Home>Finance>How To Record Employee Retention Credit In General Ledger


Finance
How To Record Employee Retention Credit In General Ledger
Published: January 10, 2024
Learn how to properly record the employee retention credit in your general ledger. This comprehensive guide will help you navigate the finance aspect of this important tax credit.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of finance, where the intricacies of money management can seem daunting. One important aspect of finance is employee retention credit, which plays a significant role in fostering employee loyalty and reducing turnover. In this article, we will explore the concept of employee retention credit and guide you on how to record it in your general ledger.
Employee retention credit is a tax credit that incentivizes businesses to retain their employees during challenging times, such as the COVID-19 pandemic. It is designed to provide financial relief to businesses by reducing their tax liability. By taking advantage of this credit, businesses can not only support their employees but also enjoy significant cost savings.
Understanding and maximizing the employee retention credit can greatly benefit your organization, particularly in times of economic uncertainty. However, it is crucial to have a clear understanding of the eligibility criteria and calculation methodology to accurately record and utilize this credit.
In this article, we will cover the essential aspects of employee retention credit, including the eligibility criteria, calculation methods, and how to record it in your general ledger. By the end, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how to leverage this credit to your advantage and ensure compliance with relevant financial regulations.
So, let’s dive into the world of employee retention credit and discover the practical steps to record it effectively in your general ledger.
Understanding Employee Retention Credit
Employee retention credit is a tax incentive introduced by the government to encourage businesses to retain their employees during challenging economic times. It was initially established as part of the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. The credit was extended and expanded under subsequent legislation, such as the Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2021 (CAA) and the American Rescue Plan Act (ARPA).
The purpose of the employee retention credit is to provide financial assistance to businesses struggling to retain their workforce. By offering this credit, the government aims to alleviate the burden on businesses and prevent widespread layoffs and closures.
Eligible employers can claim the employee retention credit against their payroll taxes. The credit amount is based on a percentage of qualified wages paid to eligible employees during a specific time period. These qualified wages include both cash compensation and certain types of health plan expenses.
It is important to note that the eligibility criteria and calculation methods for employee retention credit have evolved over time due to legislative changes. To ensure compliance and accurately claim the credit, businesses need to stay updated with the latest guidelines and consult with tax professionals or financial advisors.
One key aspect of employee retention credit is that it is mutually exclusive with other government assistance programs, such as the Paycheck Protection Program (PPP) loans. If a business received a PPP loan, they may be ineligible for certain periods of the employee retention credit. It is essential to carefully evaluate the overlap and determine the most beneficial option for your unique circumstances.
Overall, employee retention credit is a powerful tool that can help businesses navigate through challenging economic conditions and maintain their workforce. By understanding the intricacies of this credit, businesses can make informed decisions, minimize financial strain, and contribute to employee stability and job security.
Eligibility Criteria for Employee Retention Credit
To take advantage of the employee retention credit, businesses must meet certain eligibility criteria. Understanding these criteria is crucial to determine if your organization qualifies for the credit. The following are the key requirements:
- Impact on Business Operations: To be eligible for the employee retention credit, a business must demonstrate a significant decline in gross receipts. Under the initial CARES Act, businesses were required to show a decline of at least 50% in gross receipts compared to the same quarter in the previous year. However, with subsequent legislation, the threshold was lowered to 20%. This change enables more businesses to qualify for the credit.
- Employment Status: The credit is available to businesses that have experienced either a full or partial suspension of operations due to government orders or have faced a significant decline in gross receipts. Businesses that were partially or fully closed due to COVID-19 restrictions or experienced a substantial decrease in revenue are generally eligible for the credit.
- Number of Employees: The eligibility criteria for the employee retention credit also consider the size of the employer. For 2020, businesses with 100 or fewer full-time equivalent employees were eligible for the credit for all wages paid during the eligible period, regardless of whether the employees were working or not. However, for 2021, the threshold was increased to 500 employees. Therefore, businesses with up to 500 full-time equivalent employees can claim the credit for wages paid to employees who are not working during the eligible periods.
- Government Assistance Programs: As mentioned earlier, businesses that received a PPP loan may face limitations on claiming the employee retention credit. If a business received a PPP loan, they are generally ineligible to claim the credit for the same wages used to justify loan forgiveness. However, there may be specific circumstances and exceptions, so it is essential to consult with tax professionals or advisors to determine eligibility.
It is important to note that the eligibility criteria for the employee retention credit can vary depending on the specific legislation in effect and any subsequent updates. Therefore, businesses must stay informed about the latest guidelines and consult with tax professionals to ensure compliance and accurate determination of eligibility.
By meeting the eligibility criteria, businesses can leverage the employee retention credit to reduce their tax liability and provide financial support to their workforce during challenging times.
Calculating Employee Retention Credit
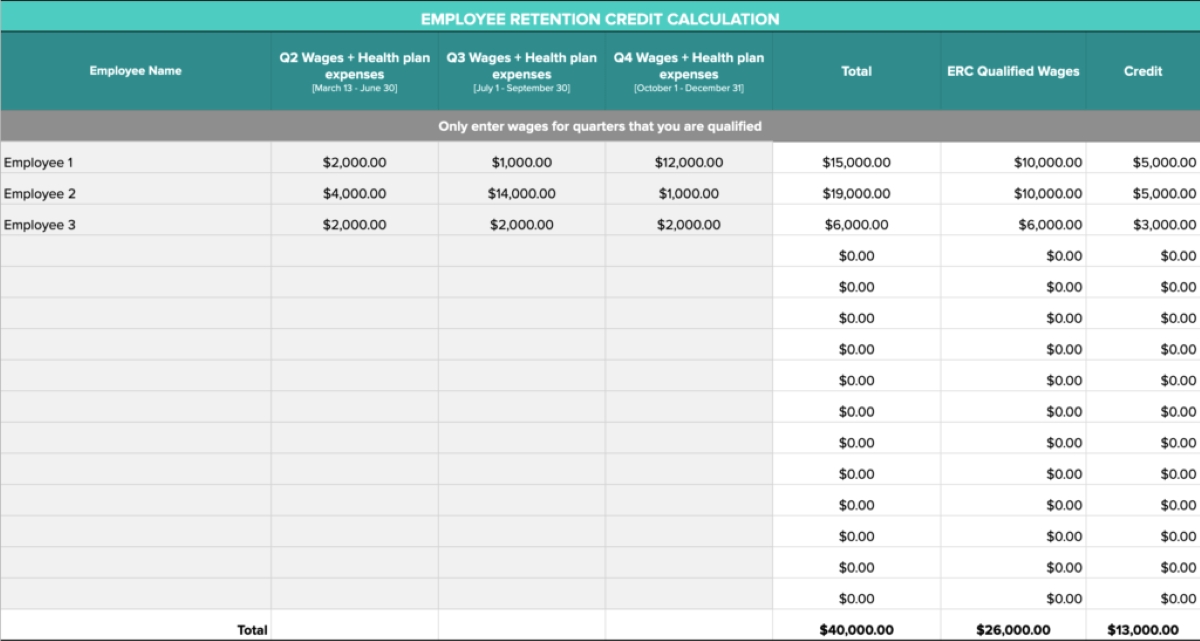
Calculating the employee retention credit involves determining the eligible wages and applying the appropriate percentage to calculate the credit amount. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to calculate the employee retention credit:
- Determine the eligible wages: Start by identifying the wages that qualify for the employee retention credit. For eligible employers, qualified wages include wages paid to employees who are not working due to full or partial suspension of operations or significant decline in gross receipts. It’s important to note that there is a cap on eligible wages per employee per quarter. For 2020, the maximum eligible wages per employee per quarter were $10,000. However, for 2021, the cap was increased to $10,000 per employee per quarter.
- Calculate the credit amount: Once you have determined the eligible wages, apply the applicable percentage to calculate the employee retention credit. The initial percentage under the CARES Act was 50% of qualified wages, up to a maximum of $10,000 per employee for all quarters combined. However, the subsequent legislation expanded the credit, and for 2021, businesses can claim up to 70% of qualified wages, up to a maximum of $10,000 per employee per quarter.
- Offset against payroll taxes: The employee retention credit is applied against the employer’s share of Social Security taxes. If the credit amount exceeds the employer’s payroll taxes for the quarter, the excess can be carried forward to future quarters or even claimed as a refund, depending on the specific circumstances.
It’s important to remember that businesses cannot claim the employee retention credit and the Work Opportunity Tax Credit (WOTC) for the same employee and qualified wages. Therefore, it’s crucial to evaluate which credit provides greater financial benefits and make an informed decision.
Calculating the employee retention credit can be complex, especially with changing legislation and evolving eligibility criteria. Working with tax professionals or financial advisors can help ensure accurate calculations and maximize the benefits of the credit.
By understanding the calculation methodology, businesses can make informed decisions and take full advantage of the employee retention credit to alleviate financial strain and support their workforce.
Recording Employee Retention Credit in General Ledger
Recording employee retention credit in your general ledger is essential to accurately track and document the credit for financial reporting purposes. Here are the steps to record employee retention credit in your general ledger:
- Create a new account: Start by creating a new account in your general ledger specifically for the employee retention credit. This account should be categorized under a relevant expense or income account, depending on your accounting system and practices.
- Enter the credit amount: Once you have created the account, enter the credit amount in the designated field. The credit amount will be based on the calculation as determined by the qualified wages and applicable percentage.
- Include appropriate descriptions: Provide clear and concise descriptions for the entry, ensuring that it identifies the purpose of the credit, the specific period it pertains to, and any other relevant details. This information will help with future reference and audits.
- Offset against payroll taxes: If the employee retention credit exceeds the employer’s share of Social Security taxes for the applicable quarter, record the excess amount as a liability or carry it forward to future quarters, depending on your accounting practices and the specific circumstances.
- Reconcile and review: Regularly reconcile and review the employee retention credit account in your general ledger to ensure accuracy and compliance. This step will help identify any discrepancies or potential errors that may need to be rectified.
- Document supporting documents: Maintain proper documentation, including payroll information, financial statements, and any other relevant records, to substantiate the employee retention credit claimed. This documentation will be essential for future reference and audits.
It is important to consult with your accounting team, tax professionals, or financial advisors to ensure that you are following the appropriate accounting standards and regulations when recording employee retention credit in your general ledger. They can provide guidance and expertise specific to your organization’s circumstances.
By accurately recording employee retention credit in your general ledger, you can effectively track and report the credit, ensuring compliance and transparency in your financial records.
Examples of Recording Employee Retention Credit in General Ledger
Let’s explore a couple of examples to demonstrate how employee retention credit can be recorded in your general ledger:
Example 1: Company ABC, a small business, experienced a significant decline in gross receipts due to the COVID-19 pandemic. They have determined that they are eligible for the employee retention credit for the second quarter of 2021. The total credit amount for the quarter is $20,000.
In their general ledger, they create a new account called “Employee Retention Credit” under the expense category. They enter the credit amount of $20,000 and provide a clear description, specifying the period and purpose of the credit. Additionally, they offset the credit against their quarterly payroll taxes, which amount to $15,000. As a result, they record a liability of $5,000 for the excess credit amount that will be carried forward to the next quarter or subsequent quarters, depending on their accounting practices.
Example 2: Company XYZ, a larger organization, determines that they are eligible for the employee retention credit for the third quarter of 2021. The total credit amount for the quarter is $100,000, and their quarterly payroll taxes amount to $80,000.
In their general ledger, they create a new account called “Employee Retention Credit” under the income category. They enter the credit amount of $100,000 and provide a detailed description, specifying the period and purpose of the credit. As the credit amount exceeds their quarterly payroll taxes, they do not record any excess liability. Instead, they offset the entire credit amount against their payroll taxes for the quarter, resulting in a reduced tax liability of $0 and a net credit of $20,000. This net credit can be carried forward to future quarters or potentially claimed as a refund, depending on their specific circumstances.
Remember, the exact recording method may vary based on your organization’s accounting system and practices. It is advisable to consult with your accounting team or financial advisors to ensure accurate and compliant recording of the employee retention credit in your general ledger.
By reviewing these examples and following proper accounting practices, you can effectively record and track employee retention credit, maintaining transparent financial records and compliance with applicable regulations.
Conclusion
Employee retention credit is a valuable tax incentive that can provide significant financial relief to businesses facing economic challenges. Understanding the eligibility criteria, calculating the credit amount, and recording it accurately in your general ledger are essential steps to leverage this credit effectively.
In this article, we covered the fundamental aspects of employee retention credit, including its purpose, eligibility criteria, calculation methods, and how to record it in your general ledger. By meeting the eligibility requirements and accurately capturing the credit in your financial records, you can not only reduce your tax liability but also support your employees during difficult times.
It’s important to stay informed about the evolving guidelines and consult with tax professionals or financial advisors to ensure compliance with current regulations and take advantage of any updates or changes to the employee retention credit program.
Remember, accurate recording and documentation of the employee retention credit in your general ledger is crucial for financial reporting, audits, and maintaining transparency. Employing best accounting practices and consulting with experts will help ensure compliance and maximize the benefits of the credit for your organization.
By effectively utilizing the employee retention credit, you can contribute to employee stability, reduce turnover, and navigate through economic uncertainties with greater financial resilience.