Finance
How Do You Calculate Employee Retention Credit
Published: January 10, 2024
Learn how to calculate the Employee Retention Credit and optimize your finance strategy. Stay informed and boost your business growth with expert advice.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
The Employee Retention Credit (ERC) is a valuable tax credit introduced by the U.S. government to help businesses retain their employees during challenging times, such as economic downturns or periods of significant revenue loss due to the COVID-19 pandemic. This credit provides financial relief to qualifying employers, allowing them to offset a portion of the wages paid to employees.
The ERC was first implemented as part of the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act (CARES Act) in March 2020 and has since been extended and expanded under subsequent legislation. To date, it remains an essential tool for businesses seeking financial assistance and support to retain their workforce.
In this article, we will explore the key aspects of the Employee Retention Credit, including eligibility criteria, calculation methods, and the process of claiming the credit. We will also provide examples to help you understand how the credit is calculated in different scenarios.
Understanding the Employee Retention Credit is crucial for businesses looking to take advantage of the available financial relief. By navigating this credit effectively, businesses can not only retain their valuable employees but also alleviate some of the financial burden caused by unforeseen circumstances.
So, let’s dive into the details of the Employee Retention Credit and discover how it can benefit your business.
Overview of Employee Retention Credit
The Employee Retention Credit is a tax credit designed to incentivize businesses to retain their employees during challenging economic times. It was introduced as part of the CARES Act in response to the COVID-19 pandemic and has been extended and expanded in subsequent legislation.
The purpose of the credit is to provide financial relief to eligible businesses, thereby encouraging them to keep employees on their payroll and avoid layoffs or furloughs. By reducing the financial strain on businesses, the credit aims to help stabilize the economy and support employment stability.
The Employee Retention Credit is available to both small and large businesses, including for-profit and non-profit organizations. However, there are certain eligibility criteria that must be met to qualify for the credit.
The credit is calculated based on qualified wages paid to eligible employees during a designated period. The maximum credit amount is determined by the number of full-time equivalent employees retained and the amount of qualified wages paid.
It’s important to note that the Employee Retention Credit is a refundable credit, meaning that even if a business doesn’t owe any taxes, they can still receive the full amount of the credit as a refund. This makes it a valuable resource for businesses looking to recover some of the financial losses incurred during difficult times.
It’s worth mentioning that businesses cannot claim both the Employee Retention Credit and other COVID-19 relief programs, such as the Paycheck Protection Program (PPP), for the same wages. However, they can choose which program provides the greatest benefit and apply accordingly.
In the following sections, we will delve into the eligibility criteria and the process of calculating and claiming the Employee Retention Credit, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of how this tax credit can support your business during challenging times.
Eligibility for Employee Retention Credit
In order to qualify for the Employee Retention Credit (ERC), businesses must meet specific eligibility criteria set by the IRS. Understanding these criteria is essential for determining whether your business is eligible to claim the credit.
Eligible employers fall into two categories:
- Businesses that experienced a full or partial suspension of operations due to a government order related to COVID-19
- Businesses that experienced a significant decline in gross receipts
For the first category, a business must demonstrate that it was required to fully or partially suspend its operations due to a governmental order related to the COVID-19 pandemic. This could include closure orders, stay-at-home orders, or other restrictions that directly impacted the company’s ability to operate normally.
For the second category, a business must show that it experienced a significant decline in gross receipts. This is defined as a decline of 50% or more compared to the same quarter in the previous year. Once the business experiences a significant decline in gross receipts, it remains eligible for the credit until gross receipts recover to 80% or more of the corresponding quarter in the prior year.
It’s important to note that the eligibility requirements for claiming the Employee Retention Credit have changed over time due to legislative updates. Initially, the ERC was only available to businesses that did not receive a Paycheck Protection Program (PPP) loan. However, this requirement was later lifted, allowing businesses to claim both the ERC and PPP loan forgiveness as long as they do not use the same wages for both purposes.
Furthermore, the IRS has provided guidance stating that governmental entities and tax-exempt organizations, including colleges and universities, are now eligible to claim the Employee Retention Credit.
It’s recommended to consult with a tax professional or refer to the official IRS guidelines to ensure your business meets the eligibility requirements for claiming the Employee Retention Credit. By understanding and fulfilling these requirements, you can take advantage of this valuable tax credit to support your business and retain your employees during challenging economic times.
Calculating Employee Retention Credit
Calculating the Employee Retention Credit (ERC) involves determining the amount of qualified wages paid to eligible employees during the designated period. The credit is calculated as a percentage of the qualified wages, subject to certain limitations.
The maximum credit amount is 70% of qualified wages, up to a maximum of $10,000 per employee for each eligible quarter. This means that for each quarter, a business can claim a maximum of $7,000 per employee as a credit.
To calculate the ERC, follow these steps:
- Determine the eligible quarters: Identify the specific quarters in which your business meets the eligibility criteria for the credit, either due to a government order suspension or a significant decline in gross receipts.
- Calculate the qualified wages: Determine the amount of wages paid to eligible employees during the eligible quarters. Qualified wages are generally defined as wages and certain health plan expenses paid to employees. There are limitations based on the number of employees.
- Apply the credit percentage: Multiply the qualified wages for each employee by the applicable percentage, which is 70% of qualified wages.
- Cap the credit amount: The maximum credit amount per employee for each quarter is $7,000. If the qualified wages for an employee exceed $10,000 in a quarter, you can only claim the credit for up to $10,000 of those wages.
- Calculate the total credit: Add up the credits for each eligible employee in each quarter to determine the total Employee Retention Credit for that quarter.
It’s important to keep accurate records of the qualified wages and supporting documentation to substantiate the credit claimed. Documentation may include payroll records, accounting records, and other relevant documents.
It’s recommended to work with a qualified tax professional or use payroll software that can help calculate and track the Employee Retention Credit accurately. Additionally, consulting the official IRS guidelines and seeking professional advice will ensure compliance with the complex requirements of calculating the credit.
By carefully calculating the Employee Retention Credit, your business can take advantage of this financial relief and retain valuable employees during challenging economic times.
Factors Considered in Calculation
When calculating the Employee Retention Credit (ERC), several factors come into play to determine the eligibility and amount of the credit. It’s important to understand these factors to accurately calculate the credit and maximize its benefits for your business.
Here are the key factors considered in the calculation of the ERC:
- Employee eligibility: Only certain employees are considered eligible for the credit. Generally, this includes individuals who were employed by the business during the eligible quarters and were not counted as “excluded employees.” Excluded employees include business owners, relatives of owners, and certain high-income executives.
- Qualified wages: Qualified wages refer to the wages paid to eligible employees during the eligible quarters. For businesses with an average of more than 100 full-time employees in 2019, qualified wages are limited to those paid to employees who are not providing services due to a government order suspension or experiencing a significant decline in gross receipts. For businesses with an average of 100 or fewer full-time employees in 2019, all wages paid during the eligible quarters are considered qualified wages.
- Health plan expenses: In addition to qualified wages, certain health plan expenses can be included in the calculation of the credit. This includes both the employer’s share and the employee’s share of health plan premiums.
- FTE calculation: Full-time equivalent (FTE) employees are an important factor in determining the maximum credit amount per employee. The credit is calculated based on wages paid to each eligible employee, up to a maximum of $10,000 per employee for each eligible quarter. If an employee’s qualified wages exceed $10,000 in a quarter, the excess amount is not eligible for the credit.
- Maximum credit limit: The maximum ERC available per employee per quarter is 70% of qualified wages, up to a maximum of $7,000. This means that the credit is capped at $7,000 per employee for each eligible quarter, even if their qualified wages exceed that amount.
It’s important to note that the calculation and eligibility criteria for the ERC have evolved over time due to legislative updates. Therefore, it’s crucial to refer to the official IRS guidelines and consult with a tax professional to ensure compliance and accurate calculation of the credit.
By carefully considering these factors and accurately calculating the Employee Retention Credit, your business can leverage this valuable tax credit to retain employees and ease the financial burden during challenging economic times.
Claiming Employee Retention Credit
Claiming the Employee Retention Credit (ERC) requires businesses to follow specific procedures and provide the necessary documentation to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). Understanding the process of claiming the credit is crucial to ensure that your business receives the financial relief it deserves.
Here are the steps to claim the Employee Retention Credit:
- Calculate the credit: Carefully calculate the ERC by following the guidelines provided by the IRS. Determine the eligible quarters and calculate the qualified wages for each eligible employee. Apply the credit percentage and cap the credit amount per employee per quarter accordingly.
- Complete Form 941: If you are an eligible employer that pays wages subject to federal employment taxes, such as income tax withholding, Social Security tax, and Medicare tax, you will report the ERC on Form 941, the Employer’s Quarterly Federal Tax Return. Ensure that you accurately report the credit amount on the designated line of the form.
- Reduce required deposits: Businesses can choose to reduce their required deposits by the anticipated credit amount for the applicable quarter. This can be done by either not depositing the portion of the employment taxes equal to the anticipated credit or requesting a refund of the excess deposit.
- File for refund: If the anticipated ERC exceeds the employment taxes owed, businesses can file for a refund using Form 7200, the Advance Payment of Employer Credits Due to COVID-19. This form allows businesses to request an advance payment of the intended credit amount.
- Keep thorough documentation: It is crucial to maintain accurate records of all necessary documents, including documentation of eligible quarters, qualified wages, health plan expenses, and any other supporting documents required by the IRS. Keeping thorough documentation will help substantiate your claim and ensure compliance in case of an audit.
It’s important to note that the process of claiming the Employee Retention Credit may vary depending on the specific circumstances of your business. Consulting with a tax professional and referring to the official IRS guidelines is highly recommended to ensure that you successfully claim the credit and receive the financial relief you are entitled to.
By following the proper procedures and submitting the required documentation, your business can claim the Employee Retention Credit and take advantage of the available financial assistance to retain employees and navigate challenging economic times.
Examples of Employee Retention Credit Calculation
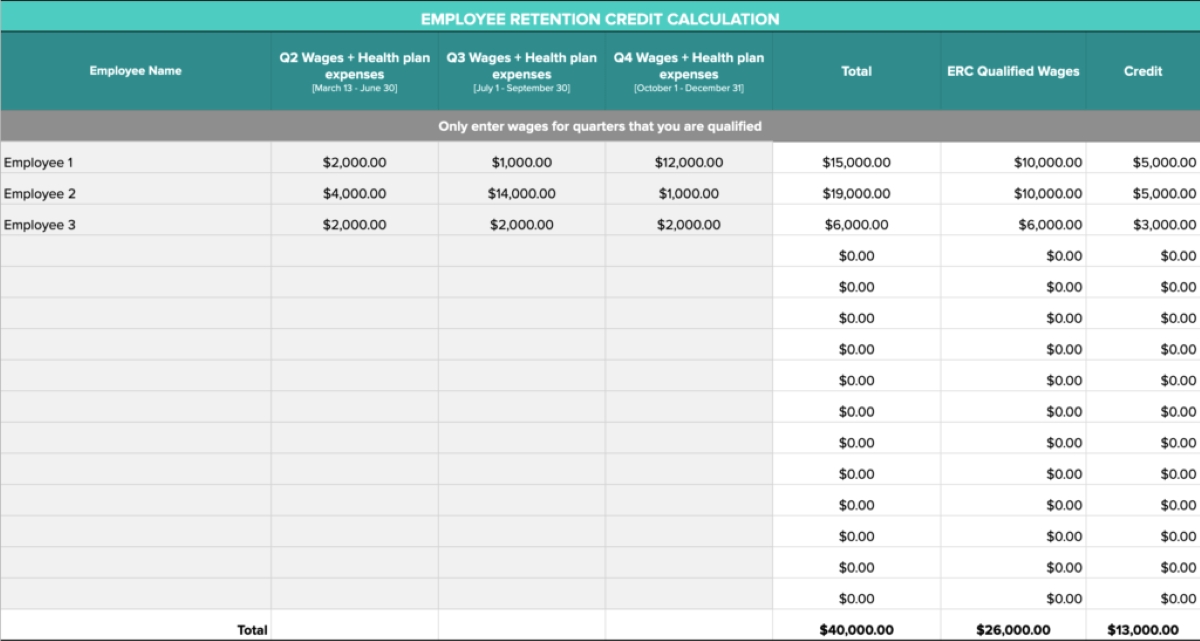
To better understand how the Employee Retention Credit (ERC) is calculated, let’s explore a few examples that illustrate different scenarios and demonstrate how the credit amount can vary based on various factors.
Example 1:
ABC Company is a small business that experienced a full suspension of operations in Q2 2020 due to a government order related to the COVID-19 pandemic. During that quarter, they had 10 eligible employees, and each employee’s qualified wages amounted to $8,000. The credit percentage is 70%.
The calculation for ABC Company’s ERC would be as follows:
- Qualified wages per employee: $8,000
- Credit per employee (70% of qualified wages): $5,600
- Total credit for the quarter (10 employees x $5,600): $56,000
Example 2:
XYZ Corporation is a larger business that experienced a significant decline in gross receipts in Q3 2021. During that quarter, they had 200 eligible employees, and each employee’s qualified wages amounted to $12,000. The credit percentage is 70%.
The calculation for XYZ Corporation’s ERC would be as follows:
- Qualified wages per employee: $10,000 (capped at this amount)
- Credit per employee (70% of qualified wages): $7,000
- Total credit for the quarter (200 employees x $7,000): $1,400,000
Example 3:
LMN Nonprofit Organization is an eligible tax-exempt entity that experienced a significant decline in gross receipts in Q4 2021. During that quarter, they had 50 eligible employees, and each employee’s qualified wages amounted to $9,000.
The calculation for LMN Nonprofit Organization’s ERC would be as follows:
- Qualified wages per employee: $9,000
- Credit per employee (70% of qualified wages): $6,300
- Total credit for the quarter (50 employees x $6,300): $315,000
Remember that these examples are for illustrative purposes only and may not reflect your specific situation. It’s important to consult with a tax professional to accurately calculate your business’s Employee Retention Credit based on your unique circumstances.
By understanding and applying the proper calculation methods, you can determine the credit amount your business is eligible for and leverage the Employee Retention Credit to retain your employees and alleviate financial strain during challenging times.
Conclusion
The Employee Retention Credit (ERC) is a valuable tax credit that provides financial relief to businesses seeking to retain their employees during challenging economic times. By understanding the eligibility criteria and calculation process, businesses can effectively leverage this credit to support their workforce and ease financial burdens.
In this article, we explored the key aspects of the Employee Retention Credit, including an overview of the credit, eligibility criteria, calculation methods, and the process of claiming the credit. We also provided examples to illustrate how the credit amount can vary based on different scenarios.
It is crucial for businesses to determine their eligibility for the ERC based on whether they experienced a government-ordered suspension of operations or a significant decline in gross receipts. By accurately calculating qualified wages and applying the credit percentage, businesses can determine the amount of credit they are eligible for.
Claiming the Employee Retention Credit involves proper reporting on Form 941 and potentially reducing required tax deposits or filing for a refund. It is essential to keep thorough documentation to substantiate the claimed credit amount.
By successfully claiming the Employee Retention Credit, businesses can obtain financial relief that can be used to retain employees, provide stability during uncertain times, and help navigate the challenges posed by economic downturns or unforeseen circumstances.
However, as the tax regulations and guidelines may change over time, it is essential to seek guidance from a qualified tax professional and refer to the official IRS guidelines to ensure compliance and accurate calculation of the credit.
Overall, the Employee Retention Credit serves as a vital tool for businesses to mitigate the impact of economic challenges and retain their valuable employees. By understanding the ins and outs of the credit, businesses can maximize its benefits and contribute to their overall financial stability and success.