Finance
How To Read A Profit And Loss Report
Published: January 22, 2024
Learn how to interpret a profit and loss report in finance. Gain insights into analyzing financial performance and making strategic decisions. Discover key metrics and trends.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Importance of a Profit and Loss Report
- Understanding the Basics of a Profit and Loss Report
- Analyzing Revenue and Sales
- Evaluating Costs and Expenses
- Interpreting Gross Profit and Net Profit
- Identifying Key Performance Indicators
- Using Profit and Loss Reports for Decision Making
- Conclusion
Introduction
Understanding the Importance of a Profit and Loss Report
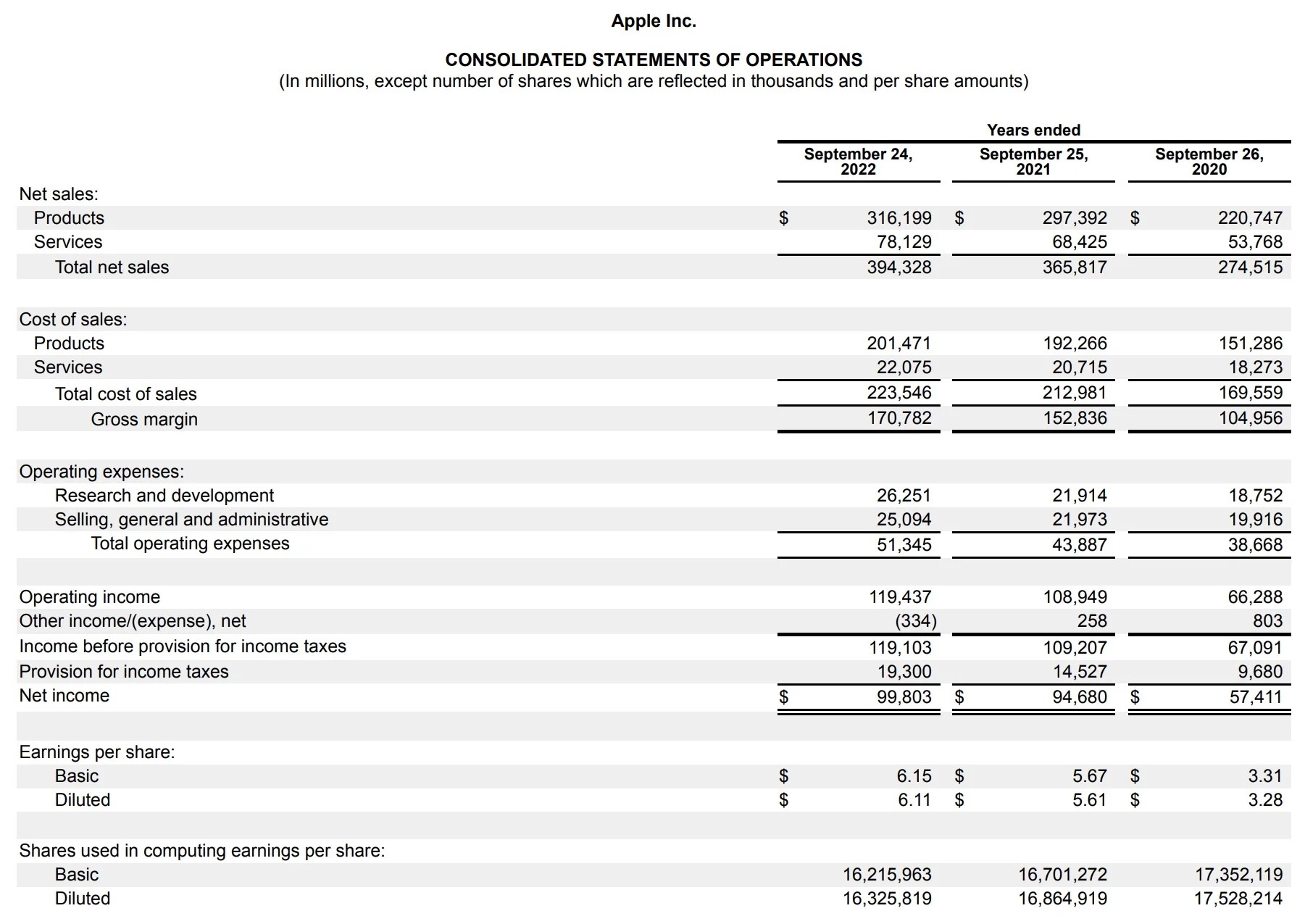
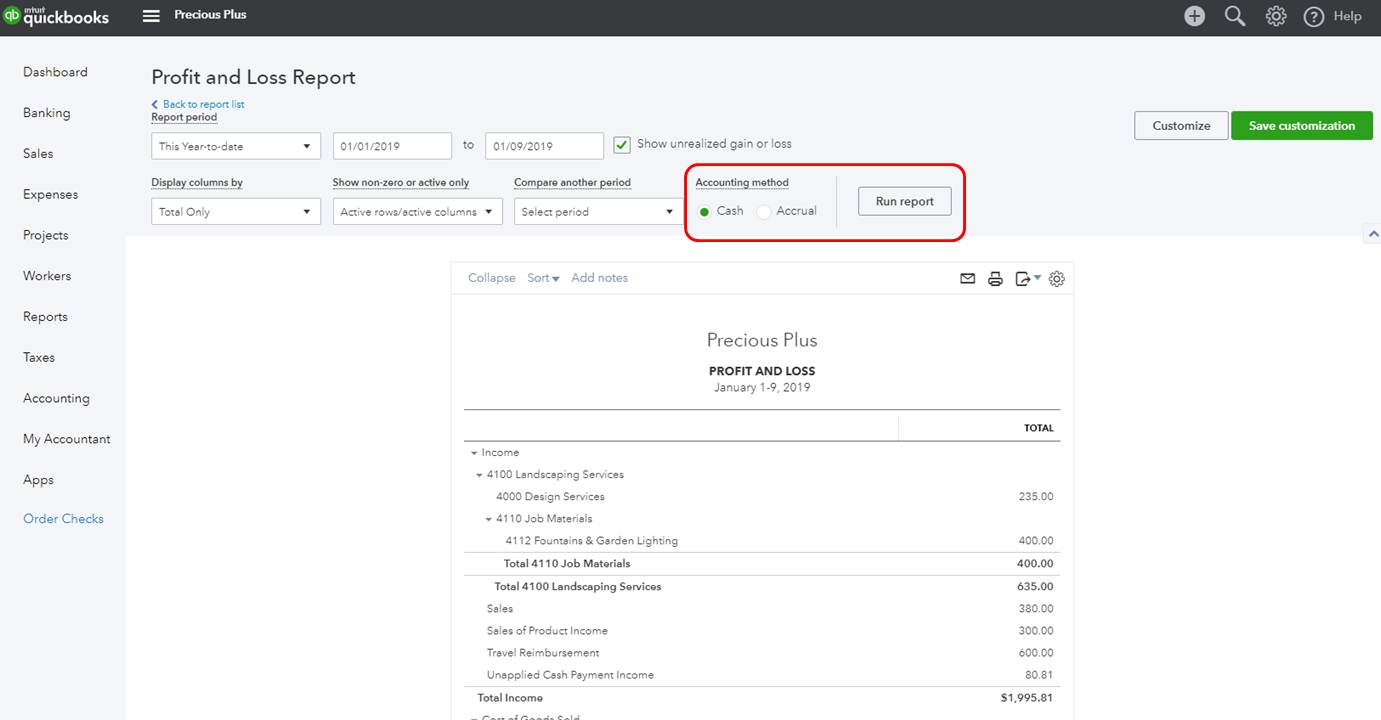
When it comes to assessing the financial health of a business, the profit and loss report, also known as the income statement, is a critical tool. This financial statement provides a comprehensive overview of a company’s revenues, costs, and expenses over a specific period, typically monthly, quarterly, or annually. By examining the information presented in the profit and loss report, stakeholders can gain valuable insights into the company’s performance and make informed decisions to drive growth and profitability.
Understanding how to read and interpret a profit and loss report is essential for business owners, managers, investors, and other stakeholders. It enables them to assess the company’s ability to generate profits, identify areas of strength and weakness, and pinpoint opportunities for improvement. Moreover, a well-analyzed profit and loss report serves as a roadmap for strategic planning and helps in evaluating the effectiveness of business operations and financial management.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of a profit and loss report, breaking down its components and shedding light on the key metrics and insights it offers. By the end of this journey, you will have a solid grasp of how to leverage this financial statement to make informed decisions and drive the success of your business.
Understanding the Basics of a Profit and Loss Report
At its core, a profit and loss report provides a snapshot of a company’s financial performance over a specific period. This essential financial statement outlines the revenues generated, the costs incurred in generating those revenues, and the resulting profitability. By examining the components of the profit and loss report, stakeholders can gain valuable insights into the company’s operational efficiency and overall financial health.
Key components of a profit and loss report include:
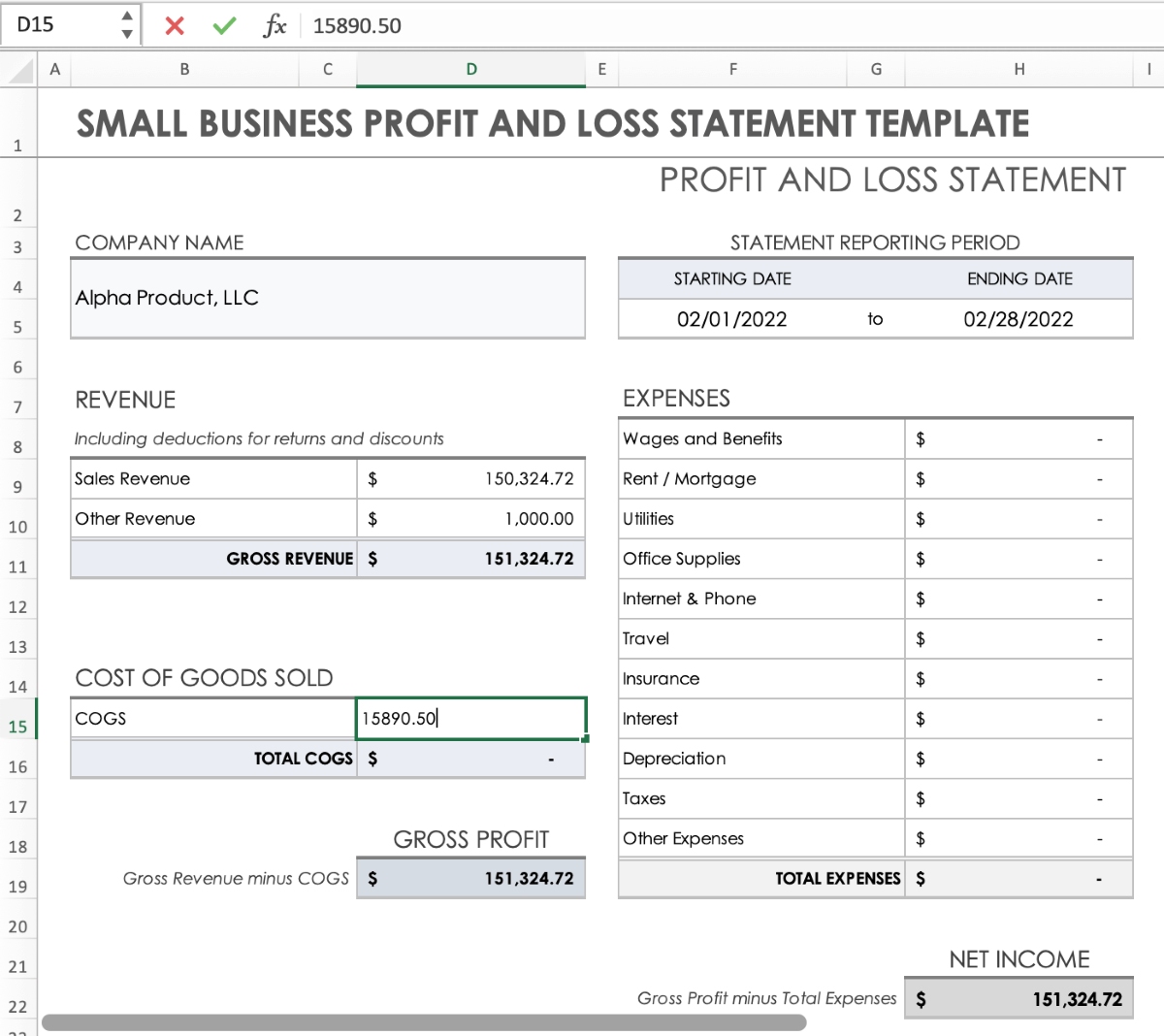
- Revenue: This section details the total income generated from the sale of goods or services. It is a fundamental indicator of the company’s ability to generate income.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Also known as the cost of sales, this section encompasses the direct costs associated with producing the goods sold by the company. It includes expenses such as raw materials, labor, and manufacturing overhead.
- Gross Profit: Calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold from the total revenue, the gross profit represents the profit made before accounting for other expenses.
- Operating Expenses: This category encompasses the day-to-day expenses incurred in running the business, including salaries, rent, utilities, marketing, and administrative costs.
- Net Profit: Also referred to as the bottom line, the net profit reflects the company’s total earnings after deducting all expenses, including taxes and interest.
By analyzing these components, stakeholders can assess the company’s revenue-generating activities, cost management strategies, and overall profitability. Understanding the basics of a profit and loss report sets the foundation for a comprehensive analysis of a company’s financial performance and aids in identifying areas for improvement and growth.
Analyzing Revenue and Sales
Revenue and sales are vital metrics within a profit and loss report, providing valuable insights into a company’s income-generating activities. Revenue encompasses the total income generated from the sale of goods or services, reflecting the core financial performance of the business. When analyzing revenue and sales within a profit and loss report, it is essential to consider various factors that contribute to these figures.
Understanding the sources of revenue is crucial. For instance, a company may derive income from the sale of products, provision of services, or other business activities. By dissecting the revenue streams, stakeholders can identify the most profitable segments of the business and allocate resources strategically.
Moreover, analyzing revenue trends over multiple reporting periods can unveil patterns and fluctuations in sales performance. Identifying revenue growth or decline provides valuable insights into market demand, customer preferences, and the effectiveness of sales and marketing strategies.
Another critical aspect of analyzing revenue and sales is assessing the impact of pricing strategies and discounts. By examining the average selling prices and the frequency of promotional activities, stakeholders can gauge the effectiveness of pricing tactics in driving sales and maximizing revenue.
Furthermore, understanding the relationship between revenue and sales volume is essential. By delving into the quantity of products or services sold and the corresponding revenue generated, stakeholders can evaluate the efficiency of the company’s sales operations and identify opportunities to optimize sales performance.
Ultimately, a comprehensive analysis of revenue and sales within a profit and loss report empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions regarding product offerings, pricing strategies, sales and marketing initiatives, and overall revenue optimization. By leveraging these insights, businesses can enhance their competitive position and drive sustainable growth.
Evaluating Costs and Expenses
Costs and expenses play a pivotal role in shaping the financial landscape of a business, and evaluating these elements within a profit and loss report is crucial for gaining a comprehensive understanding of the company’s financial performance. By dissecting the costs and expenses outlined in the report, stakeholders can identify areas of efficiency, pinpoint potential cost-saving opportunities, and assess the overall financial sustainability of the business.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) represents the direct expenses associated with producing the goods sold by the company. This includes raw materials, labor, and manufacturing overhead. Analyzing COGS provides insights into the efficiency of production processes, supply chain management, and inventory control. It also aids in assessing the cost-effectiveness of the company’s core operations.
Operating expenses encompass a broad range of costs, including salaries, rent, utilities, marketing, and administrative expenses. Evaluating these expenses sheds light on the day-to-day financial commitments of the business. By scrutinizing operating expenses, stakeholders can identify areas where cost containment or optimization measures may be implemented, thereby enhancing operational efficiency and financial performance.
Furthermore, analyzing the trends and patterns of costs and expenses over multiple reporting periods is essential. It allows stakeholders to identify fluctuations, anomalies, and potential cost drivers. For example, sudden spikes in certain expense categories may warrant further investigation to uncover underlying causes and implement corrective actions.
Understanding the relationship between costs, expenses, and revenue is also critical. By comparing the cost of goods sold and operating expenses to the revenue generated, stakeholders can assess the company’s profit margins and cost structures. This analysis provides insights into the overall cost-effectiveness of the business and its ability to generate profits from its revenue streams.
Ultimately, evaluating costs and expenses within a profit and loss report enables stakeholders to make informed decisions regarding cost management, resource allocation, and operational efficiency. By leveraging these insights, businesses can optimize their cost structures, enhance profitability, and drive sustainable financial growth.
Interpreting Gross Profit and Net Profit
Within a profit and loss report, the metrics of gross profit and net profit are pivotal indicators of a company’s financial performance, providing valuable insights into its profitability and operational efficiency. Understanding how to interpret these metrics is essential for stakeholders to gauge the overall financial health of the business and make informed strategic decisions.
Gross Profit: This metric is derived by subtracting the cost of goods sold from the total revenue. It represents the profit made before accounting for other expenses. Interpreting the gross profit is crucial as it reflects the profitability of the company’s core revenue-generating activities. A healthy gross profit margin indicates that the company is effectively generating revenue and managing its direct production costs, signaling operational efficiency and competitive strength.
Conversely, a declining gross profit margin may signify challenges in cost management, pricing strategies, or production inefficiencies, prompting stakeholders to delve deeper into these areas to identify opportunities for improvement.
Net Profit: Also known as the bottom line, net profit reflects the company’s total earnings after deducting all expenses, including taxes and interest. Interpreting the net profit is essential for assessing the overall profitability and financial viability of the business. A positive net profit indicates that the company is generating earnings after accounting for all expenses, taxes, and interest, signifying financial stability and sustainability.
Conversely, a negative net profit or declining trend may raise concerns about the company’s financial performance and long-term viability, prompting stakeholders to investigate the underlying factors contributing to the decrease in profitability and take corrective actions.
Moreover, comparing the trends of gross profit and net profit over multiple reporting periods provides insights into the company’s financial trajectory. Consistent growth in both metrics signifies a healthy and sustainable business model, while fluctuations or declining trends may warrant further analysis and strategic adjustments.
Interpreting gross profit and net profit within a profit and loss report empowers stakeholders to assess the company’s ability to generate profits, manage costs, and achieve sustainable financial growth. By leveraging these insights, businesses can make informed decisions to enhance profitability, optimize operational efficiency, and drive long-term success.
Identifying Key Performance Indicators
Key performance indicators (KPIs) within a profit and loss report serve as crucial benchmarks for evaluating the financial health and operational performance of a business. These indicators offer valuable insights into various aspects of the company’s financial activities, allowing stakeholders to track progress, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions to drive growth and profitability.
One of the fundamental KPIs within a profit and loss report is the gross profit margin. This metric, expressed as a percentage, compares the gross profit to the total revenue and reflects the efficiency of the company’s core revenue-generating activities. A healthy gross profit margin indicates strong operational performance and effective cost management.
Another essential KPI is the net profit margin, which measures the net profit as a percentage of the total revenue. This metric provides insights into the company’s overall profitability and financial viability. By tracking the net profit margin over time, stakeholders can assess the company’s ability to generate profits and manage expenses effectively.
Moreover, the analysis of operating expenses as a percentage of revenue serves as a critical KPI. This indicator provides insights into the efficiency of cost management and the allocation of resources. Monitoring the trends of operating expenses relative to revenue enables stakeholders to identify potential areas for cost optimization and operational efficiency improvements.
Additionally, the assessment of revenue growth rates and sales trends serves as vital KPIs within a profit and loss report. These metrics provide insights into the company’s ability to expand its customer base, penetrate new markets, and capitalize on emerging opportunities. By tracking revenue growth and sales trends, stakeholders can gauge the effectiveness of sales and marketing strategies and identify areas for strategic investment.
Identifying and monitoring these key performance indicators within a profit and loss report empowers stakeholders to gain a comprehensive understanding of the company’s financial performance and make informed decisions to drive sustainable growth. By leveraging these insights, businesses can optimize their operational strategies, enhance profitability, and position themselves for long-term success.
Using Profit and Loss Reports for Decision Making
Profit and loss reports are invaluable tools for guiding strategic decision-making within a business. By leveraging the insights derived from these financial statements, stakeholders can make informed choices that drive growth, optimize operational efficiency, and enhance overall financial performance.
One of the primary ways profit and loss reports aid decision-making is by providing a comprehensive overview of the company’s financial performance. By analyzing key metrics such as revenue, costs, gross profit, and net profit, stakeholders gain a holistic understanding of the company’s profitability and identify areas that require attention or improvement.
Moreover, profit and loss reports facilitate trend analysis, allowing stakeholders to track the company’s financial trajectory over time. By comparing performance across multiple reporting periods, decision-makers can identify patterns, fluctuations, and emerging trends, enabling them to make proactive adjustments to strategies and operations.
Furthermore, profit and loss reports serve as a basis for setting realistic and achievable financial goals. By understanding the company’s historical performance and current financial position, stakeholders can establish clear objectives and develop strategic plans that align with the company’s financial capabilities and growth potential.
Profit and loss reports also aid in identifying cost-saving opportunities and optimizing resource allocation. By scrutinizing costs, expenses, and profit margins, decision-makers can pinpoint areas for efficiency improvements, implement cost-saving measures, and reallocate resources to maximize profitability.
Additionally, these financial statements provide insights into the effectiveness of sales and marketing strategies. By analyzing revenue streams, sales trends, and gross profit margins, stakeholders can evaluate the performance of different product lines, customer segments, and sales channels, enabling them to refine sales and marketing initiatives for greater impact.
Ultimately, leveraging profit and loss reports for decision-making empowers stakeholders to make informed, data-driven choices that steer the company towards sustainable growth and financial success. By harnessing the insights provided by these financial statements, businesses can optimize their operations, enhance profitability, and position themselves for long-term prosperity.
Conclusion
Understanding how to read and interpret a profit and loss report is essential for stakeholders seeking to gain valuable insights into a company’s financial performance and make informed decisions to drive growth and profitability. This comprehensive financial statement provides a detailed overview of a company’s revenues, costs, and expenses, offering critical metrics and KPIs that serve as benchmarks for assessing operational efficiency and overall financial health.
By delving into the components of the profit and loss report, including revenue, costs, gross profit, net profit, and key performance indicators, stakeholders can gain a comprehensive understanding of the company’s financial landscape. The insights derived from these financial statements empower decision-makers to identify areas for improvement, set realistic financial goals, and refine operational strategies to enhance profitability and sustainability.
Furthermore, leveraging profit and loss reports for decision-making enables stakeholders to track financial trends, identify cost-saving opportunities, and optimize resource allocation. By making data-driven decisions based on the insights provided by these financial statements, businesses can position themselves for long-term success and sustainable growth.
In conclusion, the ability to interpret and utilize profit and loss reports is a fundamental skill for business owners, managers, investors, and other stakeholders. By harnessing the valuable insights offered by these financial statements, businesses can navigate financial challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and drive strategic initiatives that lead to enhanced profitability and long-term success.