
Finance
How Long Are Futures Contracts For Jet Fuel
Published: December 23, 2023
Discover the timeline for futures contracts in the finance industry, specifically for jet fuel. Learn about the length and expiration of these contracts.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Futures contracts are an integral part of the financial markets, enabling participants to mitigate risk and speculate on the price movements of various commodities, including jet fuel. These contracts serve as a vital tool for airlines, energy firms, and investors to plan and manage their exposure to fluctuations in the jet fuel market.
In this article, we will delve into the world of futures contracts for jet fuel and explore the specificities of these contracts, with a particular focus on their duration. Understanding the length of jet fuel futures contracts is crucial for anyone involved in the aviation industry or interested in the energy markets.
By grasping the intricacies of these contracts and the factors that influence their length, you can gain valuable insights into the dynamics of the jet fuel market and make more informed decisions regarding trading strategies, risk management, and fuel procurement.
So, if you’re ready to dive into the fascinating world of jet fuel futures contracts and discover how long these contracts typically last, let’s get started!
Understanding Futures Contracts
Before delving into the specifics of jet fuel futures contracts, it is essential to have a basic understanding of what futures contracts are and how they function.
A futures contract is a legally binding agreement between two parties to buy or sell a specific asset at a predetermined price and date in the future. These assets can include commodities such as agricultural products, metals, energy, and financial instruments.
The main purpose of futures contracts is to provide a standardized platform for trading and hedging against price volatility. They allow market participants to lock in future prices and protect themselves from adverse price movements.
Unlike options contracts, which provide the right but not the obligation to buy or sell an asset, futures contracts obligate both parties to fulfill their contractual obligations. This means that at the expiry of the contract, the buyer is obligated to purchase the asset, and the seller is obliged to deliver it.
Futures contracts are traded on exchanges, such as the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) or the Intercontinental Exchange (ICE), where buyers and sellers can easily execute trades. The exchange ensures liquidity, transparency, and standardized contract terms, making it easier for market participants to enter and exit positions.
The pricing of futures contracts is based on the concept of ‘marking to market,’ where the contract’s value is settled daily based on the prevailing market prices. This mechanism ensures that both parties are protected against adverse price movements and that the contract’s value remains up to date.
Overall, futures contracts play a vital role in financial markets, enabling participants to manage risk, speculate on price movements, and provide price stability for various commodities and assets.
Specifics of Jet Fuel Futures Contracts
Jet fuel futures contracts are a specific type of futures contract that focuses on the price of aviation fuel, commonly known as jet fuel. These contracts allow airlines, jet fuel suppliers, and investors to manage their exposure to price fluctuations in the jet fuel market.
In the United States, jet fuel futures are primarily traded on the New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX), a subsidiary of the CME Group. The standard jet fuel futures contract size is 42,000 gallons, and it is priced in U.S. dollars per gallon.
Jet fuel futures contracts specify the quality and delivery location of the jet fuel. The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) sets the quality standards for jet fuel, ensuring that it meets the necessary requirements for aircraft safety and performance.
The most commonly referenced jet fuel futures contract is the NYMEX Gulf Coast Jet Fuel (Platts) Futures Contract. This contract represents the price of jet fuel delivered to the U.S. Gulf Coast region, which is a major hub for the aviation industry.
Aside from the Gulf Coast contract, there are also jet fuel futures contracts that represent prices for other delivery locations, such as New York Harbor, Los Angeles, and Singapore. These contracts cater to the demands of different market participants around the world.
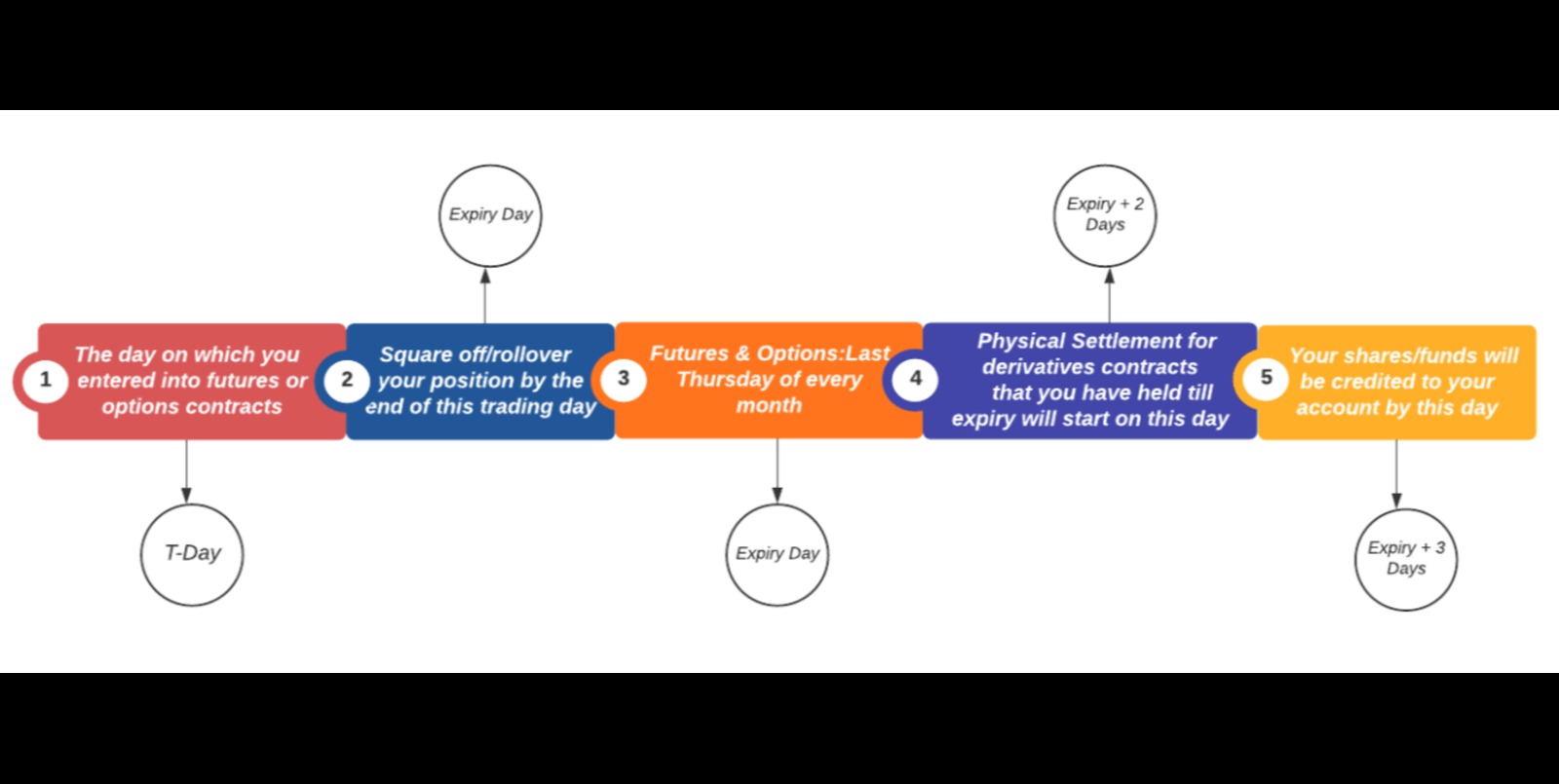
It is important to note that jet fuel futures contracts are settled through cash settlement rather than physical delivery. This means that when the contract expires, the profit or loss is settled in cash, based on the difference between the contract price and the market price at the time of expiry.
Furthermore, jet fuel futures contracts have specific contract months, which indicate when the contracts expire. These months are typically based on a standardized expiration cycle, such as the nearest three months in the March quarterly cycle (e.g., March, June, September, December).
Overall, jet fuel futures contracts provide a standardized and regulated platform for market participants to manage their exposure to jet fuel prices. By trading these contracts, airlines, fuel suppliers, and investors can hedge against price volatility and gain insights into the market’s expectations for future jet fuel prices.
Duration of Jet Fuel Futures Contracts
The duration of jet fuel futures contracts refers to the length of time between the contract’s initiation and its expiration. Jet fuel futures contracts have predefined durations, typically spanning from a few months to a couple of years.
The specific duration of a jet fuel futures contract depends on various factors, including market demand, liquidity, and the underlying delivery cycle. These factors influence the availability of contract months and determine the length of time for which participants can trade these contracts.
Generally, jet fuel futures contracts have monthly expiration dates, allowing participants to establish positions for the specific delivery months that suit their needs. For example, a contract expiring in March might be available for trading several months in advance, allowing participants to plan their positions accordingly.
The duration of a jet fuel futures contract can have significant implications for market participants. Airlines, for instance, may choose to enter into futures contracts to secure a stable price for their future fuel needs. By locking in prices through longer-term contracts, they can mitigate the risk of price fluctuations and better plan their operational expenses.
On the other hand, jet fuel suppliers may use futures contracts to hedge against the risk of price decreases or to speculate on future price increases. By taking positions in shorter-term contracts, suppliers can adjust their pricing and manage their inventory accordingly.
Additionally, investors and speculators also trade jet fuel futures contracts to capitalize on price movements and profit from market trends. The duration of their contracts depends on their trading strategies, risk appetite, and market analysis.
It’s important to note that while the duration of jet fuel futures contracts is predefined, participants have the flexibility to exit their positions before the contract’s expiration. Early termination is possible by offsetting the contract through an opposite trade or by allowing it to settle in cash.
Ultimately, the duration of jet fuel futures contracts provides market participants with the necessary flexibility to manage their risk exposure and align their trading strategies with their specific needs and market outlook.
Factors Influencing Contract Length
Several factors influence the length of jet fuel futures contracts, reflecting the dynamic nature of the energy markets and the needs of market participants. Understanding these factors is essential for both industry professionals and investors looking to effectively navigate the world of jet fuel futures.
1. Market Volatility: The level of volatility in the jet fuel market can influence the duration of futures contracts. In times of heightened volatility, market participants may prefer shorter-term contracts to quickly adjust their positions and adapt to changing market conditions.
2. Trading Liquidity: The availability of contract months and trading volumes for specific durations are influenced by liquidity in the futures market. If there is low liquidity for a certain timeframe, market participants may have limited options in terms of contract lengths.
3. Seasonal Demand: The seasonal demand for jet fuel can impact the contract length. Airlines may need to secure contracts for specific periods when travel demand is high, such as during the summer vacation season or holiday travel period.
4. Supply Chain Considerations: The length of jet fuel futures contracts can also be influenced by logistical factors in the supply chain. For example, delivery and storage constraints may limit participants’ ability to trade contracts for longer durations, especially in regions with limited infrastructure.
5. Regulatory Environment: Regulatory frameworks and market rules can also influence the duration of futures contracts. Regulatory bodies may set restrictions or guidelines on contract lengths to ensure a fair and transparent trading environment.
6. Economic Outlook: The overall economic outlook and factors such as interest rates, inflation, and geopolitical events can impact the duration of futures contracts. Participants may adjust their contract lengths based on their expectations of economic conditions and their impact on fuel prices.
7. Risk Management Strategies: Market participants’ risk management strategies and hedging needs can also shape the duration of futures contracts. Different entities have varying risk profiles and may choose to enter into contracts of different lengths to align with their risk management objectives.
It’s important to note that these factors are interrelated and can vary over time. Market conditions and participants’ needs can change, leading to shifts in the duration of jet fuel futures contracts. Staying informed about these factors and monitoring market developments is crucial for effectively navigating the jet fuel futures market.
Conclusion
Jet fuel futures contracts play a critical role in the aviation industry and energy markets, allowing participants to manage risk, hedge against price volatility, and gain insights into future fuel prices. Understanding the duration of these contracts is essential for effective fuel procurement, risk management, and trading strategies.
While the specific length of jet fuel futures contracts can vary, they typically range from a few months to a couple of years. The available contract months and durations are influenced by market demand, liquidity, delivery cycles, and other factors.
Airlines can utilize longer-term contracts to secure stable fuel prices, enabling them to better plan their operational expenses. Jet fuel suppliers may trade shorter-term contracts to adjust pricing and manage inventory efficiently. Investors and speculators, on the other hand, can profit from price movements and capitalize on market trends using contracts of various durations.
Market volatility, trading liquidity, seasonal demand, supply chain considerations, regulatory factors, economic outlook, and risk management strategies are among the key factors that influence the contract length. Understanding these factors helps participants navigate and make informed decisions in the dynamic jet fuel futures market.
As with any financial instrument, it’s crucial for individuals and organizations engaging in jet fuel futures contracts to stay vigilant and keep abreast of market developments. By remaining informed about market conditions and monitoring the factors that impact contract lengths, participants can effectively manage risk and stay ahead in this ever-evolving industry.
In conclusion, jet fuel futures contracts provide a standardized platform for market participants to mitigate risk, speculate on fuel price movements, and make strategic decisions. The duration of these contracts is influenced by a combination of market dynamics, participant needs, and external factors. Understanding and adapting to the contract lengths enables participants to navigate the jet fuel futures market successfully and achieve their objectives.