
Finance
Where To Find AGI On An IRS Transcript
Published: October 30, 2023
Looking for AGI on an IRS transcript? Find out where to locate it easily. Get all the essential finance information you need with our step-by-step guide.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Overview
When it comes to filing taxes, understanding your Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) is crucial. Your AGI is an important figure that determines eligibility for tax credits, deductions, and other financial benefits. It also serves as a benchmark for determining the income tax you owe or the tax refund you may receive.
In order to locate your AGI, you will need to refer to your IRS transcript. An IRS transcript is a detailed record of your past tax returns, including income, deductions, and tax payments. It provides a comprehensive overview of your financial history with the IRS.
Obtaining an IRS transcript is relatively simple and can be done online, by mail, or through the IRS hotline. Once you have the transcript in hand, you can locate your AGI and use it for various purposes, such as applying for financial aid, verifying income for a mortgage or loan, or even completing future tax returns.
However, navigating an IRS transcript can be overwhelming, especially if you are unfamiliar with the document’s structure and terminology. In this article, we will guide you through the process of finding your AGI on an IRS transcript, providing helpful tips and insights along the way to ensure a smooth experience.
Understanding AGI
Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) refers to the total amount of income you earned during a tax year, minus certain deductions and exemptions. It is a key calculation that determines your taxable income and your eligibility for various tax benefits. Understanding AGI is essential for accurately assessing your financial situation and fulfilling your tax obligations.
To calculate your AGI, you start with your total income, which includes wages, salaries, tips, interest income, dividends, and other sources of earnings. From this total, you subtract specific deductions, such as student loan interest, alimony payments, and contributions to retirement accounts. The resulting figure is your AGI.
AGI serves as the starting point for determining your taxable income. After calculating your AGI, you can further reduce your tax liability by claiming additional deductions and credits specific to your circumstances.
Understanding your AGI is important for several reasons:
- Tax purposes: Your AGI determines your tax bracket and the amount of tax you owe. It also influences eligibility for certain tax credits and deductions.
- Financial aid: When applying for financial aid for education, your AGI is considered in assessing your need for assistance.
- Loans and mortgages: Lenders often request your AGI to verify your income when you apply for loans or mortgages.
- Income verification: AGI may be required to verify income when applying for government assistance programs, subsidies, or grants.
- Rollovers and conversions: If you are considering rolling over a retirement account or converting a traditional IRA to a Roth IRA, your AGI will play a role in determining the tax implications.
Having a clear understanding of your AGI allows you to make informed financial decisions and ensure accurate reporting on your tax returns. It is a critical figure that affects your overall financial well-being.
Why AGI is Important
Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) is an important measure that has significant implications for your tax liability and eligibility for various tax benefits. Understanding why AGI is important can help you navigate the complexities of the tax system and make informed financial decisions.
Here are some key reasons why AGI holds significance:
- Tax calculations: AGI serves as a starting point for calculating your taxable income. By subtracting deductions and exemptions from your total income, you arrive at your AGI. This figure determines which tax bracket you fall into and helps determine the amount of tax you owe.
- Tax credits and deductions: Many tax credits and deductions have income limitations based on your AGI. For example, certain education credits, like the Lifetime Learning Credit or the American Opportunity Credit, have phase-out limits that reduce the credit as your AGI increases. Itemized deductions, such as medical expenses or mortgage interest, may also be subject to limitations based on AGI.
- Eligibility for tax benefits: AGI plays a crucial role in rendering you eligible for various tax benefits. This includes claiming certain deductions, credits, exemptions, and other tax advantages that can significantly reduce your overall tax liability.
- Filing status: AGI influences the determination of your filing status. Whether you can file as single, married filing jointly, married filing separately, or head of household can depend on your AGI.
- Financial planning: Knowing your AGI allows you to plan your finances more effectively. Whether you are saving for retirement, considering investments, or applying for loans, understanding your AGI helps you make informed decisions about your financial future.
Ultimately, AGI is a crucial metric that provides a snapshot of your financial situation, enabling accurate tax calculations and eligibility assessments for various tax benefits. It impacts your tax liability, determines your filing status, and plays a significant role in your financial planning endeavors.
By understanding the importance of AGI, you can approach your tax and financial matters with confidence, maximizing your tax benefits and ensuring compliance with the tax laws.
How to Obtain an IRS Transcript
Obtaining an IRS transcript is a relatively straightforward process that allows you to access important information regarding your tax history, including your Adjusted Gross Income (AGI). There are several methods you can use to obtain your transcript:
- Online: The quickest and most convenient way to obtain an IRS transcript is through the IRS website. Visit the “Get Transcript” page and follow the prompts to request either an electronic copy or a mailed copy of your transcript. You will need to provide personal identification information and answer a series of verification questions to authenticate your identity.
- By mail: If you prefer to receive a hard copy of your IRS transcript, you can request it by mail. Complete Form 4506-T, Request for Transcript of Tax Return, and mail it to the appropriate IRS address listed on the form. It may take several weeks to receive your transcript via mail.
- Phone: You can also request your transcript by calling the IRS hotline at 1-800-908-9946. Follow the automated prompts to request your transcript, and be prepared to answer verification questions to authenticate your identity.
To ensure a smooth and successful request for your transcript, it is important to have the following information on hand:
- Social Security Number (SSN)
- Date of birth
- Filing status and mailing address from your most recent tax return
- Access to a mobile phone or email address for verification purposes
Keep in mind that there may be certain limitations and requirements for obtaining your IRS transcript, depending on your specific circumstances. It is advisable to consult the IRS website or seek professional assistance if you encounter any difficulties during the process.
Once you have successfully obtained your IRS transcript, you will have access to valuable information, including your AGI, that can be used for various financial and tax-related purposes.
What Information is Included on an IRS Transcript
An IRS transcript provides a wealth of information about your tax history and financial records. While the specific details may vary depending on the type of transcript requested, here are some common elements you can expect to find:
- Tax return information: This includes details about your filing status, the type of return filed (e.g., Form 1040, Form 1099), and the tax year for which the transcript is issued.
- AGI and income: One of the key pieces of information found on an IRS transcript is your Adjusted Gross Income (AGI). This figure represents your total income minus certain deductions and exemptions. It is an important metric used for tax calculations and eligibility assessments for various tax benefits.
- Tax payments and refunds: The transcript provides a record of any tax payments you made and any refunds issued by the IRS. It shows the date and amount of each payment or refund, allowing you to track your financial transactions with the IRS.
- Estimated tax payments: If you made estimated tax payments throughout the tax year, those payments will be listed on the transcript. This information can be helpful when reconciling your tax liabilities and ensuring accurate reporting.
- Penalties and interest: The transcript may also indicate if you incurred any penalties or interest charges on your tax liabilities. This information can be valuable in understanding any additional amounts owed or paid to the IRS.
- IRS account activity: The transcript provides a summary of IRS account activity, including any adjustments made to your tax return, notices issued by the IRS, and actions taken regarding your tax account.
It is worth noting that there are different types of IRS transcripts, each providing specific information based on your needs. The most common types of transcripts include the Tax Return Transcript, which provides a summary of your tax return information, and the Record of Account Transcript, which offers a more detailed overview of your tax account history.
Reviewing your IRS transcript can help you verify the accuracy of your tax records, track payments and refunds, and gather important information for financial and tax-related purposes. Understanding the information included on your transcript is valuable in maintaining compliance with tax regulations and making informed financial decisions.
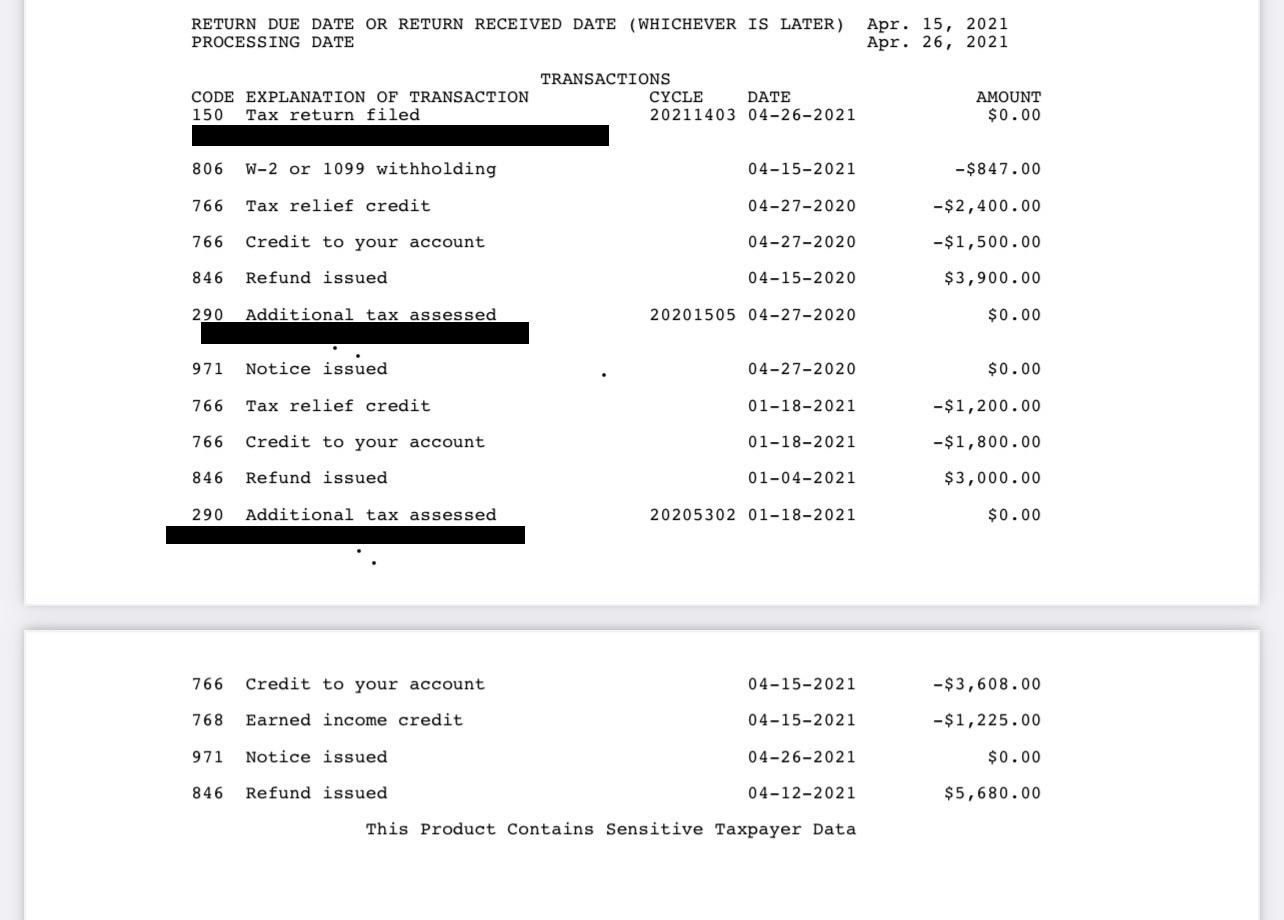
Locating AGI on an IRS Transcript
Locating your Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) on an IRS transcript may require careful navigation since the document contains various sections and codes. However, by following a few simple steps, you can easily find your AGI:
- First, obtain your IRS transcript using one of the methods mentioned earlier – either online, by mail, or by phone. Ensure you have the correct tax year and transcript type.
- Once you have your transcript, locate the “Adjusted Gross Income” line or code. This line may differ depending on the type of transcript you obtained, but it is generally labeled as “AGI.”
- Next, examine the corresponding value or number next to the AGI code. This value represents your Adjusted Gross Income for the tax year specified on the transcript.
- If you are unable to locate the exact line or code labeled “AGI,” look for any sections or codes that indicate your total income or income adjustments. The AGI is typically calculated by subtracting specific deductions and adjustments from your total income.
Remember to refer to the instructions or guides provided along with the transcript if you encounter any difficulties in locating the AGI. These guides often provide explanations and definitions for the codes and sections within the document.
Additionally, it’s important to ensure that you are looking at the correct tax year’s transcript if you have multiple years of tax history. Each transcript will contain the AGI specific to that tax year.
Once you have successfully located your AGI on the IRS transcript, you can utilize it for various financial and tax-related purposes, such as filing future tax returns, applying for loans or mortgages, or verifying income for government assistance programs.
If you are still having trouble finding your AGI on the transcript or need further clarification, it is always recommended to consult with a tax professional or contact the IRS directly for assistance.
Tips for Finding AGI on an IRS Transcript
Locating your Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) on an IRS transcript can be a bit challenging due to the document’s complexity. However, with these helpful tips, you can streamline your search and find your AGI more easily:
- Read the transcript headings: Familiarize yourself with the layout and structure of the IRS transcript. Pay attention to the headings and section titles, as they can guide you to the relevant information.
- Look for summary sections: The IRS transcript often includes summary sections that provide an overview of key figures, such as your total income, deductions, and adjustments. These sections may explicitly mention your AGI or provide the necessary information to calculate it.
- Refer to the transcript codes: The transcript may contain specific codes that represent different types of income, deductions, or adjustments. Search for codes related to AGI, such as code 37, which typically corresponds to the AGI line. Use the code cross-reference guide provided with the transcript to locate the correct section.
- Check adjacent values: If you are unable to find a line or code explicitly labeled as AGI, examine the values or numbers next to income-related lines or codes. Look for any figures that represent your total income or income adjustments, as the AGI is calculated by subtracting adjustments from total income.
- Consult IRS resources: If you encounter difficulty in finding your AGI, consult the IRS website or publications for further guidance. The IRS provides resources and tutorials that explain how to interpret and navigate the transcript.
- Consider professional assistance: If you have exhausted your efforts and are still unable to locate your AGI, consider seeking the help of a tax professional. Tax experts have experience in working with IRS transcripts and can assist you in finding the necessary information.
Remember, patience and attention to detail are key when searching for your AGI on an IRS transcript. Take your time to carefully review the document and utilize the available resources to ensure accuracy.
By following these tips, you can successfully locate your AGI on the IRS transcript and utilize this critical information for various financial and tax-related purposes.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
While obtaining and locating your Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) on an IRS transcript is usually a straightforward process, you may encounter some common issues or face troubleshooting challenges. Here are a few common scenarios and tips to help overcome them:
1. Difficulty obtaining the IRS transcript: If you encounter difficulties obtaining your IRS transcript online, try using the alternative methods of requesting it by mail or phone. Additionally, double-check that you have entered your personal identification information accurately.
2. Incorrect tax year: Ensure that you are requesting the transcript for the correct tax year. Each year has a separate transcript, and selecting the wrong one can result in finding incorrect AGI information.
3. Inaccessibility of online transcript: If you are having trouble accessing your IRS transcript online, make sure you are using a supported browser and that your computer meets the necessary technical requirements. Clearing your browser cache or trying a different device can also help resolve the issue.
4. Verifying personal information: When accessing your online transcript or requesting it by phone, you may be asked to verify personal information such as your Social Security Number (SSN), date of birth, and filing status. Ensure that you have this information readily available and double-check for any typos or mistakes while entering it.
5. Incomplete or missing AGI: In some cases, your IRS transcript may not explicitly state your AGI or contain the specific line or code labeled as such. If this occurs, carefully review the income-related lines or codes adjacent to deductions and adjustments. Remember, your AGI is calculated by subtracting adjustments from your total income.
6. Professional assistance: If you have exhausted your troubleshooting efforts and are still unable to find your AGI or face persistent issues, it may be beneficial to seek assistance from a tax professional. They have experience working with IRS transcripts and can provide guidance tailored to your specific situation.
It is essential to remain patient and persistent when dealing with any issues or challenges related to obtaining and locating your AGI on an IRS transcript. Utilize the available resources, consult the IRS website, and consider seeking professional help if needed.
Remember, maintaining accurate and up-to-date tax records is vital for fulfilling your tax obligations and availing yourself of various tax benefits and financial opportunities.
Conclusion
Understanding and locating your Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) on an IRS transcript is essential for accurate tax reporting, financial planning, and accessing various tax benefits. By obtaining an IRS transcript and finding your AGI, you gain valuable insights into your tax history and can make informed financial decisions.
In this article, we discussed the importance of AGI and how it serves as a starting point for calculating your taxable income. We explored why AGI is crucial for tax purposes, financial aid applications, loan verification, and income verification. By knowing your AGI, you can navigate these areas with confidence.
We also provided step-by-step guidance on obtaining an IRS transcript through online, mail, or phone methods. Additionally, we detailed the information included on an IRS transcript, such as tax return information, AGI and income details, tax payments and refunds, and IRS account activity. Understanding this information equips you with a comprehensive overview of your tax history.
To help you locate your AGI, we provided tips for finding it on an IRS transcript, including reading the transcript headings, looking for summary sections, referring to transcript codes, and checking adjacent values. If you encounter any issues or challenges, we advised seeking professional assistance or referring to IRS resources.
Remember, maintaining accurate tax records and understanding your AGI is crucial for fulfilling your tax obligations, availing yourself of tax benefits, and making informed financial decisions. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can confidently locate your AGI and utilize it for various financial and tax-related purposes.
Always remember to consult the IRS website, publications, or seek professional advice for specific concerns or complex tax situations. With the knowledge gained from this article, you are equipped to navigate the world of AGI and IRS transcripts with ease and confidence.