
Finance
Where To Buy Futures Contracts
Published: December 24, 2023
Looking to invest in the future of finance? Discover where to buy futures contracts and secure your financial success today.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of futures contracts, where buying and selling financial assets can be an exciting and potentially profitable endeavor. Futures contracts are derivative financial instruments that allow traders to speculate on the future price movement of various assets, including commodities, stocks, bonds, and currencies. In this article, we will explore the ins and outs of buying futures contracts, including the benefits, factors to consider, and where you can purchase them.
Understanding futures contracts is essential before diving into the market. Unlike stocks or bonds, which represent ownership in a company or debt obligation, futures contracts are agreements to buy or sell a specific asset at a predetermined price and date in the future. These contracts are standardized, traded on regulated exchanges, and offer leverage, allowing traders to control a larger position with a smaller amount of capital.
One of the primary benefits of trading futures contracts is the potential for significant profit. Due to the leverage provided, even small price movements in the underlying asset can result in substantial returns. Additionally, futures contracts offer the opportunity to take both long (buy) and short (sell) positions, allowing traders to profit from both upward and downward price movements.
Before buying futures contracts, there are several factors to consider. Firstly, it’s important to understand the risks involved, as trading futures can be highly volatile and may result in significant financial loss. Traders should have a clear understanding of their risk tolerance and develop a comprehensive trading strategy.
In addition, it’s crucial to determine the specific asset or market you wish to trade. Futures contracts are available for a wide range of assets, including commodities like gold, oil, and agricultural products, as well as financial instruments like stock indices and interest rates. Each market has its own unique characteristics, and it’s important to have a solid understanding of the fundamentals and dynamics before diving in.
Now that you have a grasp of the basics, let’s explore where you can buy futures contracts. There are three primary avenues for purchasing futures contracts:
Understanding Futures Contracts
Before delving into the world of buying futures contracts, it’s crucial to have a solid understanding of how these financial instruments work. Futures contracts are agreements between two parties to buy or sell a specific asset at a predetermined price and date in the future.
One key characteristic of futures contracts is their standardization. They are traded on regulated exchanges, such as the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) or the New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX), and have specific contract specifications. These specifications include the size of the contract, the delivery or settlement date, the quality or grade of the asset, and the tick size, which represents the minimum price increment at which the contract can fluctuate.
The standardized nature of futures contracts ensures a liquid market, where traders can easily buy and sell contracts without the need for a willing counterparty. This liquidity is vital for efficient price discovery and allows traders to enter and exit positions with ease.
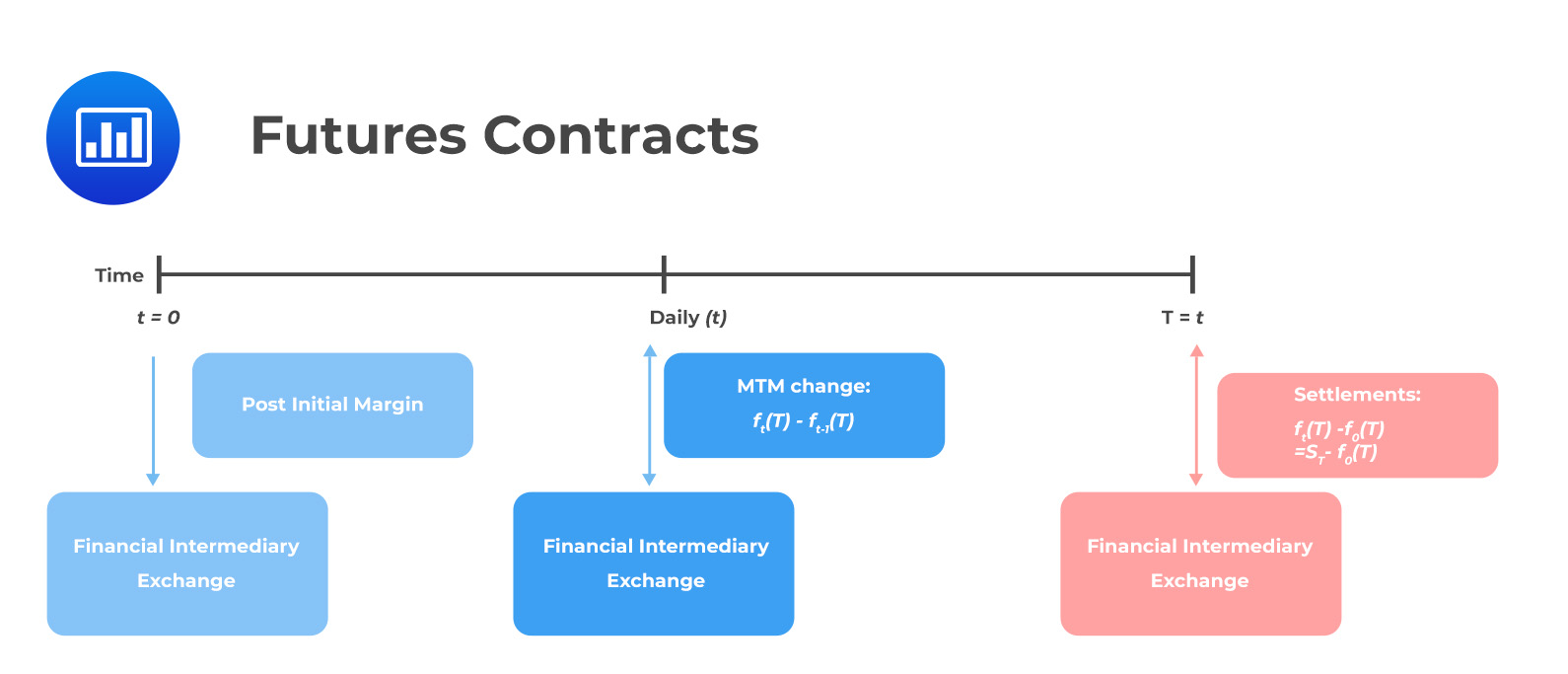
Futures contracts offer leverage, which means that traders can control a larger position with a relatively small amount of capital. The concept of leverage in futures trading is achieved through margin requirements. When entering a futures trade, traders are required to deposit a certain percentage of the contract’s value as margin. This margin serves as collateral and provides a level of protection for the exchange and counterparties in case of adverse price movements.
It’s important to note that leverage amplifies both potential profits and losses. While leverage can enhance returns, it also exposes traders to higher risks. Therefore, it’s crucial to exercise caution and manage risk appropriately when trading futures contracts.
Futures contracts are available for various asset classes, including commodities, stocks, bonds, and currencies. Commodities futures contracts are among the most popular, allowing traders to speculate on the future prices of items such as crude oil, gold, wheat, or natural gas. Stock index futures, on the other hand, enable investors to trade on the direction of entire stock market indexes, such as the S&P 500 or the Dow Jones Industrial Average.
Furthermore, futures contracts also offer the flexibility to take both long (buy) and short (sell) positions. When taking a long position, traders expect the price of the underlying asset to rise, allowing them to profit from the price difference between the contract’s entry and exit. Conversely, when taking a short position, traders anticipate the price of the asset to decline, enabling them to profit from the downward price movement.
Understanding the mechanics and characteristics of futures contracts is vital before venturing into the market. By grasping these concepts, traders can make informed decisions and navigate the futures market with confidence.
Benefits of Trading Futures Contracts
Trading futures contracts offer numerous benefits for investors and traders alike. Let’s explore some of the key advantages:
- Opportunity for Diversification: Futures contracts provide access to a wide range of asset classes, including commodities, stocks, bonds, and currencies. This allows traders to diversify their investment portfolios, spreading risk across different markets and potentially reducing the impact of market fluctuations on overall returns.
- Leverage: As mentioned earlier, futures contracts offer leverage, enabling traders to control a larger position with a smaller amount of capital. This leverage can amplify potential profits, allowing traders to magnify their returns if the market moves in their favor. However, it is important to exercise caution and manage risk appropriately when using leverage, as it also amplifies potential losses.
- Flexibility to Take Both Long and Short Positions: Futures contracts allow traders to take advantage of both upward and downward price movements. Whether a market is bullish or bearish, traders can profit by going long (buying) or short (selling) futures contracts. This flexibility to bet on both sides of the market provides opportunities to make money regardless of the overall market direction.
- Liquidity: Futures contracts are traded on regulated exchanges, which ensures a liquid market with a high volume of buyers and sellers. This liquidity allows traders to enter and exit positions with ease, ensuring efficient pricing and minimizing the risk of slippage (a significant difference between the expected price and the executed price).
- Price Transparency: Futures markets are highly transparent, with real-time price quotes and up-to-date market information readily available. This transparency allows traders to make informed decisions based on market trends, historical data, and other relevant information, enhancing the chances of successful trading.
- Hedging and Risk Management: Futures contracts are not only used for speculative purposes but also for hedging and risk mitigation. For example, commodities producers may use futures contracts to lock in prices for their products, reducing the risk of price volatility. Similarly, investors can hedge their investment portfolios by taking offsetting positions in futures contracts, mitigating potential losses in case of adverse market movements.
- Diverse Trading Opportunities: With a wide range of futures contracts available, traders have access to various markets and investment opportunities. Whether it’s trading agricultural commodities, energy products, stock indices, or interest rates, there are ample choices to suit individual preferences and trading strategies.
These benefits make trading futures contracts an attractive option for both experienced and novice traders. However, it’s crucial to understand the risks involved and thoroughly educate oneself before diving into the futures market.
Factors to Consider Before Buying Futures Contracts
Before buying futures contracts, it’s essential to carefully consider several key factors that can significantly impact your trading experience and outcomes. Here are some factors to keep in mind:
- Risk Tolerance: Trading futures contracts inherently involves a level of risk. Prices can be volatile, and substantial losses can occur. Assess your risk tolerance and ensure that you are mentally and financially prepared to handle potential fluctuations in the market.
- Trading Strategy: Develop a well-defined trading strategy that suits your goals and aligns with your risk tolerance. Determine whether you will be engaged in day trading, swing trading, or long-term position trading, and have a clear plan for entry and exit points, stop-loss orders, and profit targets.
- Market Knowledge: Gain a deep understanding of the market you are interested in trading. Different markets have unique characteristics, factors influencing price movements, and market dynamics. Stay updated on relevant news, economic indicators, and trends to make informed trading decisions.
- Market Analysis: Utilize technical and fundamental analysis techniques to evaluate the market and anticipate price movements. Technical analysis involves studying historical price patterns and indicators, while fundamental analysis focuses on analyzing factors such as supply and demand fundamentals, economic conditions, and geopolitical events. Combining both approaches can provide a comprehensive view of the market.
- Capital Requirements: Consider the amount of capital you are willing to allocate for trading futures contracts. Remember that leverage can amplify both profits and losses, so it’s important to use capital wisely and not overextend yourself. Determine how much capital you can afford to risk without adversely affecting your financial well-being.
- Brokers and Platforms: Choose a reputable and reliable brokerage firm that offers a user-friendly trading platform. Ensure that the platform provides the necessary tools and resources for your trading needs, including real-time market data, charting capabilities, order execution speed, and risk management features.
- Transaction Costs: Be aware of the transaction costs associated with trading futures contracts. These costs may include commissions, exchange fees, and other charges. Be mindful of how these costs can impact your overall profitability, especially for frequent traders.
- Regulatory and Tax Considerations: Familiarize yourself with the regulatory requirements and tax implications of trading futures contracts in your jurisdiction. Different countries may have specific regulations governing futures trading, and tax obligations can vary. Consult with a professional tax advisor to ensure compliance with the applicable rules.
By carefully considering these factors, you can make more informed decisions and approach buying futures contracts with a clear understanding of the risks and rewards involved. Remember to continuously learn and adapt your approach as you gain experience in the market.
Where to Buy Futures Contracts
When it comes to buying futures contracts, there are several options available to traders. Here are the primary avenues where you can access and trade futures contracts:
- Online Brokers: Online brokerage firms provide a convenient and accessible platform for individuals to trade futures contracts. These brokers offer user-friendly trading interfaces, real-time market data, research tools, and order execution capabilities. Many online brokers also provide educational resources and support for traders of all experience levels. It’s important to choose a reputable and regulated online broker that offers competitive pricing and a variety of futures contracts to trade.
- Futures Exchanges: Futures contracts are traded on reputable exchanges worldwide, such as the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) in the United States, the London International Financial Futures Exchange (LIFFE) in the United Kingdom, and the Tokyo Commodity Exchange (TOCOM) in Japan. These exchanges act as intermediaries, facilitating the trading of futures contracts between buyers and sellers. To access futures contracts through an exchange, traders typically need to open an account with a registered broker or financial institution that has direct access to the exchange.
- Clearinghouses: Clearinghouses play a vital role in the futures market by acting as intermediaries between buyers and sellers. When a futures contract is traded, the clearinghouse becomes the counterparty to both sides of the trade, reducing the risk of default for market participants. Clearinghouses handle the clearing, settlement, and margin requirements for futures trades. While individual traders do not typically deal directly with clearinghouses, it’s important to understand their role in the market and their impact on trading futures contracts.
- Contract Specifications: Each futures contract traded on an exchange has specific contract specifications that define the details of the contract, including the underlying asset, contract size, expiration date, tick size, and delivery or settlement method. It’s crucial to be familiar with these specifications before buying futures contracts to ensure you understand the terms and obligations associated with the trade.
- Choosing the Right Platform: When deciding where to buy futures contracts, it’s essential to choose a platform or provider that best suits your trading needs. Consider factors such as fees and commissions, available markets and contract offerings, technology and platform reliability, customer support, and educational resources. Comparing different platforms and conducting thorough research can help you select the best option for your trading goals.
Overall, the availability of online brokers, futures exchanges, and clearinghouses provides multiple avenues for individuals to access and trade futures contracts. It’s important to evaluate your trading requirements, conduct due diligence on available options, and select a reliable and reputable platform that aligns with your needs and preferences.
Online Brokers
Online brokers have revolutionized the way individuals trade futures contracts. These platforms provide a convenient and accessible avenue for traders to enter the futures market. Here are some key points to consider about online brokers:
Convenience and Accessibility: Online brokers offer a user-friendly and intuitive trading platform that allows individuals to trade futures contracts from the comfort of their own homes. With a computer or mobile device and an internet connection, traders can access real-time market data, place trades, monitor positions, and manage their portfolios with ease.
Wide Range of Markets and Instruments: Online brokers provide access to a wide range of futures contracts across various asset classes. Whether you are interested in trading commodities, stock indices, interest rates, or currencies, online brokers typically offer a diverse selection of markets and instruments to choose from.
Research and Analysis Tools: Many online brokers offer robust research and analysis tools to assist traders in making informed decisions. These tools may include charting capabilities, technical analysis indicators, economic calendars, and news feeds. By utilizing these resources, traders can analyze market trends, identify potential entry and exit points, and stay updated on relevant market developments.
Education and Support: Online brokers often provide educational resources and support for traders of all experience levels. These educational materials may include webinars, tutorials, articles, and trading guides. Additionally, customer support is typically available to assist with any technical or trading-related inquiries.
Pricing and Fees: When selecting an online broker, it’s important to consider the pricing structure and fees associated with trading futures contracts. Online brokers may charge commissions, spreads, and other transaction fees. It’s crucial to understand the cost structure and compare different brokers to ensure you are getting competitive pricing and transparent fee arrangements.
Regulation and Security: It’s essential to choose an online broker that is regulated by relevant authorities to ensure the safety of your funds and trading activities. Regulatory bodies provide oversight and enforce rules to protect traders from fraudulent activities. Look for brokers that are registered with reputable regulatory bodies in your country or region.
Platform Reliability: Online brokers should provide a stable and reliable trading platform, ensuring seamless execution of trades and accurate real-time data. It’s crucial to choose a broker with a platform that is technologically advanced, secure, and capable of handling the demands of fast-paced futures trading.
When selecting an online broker, it’s advisable to consider your trading preferences, financial goals, and the level of support and resources you require. Research and compare different online brokers, read client reviews, and take advantage of trial accounts or demo versions to get a feel for the platform before making a choice.
Remember, trading futures contracts involves risk, and it’s important to fully understand the market dynamics, develop a trading strategy, and manage your risk appropriately. Utilizing the services of a reputable online broker can enhance your trading experience and provide you with the tools and support needed to navigate the futures market effectively.
Futures Exchanges
Futures exchanges are central marketplaces where futures contracts are traded. These exchanges play a crucial role in facilitating the buying and selling of futures contracts, ensuring transparency, liquidity, and fair price discovery for market participants. Here are some key considerations regarding futures exchanges:
Regulated Trading Environment: Futures exchanges operate under the supervision of regulatory bodies and are subject to strict rules and regulations. This regulatory oversight ensures that trading activities on the exchange are fair, transparent, and in compliance with established standards. Regulatory authorities monitor the exchanges to safeguard market integrity and protect the interests of traders.
Liquid Market: Futures exchanges provide a liquid trading environment, where buyers and sellers can easily enter and exit positions. Liquidity is important because it ensures that there is sufficient trading activity and a depth of buyers and sellers, reducing the risk of significant price slippage or difficulties in executing trades.
Price Transparency: Futures exchanges provide real-time price information, allowing traders to see the prevailing market prices and analyze historical price data. This price transparency enables traders to make informed decisions regarding their trading strategies and entry/exit points based on accurate and up-to-date market information.
Diverse Range of Futures Contracts: Futures exchanges offer a wide range of futures contracts covering various asset classes, including commodities, stock indices, interest rates, currencies, and more. This variety allows traders to choose contracts that align with their investment goals and preferences, providing ample opportunities for trading and diversification.
Standardization of Contracts: Futures contracts traded on exchanges are standardized with specific contract specifications. These specifications define the underlying asset, contract size, tick size, settlement terms, and expiration date. Standardization ensures consistency and facilitates a transparent and efficient market, enabling traders to easily compare and trade different contracts.
Market Surveillance and Risk Management: Futures exchanges have robust surveillance systems in place to monitor trading activities and detect any irregularities or market manipulation attempts. Clearinghouses associated with the exchanges also play a critical role in risk management by serving as intermediaries and managing counterparty risk.
Access through Brokers: Individual traders typically access futures exchanges through registered brokers or financial institutions that have direct access to the exchange. These brokers provide the necessary infrastructure, technology, and market connectivity to execute trades on behalf of their clients.
Famous examples of futures exchanges include the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME), the New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX), the Intercontinental Exchange (ICE), and Eurex. Each exchange may specialize in specific types of futures contracts, so it’s important to familiarize yourself with the offerings and contract specifications of the respective exchanges.
When trading on futures exchanges, it’s crucial to understand the rules and regulations, contract specifications, and trading hours associated with each market. This knowledge will enable you to make informed decisions and navigate the futures exchanges effectively as you buy and sell futures contracts.
Clearinghouses
Clearinghouses play a vital role in the futures market by acting as intermediaries between buyers and sellers of futures contracts. These entities facilitate the clearing, settlement, and risk management processes for trades conducted on futures exchanges. Here are some key considerations regarding clearinghouses:
Counterparty Risk Reduction: One of the primary functions of clearinghouses is to mitigate counterparty risk. When a futures contract is traded, the clearinghouse becomes the counterparty to both the buyer and the seller. This arrangement ensures that market participants are not exposed to the credit risk of individual traders. By stepping in as the central counterparty, clearinghouses protect the integrity of the market and reduce the risk of default.
Margin Requirements: Clearinghouses set and enforce margin requirements for futures contracts. Margin serves as a form of collateral and acts as a protection mechanism against potential losses. Traders must deposit an initial margin and maintain a minimum level of margin throughout the duration of their positions. By requiring margin, clearinghouses ensure that participants have sufficient capital to cover potential losses and minimize the risk of default.
Clearing and Settlement: Clearinghouses facilitate the clearing and settlement process for futures contracts. This involves matching trades, assigning obligations, and ensuring accurate and timely transfer of funds and assets between buyers and sellers. By streamlining the clearing and settlement process, clearinghouses enhance efficiency and reduce the risk associated with manual reconciliation between market participants.
Regulation and Oversight: Clearinghouses are subject to regulatory oversight to ensure their operations adhere to industry standards and regulatory requirements. Regulatory bodies establish rules and monitor the activities of clearinghouses to maintain market integrity and protect market participants. By imposing these regulations, authorities minimize systemic risks and contribute to the overall stability of the futures market.
Risk Management: Clearinghouses employ risk management techniques to monitor and mitigate potential risks in the market. They assess the creditworthiness of participants and require additional margin or collateral from traders who hold riskier positions. Clearinghouses also monitor market activity, identify suspicious or abnormal trading patterns, and take appropriate actions to maintain a fair and orderly market.
Financial Safeguards: Clearinghouses establish financial safeguards to protect the market in case of a default or significant price movement. These safeguards may include mutualized default funds, which are contributed by clearing members, as well as other risk management tools and mechanisms. Financial safeguards help ensure the stability of the clearinghouse and protect the interests of market participants.
Role in Delivery and Settlement: In certain futures contracts, such as those involving physical delivery of assets, clearinghouses facilitate the delivery and settlement process. They ensure that the parties involved meet their respective obligations and coordinate the transfer of assets between the buyer and the seller upon contract expiration.
Clearinghouses, along with futures exchanges, form a critical infrastructure that enables the efficient and secure trading of futures contracts. Through risk management, margin requirements, and effective clearing and settlement processes, clearinghouses contribute to the overall stability and integrity of the futures market.
Contract Specifications
Contract specifications are a critical component of futures trading as they define the details of each futures contract traded on an exchange. These specifications establish the terms and conditions under which the contract is traded, ensuring consistency and transparency throughout the market. Here are some key points to understand about contract specifications:
Underlying Asset: Contract specifications specify the underlying asset being traded. Futures contracts can be based on a wide range of assets, including commodities, stock indices, interest rates, currencies, and more. The underlying asset determines the contract’s price movements and influences the strategies and risks associated with trading it.
Contract Size: The contract size, also known as the lot size, represents the quantity of the underlying asset that the contract controls. It indicates the amount of the asset that will be delivered or settled upon contract expiration. Contract sizes may vary significantly depending on the asset class. For example, commodity futures contracts often have standardized sizes, such as 1,000 barrels of oil or 5,000 bushels of wheat.
Expiration or Delivery Date: Contract specifications include the expiration or delivery date, which denotes the date when the contract ends. After this date, futures contracts can no longer be actively traded. Depending on the contract, settlement can occur through physical delivery of the underlying asset or a cash settlement, where the difference between the contract’s price and the market price is exchanged.
Tick Size: The tick size, also known as the minimum price fluctuation, represents the minimum increment by which the contract’s price can change. It determines the smallest unit of price movement for the contract. Smaller tick sizes offer more precise price discovery, while larger tick sizes can result in greater price volatility.
Contract Months: Futures contracts are typically available for multiple contract months into the future. Contract specifications indicate the months in which the contracts are listed for trading. For example, a futures contract may be available for trading in the current month, as well as several upcoming months.
Trading Hours: Contract specifications also specify the trading hours for each futures contract. These hours indicate the specific times during which the contract can be actively traded. Trading hours can vary depending on the exchange and the asset being traded, accommodating different time zones and market preferences.
Settlement Method: Some futures contracts require physical delivery of the underlying asset upon expiration, while others are settled in cash. The settlement method is outlined in the contract specifications. For example, commodity futures contracts may involve physical delivery, where the buyer takes possession of the asset, while stock index futures contracts are typically cash-settled based on the index’s value at maturity.
Contract Codes: Each futures contract has a unique code or symbol that identifies it on the exchange. These codes are used to differentiate between different contracts and are commonly composed of letters, numbers, or a combination of both. Traders use these codes to specify the contract they want to trade.
Understanding the contract specifications for the futures contracts you are interested in trading is crucial. It allows you to accurately assess the risks, costs, and potential profitability of each contract, helping you make informed trading decisions and manage your positions effectively.
Choosing the Right Platform
When it comes to trading futures contracts, choosing the right platform is essential to ensure a smooth and effective trading experience. Here are some key factors to consider when selecting a trading platform:
Functionality and User-Friendliness: A good trading platform should be user-friendly and offer a seamless trading experience. It should provide easy navigation, intuitive order placement, and efficient access to real-time market data. Look for a platform that offers a clean and organized interface, allowing you to monitor positions, view charts, and execute trades with ease.
Market Access: Ensure that the platform you choose offers access to the markets and futures contracts you are interested in trading. Different platforms may provide varying levels of access to different exchanges and asset classes. Make sure the platform supports the futures contracts you want to trade and provides access to the necessary market data and order execution capabilities.
Reliability and Stability: The platform you choose should be reliable and capable of handling the demands of fast-paced futures trading. Look for a platform with a proven track record for stability, minimal downtime, and robust risk management systems. A stable platform ensures that you can execute trades at the desired price points without disruptions.
Trading Tools and Resources: Evaluate the trading tools and resources offered by the platform. Look for features such as advanced charting capabilities, technical analysis indicators, market news, economic calendars, and order management tools. These tools can assist in market analysis, trade execution, and risk management.
Pricing and Fees: Consider the pricing structure and fees associated with using the trading platform. Different platforms may have varying commission rates, spreads, and additional fees. Find a platform that offers competitive pricing and transparent fee structures, ensuring that your trading costs don’t significantly eat into your profits.
Customer Support: Reliable customer support is crucial when trading futures contracts. Look for a platform that provides responsive customer support, whether through live chat, email, or phone. Prompt and helpful support can assist with technical issues, account inquiries, and trading-related questions, enhancing your overall trading experience.
Educational Resources: Evaluate the educational resources provided by the platform. Look for platforms that offer educational materials, such as trading guides, webinars, tutorials, or market analysis. These resources can help enhance your trading knowledge and skills, particularly if you are new to trading futures contracts.
Account Security: Ensure that the platform you choose prioritizes account security and data protection. Look for platforms that utilize strong encryption protocols, have robust security measures in place, and offer two-factor authentication for account access. Your personal and financial information should be safeguarded against unauthorized access.
Platform Compatibility: Consider the compatibility of the trading platform with your devices. The platform may be available for desktop computers, web browsers, or mobile devices. Choose a platform that suits your preferred method of trading and offers platform access across different devices.
Ultimately, choosing the right trading platform is a personal decision that depends on your trading preferences, goals, and level of experience. Consider these factors, do thorough research, and if possible, use demo accounts or trial versions to test the platform’s features and functionalities before committing to a specific platform for trading futures contracts.
Conclusion
Trading futures contracts can be an exciting and potentially profitable venture for investors and traders. Before diving into the world of futures trading, it is crucial to understand the fundamentals and various factors that can impact your trading experience and outcomes.
In this article, we explored the ins and outs of buying futures contracts. We discussed the benefits of trading futures contracts, including the potential for diversification, leverage, and the flexibility to take both long and short positions. We also highlighted the factors to consider before buying futures contracts, such as risk tolerance, trading strategy, market knowledge, and capital requirements.
When it comes to purchasing futures contracts, there are several avenues available. Online brokers provide a convenient and accessible platform for individuals to enter the futures market. These platforms offer a wide range of markets, research tools, and educational resources to assist traders in making informed decisions. Futures exchanges play a vital role in facilitating trading and ensuring transparent price discovery, while clearinghouses reduce counterparty risk and manage the clearing and settlement process.
Understanding contract specifications is crucial in effectively trading futures contracts. These specifications define the underlying asset, contract size, expiration date, tick size, and settlement method, among other details. By familiarizing yourself with contract specifications, you can accurately assess the risks and potential profitability associated with each futures contract.
Lastly, choosing the right trading platform is essential for an optimal trading experience. Consider factors such as functionality, market access, reliability, trading tools, pricing, customer support, educational resources, and account security when selecting a platform that aligns with your trading needs.
Trading futures contracts involves risk, and it’s important to approach it with caution and proper risk management. Continuously educate yourself, stay updated on market trends, and adapt your trading strategies as needed.
With the right knowledge, preparation, and platform, you can navigate the exciting world of futures trading and potentially capitalize on the opportunities provided by these derivative financial instruments.