Finance
What Is Surrender Value Of Life Insurance?
Published: November 29, 2023
Learn about the surrender value of life insurance and how it impacts your financial plans. Discover the benefits and considerations associated with this key aspect of your insurance policy.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Surrender Value
- Calculation of Surrender Value
- Factors Affecting Surrender Value
- Surrender Value vs Cash Value
- Importance of Surrender Value
- Surrender Value for Different Types of Life Insurance Policies
- Surrender Value: Pros and Cons
- Surrender Value and Policyholder’s Rights
- Surrender Value and Tax Implications
- Surrender Value: Considerations Before Surrendering
Introduction
Welcome to the world of life insurance, where every policy comes with its own set of terms, conditions, and benefits. One important aspect of life insurance that every policyholder should be aware of is the surrender value. The surrender value is the amount of money that a policyholder receives if they choose to surrender or terminate their life insurance policy before its maturity or the end of the policy term.
Surrendering a life insurance policy is a decision that should not be taken lightly, as it has both financial and long-term implications. Understanding the concept of surrender value is crucial for any policyholder who may be considering this option.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of surrender value, including its calculation, factors affecting it, and its importance in the context of different types of life insurance policies. We will also explore the pros and cons of surrendering a policy, along with the policyholder’s rights and tax implications associated with surrender value.
Whether you are a new policyholder or have had a life insurance policy for some time, understanding surrender value will empower you to make well-informed decisions regarding your policy. So let’s dive into the world of surrender value and discover how it can impact your financial future in unexpected ways.
Understanding Surrender Value
Surrender value is the amount of money that a policyholder is entitled to receive if they choose to surrender their life insurance policy before its maturity or the end of the policy term. This value is determined by the insurance company and is a reflection of the accumulated cash value of the policy. Cash value refers to the amount of money that has been invested and grown within the policy over time.
Surrender value serves as a form of financial compensation for the policyholder in exchange for giving up their rights to the policy. Essentially, it is the policyholder’s right to access the funds that have been accumulated in the policy, minus any applicable fees or charges set by the insurance company.
It’s important to note that surrendering a policy means you are opting out of the life insurance coverage provided by the policy. This means that, once the policy is surrendered, you will no longer receive any death benefit or other benefits associated with the policy. Surrendering a policy should be carefully considered, as it can have long-term implications on your financial protection and goals.
The surrender value is typically lower than the total premiums paid by the policyholder. This is due to various factors, such as administrative fees, mortality charges, and other deductions that may be applied by the insurance company. The surrender value may also be affected by the length of time the policy has been in force, the type of policy, and the performance of the underlying investment funds.
It’s important to understand that surrender value is different from the cash value of a policy. While surrender value refers to the amount that can be obtained upon surrendering the policy, the cash value refers to the amount of money that has built up within the policy over time. The cash value can be used for various purposes, such as taking out a loan against the policy or making premium payments.
Now that we have a basic understanding of surrender value, let’s take a closer look at how it is calculated and the factors that can affect it.
Calculation of Surrender Value
The calculation of surrender value can vary from one insurance company to another, as different companies may have their own specific formulas and methods. However, there are some general principles that are commonly used in the industry when determining the surrender value of a life insurance policy.
The surrender value is typically calculated based on the cash value of the policy. The cash value represents the total amount of money that has accumulated within the policy, taking into account factors such as premiums paid, interest earned, and any deductions or charges. Insurance companies may also consider factors such as the policyholder’s age, the length of time the policy has been in force, and the type of policy.
Insurance companies use a variety of methods to calculate the surrender value, such as the “cash surrender value” method or the “net surrender value” method. The cash surrender value method calculates the surrender value by subtracting any outstanding policy loans, outstanding premiums, or fees from the cash value. The net surrender value method takes into account the same factors but may also consider additional adjustments, such as surrender charges or market value adjustments.
It is important for policyholders to carefully review the policy documents or consult with their insurance company to understand the specific calculation method used for their policy’s surrender value. By doing so, they can have a clear understanding of the amount they would receive if they were to surrender the policy.
Additionally, it’s worth noting that the surrender value may change over time. If the policy has not reached its maturity, the surrender value may be lower due to early surrender charges or penalties. On the other hand, if the policy has surpassed its surrender charge period, the surrender value may be higher as these charges no longer apply.
Overall, the calculation of surrender value is complex and can depend on several factors. It’s important for policyholders to carefully review their policy documents and consult with their insurance company to fully understand how the surrender value is calculated for their specific situation.
Factors Affecting Surrender Value
When it comes to determining the surrender value of a life insurance policy, several factors come into play. These factors can have a significant impact on the final amount that a policyholder will receive if they choose to surrender their policy. It’s important to understand these factors in order to make informed decisions regarding your life insurance coverage.
1. Policy Duration: The length of time the policy has been in force can affect the surrender value. Generally, the longer the policy has been active, the higher the surrender value is likely to be. This is because the policy has had more time to accumulate cash value.
2. Premium Payments: The amount and frequency of premium payments made by the policyholder can also impact the surrender value. Policies with higher premium payments may have a higher cash value and consequently a higher surrender value.
3. Investment Performance: Some life insurance policies, such as universal life or variable life insurance, allow policyholders to invest a portion of their premiums in variable accounts, such as stocks or bonds. The performance of these investments can affect the cash value and, by extension, the surrender value. If the investments perform well, the surrender value may increase, and vice versa.
4. Surrender Charges: Many life insurance policies have surrender charges, which are fees imposed by the insurance company if the policy is surrendered within a certain period, typically within the first several years of the policy. These charges are designed to recoup the costs associated with issuing the policy and can significantly reduce the surrender value.
5. Policy Type: The type of life insurance policy can also impact the surrender value. For example, whole life insurance policies tend to have higher cash values and surrender values compared to term life insurance policies.
6. Outstanding Policy Loans: If the policyholder has taken out loans against the policy, the outstanding loan amount will be deducted from the surrender value. This means that the surrender value will be reduced by the loan balance.
7. Policy Expenses: Insurance policies may have various expenses, such as administrative fees, premium loads, and mortality charges. These expenses can reduce the cash value and, subsequently, the surrender value.
Remember that each insurance company may have their own specific method of calculating surrender value, and these factors may be weighted differently by different companies. It’s crucial to review your policy documents or consult with your insurance company to understand how these factors affect the surrender value of your specific policy.
Surrender Value vs Cash Value
While surrender value and cash value are related terms in life insurance, they represent different aspects of the policy and serve different purposes. It’s important to understand the distinction between these two terms to make informed decisions regarding your life insurance coverage.
Cash value refers to the amount of money that has accumulated within the life insurance policy over time. It represents the savings component of the policy and can be considered as a type of investment. The cash value grows as premiums are paid, and it earns interest or investment returns, depending on the type of policy.
Surrender value, on the other hand, is the amount of money that a policyholder is entitled to receive if they choose to surrender or terminate their life insurance policy before its maturity or the end of the policy term. Surrender value is calculated based on the cash value of the policy, but it may be subject to deductions, fees, and surrender charges imposed by the insurance company.
One key difference between surrender value and cash value is that surrender value is the actual amount that can be obtained by the policyholder upon surrendering the policy, while cash value is the total accumulated value within the policy that can be accessed for various purposes.
Policyholders can withdraw or borrow against the cash value of their life insurance policy while keeping the policy in force. This enables them to use the funds for emergencies, education expenses, or any other financial needs. These withdrawals or loans may reduce the available cash value and, in turn, impact the surrender value.
It’s important to note that surrendering a policy and receiving the surrender value means giving up the life insurance coverage provided by the policy. This may not be advisable if you still need the coverage or if the surrender value is significantly lower than the premiums you have paid.
Both the cash value and the surrender value are important considerations when evaluating the financial aspects of a life insurance policy. Policyholders should review their policy documents and consult with their insurance company to fully understand the cash value and surrender value, as well as any potential fees or charges associated with surrendering the policy.
Importance of Surrender Value
The surrender value of a life insurance policy holds significant importance for policyholders. It serves as a financial safety net and provides flexibility in managing one’s life insurance coverage. Understanding the importance of surrender value can help policyholders make informed decisions about their insurance policies.
1. Financial Flexibility: Life is unpredictable, and there may be times when policyholders need access to funds. The surrender value provides an option to access a portion of the accumulated cash value if the policyholder decides to surrender the policy. This can be beneficial in times of financial emergencies or when there is a need for liquidity.
2. Changing Circumstances: Over time, a policyholder’s needs and circumstances may change. The surrender value offers the flexibility to adapt to these changes. If, for example, a policyholder finds that they no longer require the life insurance coverage or wish to switch to another policy, surrendering the policy and receiving the surrender value can be a viable option.
3. Investment Opportunities: Depending on the type of policy and its associated cash value, the surrender value can be used as an investment opportunity. By surrendering the policy and receiving the surrender value, policyholders can allocate these funds towards other investments or financial goals that align with their evolving needs and priorities.
4. Cost Optimization: Surrendering a life insurance policy can be a strategic move to optimize costs. If a policyholder finds that the premiums are becoming unaffordable or no longer align with their budget, surrendering the policy can prevent the accumulation of additional premiums while providing access to the surrender value.
5. Policy Switching: Surrendering a policy with a low surrender value may be an opportunity for policyholders to consider switching to a more suitable or better-performing life insurance policy. Evaluating the surrender value can assist in making informed decisions about alternative coverage options.
It’s important to note that surrendering a life insurance policy should not be the first course of action. The surrender value should be carefully evaluated in comparison to the premiums paid and the remaining coverage benefits. Additionally, policyholders should consider any potential tax implications or penalties associated with surrendering the policy.
By understanding the importance of surrender value, policyholders can better navigate their life insurance journey and make well-informed decisions that align with their financial goals and changing circumstances.
Surrender Value for Different Types of Life Insurance Policies
The surrender value of a life insurance policy can vary depending on the type of policy. Different types of life insurance policies have unique features and structures, which can impact the calculation and availability of surrender value. Let’s explore how surrender value applies to common types of life insurance policies:
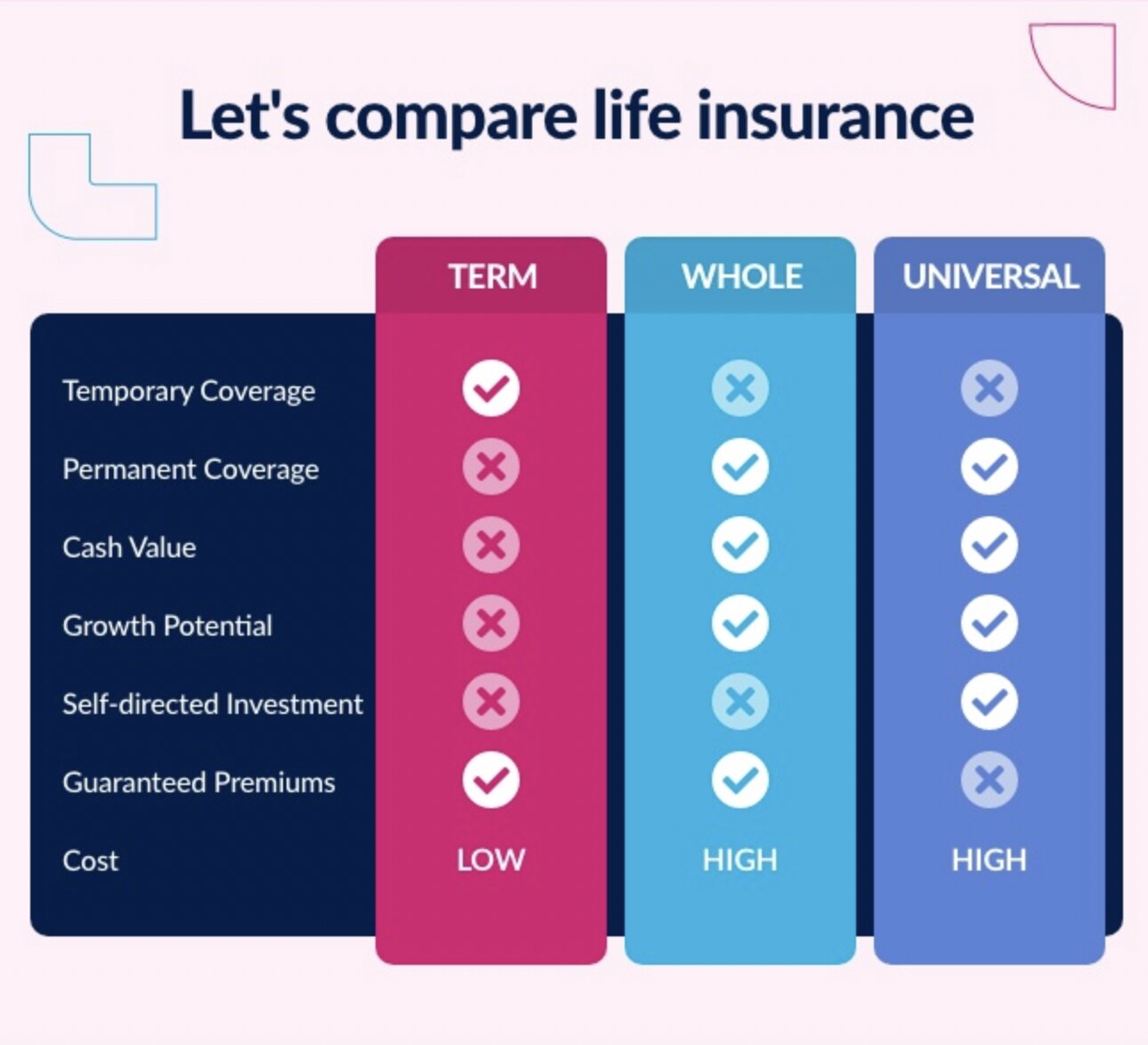
1. Whole Life Insurance: Whole life insurance policies typically have a higher surrender value compared to term life insurance policies. This is because whole life insurance policies have a cash value component that grows over time. The surrender value of a whole life insurance policy is based on the accumulated cash value and may be subject to surrender charges or fees imposed by the insurance company.
2. Universal Life Insurance: Universal life insurance policies also accumulate cash value over time. The surrender value for universal life insurance is calculated based on the cash value, but it may be influenced by factors such as investment performance, policy expenses, and surrender charges. Policyholders should review their policy documents to understand the specific surrender value provisions of their universal life insurance policy.
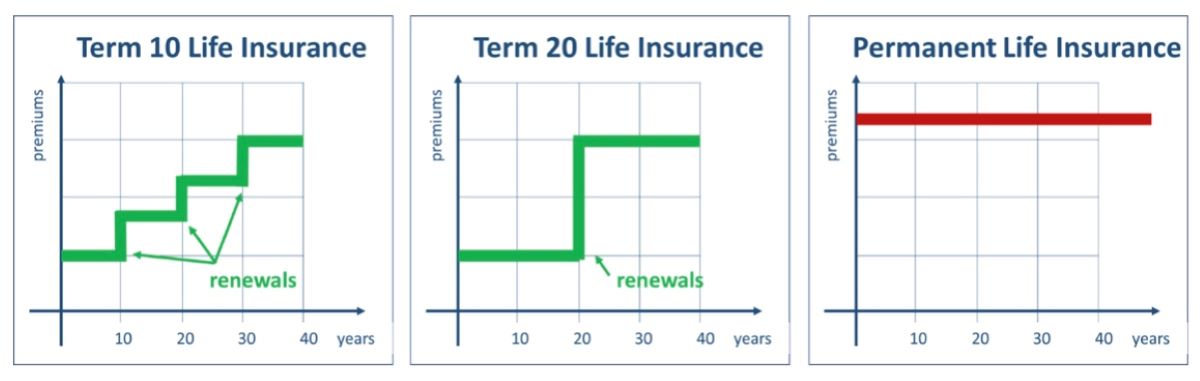
3. Term Life Insurance: Term life insurance policies typically do not have a surrender value because they provide coverage for a specific period, such as 10, 20, or 30 years. These policies do not accumulate cash value like whole life or universal life insurance policies. Once the term expires, the coverage ends, and there is no surrender value to be received.
4. Variable Life Insurance: Variable life insurance policies allow policyholders to invest a portion of their premiums in various investment accounts. The surrender value of a variable life insurance policy is influenced by the cash value accumulated through these investments. However, the surrender value can be subject to market fluctuations, making it more volatile compared to other types of life insurance.
It’s important to note that surrender value can be impacted by factors such as the premiums paid, policy duration, surrender charges, outstanding loans, and policy expenses. Additionally, surrendering a policy may have tax implications, especially for policies with accumulated cash value. Policyholders should consult with their insurance company or a financial advisor for guidance specific to their type of life insurance policy.
Before surrendering a life insurance policy, it’s crucial to carefully consider your financial needs, long-term goals, and the impact surrendering may have on your coverage. Review your policy documents, understand the surrender value provisions, and seek professional advice if needed to make an informed decision.
Surrender Value: Pros and Cons
Before deciding to surrender a life insurance policy, it’s important to weigh the pros and cons associated with surrender value. While surrendering a policy may provide financial flexibility and other benefits, it also comes with certain drawbacks. Let’s explore the pros and cons of surrender value:
Pros:
- Financial Flexibility: Surrender value provides access to a portion of the accumulated cash value within the policy, offering financial flexibility in times of need or emergencies.
- Opportunity for Investments: Surrender value can be used as an investment opportunity, allowing policyholders to allocate the funds towards other investments that may align better with their financial goals.
- Cost Optimization: Surrendering a policy with high premiums can help optimize costs, especially if the policy no longer fits within the policyholder’s budget.
- Policy Switching: Surrendering a policy with a low surrender value can be an opportunity to switch to a different life insurance policy that better meets the policyholder’s current needs and goals.
Cons:
- Loss of Coverage: Surrendering a policy means giving up the life insurance coverage provided by the policy. This can leave the policyholder and their beneficiaries without the financial protection that the policy offered.
- Reduced Value: Surrender value is typically lower than the total premiums paid due to deductions and charges imposed by the insurance company. This means that policyholders may not recoup the full value of their premium payments.
- Tax Implications: Surrendering a policy with accumulated cash value may have tax implications. Depending on the amount and nature of the surrender value, it may be subject to taxes, potentially reducing the final amount received.
- Loss of Long-term Benefits: Surrendering a policy early means forfeiting any potential long-term benefits, such as a death benefit or additional coverage options, which could have been beneficial in the future.
It’s crucial to carefully consider the pros and cons of surrender value before making a decision. Policyholders should assess their financial situation, long-term goals, and the impact surrendering a policy may have on their coverage and future needs. Consulting with an insurance professional or financial advisor can provide valuable guidance in evaluating the pros and cons specific to a policyholder’s circumstances.
Surrender Value and Policyholder’s Rights
Understanding the relationship between surrender value and policyholder’s rights is essential for every policyholder. Surrendering a life insurance policy is a decision that affects both the financial aspect and the policyholder’s overall rights. Here are some key considerations regarding surrender value and policyholder’s rights:
1. Voluntary Surrender:
Policyholders have the right to voluntarily surrender their life insurance policy at any time. This means they can choose to terminate the policy before its maturity or the end of the policy term. Surrendering a policy gives policyholders the ability to access the surrender value, which represents the accumulated cash value of the policy.
2. Surrender Charges and Penalties:
Insurance companies may impose surrender charges or penalties for policyholders who choose to surrender their policy before a certain period. These charges are designed to recoup the costs associated with issuing the policy and can significantly reduce the surrender value. Policyholders should be aware of any surrender charges or penalties outlined in their policy documents and understand how they may impact the surrender value.
3. Policy Loan Repayment:
If the policyholder has taken out loans against the policy, the outstanding loan amount will be deducted from the surrender value. This means that the policyholder must repay the loan balance before receiving the remaining surrender value.
4. Right to Termination:
The surrender value represents the policyholder’s right to terminate the life insurance policy and receive a financial compensation in return. Surrendering the policy allows the policyholder to exercise their right to discontinue the coverage provided by the policy.
5. Loss of Coverage:
It’s important to recognize that surrendering a policy means giving up the life insurance coverage provided by the policy. This can be a trade-off as the policyholder will no longer have the financial protection offered by the policy in the event of their death.
6. Review of Policy Documents:
Policyholders should carefully review their policy documents to understand the terms and conditions related to surrender value and their rights as a policyholder. It is recommended to seek guidance from the insurance company or a financial advisor to fully comprehend the implications of surrendering the policy.
Policyholders have the right to evaluate their life insurance policy and make decisions based on their unique financial circumstances. Understanding surrender value and its connection to policyholder’s rights empowers policyholders to make informed choices about their life insurance coverage.
Surrender Value and Tax Implications
When it comes to surrendering a life insurance policy, it is crucial to consider the tax implications associated with the surrender value. Surrendering a policy may trigger certain tax consequences that can impact the final amount received by the policyholder. Here are some key points to understand about surrender value and tax implications:
1. Taxable Surrender:
The surrender value of a life insurance policy may be subject to taxation, particularly if the surrender value exceeds the total premiums paid. The portion of the surrender value that exceeds the premiums paid is considered taxable income and may be subject to income tax.
2. Withdrawals and Loans:
If the policyholder has made withdrawals or taken out loans against the cash value of the policy before surrendering, these transactions can also have tax implications. Any withdrawals or loans that have not been repaid will be treated as taxable income.
3. Capital Gains Tax:
If the cash value of a life insurance policy has grown due to investment gains, surrendering the policy may trigger capital gains tax. The gains are typically taxed at a lower rate than ordinary income, but it’s important to consult with a tax professional to understand the specific rules and rates that apply in your jurisdiction.
4. Policy Type Matters:
The tax implications of surrendering a policy can vary depending on the type of life insurance policy. Different policy types, such as whole life insurance or variable life insurance, may have different tax treatment for surrender value. It’s important to review your policy documents or consult with a tax advisor to understand the specific rules that apply to your policy.
5. 1035 Exchange Option:
Instead of surrendering a policy and facing potential tax consequences, policyholders may have the option to do a 1035 exchange. This allows them to transfer the cash value from one life insurance policy to another or to another financial instrument without triggering immediate taxes. This option preserves the tax-deferred status of the cash value and allows for continued growth.
Every individual’s tax situation is unique, and it is recommended to consult with a tax professional or financial advisor before making any decisions regarding surrendering a life insurance policy. They can provide guidance on the specific tax rules and implications that apply in your situation and help you make an informed decision.
Understanding the tax implications of surrender value is essential in managing your financial affairs and ensuring compliance with tax regulations. By being aware of the potential tax consequences, policyholders can make more informed decisions about surrendering a life insurance policy.
Surrender Value: Considerations Before Surrendering
Surrendering a life insurance policy is a significant decision that should be carefully considered. Before finalizing a surrender, policyholders should take the following factors into account:
1. Financial Need:
Evaluate your current financial situation and assess whether surrendering the policy aligns with your financial needs. Consider whether accessing the surrender value is necessary or if there are alternative sources of funds available.
2. Coverage Assessment:
Review your insurance coverage needs. Determine if surrendering the policy will leave you adequately covered in terms of life insurance protection. If you still require coverage, explore options for potentially adjusting or modifying the existing policy rather than surrendering it completely.
3. Future Insurance Needs:
Consider any future insurance needs or changes in circumstances. If there is a possibility that you may require life insurance coverage again in the future, surrendering the current policy may result in loss of insurability or the need to reapply for coverage, potentially at a higher cost due to age or changes in health.
4. Tax Implications:
Understand the potential tax implications of surrendering the policy, especially regarding the surrender value. Consult with a tax advisor to assess the impact on your tax liability and understand any potential taxes on the surrender amount.
5. Alternatives to Surrender:
Explore alternatives to surrendering the policy. For example, you could consider taking a loan against the cash value, adjusting the premium payment schedule, or using any available rider options to modify the coverage.
6. Policy Performance:
Evaluate the performance of your policy and its cash value growth. If the policy is performing well, surrendering it may result in a loss of potential future growth. Consider the long-term benefits of keeping the policy in force and assess the impact on your overall financial goals.
7. Professional Advice:
Seek guidance from an insurance professional or financial advisor who can provide objective insights based on your specific circumstances. They can help you evaluate the surrender value, assess your insurance needs, and explore various options to make an informed decision.
Remember that surrendering a life insurance policy is irreversible, and the decision should be made after careful consideration of all the implications. It is essential to thoroughly review your policy documents, consult with experts, and assess your financial goals before proceeding with the surrender process.
By carefully weighing these considerations, you can make an informed decision about surrendering your life insurance policy and ensure it aligns with your financial objectives and long-term needs.