Home>Finance>Where To Find Net Revenue On The Income Statement And Balance Sheet


Finance
Where To Find Net Revenue On The Income Statement And Balance Sheet
Published: March 2, 2024
Learn where to find net revenue on the income statement and balance sheet in finance. Understand the key financial metrics for analyzing business performance.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Understanding Net Revenue
Net revenue is a key financial metric that provides valuable insights into a company’s performance and financial health. It represents the total revenue generated from the sale of goods or services, minus any discounts, returns, and allowances. Essentially, net revenue is the amount of money a company actually earns from its core business activities after accounting for any deductions.
Understanding net revenue is crucial for investors, analysts, and stakeholders as it reflects the true top-line growth of a business. By analyzing net revenue, one can gauge the effectiveness of a company’s sales and pricing strategies, as well as its ability to manage expenses and maintain profitability. Additionally, net revenue is a fundamental component in various financial calculations, such as gross margin and net profit margin, making it a vital indicator of a company’s overall financial performance.
In this article, we will delve into the significance of net revenue and explore where it can be found on both the income statement and the balance sheet. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of net revenue and its implications, readers will be better equipped to assess the financial standing of a company and make informed investment decisions.
Understanding Net Revenue
Net revenue, also known as net sales or revenue, is a critical financial metric that provides a clear picture of a company’s top-line performance. It is calculated by subtracting returns, allowances, and discounts from the total revenue generated by a business. This figure represents the actual amount of money earned from primary business activities, excluding any deductions.
Net revenue is a key indicator of a company’s ability to generate income from its core operations. It reflects the effectiveness of sales strategies, pricing decisions, and overall market demand for the company’s products or services. For investors and analysts, net revenue serves as a vital measure of a company’s growth and success in the marketplace.
Furthermore, net revenue plays a crucial role in assessing a company’s financial health and performance. It serves as the starting point for calculating essential financial ratios, such as gross margin and net profit margin. These ratios provide valuable insights into a company’s profitability and operational efficiency, making net revenue a fundamental component in financial analysis.
Understanding net revenue is essential for stakeholders seeking to evaluate the strength and stability of a company. By analyzing net revenue trends over time, investors can identify patterns in sales performance and assess the company’s ability to maintain consistent revenue streams.
Overall, net revenue represents the core income generated by a business, making it a key metric for evaluating a company’s financial performance and growth prospects.
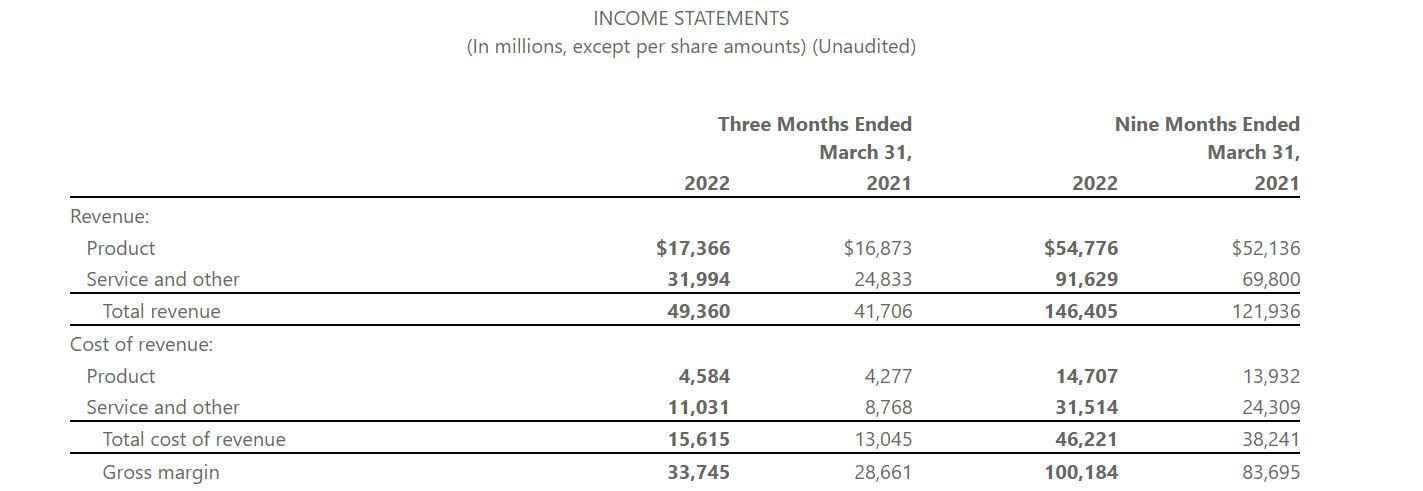
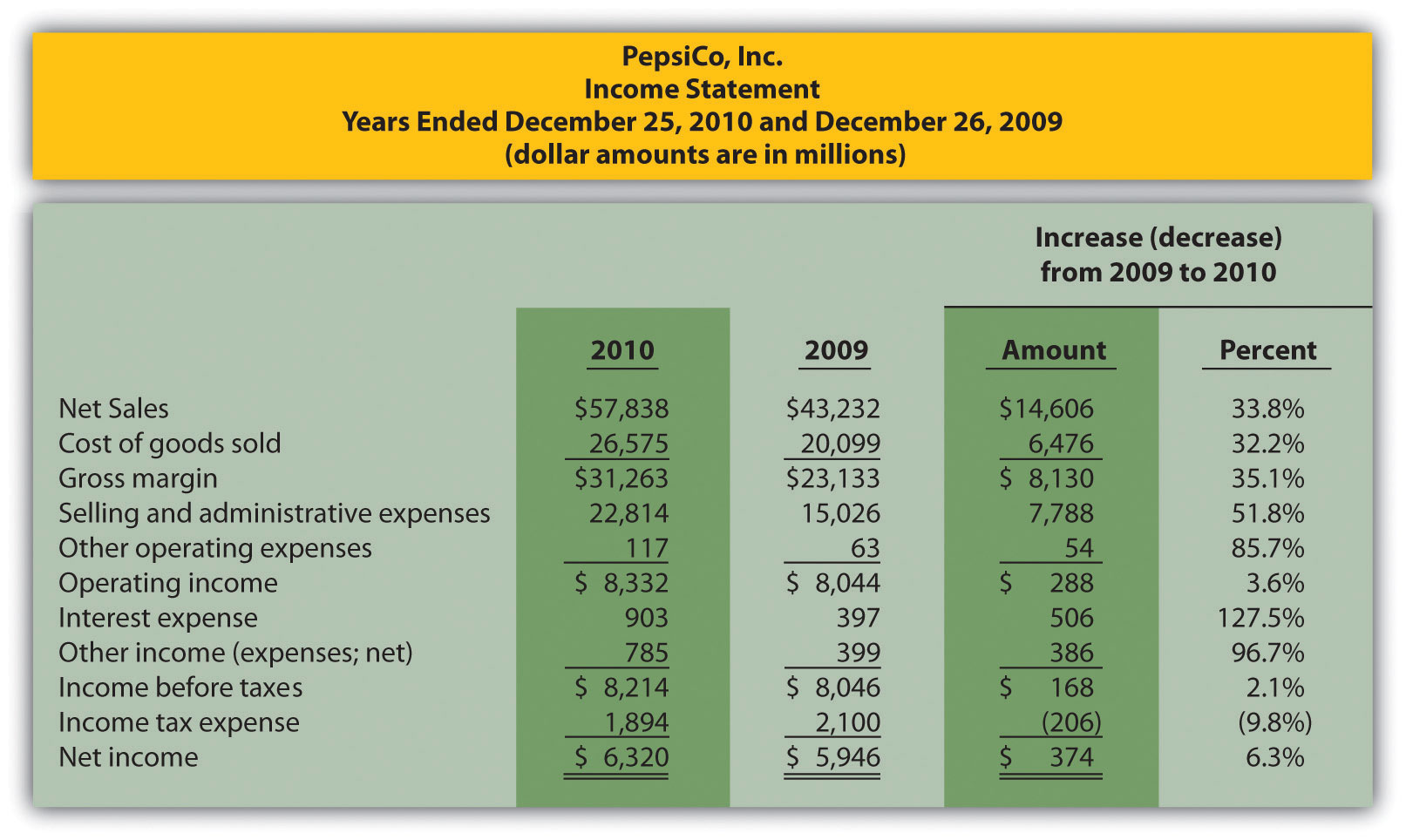
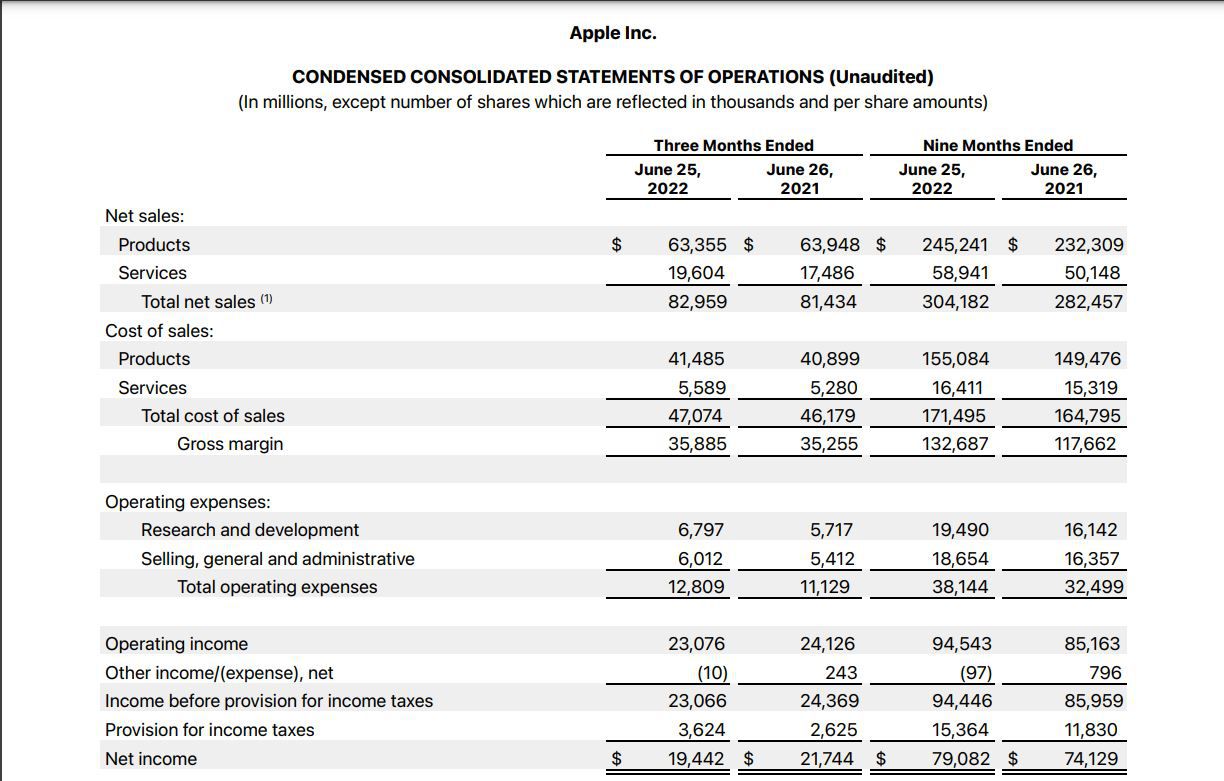
Net Revenue on the Income Statement
The income statement, also known as the profit and loss statement, provides a comprehensive overview of a company’s financial performance during a specific period. Within the income statement, net revenue holds a prominent position as it reflects the total revenue earned from core business activities after accounting for deductions.
Net revenue is typically the first line item on the income statement, representing the initial inflow of money generated by the sale of goods or services. It serves as the starting point for calculating various profitability metrics and is a primary indicator of a company’s revenue-generating capabilities.
On the income statement, net revenue is often accompanied by the cost of goods sold (COGS), which represents the direct costs associated with producing the goods sold by a company. The variance between net revenue and COGS is crucial for calculating the gross margin, a key measure of a company’s profitability.
Furthermore, the income statement provides a breakdown of operating expenses, including selling, general, and administrative expenses, as well as research and development costs. These expenses are subtracted from the net revenue to determine the operating income, reflecting the profitability of a company’s core business activities.
Net revenue on the income statement also accounts for non-operating income and expenses, such as interest income and expenses, as well as gains or losses from investments. These items contribute to the final calculation of net income, which represents the overall profitability of the company after considering all sources of revenue and expenses.
Overall, the income statement serves as a crucial financial document for investors and analysts, offering a detailed breakdown of a company’s revenue, expenses, and profitability. Net revenue, as the starting point of this financial narrative, plays a pivotal role in assessing a company’s top-line performance and growth trajectory.
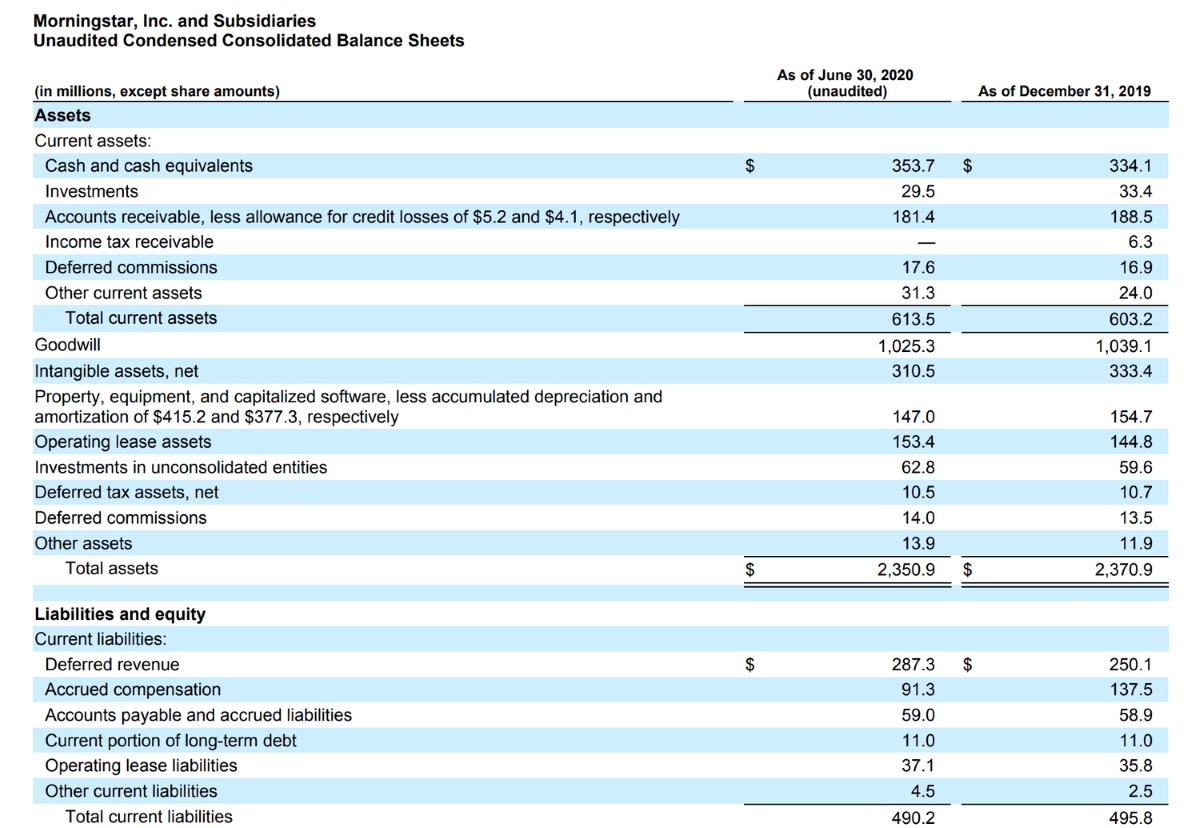
Net Revenue on the Balance Sheet
While the income statement provides a comprehensive view of a company’s financial performance over a specific period, the balance sheet offers a snapshot of its financial position at a given point in time. Although net revenue is not directly listed on the balance sheet, its impact is reflected in various components of this essential financial statement.
One of the key areas where the influence of net revenue can be observed on the balance sheet is in the form of accounts receivable. Accounts receivable represent the amounts owed to a company by its customers for goods or services delivered on credit. The net revenue generated from these transactions contributes to the accounts receivable balance, indicating the inflow of future cash into the business.
Additionally, the impact of net revenue is evident in the retained earnings section of the balance sheet. Retained earnings reflect the cumulative profits or losses of a company since its inception, adjusted for dividends and stock repurchases. The net revenue generated over time contributes to the growth of retained earnings, reflecting the overall profitability and success of the business.
Furthermore, the balance sheet showcases the impact of net revenue on the cash and cash equivalents section. The cash generated from net revenue, after accounting for operating expenses, investments, and debt obligations, is reflected in the cash reserves of the company. This liquidity position is a direct result of the net revenue earned by the business.
Moreover, the balance sheet provides insights into the long-term assets and liabilities of a company, which are influenced by the net revenue generated over time. The ability to invest in long-term assets and manage long-term liabilities is contingent upon the sustained generation of net revenue, making it a crucial factor in shaping the financial structure of a company.
Overall, while net revenue may not be explicitly stated on the balance sheet, its impact permeates various elements of this financial statement, offering a holistic view of a company’s financial standing and its ability to generate sustainable income.
Conclusion
Net revenue stands as a fundamental metric that encapsulates a company’s ability to generate income from its core business activities. Understanding the significance of net revenue is paramount for investors, analysts, and stakeholders, as it serves as a key indicator of a company’s financial performance and growth prospects.
On the income statement, net revenue takes center stage, representing the initial inflow of revenue from the sale of goods or services. It sets the foundation for calculating essential profitability metrics and offers insights into a company’s revenue-generating capabilities. The interplay between net revenue, cost of goods sold, and operating expenses provides a comprehensive view of a company’s profitability and operational efficiency.
While not explicitly listed, the impact of net revenue resonates throughout the balance sheet. From accounts receivable to retained earnings and the management of long-term assets and liabilities, the influence of net revenue shapes the financial position and structure of a company, reflecting its ability to sustain and grow its income over time.
In conclusion, net revenue serves as a vital barometer of a company’s financial health and performance. Its presence on the income statement and its ripple effect on the balance sheet offer valuable insights into the core income-generating capabilities of a business. By comprehensively analyzing net revenue, investors and stakeholders can gain a deeper understanding of a company’s revenue dynamics and make informed decisions regarding its investment potential and long-term viability.