Finance
How Are Futures Contracts Taxed In Portugal
Published: December 24, 2023
Learn about the taxation of futures contracts in Portugal and the implications for your finances. Discover how to navigate this financial aspect efficiently.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Overview of Futures Contracts
- Taxation of Futures Contracts in Portugal
- Tax Treatment of Gains from Futures Contracts
- Tax Treatment of Losses from Futures Contracts
- Reporting and Documentation Requirements
- Taxation of Foreign Futures Contracts in Portugal
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Trading Futures Contracts in Portugal
- Conclusion
Introduction
When it comes to investing in the financial markets, futures contracts are a popular instrument for traders and investors. These contracts allow individuals to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price and date in the future. However, along with the potential for significant profits, understanding the tax implications of trading futures contracts is crucial for individuals operating within the Portuguese market.
This article provides an overview of how futures contracts are taxed in Portugal. It explores the tax treatment of gains and losses from these contracts, as well as the reporting and documentation requirements that traders need to be aware of. Additionally, it touches upon the taxation of foreign futures contracts in Portugal and discusses the advantages and disadvantages of trading futures contracts within the country.
By understanding the tax regulations surrounding futures contracts in Portugal, traders can ensure compliance with the law and make informed investment decisions. It is important to note that tax laws and regulations can vary over time and are subject to change. Therefore, individuals should consult with a financial advisor or tax professional to stay up to date with the latest information.
Overview of Futures Contracts
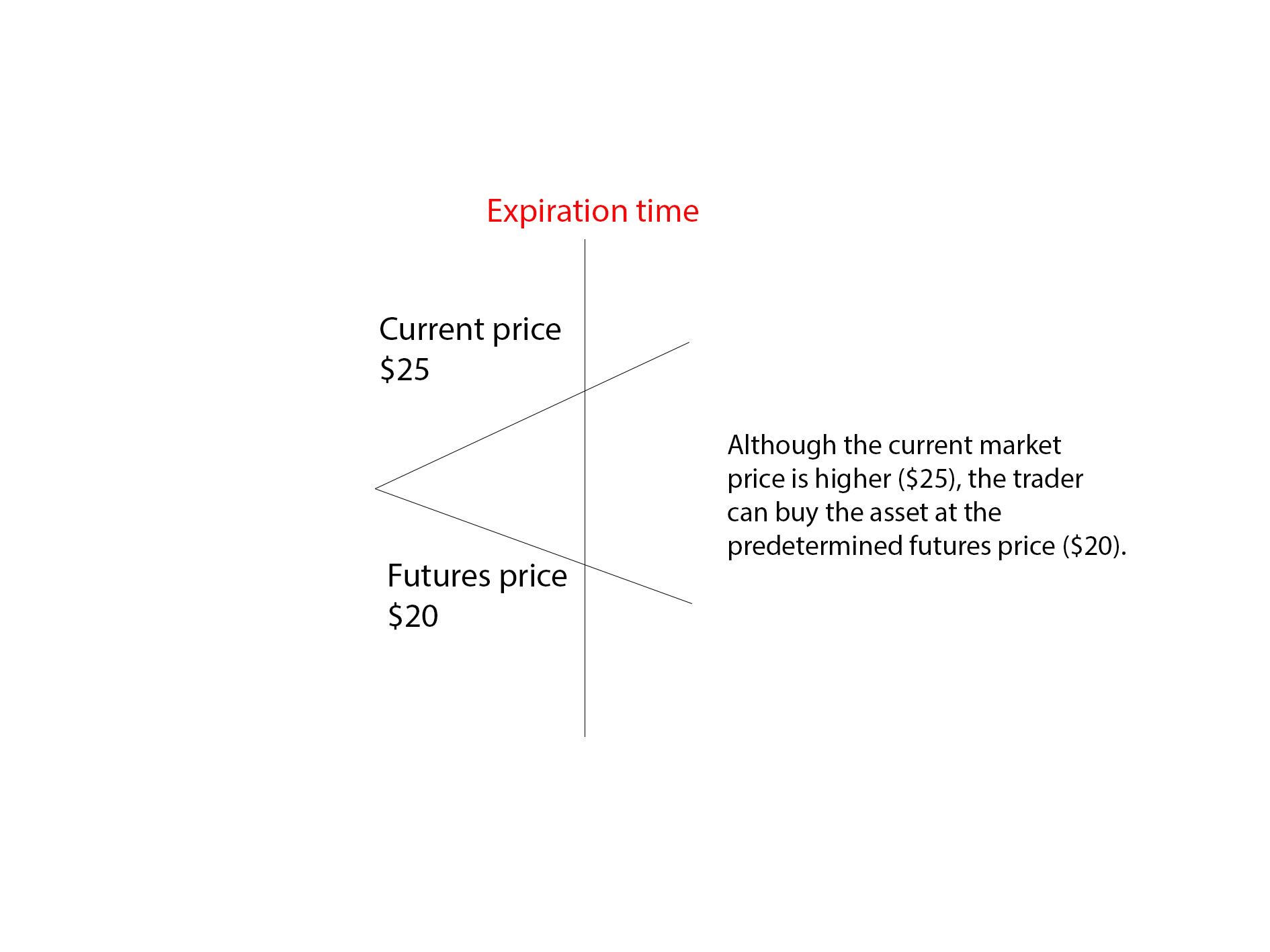
Futures contracts are derivative financial instruments that derive their value from an underlying asset such as commodities, currencies, stock indices, or even interest rates. These contracts represent an agreement between two parties to buy or sell the underlying asset at a predetermined price on a specific date in the future. In Portugal, futures contracts are primarily traded on regulated exchanges like Euronext Lisbon.
One of the key features of futures contracts is their standardized nature. They have predetermined contract sizes, expiry dates, and settlement methods, which gives traders a clear framework for trading. This standardized structure allows for easy liquidity and enables traders to speculate on price movements without owning the actual underlying asset.
Traders can take two positions in futures contracts: long or short. A long position involves buying a futures contract in anticipation of a price increase, while a short position involves selling a futures contract in anticipation of a price decrease. Profits and losses are realized based on the difference between the contract’s price at the time of opening and its price at the time of closing.
Futures contracts offer traders various advantages, including leverage, hedging opportunities, and the ability to profit from both rising and falling markets. However, they also carry risks, including market volatility and the potential for substantial losses if market movements go against the trader’s position.
It’s important for traders in Portugal to understand the tax implications associated with trading futures contracts. Let’s take a closer look at how these contracts are taxed in the country.
Taxation of Futures Contracts in Portugal
In Portugal, the taxation of futures contracts falls under the category of capital gains and is subject to specific tax rules. The tax treatment of these contracts depends on whether the trading activity is considered occasional or habitual.
For occasional traders, who engage in futures trading infrequently, gains from futures contracts are generally considered capital gains and are subject to the Capital Gains Tax (CGT). Under the CGT regime, 50% of the gains are taxable at a flat rate of 28%, resulting in an effective tax rate of 14% on the total gains. Losses from occasional futures trading can be offset against capital gains from other sources.
On the other hand, habitual traders, who trade futures contracts as their main occupation or business activity, are subject to taxation under the more complex regime of Business and Professional Income (BPI). Under the BPI regime, gains from futures contracts are treated as business income and taxed at the applicable progressive income tax rates, which range from 14.5% to 48%.
Habitual traders also have the advantage of being able to deduct their trading-related expenses, such as platform fees, data subscriptions, and professional advisory services, from their taxable income. However, they are not eligible for the 50% exemption applied to occasional traders. It’s important for habitual traders to keep accurate records of their trading activities and associated expenses for documentation and tax purposes.
Regardless of whether an individual is an occasional or habitual trader, it’s essential to track all transactions related to futures contracts. This includes documenting the dates, contract sizes, opening and closing prices, and any profits or losses incurred. Traders should also maintain records of any relevant expenses incurred during the trading process.
It’s worth noting that tax laws and regulations can change over time, so it is advisable for traders to consult with a tax professional or financial advisor to ensure compliance with the latest tax requirements in Portugal.
Tax Treatment of Gains from Futures Contracts
When it comes to the tax treatment of gains from futures contracts in Portugal, it is important to consider whether the trading activity is occasional or habitual. The tax rules differ based on the frequency and nature of the trading.
For occasional traders, gains from futures contracts are treated as capital gains. These gains are subject to the Capital Gains Tax (CGT), where 50% of the gains are taxable at a flat rate of 28%. This effectively results in an effective tax rate of 14% on the total gains. It’s worth noting that any losses incurred can be offset against capital gains from other sources.
On the other hand, habitual traders, who engage in futures trading as their main occupation or business activity, are subject to the Business and Professional Income (BPI) regime. As such, gains from futures contracts are treated as business income and taxed at the applicable progressive income tax rates in Portugal, which range from 14.5% to 48%.
It is important for traders to keep accurate records of their gains from futures contracts, including the dates of the transactions, contract sizes, opening and closing prices, as well as any associated expenses. These records are crucial for calculating the taxable gains accurately and documenting them for tax purposes.
For both occasional and habitual traders, it’s advisable to consult with a tax professional or financial advisor who specializes in Portuguese tax regulations. They can provide guidance and ensure compliance with the latest tax laws.
It is also important to note that tax laws and regulations are subject to change. Traders should stay informed about any updates or amendments to the tax rules regarding gains from futures contracts in Portugal.
By understanding the tax treatment of gains, traders can manage their tax liabilities effectively and make informed decisions regarding their futures trading activities.
Tax Treatment of Losses from Futures Contracts
When it comes to the tax treatment of losses from futures contracts in Portugal, there are specific regulations in place for both occasional and habitual traders.
For occasional traders, who engage in futures trading infrequently, losses from futures contracts can be offset against capital gains from other sources. This means that if a trader incurs a loss from a futures contract, they can use that loss to reduce the taxable capital gains they have realized from other investments. It’s important to keep detailed records of all losses and gains to accurately calculate the taxable amount.
On the other hand, habitual traders, who consider futures trading as their main occupation or business activity, are subject to the Business and Professional Income (BPI) regime. Under this regime, losses from futures contracts can be offset against other income derived from the same business activity, provided they are documented and evidenced. It’s crucial for habitual traders to maintain proper records of their trading activities and losses to support their tax deductions.
It’s worth noting that losses from futures contracts cannot be offset against other types of income, such as employment income or rental income, for either occasional or habitual traders. The offsetting is limited to capital gains or income from the same business activity. This means that losses from futures trading cannot be used to reduce the overall tax liability on different sources of income.
Traders should consult with a tax professional or financial advisor to understand the specific rules and regulations regarding the offsetting of losses from futures contracts in Portugal. These professionals can provide guidance on the proper documentation and reporting requirements to ensure compliance with tax laws.
It’s important for traders to remember that tax laws and regulations can change, and it’s crucial to stay informed about any updates or amendments. Properly managing losses from futures contracts can help traders minimize their tax liabilities and maximize their overall returns from their trading activities.
Reporting and Documentation Requirements
Traders engaged in futures trading in Portugal are subject to specific reporting and documentation requirements to ensure compliance with tax regulations. It is essential to maintain accurate records and report trading activities appropriately.
First and foremost, traders should keep detailed records of all futures trading transactions. This includes information such as the dates of the trades, contract sizes, opening and closing prices, and any profits or losses incurred. These records serve as evidence for calculating taxable gains or losses accurately.
Traders in Portugal must report their gains or losses from futures contracts on their annual tax return. Occasional traders report their gains or losses under the Capital Gains Tax (CGT) regime, while habitual traders report their trading activities under the Business and Professional Income (BPI) regime.
When reporting gains or losses from futures contracts, traders should follow the guidelines provided by the local tax authority and include all necessary documentation to support their calculations. This may involve submitting transaction records, financial statements, and other related documents to validate the accuracy of the reported figures.
It’s important to note that traders must retain their records and documentation for a certain period, as required by tax regulations in Portugal. These records may be subject to examination or audit by the tax authorities, and traders must be able to provide evidence to support the reported gains or losses.
In addition to transaction records, traders should also keep track of any expenses related to their futures trading activities. This includes expenses such as platform fees, data subscriptions, professional advisory services, and any other costs directly associated with trading. These expenses can be deducted from the taxable income for habitual traders under the BPI regime.
Traders should consult with a tax professional or financial advisor to ensure they are meeting all reporting and documentation requirements. Staying up to date with the latest guidelines and regulations is crucial to avoid penalties or legal issues.
By maintaining proper records and adhering to reporting requirements, traders can efficiently manage their tax obligations and demonstrate compliance with tax laws in Portugal.
Taxation of Foreign Futures Contracts in Portugal
Portugal has specific tax rules regarding the taxation of foreign futures contracts for individuals trading in the country. The tax treatment of these contracts depends on various factors, including residency and the classification of the trading activity.
For Portuguese tax residents, the taxation of foreign futures contracts follows similar principles as the taxation of domestic futures contracts. If an individual is considered an occasional trader, gains from foreign futures contracts are generally treated as capital gains and subject to the Capital Gains Tax (CGT) at a flat rate of 28%, with 50% of the gains being taxable. Losses can be offset against capital gains from domestic or foreign sources.
On the other hand, habitual traders who are tax residents in Portugal and actively trading foreign futures contracts as part of their business activity are subject to the Business and Professional Income (BPI) regime. Gains from foreign futures contracts are treated as business income and taxed under the progressive income tax rates applicable to the BPI regime.
Non-resident individuals trading foreign futures contracts in Portugal may also be subject to taxation depending on the specific circumstances. Tax treaties between Portugal and the individual’s home country may provide guidelines on the taxation of foreign futures contracts and the potential elimination or reduction of double taxation.
It’s important for individuals trading foreign futures contracts in Portugal to consider the reporting and documentation requirements associated with these transactions. Accurately reporting gains and losses, as well as maintaining proper records of trading activities, is essential for compliance with tax regulations.
Traders should consult with a tax professional or financial advisor with expertise in international taxation to ensure they understand and meet the tax obligations associated with foreign futures contracts in Portugal. They can provide guidance on the specific rules and regulations applicable to each individual’s situation.
It’s worth noting that tax laws and regulations are subject to change, and traders should stay informed about any updates or amendments that may affect the taxation of foreign futures contracts in Portugal.
By understanding the tax implications and fulfilling the reporting and documentation requirements, individuals trading foreign futures contracts can ensure compliance with Portuguese tax laws and effectively manage their tax liabilities.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Trading Futures Contracts in Portugal
Trading futures contracts in Portugal offers both advantages and disadvantages for individuals looking to participate in the financial markets. Understanding these pros and cons can help traders make informed decisions about their investment strategies. Let’s explore some of the key advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages:
- Leverage: Futures contracts allow traders to control a larger position with a smaller initial investment, allowing for potentially higher returns.
- Hedging Opportunities: Futures contracts can be used to hedge against price fluctuations in the underlying asset, providing a safeguard against market volatility.
- Ability to Profit from Both Rising and Falling Markets: Unlike traditional stock trading, futures contracts enable traders to profit from both upward and downward price movements in the market.
- Liquidity: Futures contracts are traded on regulated exchanges, ensuring high liquidity, which allows for easier entry and exit from positions.
- Diverse Market Exposure: Trading futures contracts provides exposure to a wide range of asset classes, including commodities, currencies, stock indices, and interest rates.
Disadvantages:
- Risk of Losses: Futures trading involves inherent risks, including the potential for substantial losses, especially when using leverage.
- Market Volatility: The volatile nature of futures markets can result in rapid price movements, making it crucial for traders to carefully manage risks.
- Complexity: Futures trading requires a good understanding of market dynamics, technical analysis, and risk management strategies, which can be challenging for newcomers to grasp.
- Trading Costs: Traders need to consider commissions, exchange fees, and other trading costs associated with futures contracts, which can eat into potential profits.
- Regulatory Risks: Changes in regulations governing futures contracts can impact trading conditions and may require traders to adapt their strategies accordingly.
It’s important for individuals interested in trading futures contracts in Portugal to carefully consider these advantages and disadvantages in the context of their own financial goals and risk tolerance. Traders should conduct thorough research, educate themselves on the intricacies of futures trading, and seek guidance from experienced professionals to mitigate risks and maximize potential returns.
By weighing the pros and cons and taking a disciplined approach to trading, individuals can navigate the futures markets with confidence and optimize their chances for success.
Conclusion
Trading futures contracts in Portugal can be an exciting and potentially lucrative endeavor for individuals looking to participate in the financial markets. However, it is essential to understand the tax implications and regulations surrounding futures trading to ensure compliance with Portuguese tax laws.
In this article, we covered the essential aspects of futures contract taxation in Portugal. We explored the tax treatment of gains and losses for both occasional and habitual traders, highlighting the differences between the Capital Gains Tax (CGT) and the Business and Professional Income (BPI) regimes. We also discussed the reporting and documentation requirements necessary for traders to fulfill their tax obligations.
Additionally, we delved into the taxation of foreign futures contracts in Portugal, emphasizing the importance of understanding the specific tax rules and considering any tax treaties that may apply. Traders should consult with tax professionals or financial advisors to navigate the complexities of international taxation.
Lastly, we highlighted the advantages and disadvantages of trading futures contracts in Portugal. While futures trading offers opportunities for leverage, hedging, and exposure to diverse markets, traders must be aware of the risks involved, including potential losses, market volatility, and regulatory changes.
Ultimately, traders in Portugal should approach futures trading with a comprehensive understanding of the tax implications, risk management strategies, and market dynamics. By staying informed, seeking professional guidance, and maintaining accurate records, traders can navigate the futures markets confidently and optimize their investment outcomes.
It is crucial to note that tax laws and regulations can evolve, and traders should stay updated with any changes. Consulting with a tax professional or financial advisor is highly recommended to ensure compliance with the latest tax requirements in Portugal.
By being knowledgeable and diligent in their trading activities, individuals can maximize their potential for success while minimizing any tax-related issues. Traders who adhere to the tax regulations and stay informed will be well-positioned to navigate the futures markets effectively in Portugal.