Home>Finance>What Is The Deadline For The Employee Retention Credit


Finance
What Is The Deadline For The Employee Retention Credit
Modified: February 21, 2024
Discover the deadline for claiming the Employee Retention Credit and its financial impact. Maximize your finance strategy with this key information.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
The Employee Retention Credit (ERC) is a valuable tax credit provided by the U.S. government to help businesses retain and keep their employees on the payroll during challenging economic times. Introduced as a part of the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, the ERC aims to provide financial relief to eligible employers and stimulate the economy.
This tax credit is designed to incentivize businesses to continue paying their employees, even if they have experienced a significant decline in revenue or were forced to suspend operations due to government orders. The ERC not only benefits businesses but also helps employees by ensuring they have a stable source of income during a time of economic uncertainty.
In order to take advantage of the Employee Retention Credit, businesses need to meet certain eligibility criteria and apply for the credit within the specified deadline. Understanding the details of the ERC and its application process is crucial for employers who want to maximize their tax benefits and support their workforce.
In this article, we will provide an overview of the Employee Retention Credit, discuss the eligibility requirements, explain how to calculate the credit amount, and explore recent extensions and changes to the program. Additionally, we will highlight the important deadline for filing for the Employee Retention Credit.
By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of the Employee Retention Credit and how it can benefit your business in retaining your valuable employees.
Overview of the Employee Retention Credit
The Employee Retention Credit (ERC) is a tax credit available to eligible employers who have experienced a significant decline in revenue or were subject to a full or partial suspension of operations due to COVID-19. It was introduced as part of the CARES Act in March 2020 and has since undergone changes and extensions to provide additional support to businesses impacted by the pandemic.
The ERC is designed to incentivize employers to maintain their workforce by offsetting a portion of the qualified wages paid to employees. The credit is calculated as a percentage of qualified wages, with a maximum credit of $5,000 per employee for the entire year.
Initially, the ERC was available to employers who experienced a decline in gross receipts of 50% or more compared to the same quarter in the previous year. However, with subsequent changes to the program, the eligibility requirements were expanded to include employers who experienced a decline of 20% or more in gross receipts.
Additionally, the ERC covers wages paid to employees even if they are not actively working. This means that if a business is unable to operate due to government-mandated closures or other factors related to COVID-19, they can still claim the credit for wages paid during the period of closure.
It’s important to note that the ERC is a refundable credit, which means that if the amount of the credit exceeds the employer’s total tax liability, they are eligible to receive the excess as a refund. This provides an immediate benefit to businesses, especially those facing financial challenges during these uncertain times.
Overall, the Employee Retention Credit serves as a lifeline for businesses, helping them to retain their employees and navigate through the economic disruptions caused by the pandemic. By providing financial assistance through tax credits, the ERC aims to support businesses and maintain the stability of the workforce.
Eligibility for the Employee Retention Credit
Understanding the eligibility requirements for the Employee Retention Credit (ERC) is crucial for employers who want to take advantage of this valuable tax credit. To qualify for the ERC, employers must meet certain criteria:
- Business operations: The ERC is available to businesses, including tax-exempt organizations, that have carried on a trade or business during the calendar year in which the credit is claimed.
- Significant decline in gross receipts: Initially, the ERC was available to employers who experienced a decline in gross receipts of 50% or more compared to the same quarter in the previous year. However, this threshold was lowered to 20% or more due to subsequent changes in the program. Employers can determine eligibility by comparing their gross receipts for the applicable calendar quarter to the same quarter in the prior year.
- Full or partial suspension: Employers can also qualify for the ERC if their business operations were fully or partially suspended by government order due to COVID-19. A full suspension means that the business has been completely shut down, while a partial suspension refers to a significant reduction in business activities due to government-imposed restrictions.
It’s important to note that there are a few exclusions to eligibility. For example, employers who received a Paycheck Protection Program (PPP) loan cannot claim the ERC for the same wages used to qualify for loan forgiveness under the PPP. Additionally, the ERC cannot be claimed for wages that are already receiving certain other tax credits, such as the Work Opportunity Tax Credit.
Furthermore, the ERC is available to both large and small employers, with a few differences in the calculation for each group. For employers with more than 100 full-time employees, qualified wages are limited to wages paid to employees who are not providing services due to the suspension of operations or a significant decline in gross receipts. However, for employers with 100 or fewer full-time employees, all wages paid during the eligible period, whether employees are providing services or not, can be considered for the credit.
It’s important to consult with a tax or financial professional to determine eligibility and properly calculate the Employee Retention Credit based on your specific circumstances. Additionally, the IRS provides detailed guidance on eligibility criteria, documentation requirements, and other aspects of the ERC, which can assist employers in navigating the application process accurately.
Calculation of the Employee Retention Credit
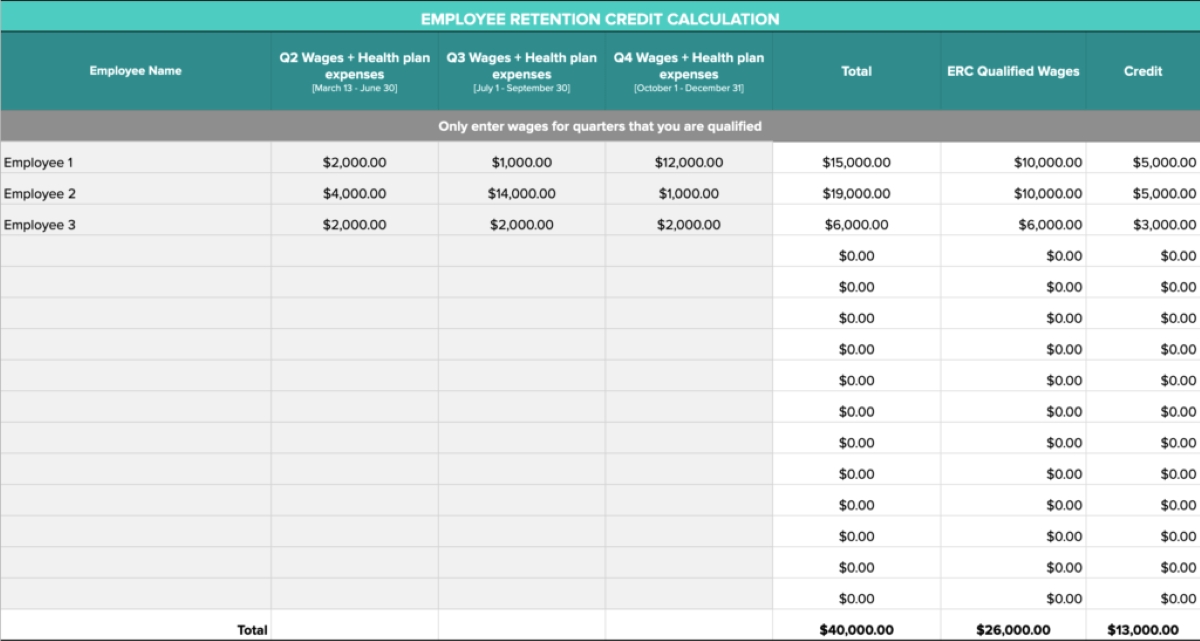
The calculation of the Employee Retention Credit (ERC) is based on the qualified wages paid to eligible employees during the eligible period. The credit amount is a percentage of these qualified wages, subject to certain limitations and maximums.
For employers with more than 100 full-time employees, qualified wages are limited to those paid to employees who are not providing services due to the suspension of operations or a significant decline in gross receipts. On the other hand, for employers with 100 or fewer full-time employees, all wages paid during the eligible period can be considered for the credit, regardless of whether employees are providing services or not.
The calculation of the ERC involves the following steps:
- Determine the eligible periods: The ERC is applicable for wages paid after March 12, 2020, and before January 1, 2022. The eligible periods can vary depending on the specific circumstances and changes in eligibility criteria.
- Determine the qualified wages: Qualified wages are determined differently for employers with more than 100 full-time employees and employers with 100 or fewer full-time employees, as mentioned earlier. The maximum amount of qualified wages considered for the credit is $10,000 per eligible employee per calendar quarter.
- Calculate the percentage of the credit: The percentage of the credit is determined based on the applicable rules for the specific eligible period. Initially, the ERC was set at 50% of qualified wages up to $10,000 per employee for all calendar quarters. However, subsequent changes allowed for an increased credit percentage of 70% for certain quarters.
Once the qualified wages and credit percentage are determined, employers can calculate the credit by multiplying the eligible wages by the credit percentage. It’s important to note that the ERC is a refundable credit, which means that if the credit exceeds the employer’s total tax liability, they are eligible for a refund of the excess amount.
Employers must maintain records and documentation to support their calculation of the ERC, including payroll records, financial statements, and other relevant documentation. It’s advisable to consult with a tax or financial professional who can guide you through the calculation process and ensure compliance with all applicable rules and regulations.
Extension and Changes to the Employee Retention Credit
Since its inception, the Employee Retention Credit (ERC) has undergone several changes and extensions to provide additional support to businesses affected by the COVID-19 pandemic. These updates have expanded the eligibility criteria and enhanced the benefits of the credit, allowing more employers to take advantage of this valuable tax incentive.
One of the major changes to the ERC was the extension of the eligible periods. Initially, the ERC was available for wages paid after March 12, 2020, and before January 1, 2021. However, the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2021 extended the eligible period to include wages paid before July 1, 2021. In other words, employers can continue to claim the credit for qualified wages throughout the first two quarters of 2021.
Another notable change is the expansion of eligibility criteria. Previously, employers who experienced a decline in gross receipts of 50% or more compared to the same quarter in the previous year were eligible for the ERC. However, the threshold was lowered to 20% or more due to subsequent updates, making it easier for businesses to qualify for the credit. This change opened up the opportunity for more employers to take advantage of the credit and receive financial relief.
Furthermore, the American Rescue Plan Act passed in March 2021 introduced additional modifications to the ERC. The Act extended the eligible periods once again, allowing employers to claim the credit for wages paid before January 1, 2022. It also increased the credit percentage from 50% to 70% of qualified wages for certain quarters, providing businesses with an even greater benefit.
Additionally, the Act expanded the credit by including certain start-up businesses that were previously ineligible. These businesses can now claim the ERC based on the wages paid to employees during the eligible period, even if they did not experience a decline in gross receipts or were subject to suspension of operations.
It’s important for employers to stay updated on the latest changes and updates to the ERC, as they may impact eligibility and the calculation of the credit amount. Consulting with a tax or financial professional can help businesses navigate through these changes and ensure compliance with all applicable rules and regulations.
Deadline for Filing for the Employee Retention Credit
The deadline for filing for the Employee Retention Credit (ERC) depends on various factors, including the specific eligible periods and the filing requirements outlined by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
For the initial eligible periods of the ERC, employers were required to file for the credit on their quarterly employment tax returns. This means that for the wages paid in the first quarter of 2020, the deadline for filing for the ERC was April 30, 2020, and subsequent quarters had corresponding deadlines.
However, the IRS has provided relief and flexibility by allowing employers to claim the ERC retroactively if they did not claim it on previous quarterly filings. This means that even if the deadline for the initial eligible periods has passed, employers can still file for the credit for those quarters.
It’s important to note that the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2021 extended the eligible periods for the ERC to include wages paid before July 1, 2021. Therefore, employers who wish to claim the credit for the first and second quarters of 2021 have until the applicable employment tax return filing deadline to submit their claim.
It’s worth mentioning that employers can either claim the ERC on their quarterly employment tax returns or file for an adjusted employment tax return to claim the credit for previous quarters. The specific form used for claiming the ERC depends on the employer’s circumstances and the quarter for which they are claiming the credit.
Employers must keep accurate records and documentation to support their claims for the ERC, including payroll records, financial statements, and other relevant documentation. These records should be kept for at least four years from the date the taxes were due or paid, whichever is later.
It’s crucial for employers to stay informed about the latest guidelines and deadlines provided by the IRS regarding the ERC. Consulting with a tax professional or accessing the official IRS resources can help ensure that employers meet all the filing requirements and deadlines for claiming the credit.
Conclusion
The Employee Retention Credit (ERC) offers valuable financial relief to eligible employers who have been impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic. It serves as an incentive for businesses to retain their employees and navigate through these challenging times. By understanding the key aspects of the ERC, including eligibility requirements, calculation methods, and filing deadlines, employers can maximize their tax benefits and support their workforce.
The ERC provides a significant opportunity for businesses to offset a portion of the qualified wages paid to employees during eligible periods. It not only helps employers financially but also ensures that employees have a stable source of income during these uncertain times.
It’s important for employers to stay updated on the changes and extensions to the ERC, as they may impact eligibility criteria and benefit calculations. Consulting with a tax or financial professional is highly recommended to navigate the complexities of the ERC and ensure compliance with all applicable rules and regulations.
Keeping accurate records and documentation is essential for claiming the ERC and supporting the calculations made. By maintaining proper documentation, employers can substantiate their claims and potentially qualify for refundable credits that can provide immediate financial relief.
In conclusion, the Employee Retention Credit is a valuable tool for businesses striving to retain their employees and navigate the economic challenges posed by the pandemic. By taking advantage of this tax credit, employers can not only support their workforce but also reduce their overall tax liabilities. Staying informed, understanding eligibility requirements, and meeting the filing deadlines are crucial steps in leveraging the benefits of the ERC and maximizing its potential impact on your business.