
Finance
How To Find An Edge In Futures Contracts
Published: December 24, 2023
Looking for a finance edge in futures contracts? Discover valuable tips and strategies to enhance your trading skills in the world of finance.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of futures contracts, where financial markets meet the future. A futures contract is a legal agreement to buy or sell a particular asset at a predetermined price at a specified time in the future. These contracts are traded on regulated exchanges and are used by investors and traders to speculate on price movements, hedge against risks, and participate in various markets.
However, with the immense popularity and competitiveness of futures trading, it is crucial to find an edge to stay ahead of the game. An edge refers to a unique and advantageous perspective or strategy that gives you an increased likelihood of success in the market. It is the key to outperforming the competition, maximizing profits, and minimizing risks.
In this article, we will explore different approaches to finding an edge in futures contracts. We will dive into fundamental analysis, technical analysis, quantitative analysis, and sentiment analysis – all essential tools for understanding market dynamics and making informed trading decisions.
Fundamental analysis involves studying various factors that can affect the value of an asset, such as economic indicators, supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical events, and company financials. By analyzing these factors, traders can gain insights into the intrinsic value of an asset and its potential for future price movements.
Technical analysis, on the other hand, focuses on studying historical price patterns and trends. By analyzing charts, indicators, and other technical tools, traders can identify support and resistance levels, trend reversals, and other patterns that can inform their trading decisions.
Quantitative analysis involves using statistical models and algorithms to analyze historical data and identify patterns, correlations, and potential market inefficiencies. This approach is commonly used by algorithmic traders and systematic hedge funds to develop and execute trading strategies.
Sentiment analysis digs deeper into the psychology and emotions of market participants. By analyzing news sentiment, social media sentiment, and other sentiment indicators, traders can gauge market sentiment and identify potential shifts in market trends.
Now that we have a basic understanding of the different approaches, let’s delve into each method more comprehensively. We will explore how to develop a strategy, backtest it using historical data, manage risk, execute trades efficiently, and monitor and adjust the strategy to adapt to changing market conditions.
Remember, finding an edge is an ongoing process that requires continuous learning, adaptation, and monitoring. The financial markets are dynamic, and what works today may not work tomorrow. Therefore, it is essential to stay informed, keep learning, and refine your approach to maintain an edge and achieve success in futures trading.
Understanding Futures Contracts
Before diving into finding an edge in futures contracts, it’s crucial to have a solid understanding of what these contracts are and how they work. A futures contract is a standardized agreement to buy or sell a specific quantity of an underlying asset at a predetermined price and date in the future.
These contracts are traded on regulated exchanges, such as the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) or the New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX), and cover a wide range of assets including commodities (like oil, gold, and agricultural products), financial instruments (such as stock indexes and interest rates), and currencies.
One key aspect of futures contracts is leverage. The leverage in futures trading allows participants to control a larger position with a smaller amount of capital. For example, if the margin requirement for a crude oil futures contract is $5,000, an investor can control 1,000 barrels of oil, which at $50 per barrel represents a total contract value of $50,000. This leverage amplifies both potential gains and losses, making futures trading a high-risk, high-reward endeavor.
Another important feature of futures contracts is their standardization. Each contract has specific terms, including the size of the contract, the quality of the underlying asset, the delivery date, and the tick size (minimum price movement). This standardization allows for easy trading and provides transparency in the market.
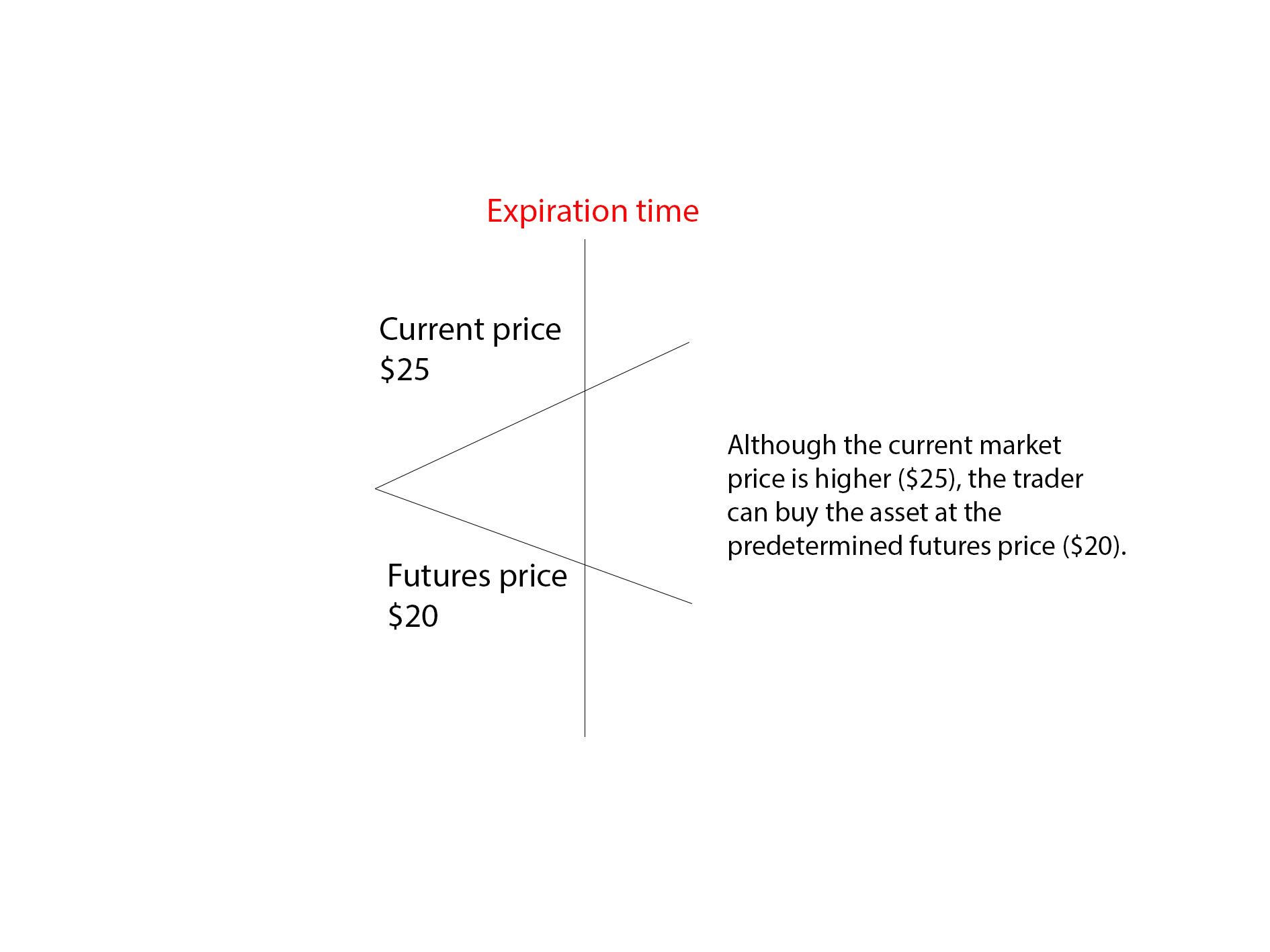
Futures contracts can be bought (long position) or sold (short position) with the expectation of profiting from price movements. If you believe the price of a specific asset will rise, you can go long by buying futures contracts. Conversely, if you think the price will fall, you can go short by selling futures contracts.
One key factor in futures trading is the concept of marking to market. Unlike stocks or other investments, futures contracts are marked to market daily. This means that at the end of each trading day, gains and losses are settled, and the account balance is adjusted accordingly. This process ensures that both parties to the contract maintain the necessary margin requirements and prevents substantial losses or gains from accumulating.
In addition to speculating on price movements, futures contracts are used for hedging. Hedging involves using futures contracts to mitigate potential risks associated with the underlying asset. For example, a corn farmer may use corn futures contracts to lock in a price for their crop, protecting against a potential decrease in the price of corn at the time of harvest.
Understanding the workings of futures contracts is crucial in finding an edge. It allows traders to make informed decisions based on market dynamics, contract specifications, and risk management principles. Armed with this knowledge, we can explore different strategies and approaches to gain an advantage in the futures market.
Importance of Finding an Edge
When it comes to trading futures contracts, finding an edge is of paramount importance. In the highly competitive and dynamic world of financial markets, having an edge can mean the difference between success and failure.
An edge provides you with a unique advantage over other market participants. It allows you to identify profitable opportunities, make informed trading decisions, and stay ahead of the curve. Without an edge, you are simply relying on luck or random chance, which is not a sustainable or reliable approach to trading.
Here are several reasons why finding an edge is crucial:
1. Increased Profitability: Having an edge improves your chances of making profitable trades. It helps you identify undervalued assets, predict market trends, and execute trades at optimal times. By consistently finding and capitalizing on profitable opportunities, you can enhance your overall profitability in the futures market.
2. Risk Management: An edge also aids in managing risk. Effective risk management is crucial to protect your capital and limit potential losses. By having an edge, you can assess and evaluate market conditions, identify potential risks, and implement risk mitigation strategies. This helps you trade with a disciplined approach and reduces the likelihood of significant financial setbacks.
3. Competitive Advantage: In the crowded and fast-paced world of futures trading, having an edge sets you apart from the competition. It allows you to stay ahead of other traders and investors by spotting opportunities or patterns that others may have missed. This gives you an edge in terms of speed, accuracy, and decision-making, which can be a significant advantage in capturing profits.
4. Consistency: Finding an edge provides consistency in your trading approach. It helps you develop a systematic and disciplined strategy that can be replicated over time. By sticking to a well-defined edge, you can avoid emotional trading decisions and maintain a consistent approach even during volatile market conditions.
5. Adaptability: Markets are constantly evolving, and what worked yesterday may not work today. Having an edge allows you to adapt and adjust your trading strategy to changing market conditions. This adaptability is crucial in staying relevant and profitable in the long run.
6. Learning and Growth: In the quest to find an edge, you must continually learn and improve your trading skills. This process of education and growth is invaluable in enhancing your understanding of the market, developing new strategies, and expanding your trading toolkit.
Overall, finding an edge in futures contracts is essential for sustained success. It enables you to navigate the complexities of the market, identify profitable opportunities, manage risk effectively, and stay ahead of the competition. By continuously seeking an edge and refining your trading approach, you can improve your profitability and achieve your trading goals in the dynamic world of futures trading.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis is a crucial tool for finding an edge in futures trading. It involves analyzing various fundamental factors that can affect the value of an asset, such as economic indicators, supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical events, and company financials. By understanding these factors, traders can gain insights into the intrinsic value of an asset and its potential for future price movements.
Here are some key aspects of fundamental analysis:
Economic Indicators: Economic indicators provide essential information about the health and performance of economies. These indicators include GDP growth, inflation rates, employment data, interest rates, and consumer sentiment. By monitoring and analyzing these indicators, traders can assess the overall economic conditions and anticipate potential impacts on asset prices. For example, positive economic data may lead to increased demand for commodities or stocks, while negative economic data may cause prices to decline.
Supply and Demand Dynamics: Understanding the supply and demand dynamics of an asset is crucial in forecasting its price movements. Factors such as changes in production levels, inventories, and consumption patterns can influence supply and demand balances. By monitoring these factors and assessing their potential impact on prices, traders can identify profitable opportunities. For instance, an expected increase in demand for oil due to growing global consumption may lead to a bullish outlook for oil futures.
Geopolitical Events: Geopolitical events, such as political instability, wars, or trade disputes, can have a significant impact on financial markets. These events can affect supply chains, trade flows, and investor sentiment. By staying informed about geopolitical developments and analyzing their potential implications, traders can anticipate market reactions and adjust their trading strategies accordingly.
Company Financials: In the case of futures contracts related to stocks or commodities tied to specific companies, analyzing company financials is essential. This involves assessing factors such as revenue growth, profitability, debt levels, and earnings reports. Company-specific news and events, such as product launches or mergers and acquisitions, can also influence the value of futures contracts. By analyzing these factors, traders can gain insights into a company’s financial health and its potential impact on asset prices.
Market Sentiment: Market sentiment refers to the overall attitude and perception of traders and investors towards a particular asset or market. It can range from extreme optimism to extreme pessimism. By monitoring market sentiment indicators, such as surveys or sentiment indexes, traders can gauge the overall market sentiment and identify potential opportunities for contrarian trades. For example, if market sentiment becomes excessively bullish, it may signal a potential market top, leading to a bearish outlook.
While fundamental analysis is a powerful tool, it does have limitations. It can be time-consuming and may require a deep understanding of the specific asset or market being analyzed. Additionally, unexpected events or changes in market dynamics can sometimes render fundamental analysis less effective. Therefore, it is important to combine fundamental analysis with other approaches to gain a comprehensive view of the market and find a well-rounded edge.
By incorporating fundamental analysis into your trading strategy, you can make more informed decisions based on a thorough understanding of the underlying factors that drive futures prices. It allows you to assess the intrinsic value of assets, anticipate market movements, and potentially profit from both short-term and long-term price fluctuations in the futures market.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis is a popular approach for finding an edge in futures trading. It involves studying historical price patterns and trends to predict future price movements. Traders who utilize technical analysis believe that past price and volume data can provide valuable insights into the behavior and sentiment of market participants.
Here are some key aspects of technical analysis:
Chart Patterns: Chart patterns are specific formations and structures that appear on price charts. These patterns can indicate the potential direction of future price movements. Common chart patterns include triangles, head and shoulders, double tops/bottoms, and trend lines. By analyzing these patterns, traders can identify potential entry and exit points for their trades.
Indicators: Technical analysts use a variety of indicators to help them make trading decisions. These indicators are mathematical calculations based on price and volume data. Popular indicators include moving averages, oscillators (such as the Relative Strength Index and Stochastic), and trend-following indicators (like the Average Directional Index). These indicators can provide signals of trend strength, momentum, and potential reversals.
Support and Resistance Levels: Support and resistance levels are key price levels where buying or selling pressure is expected to be significant. Support levels are areas where prices have historically found buying interest, causing prices to bounce higher. Resistance levels, on the other hand, are areas where prices have historically faced selling pressure, causing prices to reverse or stall. By identifying these levels, traders can make trading decisions based on potential breakout or reversal opportunities.
Volume Analysis: Volume is an important component of technical analysis. It measures the number of contracts or shares traded in a given period. Volume can provide insights into the strength of price movements and the participation of market participants. For example, an increase in volume during an uptrend may signal strong buying interest, confirming the bullish trend.
Japanese Candlestick Patterns: Japanese candlestick patterns originated in Japan in the 17th century and have become widely used in technical analysis. These patterns provide visual representations of price movements and can signify market reversals or continuations. Common candlestick patterns include dojis, hammers, engulfing patterns, and shooting stars.
Technical analysis is based on the premise that historical price patterns tend to repeat themselves. By analyzing these patterns, traders can identify potential levels of support and resistance, predict trend reversals, and take advantage of market inefficiencies.
However, it’s important to be aware that technical analysis has its limitations. It does not take into account fundamental factors that can impact the market, and it relies heavily on historical data, which may not always be indicative of future price movements. Therefore, it’s important to combine technical analysis with other approaches, such as fundamental analysis or sentiment analysis, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the market.
By incorporating technical analysis into your trading strategy, you can make more objective and systematic trading decisions. It allows you to identify potential trade setups, set appropriate entry and exit points, and manage your risk effectively. Technical analysis can be a valuable tool in finding an edge in futures trading.
Quantitative Analysis
Quantitative analysis is a powerful approach used by traders to find an edge in the futures market. It involves the use of statistical models, algorithms, and mathematical calculations to analyze historical data and identify patterns, correlations, and potential market inefficiencies. Quantitative analysis is particularly popular among algorithmic traders and systematic hedge funds.
Here are some key aspects of quantitative analysis:
Data Analysis: Quantitative analysts start by collecting and analyzing large sets of historical data, including price data, volume data, and various other market indicators. This data is processed and organized in a way that allows for statistical analysis and modeling.
Model Building: Quantitative analysts develop mathematical models and algorithms to analyze the data and derive insights. These models can range from simple statistical models to more complex machine learning algorithms. The goal is to identify patterns, relationships, and potential market opportunities that can be exploited for trading purposes.
Backtesting: Backtesting is a crucial step in quantitative analysis. Traders use historical data to test their trading models and algorithms to see how they would have performed in the past. This allows them to assess the profitability and effectiveness of their strategies before deploying them in real-time trading.
Risk Management: Quantitative analysis also involves the use of risk management techniques and calculations to assess and control potential risks. Traders use statistical tools to measure and quantify risk, such as value at risk (VaR) models and stress-testing scenarios. This helps traders manage their exposure and implement appropriate risk management strategies.
Algorithmic Trading: Quantitative analysis is closely associated with algorithmic trading, where trades are executed automatically by computer programs based on predefined rules and algorithms. These algorithms can take into account various quantitative factors, such as price patterns, historical data, and market indicators, to make trading decisions in real-time. Algorithmic trading can help improve execution speed and remove emotional biases from trading decisions.
Quantitative analysis provides a systematic and data-driven approach to trading, allowing traders to make objective decisions based on statistical evidence. It can help identify market inefficiencies, exploit price discrepancies, and generate alpha (excess returns).
However, quantitative analysis also has its limitations. It relies heavily on historical data, which may not always be indicative of future market behavior. Market conditions can change, rendering certain models or algorithms less effective. Additionally, there is always the risk of over-optimization, where models may work well in backtesting but fail to perform in real-time trading.
To overcome these challenges, quantitative analysts continuously research and refine their models, adapt to changing market conditions, and incorporate other forms of analysis, such as fundamental or technical analysis, into their trading strategies.
By incorporating quantitative analysis into your trading approach, you can gain a deeper understanding of market dynamics, make data-driven decisions, and potentially find an edge in the futures market. It requires a strong grasp of statistics, programming, and financial markets, but for those who master it, quantitative analysis can be a powerful tool for success.
Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis is a valuable approach that helps traders find an edge in futures trading by analyzing the emotions and attitudes of market participants. It involves gauging the sentiment of traders and investors towards a particular asset or market, using various sources such as news sentiment, social media sentiment, and sentiment indicators.
Here are some key aspects of sentiment analysis:
News Sentiment: News sentiment analysis involves monitoring and analyzing news articles, headlines, and financial reports to gauge the overall sentiment towards a specific asset or market. By tracking positive or negative news sentiment, traders can gain insights into the evolving market sentiment and potential market reactions.
Social Media Sentiment: Social media platforms provide a wealth of information and opinions about financial markets. Analyzing social media sentiment involves monitoring posts, tweets, and comments related to a particular asset or market. This can provide real-time insights into the sentiment and mood of a larger pool of market participants.
Sentiment Indicators: Sentiment indicators are quantitative measures that provide an overview of market sentiment. These indicators can range from simple surveys and sentiment indexes to more sophisticated sentiment models. Examples of sentiment indicators include the Investor’s Intelligence Sentiment Index, the Fear and Greed Index, and the put-call ratio. By observing and analyzing these indicators, traders can gauge the overall market sentiment and identify potential contrarian opportunities.
Contrarian Trading: Sentiment analysis can be particularly useful in contrarian trading strategies. Contrarian traders seek to take positions opposite to the prevailing sentiment. For example, if the market sentiment becomes excessively bullish, contrarian traders may consider taking a bearish position. This strategy capitalizes on market sentiment reaching extreme levels and potential reversals in market trends.
Sentiment analysis provides traders with additional insights and perspectives on market dynamics. It helps identify potential shifts in market sentiment and sentiment-driven price movements that may not be evident through fundamental or technical analysis alone.
It’s important to note that sentiment analysis is not without its limitations. Sentiment can be subjective and influenced by various factors, including biases and noise. Additionally, sentiment analysis may not necessarily align with actual market movements, as sentiment-driven price movements can be short-lived or quickly reversed.
Therefore, it is crucial to use sentiment analysis as a complement to other forms of analysis, such as fundamental or technical analysis. By integrating sentiment analysis into your trading strategy, you can gain a deeper understanding of market psychology, identify potential sentiment-driven opportunities, and make more informed trading decisions.
Developing a Strategy
Developing a well-defined trading strategy is an essential step in finding an edge in futures trading. A trading strategy outlines a set of rules and guidelines that dictate how you identify, analyze, and execute trades. It provides structure and discipline, helping you navigate the complexities of the market and make informed decisions.
Here are some key aspects to consider when developing a trading strategy:
Define Your Goals: Start by clearly defining your trading goals. Are you looking for short-term gains or long-term investments? Are you seeking consistent profits or are you willing to take on higher risks for potential high returns? Understanding your objectives will help shape your strategy and guide your decision-making process.
Choose Your Asset Class: Decide on the asset class you want to trade in, such as commodities, currencies, stocks, or interest rates. Each asset class has its characteristics and requires a specific set of skills and knowledge. Consider your expertise and interest in the asset class as you choose which market to trade in.
Select Your Approach: Determine the approach or combination of approaches you will use in your strategy. Will you be focusing on fundamental analysis, technical analysis, quantitative analysis, sentiment analysis, or a combination of these? Understanding the strengths and limitations of each approach will help you choose the most suitable one for your trading goals.
Set Entry and Exit Criteria: Establish clear criteria for entering and exiting trades. This can be based on specific price levels, technical indicators, or fundamental factors. Having predetermined entry and exit points helps remove emotions from your decision-making process and ensures consistency in your trading approach.
Risk Management Rules: Implement effective risk management rules to protect your capital and manage potential losses. Determine your risk tolerance, position sizing, and stop-loss levels. Risk management is crucial to preserving your capital and staying in the market for the long term.
Backtesting and Optimization: Backtesting involves applying your strategy to historical data to assess its performance. This helps you evaluate the profitability and effectiveness of your strategy in different market conditions. If needed, refine and optimize your strategy based on the results of your backtesting.
Monitoring and Evaluation: Continuously monitor and evaluate the performance of your strategy in real-time trading. Keep track of your trades, review your trades regularly, and analyze the outcomes to identify areas for improvement. Market conditions change, and staying adaptable and responsive to market dynamics is crucial for long-term success.
Continuous Learning: Commit to continuous learning and improvement. Stay abreast of market developments, monitor industry news, and enhance your knowledge and skills. The more you learn and adapt, the better equipped you will be to refine your strategy and find an edge in the market.
Remember, developing a successful trading strategy takes time and effort. It requires testing, refinement, and ongoing evaluation. It’s essential to stay disciplined, remain objective, and remain committed to your strategy even during periods of market volatility.
By incorporating these elements into your trading strategy, you can increase your chances of finding an edge in the futures market and achieve your trading objectives.
Backtesting
Backtesting is a critical component in the development of a trading strategy. It involves applying your trading strategy to historical data to evaluate its performance and effectiveness. By simulating trades and analyzing the results, backtesting helps you assess the profitability, risk, and reliability of your strategy.
Here are key aspects to consider when conducting backtesting:
Data Selection: Start by selecting the relevant historical data for your backtesting. Consider the time period, frequency, and accuracy of the data. Ensure that the data you use is representative of the market conditions you intend to trade in.
Testing Rules and Parameters: Define the rules and parameters of your trading strategy that will be tested during backtesting. This includes entry and exit criteria, position sizing, risk management rules, and any other rules specific to your strategy. It’s important to be consistent and precise in defining and applying these rules.
Simulation and Analysis: Use the historical data to simulate trades based on your strategy rules. Analyze the performance measures such as the profitability, risk, drawdowns, and performance statistics. This will help you understand how your strategy would have performed in the past.
Evaluation and Optimization: Evaluate the results of your backtesting and assess the strengths and weaknesses of your strategy. Identify areas for improvement and consider optimizing your strategy based on the results. Be cautious of over-optimization, as excessively tweaking your strategy to fit historical data may lead to poor performance in real-time trading.
Statistical Significance: Consider the statistical significance of your backtesting results. Ensure that any observed performance is not just due to random chance. Perform robustness tests or sensitivity analyses to determine if the strategy’s performance persists across different conditions and timeframes.
Realism and Market Conditions: While backtesting can provide valuable insights, it’s important to recognize that historical data may not perfectly replicate real-world trading conditions. Market conditions and dynamics change over time, and the past may not accurately reflect the future. Keep this in mind and remain adaptable in your trading approach.
Continuous Testing and Refinement: Backtesting is not a one-time process. As market conditions change, revisit and retest your strategy periodically. Continuously refine and adapt your strategy based on new data and insights gained from ongoing testing.
Backtesting is a crucial step in the development and evaluation of a trading strategy. It helps you gauge the performance and viability of your strategy based on historical data. While it does not guarantee future success, backtesting provides valuable information and insights that can help you refine your strategy and increase your chances of finding an edge in the futures market.
Risk Management
Risk management is a fundamental aspect of successful trading in the futures market. It involves implementing strategies and techniques to protect your capital, control potential losses, and manage overall risk exposure. Effective risk management is crucial in preserving capital and ensuring long-term trading success.
Here are key considerations for implementing risk management in futures trading:
Define Risk Tolerance: Determine your risk tolerance level before entering any trade. This is the amount of acceptable risk you are willing to take on for each trade or overall portfolio. Your risk tolerance should align with your trading goals, financial situation, and comfort level with potential losses.
Position Sizing: Proper position sizing is crucial in managing risk. Determine the appropriate size of each trade based on your risk tolerance, account size, and the specific risk-to-reward ratio of the trade. Avoid taking on excessive position sizes that could lead to substantial losses.
Stop Loss Orders: Implementing stop loss orders is an essential risk management tool. A stop loss order is placed at a predetermined price level, below the current market price for a long position or above for a short position. It serves as a risk mitigation tool, automatically closing the trade to limit potential losses if the price moves unfavorably against your position.
Use Risk-Reward Ratio: Assess the risk-reward ratio for each trade. The risk-reward ratio compares the potential profit to the potential loss of a trade. A favorable risk-reward ratio of, for example, 1:2, means you are aiming to make twice as much profit as you are risking. By consistently aiming for positive risk-reward ratios, you can help ensure that your potential gains outweigh your potential losses over time.
Diversification: Diversifying your portfolio is an effective risk management technique. Spread your capital across different asset classes, markets, or instruments to reduce the impact of individual losses. Diversification helps minimize the risk of concentrated exposure to a single asset or market.
Evaluate and Adjust: Continuously evaluate and adjust your risk management approach based on market conditions and performance. Regularly review your trades, risk-reward ratios, and stop loss levels to ensure they are aligned with your trading strategy and risk tolerance. Be prepared to make adjustments if market conditions change.
Consider Volatility and Margin Requirements: Be mindful of market volatility and margin requirements. Higher volatility can expose your positions to larger price swings and increased risk. Additionally, margin requirements need to be considered to maintain adequate account equity and reduce the risk of margin calls.
Emotional Control: Keep emotions in check and stick to your risk management plan. Avoid making impulsive, emotionally-driven trading decisions that deviate from your risk management strategy. Emotions can cloud judgment and lead to poor risk management practices.
Risk management is a continuous process that requires discipline and attentiveness. By implementing sound risk management strategies, you can protect your capital, limit potential losses, and improve the overall stability of your trading strategy. Remember, successful trading is not just about making profits, but also about mitigating risks and preserving capital for long-term success.
Execution and Implementation
Execution and implementation are key components of successful futures trading. Once you have developed a robust trading strategy and established risk management techniques, it is important to effectively execute and implement your trades. Proper execution ensures that your trading decisions are translated into actions in the markets, allowing you to take advantage of the opportunities you have identified.
Here are some considerations for executing and implementing your trades:
Market Timing: Market timing is crucial in executing trades at the optimal moment. Depending on your strategy and analysis, it’s important to identify the most opportune time to enter or exit a trade. This may involve monitoring price levels, technical patterns, or specific indicators that signal favorable market conditions.
Order Types: Utilize appropriate order types to match your execution needs. Market orders allow for immediate execution at the current market price, while limit orders enable you to set a specific entry or exit price. Stop orders are useful for triggering trades once a certain price level is reached, while stop limit orders provide an additional level of control by combining stop and limit orders.
Execution Speed: In rapidly moving markets, execution speed is critical. Ensure that your trading platform or brokerage can provide fast and reliable order execution. Delayed execution or poor execution quality can lead to missed opportunities or slippage, negatively impacting your trading results.
Position Sizing: Implement proper position sizing techniques to align your trade sizes with your risk management strategy. Calculate the appropriate position size based on your risk tolerance, account size, and stop loss levels. This helps ensure that you are not risking an excessive amount on individual trades and allows for better risk management.
Market Liquidity: Consider the liquidity of the market you are trading. High liquidity markets typically have tighter bid-ask spreads and better order execution. Conversely, illiquid markets may experience wider spreads and limited trading volume, which can impact execution quality and slippage. Adjust your trade sizes and expectations accordingly.
Trade Monitoring: Once your trades are executed, monitor them closely. Keep track of market developments, news events, and any changes that may impact your positions. Regularly review and update your stop loss levels if necessary. Being proactive in monitoring your trades ensures that you can react quickly to changing market conditions.
Record Keeping and Analysis: Maintain detailed records of your trades, including entry and exit points, position sizes, and the reasoning behind each trade. This allows you to conduct thorough post-trade analysis and identify areas for improvement. By analyzing your trades, you can refine your strategy and enhance your future trading performance.
Adaptability: Be adaptive in your execution and implementation strategies. Market conditions change, and your trading approach may need adjustment. Stay informed, be open to new information, and be willing to adapt your approach based on changing circumstances.
Executing trades with precision and implementing your trading strategy effectively is essential for realizing the potential benefits of your analysis and risk management techniques. By paying attention to factors like market timing, order types, execution speed, position sizing, and trade monitoring, you can enhance your trading performance, capitalize on opportunities, and execute your trades with confidence in the futures market.
Monitoring and Adjusting
Monitoring and adjusting your trading strategy is a vital step in staying on top of the evolving dynamics of the futures market. To maintain an edge, you must actively monitor your trades, market conditions, and other relevant factors. Regular evaluation and adjustment of your strategy allow you to adapt to changing circumstances and optimize your trading performance.
Here are key considerations for effectively monitoring and adjusting your trading strategy:
Trade Performance Analysis: Regularly analyze the performance of your trades. Assess the profitability, risk-reward ratios, win rates, and other performance metrics. Identify patterns, strengths, and weaknesses in your trading results. This analysis allows you to make data-driven decisions and refine your strategy accordingly.
Market Analysis: Continuously monitor the market and stay informed about relevant news, events, and economic indicators. Analyze how current market conditions may impact your positions and overall trading strategy. Consider the macroeconomic environment, sector-specific factors, and any emerging trends that may affect your trades.
Watch List and Trade Opportunities: Maintain a watch list of potential trade opportunities. Regularly review and update this list based on changes in market conditions. Stay vigilant for new setups and be prepared to act when favorable trading opportunities arise.
Risk Management Evaluation: Revisit and reassess your risk management approach on an ongoing basis. Ensure that your position sizing, stop loss levels, and overall risk exposure remain appropriate as market conditions evolve. Adjust these parameters if necessary to align with changes in volatility or your risk tolerance.
Review Trading Rules: Evaluate and fine-tune the rules and parameters of your trading strategy. Consider whether any rules need modification or elimination, based on your analysis of past trades and market conditions. Staying flexible allows you to adapt your strategy to ever-changing market dynamics.
Stay Emotionally Disciplined: It is essential to manage your emotions and maintain discipline in your trading approach. Emotions can cloud judgment and lead to impulsive, irrational decisions. Strive to adhere to your trading plan and risk management rules, regardless of emotions that may arise during periods of volatility or losses.
Adaptability: Be open to adjusting your trading strategy and tactics as needed. Market conditions can change rapidly, requiring you to adapt your approach to fit new circumstances. Flexibility allows you to seize opportunities, manage risks, and stay ahead in a dynamic market environment.
Continual Learning: Commit to ongoing education and learning. Stay engaged with educational resources, industry publications, and market analysis. Continuously seek new knowledge, trading techniques, and insights that can enhance your trading performance.
By actively monitoring and adjusting your trading strategy, you can respond effectively to changes in the market and optimize your trading outcomes. Regular evaluation of trade performance, market conditions, risk management, and trading rules enhances your ability to adapt, stay competitive, and maintain an edge in the futures market.
Conclusion
Successfully finding an edge in futures trading is an ongoing journey that requires a combination of skill, knowledge, and discipline. By incorporating different approaches, such as fundamental analysis, technical analysis, quantitative analysis, and sentiment analysis, traders can gain a comprehensive understanding of the market and identify potential profit opportunities.
Developing a robust trading strategy, backed by thorough research and analysis, is essential in finding an edge. It allows traders to capitalize on favorable market conditions while managing risks effectively. Proper risk management techniques, including position sizing, stop loss orders, and diversification, protect capital and ensure longevity in the market.
In the pursuit of an edge, continuous monitoring, evaluation, and adjustment of the trading strategy are crucial. Regular analysis of trade performance, market conditions, and risk management practices enables traders to adapt to changing market dynamics and optimize their trading approach.
Additionally, it’s important to remember that successful trading requires emotional control, adaptability, and a commitment to ongoing learning. Markets are dynamic, and the ability to adapt to evolving conditions and learn from both successes and failures is paramount in achieving long-term success.
Ultimately, finding an edge in futures trading is a combination of art and science. It requires technical expertise, a deep understanding of market dynamics, and the ability to make informed decisions based on analysis and data. With a well-developed strategy, effective risk management, and continuous monitoring and adjustment, traders can increase their chances of finding an edge and achieving success in the futures market.