
Finance
How To Buy Futures Contracts For Oil
Published: December 24, 2023
Learn the basics of buying futures contracts for oil and start investing in the finance industry. Gain insights into the process and make informed decisions.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Futures Contracts for Oil
- Choosing a Futures Exchange
- Selecting a Contract Type
- Researching Oil Market Trends
- Opening a Futures Trading Account
- Placing an Order for Oil Futures Contract
- Managing and Monitoring Your Futures Position
- Closing a Futures Contract
- Risks and Considerations in Oil Futures Trading
- Conclusion
Introduction
Welcome to the world of futures trading! If you have an interest in the oil market and want to potentially profit from its fluctuations, then buying futures contracts for oil could be a viable investment option for you. Futures contracts are financial agreements that allow traders to buy or sell a specific quantity of a commodity, such as oil, at a predetermined price and date in the future.
With the constantly changing dynamics of the oil market, futures trading offers an opportunity to capitalize on price movements and hedge against potential risks. However, navigating the world of oil futures can be complex, especially for beginners. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide on how to buy futures contracts for oil, equipping you with the knowledge you need to get started.
Before delving into the specifics, it’s important to note that trading oil futures involves a level of risk that should not be taken lightly. Oil prices are influenced by a myriad of factors, including geopolitical events, supply and demand fundamentals, and global economic indicators. These factors can contribute to substantial price volatility in the oil market, which can result in significant financial gains or losses.
It is essential to conduct thorough research, understand the oil market’s dynamics, and have a clear risk management strategy in place before engaging in oil futures trading. By equipping yourself with the necessary knowledge and guidance, you can navigate this exciting investment opportunity with confidence and increase your chances of success.
In the following sections, we will explore the ins and outs of trading oil futures. We’ll cover key aspects such as choosing a futures exchange, selecting the right contract type, researching oil market trends, opening a futures trading account, placing and managing your orders, and understanding the risks and considerations involved. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a solid foundation to embark on your journey as an oil futures trader.
Understanding Futures Contracts for Oil
Before diving into the world of oil futures trading, it’s crucial to have a clear understanding of what futures contracts are and how they work.
A futures contract is a legally binding agreement between two parties to buy or sell a specific quantity of a financial instrument or commodity at a predetermined price and date in the future. In the case of oil futures, the underlying asset is, of course, crude oil.
One of the key features of futures contracts is the standardized nature of the agreement. This means that the contract size, delivery date, and quality specifications are predetermined by the futures exchange. Standardization ensures that all traders are on equal footing and eliminates the need for individual negotiations for each contract.
When trading oil futures, you have two options: buying a futures contract to take a long position (betting on rising oil prices) or selling a futures contract to take a short position (betting on falling oil prices).
Each futures contract represents a specific quantity of oil, typically measured in barrels. It’s essential to understand the contract’s size as it determines the value of each price fluctuation.
For example, let’s say each futures contract represents 1,000 barrels of oil, and the contract’s price increases by $1. This means that the value of the contract would increase by $1,000. On the other hand, if the contract’s price decreases by $1, the value of the contract would decrease by $1,000.
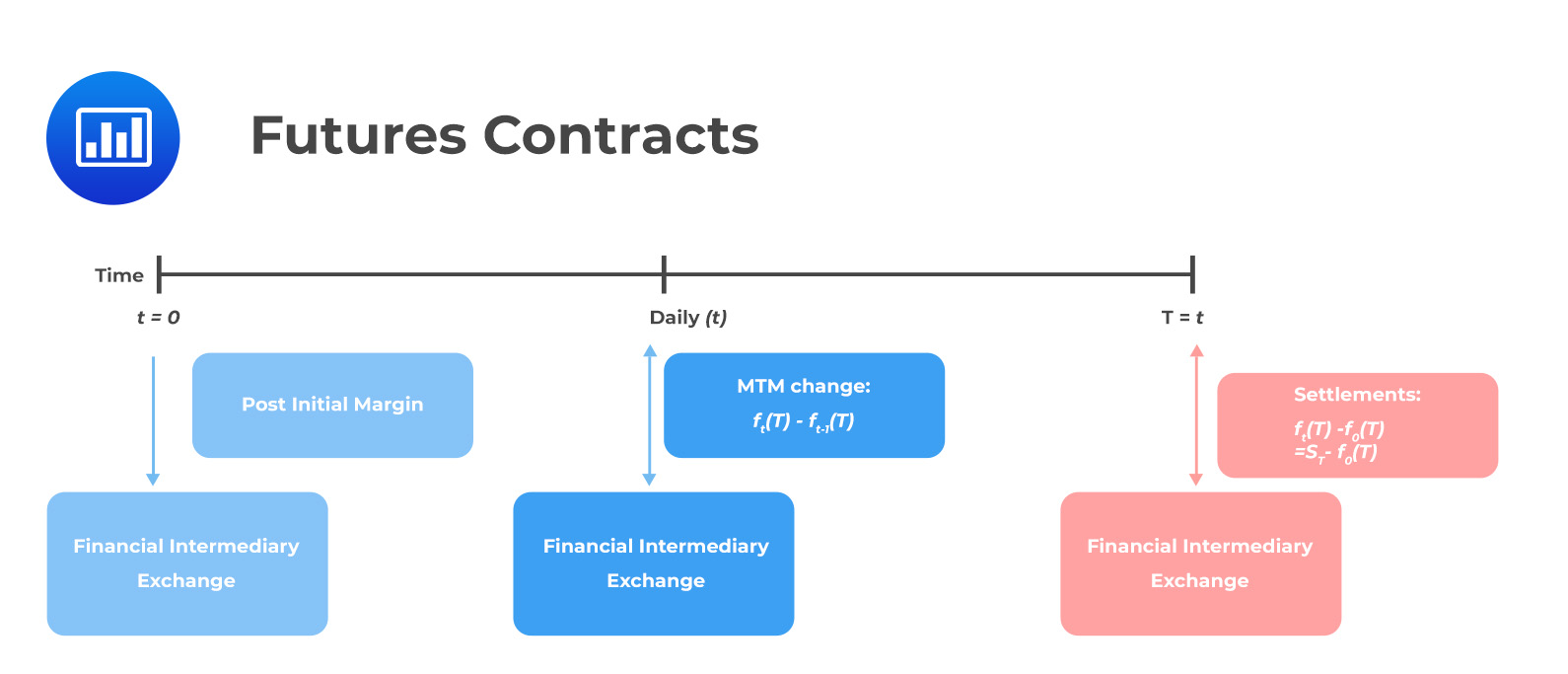
It’s worth noting that most oil futures contracts are settled in cash rather than physical delivery. This means that instead of taking delivery of barrels of oil, traders settle their positions by either paying or receiving cash based on the difference between the contract price and the market price at the time of expiration.
The futures market provides a liquid and transparent platform for traders to engage in oil trading activities. It allows participants to speculate on price movements, hedge against potential risks, and gain exposure to the oil market without physically owning or storing the commodity.
In the next sections, we’ll explore the steps to buy oil futures contracts, starting with choosing a futures exchange that suits your trading needs.
Choosing a Futures Exchange
When it comes to buying futures contracts for oil, selecting the right futures exchange is a critical decision. The futures exchange serves as the marketplace where buyers and sellers come together to trade these contracts.
There are several futures exchanges around the world that offer oil futures contracts. Some of the most prominent ones include the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME Group), Intercontinental Exchange (ICE), and the Dubai Mercantile Exchange (DME). Each exchange has its own set of rules, contract specifications, and trading hours.
When choosing a futures exchange, consider the following factors:
- Liquidity: A liquid market ensures that there are enough buyers and sellers, which enhances the ease of executing trades and reduces the likelihood of facing high bid-ask spreads.
- Contract Variety: Different futures exchanges may offer a range of contract types, such as crude oil futures, Brent crude oil futures, or natural gas futures. Consider the specific oil contract you want to trade and ensure that the exchange offers it.
- Regulation and Oversight: Look for exchanges that have strong regulatory oversight and a reputation for maintaining fair and transparent markets. This ensures a level playing field and helps protect traders’ interests.
- Access and Connectivity: Consider the accessibility and ease of connecting to the exchange’s trading platform. Some exchanges offer their own proprietary platforms, while others may be accessible through third-party trading software.
It’s also worth considering the trading hours of the exchange. Some futures exchanges have extended trading hours, allowing traders to take advantage of global market movements and news events that may impact oil prices.
Take your time to research and compare the different futures exchanges available to you. Look for reviews, consider the reputation and track record of the exchange, and evaluate the quality of their trading platform. By selecting an exchange that aligns with your trading goals and preferences, you’ll be better equipped to engage in oil futures trading.
Once you have chosen a futures exchange, the next step is to select the specific type of futures contract that aligns with your trading strategy. We will discuss this in detail in the next section.
Selecting a Contract Type
When it comes to trading oil futures contracts, there are typically different contract types available to choose from. These contract types may represent different types of oil or have varying contract specifications. Selecting the right contract type is crucial as it determines the specific characteristics and market exposure of your futures position.
Here are some common types of oil futures contracts:
- WTI Crude Oil: The West Texas Intermediate (WTI) crude oil futures contract is one of the most widely traded oil futures contracts. It represents light, sweet crude oil primarily extracted from the United States. Traders who want exposure to the U.S. oil market often opt for WTI futures.
- Brent Crude Oil: The Brent crude oil futures contract represents crude oil sourced from the North Sea region. Brent crude is generally considered the global benchmark for oil prices, and its futures contract is popular for traders looking for exposure to international oil markets.
- Mini Crude Oil: Some futures exchanges offer mini crude oil contracts, which have smaller contract sizes compared to standard contracts. Mini contracts can be appealing to traders with smaller trading capital or those looking for more flexibility in position sizing.
- Natural Gas: While not strictly oil, natural gas is often included in energy futures trading. Natural gas futures contracts allow traders to speculate on the price movements of natural gas, which is commonly used for heating and electricity generation.
When selecting a contract type, consider your trading objectives, risk tolerance, and the specific dynamics of the market you wish to focus on. If you’re interested in crude oil extracted from the United States, WTI crude oil futures may be more suitable. On the other hand, if you want exposure to the global oil market, Brent crude oil futures might be a better choice.
It’s vital to familiarize yourself with the contract specifications of the chosen futures contract, including its size, point value, tick size, and margin requirements. These details will determine the monetary value and price movements of your futures position.
Additionally, keep in mind that the price of oil futures contracts is influenced by various factors, such as supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical events, economic data, and weather conditions. Stay informed about these factors and conduct thorough research to make well-informed trading decisions.
Once you have selected the contract type that aligns with your trading goals, it’s time to delve deeper into researching the oil market trends. This will provide you with the necessary insights to make informed trading decisions. We will explore this further in the next section of our guide.
Researching Oil Market Trends
Successful futures trading, including oil futures, relies heavily on thorough research and analysis of oil market trends. By staying informed about market events, supply and demand dynamics, economic indicators, and geopolitical factors, you can make more informed trading decisions and potentially increase your chances of success.
Here are some key steps to researching oil market trends:
- Stay Updated on Industry News: Follow reputable news sources that provide comprehensive coverage of the oil market. Stay informed about oil production levels, changes in oil inventories, geopolitical tensions, regulatory developments, and any other factors that may impact oil prices.
- Analyze Supply and Demand Factors: Understand the factors that influence the supply and demand of oil, such as production levels, consumption patterns, and economic growth indicators. For example, changes in global oil demand, OPEC (Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries) production decisions, or disruptions in oil-producing regions can have a significant impact on oil prices.
- Monitor Economic Data: Keep track of economic indicators that can influence oil prices, such as GDP (Gross Domestic Product) growth, inflation rates, and employment data. Economic trends can provide insights into the overall health and future outlook of the global economy, which in turn can impact oil prices.
- Technical Analysis: Utilize technical analysis tools and indicators to analyze historical price data and identify potential patterns or trends. Technical analysis can help identify support and resistance levels, trend lines, and key price levels that may influence future price movements.
- Global Events and Geopolitical Factors: Monitor geopolitical developments and events that may impact oil prices, such as political instability in oil-producing regions, conflicts, sanctions, or trade disputes. These factors can create volatility and affect the supply and demand dynamics of oil.
It’s important to note that researching oil market trends requires a combination of fundamental and technical analysis. By combining these approaches, you gain a more holistic understanding of the oil market and can make more informed trading decisions.
There are various resources available to help you stay informed and conduct research, including financial news websites, industry reports, government data, and analysis from reputable market research firms.
Keep in mind that no strategy or research method can guarantee successful trading outcomes. The oil market is complex and subject to various factors beyond anyone’s control. Therefore, it’s essential to have a clear risk management plan in place and to carefully consider the potential risks and rewards associated with trading oil futures.
Now that you have equipped yourself with a solid understanding of oil market trends, the next step is to open a futures trading account. We will explore this process in detail in the next section of our guide.
Opening a Futures Trading Account
Before you can start trading oil futures contracts, you’ll need to open a futures trading account with a reputable brokerage firm that offers access to the futures market. Here are the key steps involved in opening a futures trading account:
- Research and Choose a Brokerage: Conduct thorough research to find a brokerage firm that offers futures trading services. Look for a brokerage that is well-established, regulated, and provides access to the futures exchanges you are interested in. Consider factors such as trading platform, fees, customer support, and educational resources.
- Complete the Account Opening Process: Once you have chosen a brokerage, visit their website or contact their customer service to start the account opening process. You will typically need to provide personal information, such as your name, address, phone number, and identification documents for verification purposes.
- Submit Required Documents: The brokerage firm will require specific documents to comply with regulatory guidelines. These documents may include proof of identity (e.g., passport or driver’s license), proof of address (e.g., utility bill or bank statement), and tax-related information. Ensure that you have all the necessary documents ready and submit them as requested by the brokerage.
- Select Account Type: The brokerage will offer different types of trading accounts, such as individual, joint, or corporate accounts. Choose the account type that suits your needs and trading goals. Consider factors such as account minimums, margin requirements, and account features offered by the brokerage for each account type.
- Fund Your Account: Once your account is approved and set up, you will need to fund it with the necessary trading capital. Most brokerages offer various funding methods, including bank transfers, credit/debit cards, or electronic payment systems. Determine the funding method that is most convenient for you and transfer the desired amount to your trading account.
It’s important to note that opening a futures trading account may require you to meet certain eligibility requirements, such as being of legal age and having a sufficient level of trading experience and financial resources. Make sure to familiarize yourself with the specific requirements of the brokerage you choose.
Once your account is funded, you can proceed to the next step of placing an order for an oil futures contract. But before you do that, it’s crucial to understand the different order types and the process of placing an order, which we will explore in the next section of our guide.
Placing an Order for Oil Futures Contract
Placing an order for an oil futures contract involves selecting the specific contract, determining the desired position (long or short), and specifying the price at which you wish to enter the market. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to place an order for an oil futures contract:
- Select the Futures Exchange: Log in to your trading account and choose the futures exchange where the oil futures contract is listed. Ensure that you have selected the correct exchange and contract type.
- Choose the Contract Month: Futures contracts have different expiration months. Select the contract month that aligns with your trading timeframe and strategy. For example, if you want to trade the August contract, specify “August” or the corresponding symbol for that contract.
- Determine your Position: Decide whether you want to take a long position (buy the contract) or a short position (sell the contract). A long position is taken if you anticipate an increase in oil prices, while a short position is taken if you expect a decline in oil prices.
- Select the Order Type: Choose the appropriate order type based on your trading strategy and preferences. Common order types include market orders, limit orders, and stop orders. A market order is executed immediately at the prevailing market price, while a limit order allows you to set a specific price at which you are willing to trade. A stop order is triggered when the market reaches a specific price level, activating a buy or sell order.
- Specify Quantity and Price: Enter the quantity (number of contracts) you want to trade and the price at which you want to enter the market. For example, if the current market price is $70 per barrel, you can specify a limit order to buy at $69 or sell at $71.
- Review and Confirm: Double-check all the order details, including the contract, position, order type, quantity, and price. Verify that the information is accurate and reflects your trading intentions. Once you are confident, confirm the order to submit it to the futures exchange.
After placing your order, it will be sent to the futures exchange, where it will be matched with a counterparty’s order. Once the order is executed, you will receive a confirmation indicating that your position has been established.
It’s important to note that the availability of order types may vary depending on the brokerage and the specific futures exchange. Familiarize yourself with the order types offered by your chosen brokerage and the rules of the particular exchange you are trading on.
Once your position is established, it’s crucial to actively manage and monitor your futures position to adapt to changing market conditions. We will explore this topic further in the next section of our guide.
Managing and Monitoring Your Futures Position
Once you have opened a futures position for an oil contract, it’s important to actively manage and monitor your position to adapt to changing market conditions. Here are some key steps to effectively manage and monitor your futures position:
- Set Stop Loss and Take Profit Levels: Determine your desired stop loss and take profit levels before entering the market. These levels help limit potential losses and secure potential profits. A stop loss order automatically closes your position if the market moves against you, while a take profit order locks in profits when the market reaches a predetermined price level.
- Utilize Trailing Stops: Consider using trailing stops, which adjust your stop loss order as the market moves in your favor. Trailing stops allow you to protect profits while giving your position room to potentially capture larger gains if the market continues to move in your favor.
- Monitor Price Movements: Keep a close eye on oil price movements, market trends, and news events that may impact the oil market. Stay updated with the latest market information to make informed decisions regarding your position. Utilize charts, technical indicators, and other analytical tools to assess market trends and potential entry or exit points.
- Follow Risk Management Strategies: Implement sound risk management techniques to protect your trading capital. This may include establishing appropriate position sizes, setting risk limits, and diversifying your portfolio. Adhere to your risk management plan to minimize potential losses and maximize long-term profitability.
- Monitor Margin Requirements: As your futures position fluctuates in value, your broker may require additional margin to maintain your position. Stay aware of the margin requirements and have sufficient funds in your trading account to meet these obligations. Failure to meet margin calls can result in forced liquidation of your position.
- Stay Informed and Adapt: Continuously stay informed about factors that impact the oil market, such as geopolitical events, economic data releases, and industry news. Be prepared to adapt your trading strategy and adjust your position based on new information that becomes available.
Effective position management requires discipline, vigilance, and the ability to make informed decisions based on market conditions. It’s important to strike a balance between being actively involved in managing your position and avoiding overtrading or making impulsive decisions based on emotions.
Regularly assess the performance of your position and evaluate whether it aligns with your trading goals and strategy. Consider taking partial profits or adjusting your stop loss levels as the market evolves. This flexibility and adaptability are key to successful futures trading.
Lastly, keep detailed records of your trades, including entry and exit points, profit/loss figures, and the rationale behind each trade. Analyzing past trades can help you identify patterns, strengths, and areas for improvement in your trading approach.
As you gain experience and develop a deeper understanding of the oil market, you’ll become better equipped to manage and monitor your futures position effectively.
Next, we’ll discuss the process of closing a futures contract when you decide to exit your position.
Closing a Futures Contract
Closing a futures contract involves liquidating your position and exiting the market. There are several reasons why you may choose to close a futures contract, such as achieving your desired profit target, limiting losses, or simply because the contract is nearing its expiration date. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to close a futures contract:
- Assess Your Position: Evaluate the performance of your futures position and determine if it aligns with your trading objectives. Consider factors such as profit/loss, market conditions, and any new information that may impact your decision to close the position.
- Monitor Price Movements: Stay informed about the current market price and track any relevant market trends or events. Keep in mind that futures contracts are marked-to-market daily, which means the value of your position fluctuates based on the prevailing market prices.
- Decide on Closure Method: There are two general ways to close a futures contract: offsetting and physical delivery. Offset or liquidation involves entering an equal and opposite transaction to your existing position, effectively canceling it out. Physical delivery occurs when you hold the position until the contract’s expiration date and take delivery of the physical underlying commodity (in this case, oil). Note that most traders opt for offsetting rather than physical delivery.
- Select the Closure Order Type: Depending on the brokerage and futures exchange, you can choose from various order types to close your position. Common options include market orders, limit orders, and stop orders. A market order allows you to close the position at the prevailing market price, while a limit order lets you specify a specific price at which you want the order to be executed.
- Submit the Closure Order: Enter the necessary details, such as the contract symbol, order type, quantity, and desired price (if applicable). Review the information for accuracy, ensuring that you are closing the correct contract and position. Once you are confident, submit the closure order to the futures exchange.
After submitting the closure order, it will be executed by matching your order with a counterparty’s order. Once the trade is complete, your position will be closed, and you will receive a confirmation from your broker indicating that the contract has been successfully closed.
It’s important to note that closing a futures contract may result in a profit or loss, depending on the difference between the contract’s opening and closing prices. It’s essential to manage your risk and adhere to your risk management strategy when deciding to close a position.
Keep in mind that if the futures contract is still open as it approaches its expiration date, you may need to consider rolling over the position to a contract with a later expiration date. Rollover involves closing the existing contract and simultaneously opening a new one to maintain exposure to the market.
By actively monitoring your position, being aware of market trends, and making informed decisions, you can effectively manage your futures contracts and close them when the time is right.
Now that we have covered the process of closing a futures contract, let’s explore the risks and considerations involved in oil futures trading.
Risks and Considerations in Oil Futures Trading
While oil futures trading can offer exciting opportunities for profit, it’s important to understand the risks and considerations involved. Trading oil futures carries inherent risks, and being aware of these factors can help you make informed decisions and manage your trading effectively. Here are some key risks and considerations in oil futures trading:
- Price Volatility: The oil market is known for its price volatility, which can result in significant price fluctuations within short periods. Sudden geopolitical events, changes in global supply and demand, and economic data releases can all contribute to sharp price movements. It’s important to be prepared for these price swings and have a risk management strategy in place.
- Margin and Leverage: Futures trading involves using leverage, which means that you can control a larger position with a relatively small margin deposit. While leverage can amplify potential profits, it also magnifies potential losses. It’s crucial to understand the margin requirements and the potential impact of leverage on your trading account. Consider carefully managing your positions and ensuring you have enough margin to meet obligations.
- Liquidity: Liquidity can vary in the oil futures market, especially during off-peak trading hours or when there is low market participation. Lower liquidity can result in wider bid-ask spreads and have implications for executing trades at desired prices. It’s important to consider the liquidity of the specific futures contract you are trading and factor this into your trading plan.
- Market Influence: The oil market can be influenced by several external factors, including political events, global economic conditions, weather patterns, and regulatory changes. These factors are beyond the control of individual traders and can significantly impact price movements. Stay informed about market news and events to anticipate and adapt to potential market shifts.
- Risk of Incomplete Information: Like in any market, there is always a risk of incomplete or inaccurate information. It’s crucial to conduct thorough research, rely on reputable sources, and validate information before making trading decisions. Be cautious of rumors or unverified news that may impact the oil market.
- Market Bias: It’s essential to be mindful of potential biases in the market, such as herd mentality or overwhelming optimism/pessimism. These biases can lead to price distortions and market inefficiencies. Develop a trading plan with objective criteria and stick to it, avoiding impulsive decisions based on emotions or market sentiment.
It’s important to remember that trading oil futures involves the risk of substantial financial loss, and past performance is not indicative of future results. Before engaging in oil futures trading, it’s advisable to gain a solid understanding of the market, develop a trading plan, and practice with demo accounts or smaller positions to gain experience.
Consider seeking professional advice or guidance if you are new to futures trading or if you need assistance understanding the complexities of the oil market. A qualified financial advisor or broker can help you navigate the risks and guide you in making informed trading decisions.
By understanding and managing the risks associated with oil futures trading, you can approach this investment opportunity with caution and potentially maximize your chances of success.
Now let’s conclude our guide on buying futures contracts for oil.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You have now reached the end of our comprehensive guide on buying futures contracts for oil. We have covered essential aspects of oil futures trading, including understanding futures contracts, choosing a futures exchange, selecting contract types, researching market trends, opening a trading account, placing and managing orders, closing contracts, and considering risks and considerations.
While oil futures trading can be exciting and potentially profitable, it’s crucial to approach it with care and a solid understanding of the market dynamics. Conduct thorough research, stay informed about market trends, and develop a comprehensive trading plan that includes risk management strategies. Keep in mind that successful trading requires ongoing learning, adaptability, and the ability to make informed decisions.
Remember, the oil market is affected by numerous factors beyond anyone’s control, including geopolitical events, supply and demand dynamics, and economic conditions. Monitor the market, stay updated with relevant news, and be prepared to adjust your strategies as needed.
Lastly, always prioritize risk management. Determine your risk tolerance, set stop loss levels, and avoid over-leveraging your positions. Trading oil futures involves the potential for substantial gains but also significant losses, so be prudent and trade with caution.
By following this guide, staying disciplined, and continuously expanding your knowledge of the oil market, you can increase your chances of success in trading oil futures contracts.
Good luck on your trading journey, and may the oil market bring you prosperous opportunities!