
Finance
How Do I Do A Profit And Loss Statement
Published: January 22, 2024
Learn how to create a profit and loss statement for your business with our comprehensive guide. Understand the financial health of your company with this essential finance tool.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Creating a profit and loss statement is a crucial aspect of financial management for businesses of all sizes. This comprehensive financial document provides a snapshot of a company's revenues, expenses, and profits over a specific period, offering valuable insights into its financial performance. Understanding how to create and analyze a profit and loss statement is essential for making informed business decisions, securing financing, and assessing the overall health of a company.
In the following sections, we will delve into the intricacies of profit and loss statements, exploring their significance, components, and the process of creating one. Additionally, we will discuss key tips for effectively analyzing these statements to extract meaningful data that can drive strategic decision-making. Whether you're a seasoned entrepreneur, a budding business owner, or an individual seeking to expand your financial acumen, mastering the art of profit and loss statements is a valuable skill that can contribute to your success.
Throughout this guide, we will navigate the terrain of profit and loss statements, shedding light on their importance and equipping you with the knowledge to harness their potential as a powerful financial tool. Let's embark on this journey to unravel the mysteries of profit and loss statements and harness their potential to drive financial success.
What is a Profit and Loss Statement?
A profit and loss statement, also known as an income statement, is a fundamental financial document that provides a summary of a company’s revenues, expenses, and profits over a specific period, typically a fiscal quarter or year. This essential report offers a comprehensive overview of a business’s financial performance, showcasing its ability to generate profits by increasing revenue, managing expenses, and optimizing operational efficiency.
At its core, a profit and loss statement serves as a financial barometer, offering valuable insights into a company’s profitability and viability. By analyzing this statement, stakeholders can assess the effectiveness of the company’s operations, identify potential areas for improvement, and make informed decisions to drive sustainable growth.
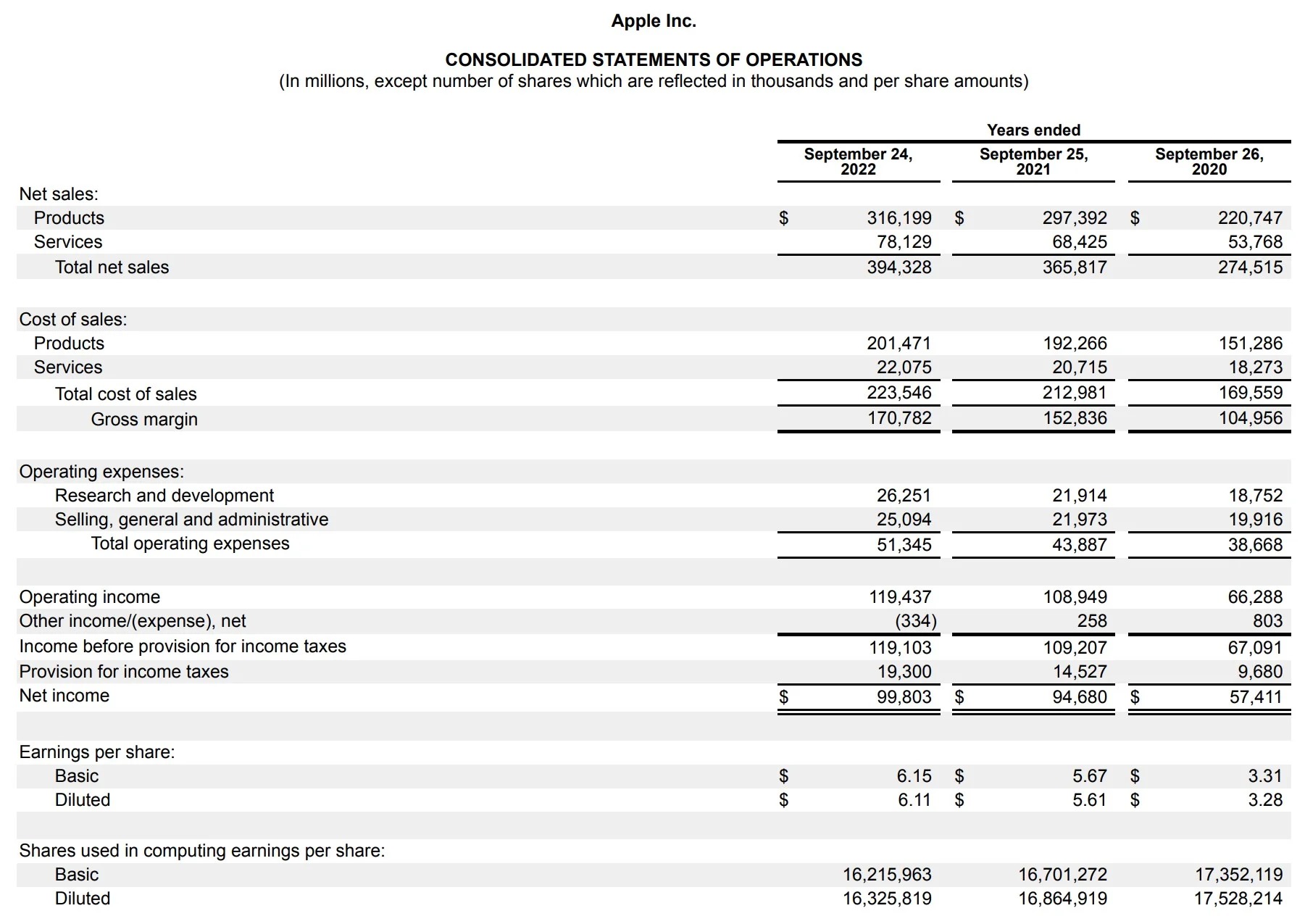
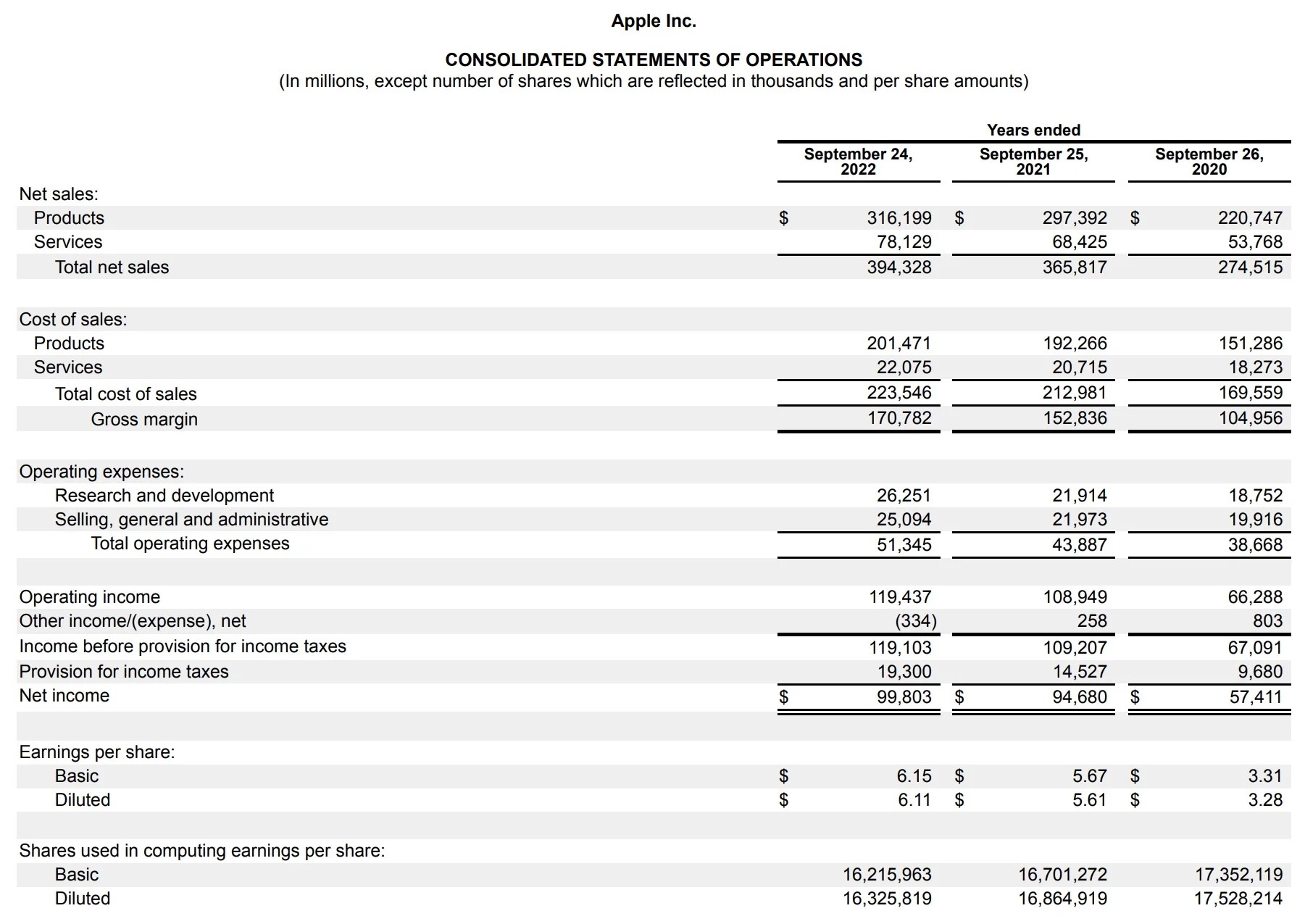
The profit and loss statement follows a structured format, typically beginning with the company’s total revenues or sales at the top, followed by the cost of goods sold (COGS) or direct costs, which are subtracted to calculate the gross profit. Subsequently, operating expenses, such as marketing, salaries, rent, utilities, and depreciation, are deducted from the gross profit to determine the operating profit or loss. Finally, non-operating revenues and expenses, taxes, and extraordinary items are factored in to arrive at the net profit or loss for the period.
By encapsulating these financial metrics, a profit and loss statement provides a comprehensive overview of a company’s financial performance, offering stakeholders, investors, and management a clear understanding of its revenue-generating capabilities, cost management strategies, and overall profitability.
Understanding the intricacies of a profit and loss statement is essential for entrepreneurs, business owners, investors, and financial professionals, as it serves as a vital tool for assessing a company’s financial health, identifying trends, and making informed decisions to drive sustainable growth and profitability.
Why is a Profit and Loss Statement Important?
A profit and loss statement holds significant importance as a foundational component of financial management for businesses. Its relevance stems from its ability to offer a comprehensive snapshot of a company’s financial performance, enabling stakeholders to assess its profitability, operational efficiency, and overall financial health. Here are several key reasons why the profit and loss statement is crucial:
- Financial Performance Evaluation: The profit and loss statement provides a clear overview of a company’s revenue generation, cost management, and profitability, allowing stakeholders to evaluate its financial performance over a specific period.
- Strategic Decision-Making: By analyzing the data presented in the profit and loss statement, business owners, management, and investors can make informed decisions regarding resource allocation, expansion strategies, cost-cutting measures, and revenue enhancement initiatives.
- Investor and Creditor Confidence: Investors and creditors rely on the profit and loss statement to gauge a company’s financial stability and growth potential, influencing their decisions to invest, extend credit, or engage in financial partnerships.
- Performance Trend Analysis: Over time, comparing multiple profit and loss statements enables stakeholders to identify performance trends, assess the impact of strategic initiatives, and make data-driven forecasts for future financial outcomes.
- Regulatory Compliance: For publicly traded companies and those subject to regulatory requirements, the profit and loss statement is essential for meeting financial reporting standards and compliance obligations.
Moreover, the profit and loss statement serves as a valuable tool for internal management, aiding in the assessment of departmental performance, identification of cost-saving opportunities, and the formulation of effective budgeting and forecasting strategies.
By encapsulating critical financial data in a structured and accessible format, the profit and loss statement empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions, drive strategic initiatives, and ensure the long-term financial sustainability of a business. Its role as a barometer of financial health and performance underscores its indispensable value in the realm of business and financial management.
Components of a Profit and Loss Statement
A profit and loss statement comprises several key components that collectively provide a comprehensive overview of a company’s financial performance. Understanding these components is essential for interpreting the statement and extracting valuable insights. Here are the primary elements of a profit and loss statement:
- Revenue: This section represents the total income generated from the sale of goods or services. It is the top-line figure that forms the basis for calculating the company’s gross profit.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Also known as direct costs, this component encompasses the expenses directly associated with producing the goods or services sold. It includes raw materials, labor, and manufacturing overhead. Subtracting COGS from revenue yields the gross profit.
- Gross Profit: This figure reflects the company’s revenue minus the cost of goods sold, representing the profit generated from core business operations before accounting for operating expenses.
- Operating Expenses: These expenses encompass the costs incurred in the day-to-day operations of the business, including salaries, rent, utilities, marketing, depreciation, and administrative expenses. They are subtracted from the gross profit to calculate the operating profit or loss.
- Operating Profit (or Loss): This metric indicates the company’s profitability from its core business activities, excluding non-operating revenues and expenses.
- Non-Operating Revenues and Expenses: This section includes income and expenses not directly related to the core business operations, such as interest income, interest expenses, gains or losses from investments, and other non-operating activities.
- Net Profit (or Loss): The net profit represents the company’s total earnings after accounting for all expenses, including taxes and extraordinary items. It is a key indicator of the company’s overall financial performance.
Each of these components plays a pivotal role in providing a comprehensive overview of a company’s financial performance, offering valuable insights into its revenue generation, cost management, and overall profitability. By analyzing these elements collectively, stakeholders can gain a deeper understanding of the company’s financial health and make informed decisions to drive sustainable growth and success.
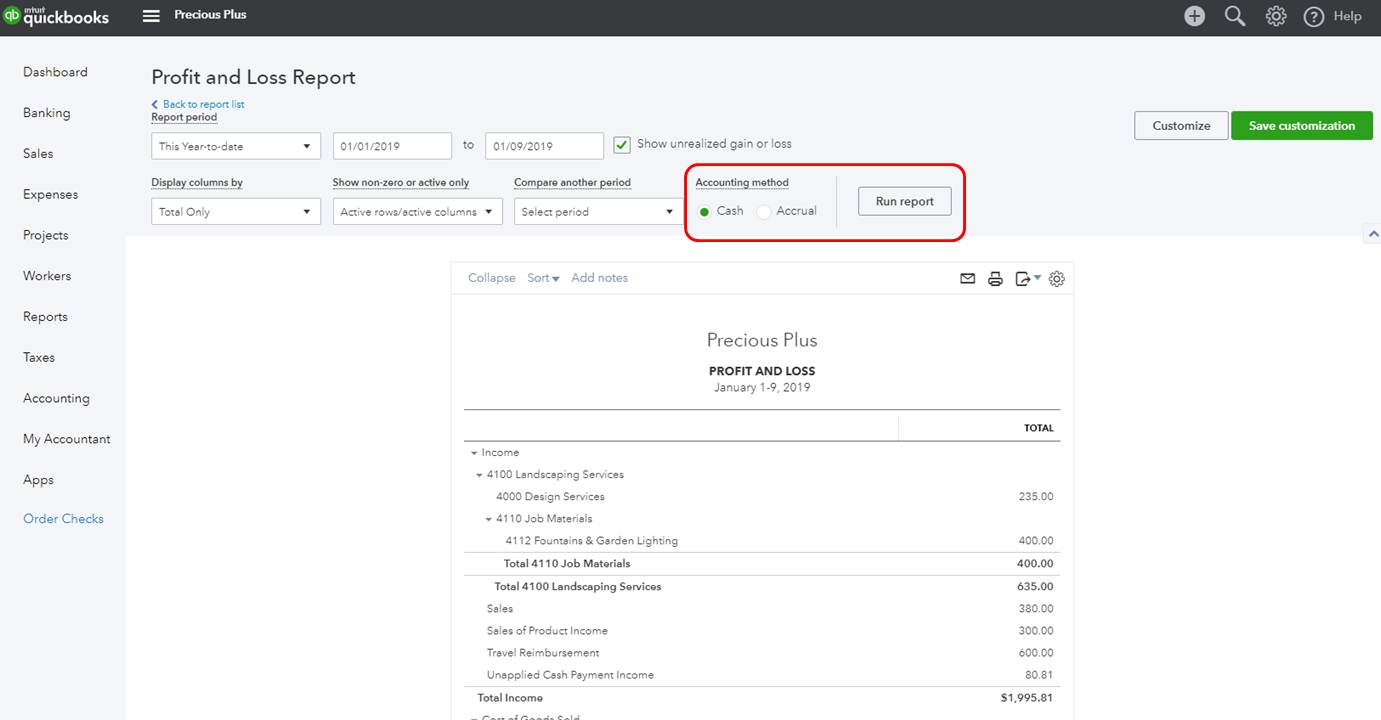
How to Create a Profit and Loss Statement
Creating a profit and loss statement involves a structured process that encompasses gathering financial data, categorizing expenses and revenues, and organizing the information into a cohesive financial report. Here are the essential steps to create a comprehensive profit and loss statement:
- Compile Financial Data: Gather all relevant financial records, including sales invoices, expense receipts, and other financial documentation for the specified period, typically a fiscal quarter or year.
- Categorize Revenues: Identify and categorize all sources of revenue, including sales of goods, services, and other income streams. Ensure that all revenue sources are accurately documented and accounted for.
- Calculate Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): For businesses involved in the sale of goods, calculate the direct costs associated with production or procurement, including raw materials, labor, and manufacturing overhead. This figure constitutes the COGS.
- Account for Operating Expenses: Identify and categorize all operating expenses incurred during the specified period, such as salaries, rent, utilities, marketing expenses, depreciation, and administrative costs.
- Calculate Gross Profit: Subtract the COGS from the total revenue to determine the gross profit, representing the profit generated from core business activities.
- Deduct Operating Expenses: Subtract the total operating expenses from the gross profit to arrive at the operating profit or loss, reflecting the company’s profitability from its primary operations.
- Factor in Non-Operating Revenues and Expenses: Include non-operating income and expenses, such as interest income, interest expenses, gains or losses from investments, and other non-core business activities.
- Calculate Net Profit (or Loss): After factoring in non-operating revenues and expenses, calculate the net profit or loss, representing the company’s total earnings after accounting for all expenses, taxes, and extraordinary items.
Once the financial data has been organized and the calculations have been completed, the profit and loss statement can be formatted according to standard accounting practices, ensuring that it presents a clear and accurate representation of the company’s financial performance.
By following these steps and meticulously documenting the relevant financial information, businesses can create a robust and informative profit and loss statement that serves as a vital tool for financial analysis, decision-making, and strategic planning.
Tips for Analyzing a Profit and Loss Statement
Analyzing a profit and loss statement is a critical aspect of financial management, providing valuable insights into a company’s financial performance and guiding strategic decision-making. Here are essential tips for effectively interpreting and analyzing a profit and loss statement:
- Identify Key Trends: Compare the current profit and loss statement with previous periods to identify trends in revenue, expenses, and profitability. Understanding these trends can reveal patterns and provide insights into the company’s financial trajectory.
- Assess Gross and Net Profit Margins: Calculate the gross profit margin (gross profit divided by total revenue) and net profit margin (net profit divided by total revenue) to evaluate the company’s profitability relative to its revenue. These margins offer valuable insights into the efficiency of operations and cost management.
- Examine Expense Ratios: Analyze the proportion of various expenses, such as cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and non-operating expenses, in relation to total revenue. Understanding these ratios can highlight areas of excessive spending or inefficiency.
- Compare Industry Benchmarks: Benchmark the company’s profit and loss statement against industry standards to assess its performance relative to competitors. This comparative analysis can identify areas for improvement and potential competitive advantages.
- Identify Seasonal Variations: Recognize any seasonal fluctuations in revenue and expenses, as these can impact overall profitability. Understanding seasonal patterns is crucial for accurate financial forecasting and resource allocation.
- Assess Cost Control Measures: Evaluate the effectiveness of cost management strategies by examining trends in operating expenses and identifying areas where cost-saving measures can be implemented without compromising operational efficiency.
- Consider Non-Operating Items: Scrutinize non-operating revenues and expenses to assess their impact on the company’s overall financial performance. Understanding the influence of these items is essential for a comprehensive analysis.
- Review Tax Implications: Understand the tax obligations and implications reflected in the profit and loss statement, ensuring compliance with tax regulations and optimizing tax planning strategies.
By applying these analytical tips, stakeholders can gain a deeper understanding of the company’s financial performance, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions to drive sustainable growth and profitability. The profit and loss statement serves as a valuable tool for financial analysis and strategic planning, offering a comprehensive view of a company’s revenue generation, expense management, and overall profitability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the profit and loss statement stands as a cornerstone of financial reporting, offering a comprehensive overview of a company’s revenue, expenses, and profitability. This vital financial document serves as a powerful tool for stakeholders, investors, and management, providing valuable insights into a company’s financial performance and guiding strategic decision-making.
By understanding the components of a profit and loss statement and the process of creating one, businesses can harness its potential to drive informed decision-making, optimize operational efficiency, and ensure long-term financial sustainability. Furthermore, the analytical tips for interpreting a profit and loss statement empower stakeholders to extract meaningful data, identify trends, and make strategic adjustments to enhance profitability and competitiveness.
As businesses navigate the dynamic landscape of the global economy, the ability to effectively analyze and leverage the insights derived from profit and loss statements becomes increasingly essential. Whether it’s evaluating cost control measures, assessing industry benchmarks, or identifying seasonal variations, the profit and loss statement offers a wealth of information that can shape the trajectory of a company’s financial success.
Ultimately, the profit and loss statement transcends its role as a financial report; it becomes a compass for guiding businesses toward sustainable growth, informed decision-making, and financial resilience. Embracing its significance and mastering the art of interpreting its data empowers businesses to navigate challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and chart a course toward enduring financial prosperity.
As the financial landscape continues to evolve, the profit and loss statement remains a steadfast ally, offering invaluable insights and serving as a catalyst for sound financial management and strategic planning. Its enduring relevance underscores its indispensable role in the realm of business and financial acumen, shaping the decisions that drive success and prosperity.