
Finance
What Is M&A In Investment Banking
Published: February 23, 2024
Learn about M&A in investment banking and its significance in finance. Explore the role of M&A in shaping the financial landscape and driving business growth.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) play a pivotal role in the financial landscape, shaping the strategies of companies and influencing industry dynamics. In the realm of investment banking, M&A serves as a cornerstone of advisory services, facilitating transactions that drive growth, consolidation, and diversification. Understanding the intricacies of M&A in investment banking is essential for professionals and enthusiasts seeking insights into this dynamic field.
The world of M&A is a captivating blend of strategy, negotiation, and finance, where companies come together to create synergies, expand market presence, or gain a competitive edge. The allure of M&A lies in its ability to reshape industries, redefine corporate landscapes, and unlock value for stakeholders. As such, delving into the fundamentals of M&A in investment banking unveils a tapestry of opportunities, risks, and strategic maneuvers that underpin the financial markets.
At its core, M&A involves the consolidation of companies through various financial transactions, including mergers, acquisitions, and divestitures. These transactions are often complex and multifaceted, requiring astute financial analysis, meticulous due diligence, and strategic foresight to navigate successfully. Investment bankers specializing in M&A are instrumental in orchestrating these transactions, leveraging their expertise to guide clients through the intricacies of deal-making.
As we embark on this exploration of M&A in investment banking, we will unravel the nuances of M&A transactions, dissect the role of investment bankers in driving these deals, and evaluate the inherent benefits and risks associated with M&A. By illuminating the inner workings of M&A within the realm of investment banking, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of this dynamic field, shedding light on its significance in shaping the corporate landscape and driving economic growth.
Definition of M&A
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) encompass a spectrum of transactions that involve the consolidation of companies, leading to structural and strategic realignment within the corporate landscape. A merger occurs when two companies combine to form a new entity, pooling their assets, human resources, and operational capabilities to create a synergistic whole. On the other hand, an acquisition involves one company purchasing another, thereby gaining control of its assets, intellectual property, customer base, and market presence.
These transactions are driven by a myriad of strategic objectives, including expanding market reach, diversifying product offerings, achieving cost efficiencies, and gaining a competitive advantage. M&A transactions can take various forms, such as horizontal mergers between competitors operating in the same industry, vertical mergers involving companies within the same supply chain, or conglomerate mergers uniting firms with diverse business interests.
Furthermore, divestitures represent a crucial facet of M&A, wherein companies sell or spin off a portion of their business to streamline operations, unlock value, or refocus their strategic priorities. Divestitures can involve the sale of subsidiaries, divisions, or product lines, allowing companies to sharpen their strategic focus and allocate resources more effectively.
Within the realm of investment banking, M&A transactions are meticulously structured and executed to optimize value for the parties involved. Investment bankers play a pivotal role in facilitating these transactions, offering strategic counsel, conducting valuation analyses, identifying potential acquirers or targets, and negotiating deal terms to ensure favorable outcomes for their clients.
Ultimately, M&A transactions represent a strategic avenue for companies to pursue growth, transformation, and value creation, underlining the dynamic nature of the corporate landscape and the pivotal role of investment banking in driving these transformative endeavors.
Types of M&A Transactions
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) encompass a diverse array of transactions, each characterized by distinct strategic objectives and operational implications. Understanding the various types of M&A transactions is essential for comprehending the multifaceted nature of corporate realignment and strategic consolidation within the business landscape.
1. Horizontal Mergers: Horizontal mergers occur between companies operating in the same industry and market segment. These transactions aim to consolidate market share, achieve economies of scale, and enhance competitive positioning. By combining complementary resources and capabilities, companies can leverage synergies to drive growth and operational efficiencies.
2. Vertical Mergers: Vertical mergers involve the integration of companies within the same supply chain or distribution network. This type of M&A transaction seeks to streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance control over the production and distribution process. By vertically integrating, companies can optimize supply chain coordination and gain greater autonomy over critical business functions.
3. Conglomerate Mergers: Conglomerate mergers bring together companies with diverse business interests and operational scopes. These transactions are driven by the pursuit of diversification, risk mitigation, and expansion into new markets. By uniting disparate business entities, conglomerate mergers enable companies to access new revenue streams and capitalize on cross-industry synergies.
4. Acquisitions: Acquisitions involve one company acquiring another, either through a purchase of assets or a controlling stake in the target company. Acquisitions can be categorized as friendly or hostile, depending on the willingness of the target company to be acquired. Friendly acquisitions are characterized by mutual consent and collaboration, while hostile acquisitions involve unsolicited bids and contentious negotiations.
5. Divestitures: Divestitures entail the sale or spin-off of a portion of a company’s assets, subsidiaries, or business units. Companies pursue divestitures to streamline operations, unlock value, and refocus their strategic priorities. Divestitures enable companies to shed non-core assets, reduce debt, and reallocate resources to core business segments.
Each type of M&A transaction presents unique opportunities and challenges, shaping the strategic landscape of companies and industries. Investment bankers play a pivotal role in advising clients on the most suitable M&A strategies, guiding them through the complexities of deal structuring, valuation, and negotiation to achieve their strategic objectives.
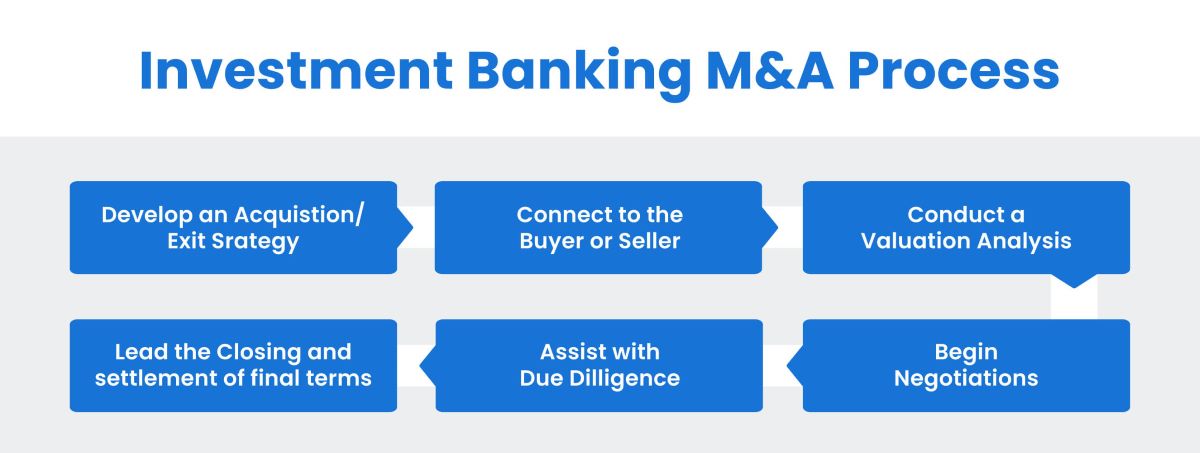
M&A Process
The mergers and acquisitions (M&A) process is a multifaceted journey characterized by strategic planning, meticulous due diligence, and intricate deal structuring. Understanding the intricacies of the M&A process is crucial for companies and investors embarking on transformative transactions, as it involves a series of strategic, financial, and legal considerations.
1. Strategic Planning: The M&A process commences with strategic planning, wherein companies identify their objectives, assess potential synergies, and evaluate the strategic fit of target companies. This phase involves defining the strategic rationale for the transaction, conducting market research, and outlining the desired outcomes of the M&A endeavor.
2. Target Identification: Once the strategic objectives are established, companies engage in the process of identifying potential acquisition targets or merger partners. This involves evaluating industry dynamics, conducting competitive analyses, and assessing the financial and operational performance of prospective targets to ascertain their suitability for the transaction.
3. Due Diligence: Due diligence represents a critical phase of the M&A process, wherein comprehensive assessments of the target company’s financial, operational, and legal aspects are conducted. This involves scrutinizing financial statements, assessing regulatory compliance, and evaluating potential risks and liabilities that may impact the transaction.
4. Valuation and Negotiation: Valuation analyses are conducted to determine the fair value of the target company, considering factors such as market trends, industry multiples, and future growth prospects. Subsequently, negotiations ensue, wherein deal terms, purchase price, and transaction structure are deliberated to reach mutually beneficial agreements between the parties involved.
5. Deal Structuring and Financing: Once the terms of the transaction are finalized, the deal structure is formalized, outlining the legal and financial framework of the M&A transaction. This phase also involves securing financing for the transaction, whether through equity, debt, or a combination of both, to fund the acquisition or merger.
6. Regulatory Approval and Closing: Regulatory approvals and compliance play a pivotal role in the M&A process, as companies must navigate antitrust regulations, industry-specific guidelines, and shareholder approvals. Upon obtaining the necessary approvals, the transaction is consummated, and the companies integrate their operations and resources to realize the strategic objectives of the M&A endeavor.
The M&A process is a dynamic and intricate undertaking, necessitating astute strategic planning, rigorous due diligence, and adept negotiation skills to navigate the complexities of deal-making. Investment bankers serve as trusted advisors throughout this process, offering strategic counsel, financial expertise, and transactional guidance to facilitate successful M&A transactions.
Role of Investment Bankers in M&A
Investment bankers play a pivotal role in facilitating mergers and acquisitions (M&A) transactions, leveraging their financial expertise, industry insights, and deal-making acumen to guide clients through the complexities of strategic realignment and corporate consolidation. Their involvement spans various stages of the M&A process, encompassing strategic advisory, valuation analyses, deal structuring, and negotiation, thereby serving as trusted advisors to companies seeking to pursue transformative transactions.
1. Strategic Advisory: Investment bankers provide strategic counsel to companies embarking on M&A transactions, offering insights into market dynamics, industry trends, and strategic positioning. They assist in defining the strategic rationale for the transaction, identifying potential targets or acquirers, and assessing the synergies and value creation opportunities inherent in the M&A endeavor.
2. Valuation Analyses: Investment bankers conduct comprehensive valuation analyses to determine the fair value of the target company or the synergistic benefits of a potential merger. This involves assessing financial metrics, market comparables, and future growth prospects to arrive at a defensible valuation that aligns with the strategic objectives of the M&A transaction.
3. Deal Structuring and Negotiation: Investment bankers play a central role in structuring M&A transactions, outlining the optimal deal structure, financing options, and transactional framework to maximize value for their clients. They engage in negotiations with the counterparties, striving to secure favorable terms, mitigate risks, and navigate complexities to ensure a successful and mutually beneficial transaction.
4. Regulatory and Legal Expertise: Investment bankers possess a deep understanding of regulatory requirements, compliance considerations, and legal nuances that underpin M&A transactions. They collaborate with legal and regulatory experts to navigate antitrust regulations, industry-specific guidelines, and governance frameworks, ensuring that the transaction adheres to all legal and regulatory mandates.
5. Transaction Execution and Integration: Throughout the M&A process, investment bankers oversee the seamless execution of the transaction, coordinating with various stakeholders, conducting due diligence, and orchestrating the integration of operations and resources post-closing. Their involvement extends beyond deal completion, as they continue to support clients in realizing the strategic objectives and synergies envisioned in the M&A transaction.
Investment bankers serve as trusted advisors and strategic partners to companies navigating the complexities of M&A, offering a blend of financial acumen, industry expertise, and transactional proficiency to drive successful and value-enhancing transactions. Their multifaceted role underscores the significance of investment banking in shaping the corporate landscape and driving transformative M&A endeavors.
Benefits and Risks of M&A
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) transactions present a myriad of potential benefits and risks for companies seeking to pursue strategic realignment, market expansion, and value creation. Understanding the inherent advantages and challenges of M&A is essential for companies and investors evaluating the feasibility and impact of these transformative transactions.
Benefits of M&A:
- Market Expansion: M&A transactions offer companies the opportunity to expand their market reach, access new customer segments, and diversify their geographic presence, thereby driving revenue growth and market penetration.
- Synergies and Cost Efficiencies: Mergers and acquisitions enable companies to leverage synergies, streamline operations, and achieve cost efficiencies through the consolidation of resources, elimination of duplicative functions, and optimization of supply chain and distribution networks.
- Strategic Diversification: M&A transactions facilitate strategic diversification, allowing companies to broaden their product offerings, enter new industry segments, and mitigate risks associated with overreliance on specific markets or product lines.
- Talent and Intellectual Capital: Acquiring companies can gain access to specialized talent, intellectual property, and technological capabilities, fostering innovation, and enhancing their competitive positioning in the market.
- Value Creation and Shareholder Returns: Successful M&A transactions have the potential to unlock value for shareholders, generate economies of scale, and enhance the overall financial performance of the combined entity, thereby driving shareholder returns and long-term value creation.
Risks of M&A:
- Integration Challenges: Post-merger integration poses significant challenges, including cultural alignment, operational harmonization, and organizational restructuring, which can impede the realization of synergies and value creation envisioned in the M&A transaction.
- Financial Uncertainty: M&A transactions may introduce financial uncertainties, including increased debt levels, liquidity constraints, and unforeseen liabilities, which can impact the financial stability and creditworthiness of the acquiring company.
- Regulatory and Legal Complexities: Navigating regulatory approvals, compliance requirements, and legal intricacies can be arduous, particularly in cross-border transactions, exposing companies to regulatory risks and legal disputes that may impede the transaction’s success.
- Reputational Risks: M&A transactions can engender reputational risks, particularly if the integration process is mismanaged, leading to customer dissatisfaction, employee disengagement, and adverse market perceptions that may erode brand equity and stakeholder confidence.
- Strategic Misalignment: Incompatibilities in strategic objectives, cultural fit, or operational synergies between the merging entities can undermine the success of the M&A transaction, leading to value destruction and operational disruptions.
By comprehensively assessing the potential benefits and risks of M&A transactions, companies can make informed decisions, mitigate inherent challenges, and optimize the strategic outcomes of these transformative endeavors, thereby enhancing their competitive positioning and long-term sustainability.
Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of mergers and acquisitions (M&A) in the realm of investment banking, it becomes evident that M&A transactions embody a complex interplay of strategic vision, financial acumen, and operational execution. The dynamic nature of M&A transactions underscores their significance in shaping the corporate landscape, driving industry consolidation, and unlocking value for stakeholders.
Throughout this journey, we have delved into the intricacies of M&A, unraveling the diverse types of transactions, the multifaceted M&A process, and the pivotal role of investment bankers in orchestrating successful M&A endeavors. We have delineated the potential benefits and risks inherent in M&A transactions, emphasizing the strategic imperatives and operational challenges that companies must navigate to realize the full potential of these transformative endeavors.
At its core, M&A represents a strategic avenue for companies to pursue growth, diversification, and market expansion, enabling them to capitalize on synergies, optimize operational efficiencies, and enhance shareholder value. However, the inherent complexities and risks associated with M&A transactions underscore the critical importance of meticulous planning, rigorous due diligence, and adept execution to mitigate potential pitfalls and maximize the strategic outcomes of these transactions.
Investment bankers, as trusted advisors and strategic partners, play a pivotal role in guiding companies through the intricacies of M&A, offering a blend of financial expertise, industry insights, and transactional proficiency to drive successful and value-enhancing transactions. Their multifaceted involvement underscores the significance of investment banking in shaping the corporate landscape and driving transformative M&A endeavors.
As companies navigate the dynamic terrain of M&A, it is imperative for them to leverage comprehensive strategic planning, astute financial analysis, and adept negotiation to optimize the strategic outcomes of these transactions. By embracing a holistic approach to M&A, companies can unlock new growth opportunities, enhance their competitive positioning, and create sustainable value for their stakeholders, thereby propelling their strategic aspirations and long-term success in the ever-evolving business landscape.
In essence, M&A in investment banking represents a compelling nexus of strategy, finance, and operational synergy, underscoring its pivotal role in shaping the corporate landscape and driving transformative growth initiatives. By embracing a nuanced understanding of M&A and leveraging the expertise of investment bankers, companies can navigate the complexities of M&A transactions with confidence, resilience, and strategic foresight, thereby unlocking new horizons of growth and value creation in the dynamic realm of corporate realignment and consolidation.














