
Finance
How To Find Total Revenue On Balance Sheet
Published: December 27, 2023
Learn how to find the total revenue on a balance sheet and gain valuable insights into finance. Discover key strategies and tools for financial analysis.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Total Revenue
- Factors Affecting Total Revenue Calculation
- Finding Total Revenue on the Balance Sheet
- Method 1: Reviewing the Income Statement
- Method 2: Analyzing the Sales and Revenue Account
- Method 3: Examining the Cash Flow Statement
- Method 4: Calculating Total Revenue through Other Financial Statements
- Example Calculation of Total Revenue
- Conclusion
Introduction
Understanding and analyzing a company’s financial performance is crucial for investors, stakeholders, and financial professionals. One important metric to consider is total revenue, which refers to the amount of money a company generates from its sales or services. Total revenue is a key indicator of a company’s ability to generate income, sustain growth, and meet financial obligations.
In this article, we will delve into the concept of total revenue and discuss how to find it on the balance sheet. We will explore various methods and financial statements that can help us calculate total revenue accurately. Whether you are an investor assessing a potential investment opportunity or a business owner monitoring your company’s financial health, understanding how to find total revenue will provide valuable insights into a company’s financial performance.
Before we dive into the details of finding total revenue, let’s gain a clear understanding of what total revenue represents. Total revenue, also known as gross revenue or sales revenue, encompasses all the income a company generates from its primary operations, such as selling products or providing services. It is an essential measure of a company’s top line performance and reflects the overall demand for its products or services.
Monitoring and analyzing total revenue can provide valuable insights into a company’s growth trajectory, market presence, and profitability. By comparing total revenue over different periods, investors and financial professionals can assess a company’s ability to generate consistent revenue streams and drive sustainable growth.
Now that we have established the significance of total revenue, let’s explore the factors that can affect its calculation on the balance sheet.
Understanding Total Revenue
Before diving into the methods of finding total revenue on the balance sheet, it is important to have a solid understanding of what total revenue represents. Total revenue is the aggregate amount of money a company generates from all its sales or services. It is a critical financial metric that provides insights into a company’s overall sales performance and revenue generation.
Total revenue is calculated by multiplying the quantity of goods or services sold by the sale price per unit. It includes revenue from both cash and credit sales, as well as any discounts, allowances, or returns. However, it does not consider the cost of goods sold (COGS) or any other expenses incurred by the company in generating that revenue. Total revenue represents the inflow of cash or accounts receivable from customers and is a key component in determining a company’s gross profit.
Monitoring total revenue is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it provides an indication of a company’s market position and overall demand for its products or services. Higher total revenue usually suggests a strong market presence and customer demand. Conversely, declining total revenue may indicate a decrease in customer interest or an adverse market condition.
Secondly, total revenue is a crucial measure for assessing a company’s ability to generate income and cover its expenses. By comparing total revenue to the company’s expenses, investors and financial professionals can evaluate its profitability and determine its financial viability.
Thirdly, total revenue is often used as a basis for calculating other important financial metrics, such as gross profit margin, operating profit, and net profit. The relationship between total revenue and these metrics provides insights into a company’s operational efficiency, cost management, and overall financial performance.
It is important to note that total revenue is different from net revenue or net sales. Net revenue deducts any sales returns, allowances, and discounts from the total revenue figure, providing a more accurate picture of the company’s revenue after accounting for these adjustments.
Understanding the concept and importance of total revenue is essential for investors, stakeholders, and financial professionals. Now, let’s explore the factors that can affect the calculation of total revenue on the balance sheet.
Factors Affecting Total Revenue Calculation
The calculation of total revenue on the balance sheet can be influenced by various factors that affect a company’s sales or revenue generation. It is important to consider these factors to accurately assess the financial performance and growth potential of a company. Let’s explore some of the key factors that can impact the calculation of total revenue:
- Pricing Strategy: The pricing strategy adopted by a company can have a significant impact on total revenue. Setting the right price for products or services is crucial to attract customers and maximize sales. Higher prices can result in higher revenue per unit sold, but it may also reduce the quantity of units sold. On the other hand, lower prices may lead to higher sales volume but lower revenue per unit. Companies must strike a balance between pricing and volume to optimize total revenue.
- Customer Demand: The level of customer demand for a company’s products or services is a critical determinant of total revenue. Changes in consumer preferences, market trends, or economic conditions can affect the demand for certain products or services. Companies must monitor and respond to these changes to ensure sustained revenue growth.
- Competition: The competitive landscape plays a significant role in total revenue calculation. The presence of direct competitors and their pricing, marketing strategies, and market share can impact a company’s revenue. Companies need to differentiate themselves through product quality, innovation, customer service, or other competitive advantages to maintain or increase their total revenue.
- Sales and Marketing Efforts: The effectiveness of a company’s sales and marketing efforts can directly impact total revenue. Well-executed marketing campaigns, effective sales strategies, and customer relationship management contribute to increased sales and revenue generation. Investing in sales training, advertising, and promotional activities can drive higher customer acquisition and retention, resulting in higher total revenue.
- Seasonality: Seasonal fluctuations can affect the calculation of total revenue for companies in certain industries. For example, retailers may experience higher sales during the holiday season, while tourism companies may have peak periods during summer months. Companies need to account for seasonal variations in their revenue forecasts and financial planning.
These are just a few examples of the factors that can influence total revenue calculation on the balance sheet. It’s important to consider these factors along with other industry-specific variables when assessing a company’s financial performance and growth potential. Now, let’s move on to the methods of finding total revenue on the balance sheet.
Finding Total Revenue on the Balance Sheet
Locating total revenue on the balance sheet requires a careful analysis of the financial statements. While total revenue is primarily reported on the income statement, it can also be derived from other financial statements such as the sales and revenue account or the cash flow statement. Let’s explore the different methods of finding total revenue on the balance sheet:
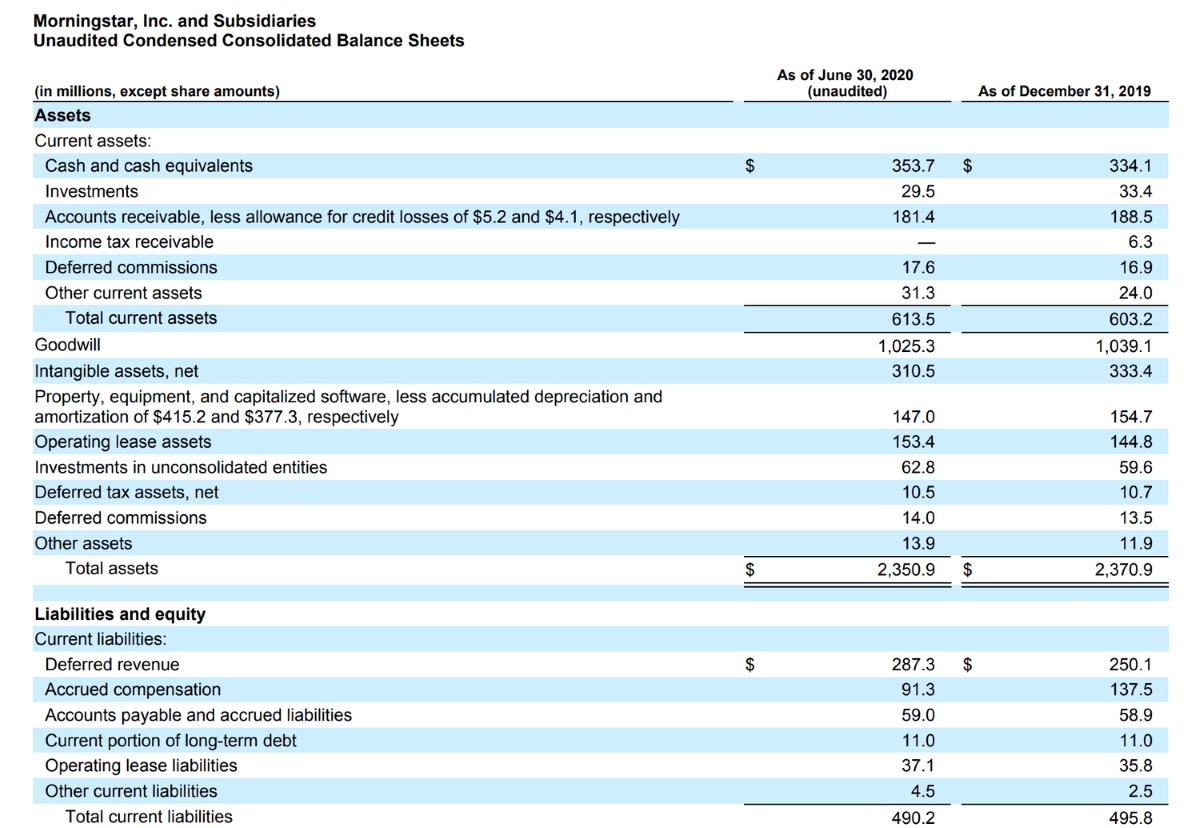
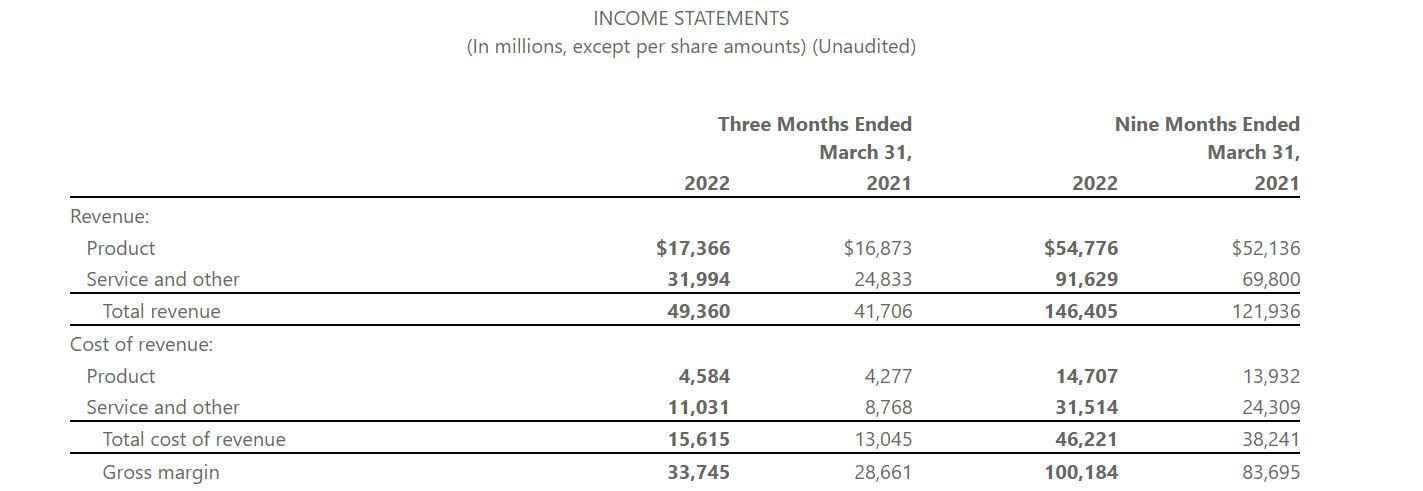
- Method 1: Reviewing the Income Statement: The income statement provides a comprehensive overview of a company’s revenue and expenses during a specific period. Total revenue is typically listed at the top under the heading “Revenue,” “Sales,” or “Net Sales.” It represents the sum of all sales or services rendered by the company during that period. The income statement also reveals other important metrics such as the cost of goods sold (COGS), gross profit, operating expenses, and net profit.
- Method 2: Analyzing the Sales and Revenue Account: Some companies may maintain a separate sales and revenue account within their financial statements. This account provides a detailed breakdown of different sources of revenue, such as product sales, service revenue, licensing fees, or royalties. Total revenue can be calculated by summing up the values reported in the sales and revenue account.
- Method 3: Examining the Cash Flow Statement: The cash flow statement provides insights into a company’s cash inflows and outflows. While it does not directly report total revenue, it can indirectly help in calculating total revenue. By analyzing the operating activities section of the cash flow statement, one can identify the cash received from customers for sales or services rendered. This figure can be used as an estimate of total revenue.
- Method 4: Calculating Total Revenue through Other Financial Statements: In some cases, total revenue may not be explicitly stated in the financial statements. However, it can be calculated using information provided in other financial statements. For example, one can derive total revenue by subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from the gross profit reported on the income statement.
It is important to note that the specific location of total revenue may vary depending on the company and the reporting framework followed. Therefore, it is advisable to carefully review the financial statements, including the income statement, sales and revenue account, and the cash flow statement, to accurately locate and calculate total revenue on the balance sheet.
Now that we have explored the methods of finding total revenue on the balance sheet, let’s move on to an example calculation to illustrate the process.
Method 1: Reviewing the Income Statement
The income statement is a primary financial statement that provides a comprehensive overview of a company’s revenue and expenses during a specific period. This statement is a key source for finding total revenue on the balance sheet. Let’s delve into the process of locating and calculating total revenue using the income statement:
1. Locating Total Revenue: On the income statement, total revenue is typically listed at the top, under the heading “Revenue,” “Sales,” or “Net Sales.” It represents the sum of all sales or services rendered by the company during the period being reported.
2. Understanding Revenue Breakdown: Carefully review the income statement to understand the breakdown of revenue sources. Companies may generate revenue from various sources such as product sales, service revenue, licensing fees, or royalties. Analyzing the revenue breakdown can provide insights into the company’s primary revenue drivers.
3. Calculating Total Revenue: Total revenue can be determined by adding up the individual revenue figures reported in the income statement. Ensure that all relevant revenue sources are considered in the calculation. If there are multiple revenue streams, sum up the values to obtain the total revenue figure.
4. Additional Considerations: While calculating total revenue from the income statement, it is important to understand any adjustments or specific reporting practices followed by the company. Some companies may report net revenue or net sales, which deducts returns, allowances, and discounts from the total revenue figure. Make sure to account for any adjustments to derive the accurate total revenue.
By carefully reviewing and analyzing the income statement, investors, stakeholders, and financial professionals can locate total revenue and gain insights into a company’s sales performance and revenue generation capabilities. The income statement also provides additional information such as the cost of goods sold (COGS), gross profit, operating expenses, and net profit, which offer a holistic view of the company’s financial performance.
Now that we have explored the method of finding total revenue through the income statement, let’s move on to the next method of analyzing the sales and revenue account.
Method 2: Analyzing the Sales and Revenue Account
In addition to the income statement, some companies maintain a separate sales and revenue account within their financial statements. This account provides a detailed breakdown of different sources of revenue, such as product sales, service revenue, licensing fees, or royalties. Analyzing the sales and revenue account can be another effective method of finding total revenue on the balance sheet. Let’s explore the process:
1. Locating the Sales and Revenue Account: Look for the sales and revenue account in the financial statements. It is usually listed under the income statement or the statement of comprehensive income section.
2. Analyze Revenue Breakdown: Within the sales and revenue account, review the individual revenue sources and their respective values. This breakdown provides a detailed overview of the company’s primary revenue streams and their contribution to total revenue.
3. Summing Up the Revenue Sources: To calculate total revenue, sum up the values reported in the sales and revenue account. Ensure that you include all the relevant revenue sources mentioned in the account. This will give you the total revenue generated by the company.
4. Understanding Adjustments and Reporting Practices: Take note of any adjustments or specific reporting practices followed by the company. Some companies may report net revenue or net sales in the sales and revenue account. This figure deducts returns, allowances, and discounts from the total revenue. Make sure to consider any adjustments to derive the accurate total revenue.
Analyzing the sales and revenue account provides a more granular view of a company’s revenue sources and their impact on total revenue. It allows investors and financial professionals to identify the primary drivers of revenue generation and gain insights into the company’s market presence and sales performance.
In the next section, we will explore another method of finding total revenue on the balance sheet by examining the cash flow statement.
Method 3: Examining the Cash Flow Statement
In addition to the income statement and the sales and revenue account, the cash flow statement provides valuable insights into a company’s cash inflows and outflows. While the cash flow statement does not directly report total revenue, it can indirectly assist in estimating total revenue. Let’s explore how to find total revenue by examining the cash flow statement:
1. Locating the Cash Flow Statement: Find the cash flow statement within the company’s financial statements. It is typically presented as a separate statement or as a section of the statement of cash flows within the financial report.
2. Analyzing the Operating Activities Section: Within the cash flow statement, focus on the operating activities section. This section provides insights into the company’s cash transactions related to its core operations, including customer payments for sales or services.
3. Identifying Cash Inflows from Sales: Scan the operating activities section to identify the cash inflows related to sales or services. Look for line items such as “cash received from customers” or “sales revenue” that signify cash received from sales or services rendered by the company.
4. Estimating Total Revenue: Once you have identified the cash inflows from sales in the operating activities section, you can use this figure as an estimate of total revenue. While it may not capture all revenue sources, it provides a close approximation of the cash received from customers for the period.
It is important to note that the cash flow statement reflects actual cash inflows and outflows, which may differ from the revenue recognized on the income statement. Factors such as credit sales or delayed cash receipts can impact the timing of revenue recognition on the income statement. However, the cash flow statement can give a clear indication of the cash inflows related to sales or services.
By examining the cash flow statement, investors and financial professionals can obtain insights into the company’s cash flows and derive an estimate of total revenue. However, it is recommended to combine this method with others, such as reviewing the income statement or analyzing the sales and revenue account, to gain a comprehensive understanding of total revenue on the balance sheet.
In the next section, we will explore an additional method of calculating total revenue by using information from other financial statements.
Method 4: Calculating Total Revenue through Other Financial Statements
In some cases, total revenue may not be explicitly stated in the financial statements. However, it can be calculated by utilizing information provided in other financial statements. This method allows investors and financial professionals to derive total revenue by considering specific financial metrics and relationships. Let’s explore how to calculate total revenue through other financial statements:
1. Using the Gross Profit Figure: Locate the gross profit figure on the income statement. Gross profit represents the revenue remaining after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS). By adding the COGS figure back to the gross profit, you can derive the total revenue. This method assumes that all other expenses, such as operating expenses, are already accounted for in the COGS and gross profit calculations.
2. Utilizing the Balance Sheet: Analyze changes in specific balance sheet items to infer total revenue. For example, reviewing the accounts receivable balance and comparing it to the previous period can provide insights into the sales made during the period. By considering the change in accounts receivable and factoring in credit sales and collections, you can estimate the total revenue for the period.
3. Considering the Retained Earnings: If the company does not explicitly report total revenue, you can analyze the retained earnings account on the balance sheet. Retained earnings represent the accumulated profits or losses of the company since its inception. By comparing the retained earnings at the end of the period with the retained earnings at the beginning, and accounting for any dividends or changes in capital, you can calculate the total revenue for the period.
It is important to note that these methods provide estimates of total revenue based on specific financial statement relationships. They may not capture all revenue sources or adjustments made within the financial statements. Therefore, it is advisable to combine these methods with other approaches, such as reviewing the income statement or analyzing the sales and revenue account, to ensure a comprehensive understanding of total revenue on the balance sheet.
In the next section, we will provide an example calculation of total revenue to illustrate the concepts discussed.
Example Calculation of Total Revenue
To illustrate how total revenue can be calculated, let’s consider a hypothetical company, ABC Electronics, and walk through the process of deriving its total revenue:
1. Reviewing the Income Statement: Start by locating the income statement of ABC Electronics. Scan the statement to find the figure labeled as “Net Sales” or “Total Revenue.” Let’s assume that ABC Electronics reports a net sales figure of $5,000,000.
2. Considering Adjustments: Take note of any adjustments mentioned in the income statement. If there are adjustments such as returns, allowances, or discounts, make sure to deduct them from the net sales figure. For example, if returns and allowances amount to $200,000, the adjusted net sales figure would be $4,800,000.
3. Examining the Sales and Revenue Account: If ABC Electronics provides a separate sales and revenue account, analyze the breakdown to identify specific revenue sources. Let’s assume that the sales and revenue account lists product sales of $4,000,000 and service revenue of $1,000,000. Summing up these figures gives us a total revenue of $5,000,000.
4. Analyzing the Cash Flow Statement: Turn to the cash flow statement to understand the operating activities section. If the operating activities section indicates that $4,500,000 was received from customers as cash inflows, it can be considered as an estimate of the total revenue for the period.
In this example, we have utilized different methods to calculate total revenue for ABC Electronics. The income statement, the sales and revenue account, as well as the cash flow statement, have provided us with various figures that can be used to derive the total revenue. The final total revenue calculation will depend on the specific information available in the financial statements and the reporting practices followed by the company.
Calculating total revenue through these methods allows investors and financial professionals to gain a comprehensive understanding of a company’s performance and revenue generation. It provides insights into the company’s sales trends, market presence, and growth potential.
Next, let’s summarize the key points discussed in this article.
Conclusion
Understanding how to find total revenue on the balance sheet is essential for investors, stakeholders, and financial professionals. Total revenue represents the aggregate amount of money a company generates from its sales or services and is a key indicator of a company’s financial performance and growth potential.
In this article, we explored various methods of finding total revenue on the balance sheet. We discussed the importance of understanding total revenue and how it reflects a company’s market presence and revenue generation capabilities. We also highlighted the factors that can affect total revenue calculation, such as pricing strategy, customer demand, competition, sales and marketing efforts, and seasonality.
We then explained the different methods of finding total revenue on the balance sheet. These methods included reviewing the income statement, analyzing the sales and revenue account, examining the cash flow statement, and deriving total revenue through other financial statements.
By carefully analyzing these financial statements, investors and financial professionals can accurately calculate total revenue and gain insights into a company’s revenue sources, growth trajectory, and financial health. It is important to consider any adjustments made within the financial statements and to use multiple methods for a comprehensive understanding of total revenue.
In conclusion, total revenue is a critical metric for evaluating a company’s financial performance. By understanding how to find total revenue on the balance sheet, investors and financial professionals can make more informed investment decisions, assess a company’s growth potential, and evaluate its ability to generate sustained revenue streams.
Remember, total revenue is just one aspect of a company’s financial analysis. It is important to consider it in conjunction with other financial metrics, industry trends, and qualitative factors to paint a complete picture of a company’s financial health and prospects.