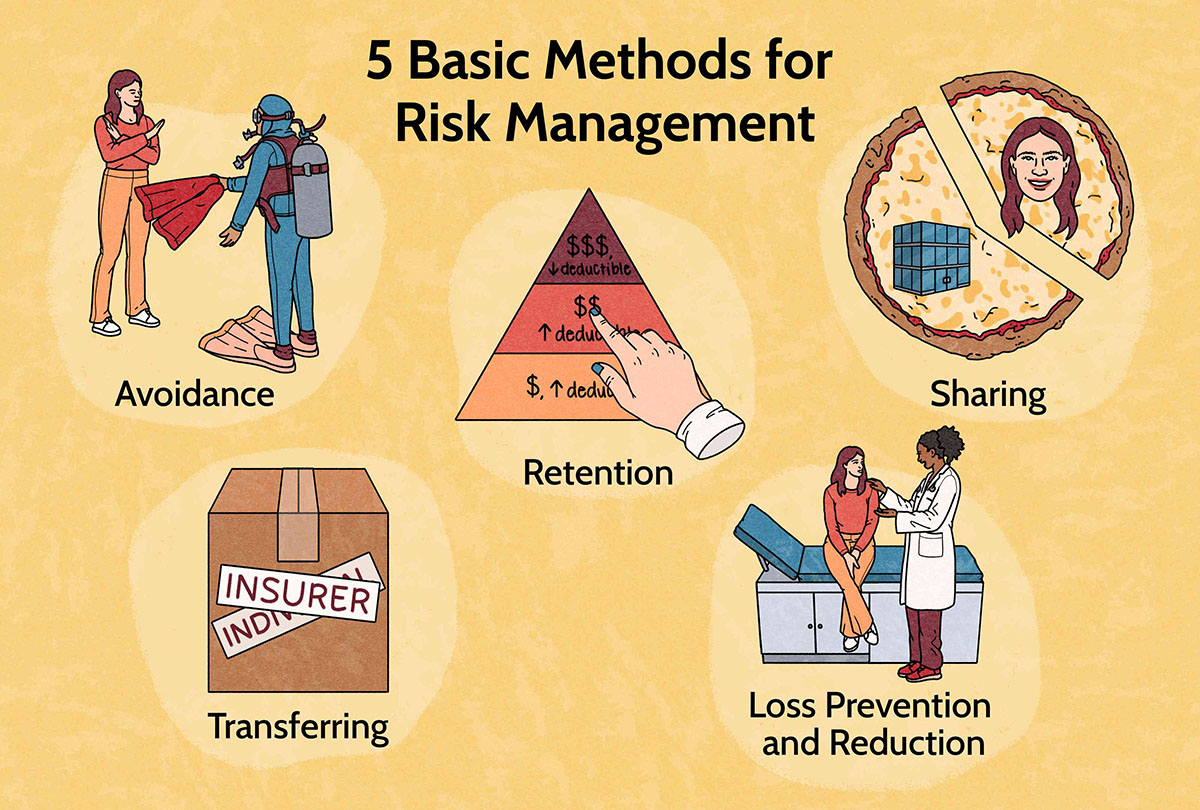
Importance of Financial Risk Management
Financial risk management is of utmost importance for organizations in maintaining their financial stability and ensuring long-term success. Let’s explore why financial risk management is crucial:
- Preserving financial stability: Financial risk management helps organizations protect their financial resources and maintain stability even in the face of uncertainty. By identifying and mitigating potential risks, organizations can minimize the negative impact of adverse events such as economic downturns, market volatility, or unexpected financial losses.
- Enhancing decision-making: Effective financial risk management provides organizations with valuable insights and data-driven information. By analyzing risks and their potential impact on financial performance, organizations can make informed decisions and allocate resources more effectively. This reduces the likelihood of making ill-advised investments or taking on excessive risks.
- Meeting regulatory requirements: Regulatory bodies, such as government institutions and industry regulators, enforce certain financial risk management standards and guidelines. Compliance with these regulations is not only a legal requirement but also crucial for maintaining organizational reputation and trust. Financial risk management ensures that organizations are aware of and comply with relevant regulations, reducing the risk of legal penalties and reputational damage.
- Protecting stakeholders’ interests: Financial risk management is essential for safeguarding the interests of various stakeholders, including shareholders, investors, employees, and customers. By anticipating and addressing potential risks, organizations can protect stakeholders from financial losses and ensure the long-term viability of the company.
- Improving creditworthiness: Financial risk management is closely tied to creditworthiness. Organizations with robust risk management practices are seen as more reliable and trustworthy by lenders, investors, and creditors. This enhances the organization’s ability to access financing, negotiate favorable terms, and build strong business relationships.
- Enabling strategic planning: Financial risk management contributes to the development of effective strategic plans. By understanding and managing risks, organizations can assess their risk appetite and align their goals and objectives accordingly. This allows for more focused and targeted strategies, ultimately leading to improved business performance and sustainable growth.
- Adapting to a changing business environment: The business landscape is constantly evolving, with new technologies, economic shifts, and regulatory changes. Effective financial risk management enables organizations to adapt to these changes more efficiently. By identifying emerging risks and opportunities, organizations can adjust their strategies and operations to stay ahead of the curve.
In summary, financial risk management is essential for organizations to navigate the complexities of today’s financial landscape. It helps protect financial stability, enhance decision-making, comply with regulations, protect stakeholders’ interests, improve creditworthiness, enable strategic planning, and adapt to changing business environments. By proactively managing risks, organizations can strive for long-term success and sustainability.
Skills Required to be a Financial Risk Manager
Being a Financial Risk Manager requires a unique set of skills and expertise to effectively identify, assess, and manage financial risks. Let’s explore some of the key skills required to excel in this role:
- Financial acumen: A strong understanding of financial markets, instruments, and concepts is crucial for a Financial Risk Manager. They should have knowledge of financial statements, risk assessment techniques, and valuation methods. They should also stay updated on industry trends, regulatory changes, and best practices.
- Analytical and problem-solving skills: Financial Risk Managers need strong analytical skills to analyze complex data, identify patterns, and make informed decisions. They should be able to assess risks and their potential impact on financial performance. Additionally, they should have strong problem-solving skills to develop effective risk management strategies and mitigate potential threats.
- Risk assessment and management: A deep understanding of risk assessment and management techniques is essential for a Financial Risk Manager. They should be able to identify various types of risks, such as market risk, credit risk, liquidity risk, operational risk, and regulatory risk. They should also have the ability to assess the likelihood and impact of these risks on the organization.
- Attention to detail: Financial risk management requires meticulous attention to detail. Financial Risk Managers need to analyze large volumes of data, identify potential inconsistencies or anomalies, and ensure accuracy in their risk assessments. They should have a keen eye for detail to identify potential risks that may be overlooked by others.
- Communication and presentation skills: Financial Risk Managers need to effectively communicate complex risk-related information to various stakeholders. They should have excellent written and verbal communication skills to convey their findings, recommendations, and insights in a clear and concise manner. They should also be able to present information in a visually appealing and engaging way.
- Decision-making and judgment: Financial Risk Managers often face situations where they need to make quick and well-informed decisions. They should have strong judgment skills to assess risks, evaluate potential outcomes, and make strategic decisions that align with the organization’s goals and risk appetite. They should consider both quantitative and qualitative factors in their decision-making process.
- Ethical and professional conduct: Financial Risk Managers deal with sensitive financial information and have a fiduciary responsibility towards the organization. They should adhere to high ethical standards and maintain strict confidentiality. They should also demonstrate professionalism, integrity, and accountability in their work.
- Adaptability and resilience: The financial landscape is constantly evolving, and Financial Risk Managers should be able to adapt to changes and challenges. They should have the ability to quickly grasp new concepts, understand emerging risks, and adjust risk management strategies accordingly. They should also be resilient in the face of setbacks and be proactive in finding solutions.
Developing and honing these skills through experience, education, and professional development opportunities will help aspiring Financial Risk Managers excel in their roles and make meaningful contributions to organizations.
Steps to Become a Financial Risk Manager
Becoming a Financial Risk Manager requires a combination of education, experience, and professional certifications. If you’re interested in pursuing a career in this field, here are the steps you can take:
- Educational foundation: Obtain a bachelor’s degree in finance, economics, or a related field. A strong understanding of financial principles and concepts is essential for a Financial Risk Manager.
- Gain industry knowledge and experience: Seek internships or entry-level positions in financial institutions, such as banks, insurance companies, or investment firms. This will provide you with practical knowledge of financial markets, products, and risk management practices.
- Develop analytical skills: Enhance your analytical skills by learning statistical analysis, quantitative methods, and financial modeling. Proficiency in data analysis tools, such as Excel, is crucial for a Financial Risk Manager.
- Pursue advanced education: Consider pursuing a master’s degree in finance, economics, or risk management. This will provide you with a deeper understanding of financial principles and advanced risk management techniques.
- Obtain professional certifications: Consider earning professional certifications relevant to financial risk management, such as the Certified Financial Risk Manager (FRM) designation. These certifications demonstrate your expertise and enhance your credibility in the field.
- Gain practical experience: Seek opportunities to work on risk management projects or collaborate with risk management teams within your organization. This hands-on experience will help you develop practical skills and knowledge in assessing and managing financial risks.
- Continuing education: Stay updated on industry trends, regulations, and best practices through continuous learning. Attend seminars, workshops, and conferences related to financial risk management and join professional organizations in the field.
- Network and build connections: Engage in professional networking by attending industry events and connecting with professionals in the field. Networking can provide valuable insights, job opportunities, and mentorship.
- Apply for Financial Risk Manager positions: Once you have gained the necessary education, certifications, and experience, start applying for Financial Risk Manager roles in organizations that align with your career goals and interests.
- Continuously improve: As a Financial Risk Manager, never stop learning and evolving. Stay updated on emerging risks, market trends, and regulatory changes. Continuously enhance your skills and adapt your risk management strategies to the evolving financial landscape.
By following these steps and staying committed to professional growth, you can build a successful career as a Financial Risk Manager and make valuable contributions to the organizations you serve.
Career Opportunities for Financial Risk Managers
Financial Risk Managers have a wide range of career opportunities across various industries. Here are some of the potential career paths for individuals in this field:
- Banking and Financial Institutions: Financial Risk Managers are highly sought after in banks and financial institutions. They play a crucial role in managing risks associated with lending, investment portfolios, and regulatory compliance. They assess credit risk, market risk, and liquidity risk to ensure the stability and profitability of the organization.
- Insurance Companies: Insurance companies rely on Financial Risk Managers to assess and manage risks associated with their underwriting and investment activities. These professionals analyze risks related to claims and policy coverage while also evaluating investment risks to safeguard the financial position of the company.
- Consulting Firms: Many consulting firms provide risk management services to clients across industries. Financial Risk Managers in consulting firms work closely with clients to identify and mitigate risks, develop risk management strategies, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Investment Firms: Financial Risk Managers in investment firms focus on analyzing risks associated with investment decisions. They assess market risks, perform due diligence on potential investments, and develop risk mitigation strategies. They also monitor market trends and adjust investment portfolios accordingly.
- Corporate Risk Management Departments: Large corporations often have dedicated risk management departments, where Financial Risk Managers play a vital role. They assess and mitigate risks across various areas, including finance, operations, supply chain, and compliance. Effective risk management helps protect the organization’s assets and ensures long-term financial success.
- Government and Regulatory Bodies: Financial Risk Managers are also in demand in government agencies and regulatory bodies. They assess systemic risks in financial markets, develop risk management policies, and ensure compliance with regulations. They contribute to the stability and integrity of the financial system.
- Academia and Research: Some Financial Risk Managers choose to pursue careers in academia, conducting research and teaching risk management principles. They contribute to the academic knowledge base and help shape the future generation of risk management professionals.
- Entrepreneurship and Risk Consulting: Experienced Financial Risk Managers with strong business acumen may choose to start their own risk consulting firms or provide independent risk consulting services. They offer specialized risk management advice and solutions to clients across industries.
As the importance of financial risk management continues to grow, the demand for skilled professionals in this field is expected to increase. Financial Risk Managers can find rewarding careers in a variety of industries, making a significant impact on the financial stability and success of organizations.
Challenges Faced by Financial Risk Managers
While a career as a Financial Risk Manager can be rewarding, it also comes with its own set of challenges. Here are some of the challenges that these professionals often face:
- Complex and evolving financial landscape: Financial Risk Managers operate in a complex and ever-changing financial environment. They need to stay updated on market trends, financial regulations, and emerging risks to effectively identify and manage potential threats.
- Data availability and quality: Gathering accurate and reliable data is crucial for risk management. However, obtaining timely and relevant data can be challenging. Financial Risk Managers must navigate data limitations, such as incomplete or inconsistent data, to make informed risk assessments.
- Balancing risk and reward: Financial Risk Managers face the challenge of balancing risk and reward in decision-making. They need to strike a balance between taking on enough risk to achieve growth and profitability while avoiding excessive risk exposure that could lead to significant losses.
- Managing multiple types of risks: Financial Risk Managers must be well-versed in managing various types of risks, including market risk, credit risk, liquidity risk, operational risk, and regulatory risk. Juggling these different types of risks and developing comprehensive risk management strategies can be a complex task.
- Uncertainty and unpredictability: Financial markets are inherently unpredictable, and unforeseen events can significantly impact an organization’s risk profile. Financial Risk Managers must be prepared for unexpected events, such as economic downturns, natural disasters, or geopolitical crises, and be able to adjust risk management strategies accordingly.
- Communicating risk-related information: Effectively articulating complex risk-related information to stakeholders can be challenging. Financial Risk Managers need to convey risks, their potential impact, and risk mitigation strategies in a clear and concise manner that can be understood by individuals with varying levels of financial knowledge.
- Regulatory compliance: Financial Risk Managers must navigate a complex landscape of regulations and ensure compliance with legal requirements. Staying updated on regulatory changes and adapting risk management practices accordingly can be demanding, especially in highly regulated industries.
- Pressure to perform: Financial Risk Managers often face pressure to make accurate risk assessments and implement effective risk management strategies. The consequences of poor risk management can be significant, leading to financial losses and negative impacts on the organization’s reputation.
- Balancing short-term and long-term goals: Financial Risk Managers need to balance the organization’s short-term financial objectives with long-term sustainability. This requires finding a middle ground between risk-taking for immediate gains and prioritizing risk mitigation for long-term stability.
Despite these challenges, skilled Financial Risk Managers can navigate the complexities and uncertainties of the financial landscape, contributing to risk-informed decision-making and helping organizations thrive in a volatile environment.
Conclusion
Financial Risk Managers play a critical role in today’s complex and dynamic financial landscape. They are responsible for identifying, assessing, and managing potential risks that can impact an organization’s financial stability. Through their expertise, they help organizations navigate uncertainties, make informed decisions, and protect their financial resources.
In this article, we explored the definition of a Financial Risk Manager and their key roles and responsibilities. We discussed the importance of financial risk management in preserving stability, enhancing decision-making, and meeting regulatory requirements. We also highlighted the essential skills required to excel in this field, such as financial acumen, analytical abilities, and communication skills.
Furthermore, we outlined the steps individuals can take to become Financial Risk Managers, including pursuing relevant education, gaining industry knowledge and experience, obtaining professional certifications, and continuously improving their skills and knowledge. We also explored the diverse career opportunities available for Financial Risk Managers in banking, insurance, consulting, and other sectors.
However, we mustn’t overlook the challenges that Financial Risk Managers face, including the complex financial landscape, data availability and quality, and the need to balance risk and reward. Additionally, they must navigate uncertainties, communicate risk-related information effectively, and stay compliant with regulatory requirements.
In conclusion, a career as a Financial Risk Manager offers exciting possibilities for individuals passionate about finance, risk management, and making a meaningful impact on organizational success. With the right skills, education, and experience, Financial Risk Managers can help organizations thrive in a constantly evolving financial landscape and safeguard their financial stability for the long term.