Home>Finance>How To Incorporate Merchant Fees Into Cost Of Goods


Finance
How To Incorporate Merchant Fees Into Cost Of Goods
Published: February 24, 2024
Learn how to calculate and incorporate merchant fees into your cost of goods with our comprehensive finance guide. Optimize your pricing strategy and maximize profits today!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
In the realm of commerce, understanding the intricacies of cost analysis is pivotal to maintaining a profitable business. One crucial component of this analysis is the incorporation of merchant fees into the cost of goods. Merchant fees, also known as credit card processing fees, are charges imposed by financial institutions for processing electronic payments. These fees can significantly impact a company's bottom line, making it essential for businesses to comprehend how to factor them into their cost structures.
Navigating the landscape of merchant fees necessitates a comprehensive understanding of their implications on pricing strategies and overall profitability. This article aims to elucidate the concept of merchant fees, provide insights into calculating these fees, and offer guidance on incorporating them into the cost of goods. By delving into this subject, businesses can make informed decisions that optimize their financial performance and bolster their competitive edge in the market.
Understanding the nuances of merchant fees and their integration into cost analysis is a fundamental aspect of financial management. As such, this article endeavors to equip entrepreneurs and business professionals with the knowledge and strategies necessary to navigate the terrain of merchant fees effectively. Let's dive into the realm of merchant fees and unravel the methods for seamlessly integrating them into the cost of goods, thereby empowering businesses to make informed financial decisions and enhance their profitability.
Understanding Merchant Fees
Merchant fees, also referred to as credit card processing fees, encompass the charges imposed by financial institutions to facilitate electronic payment processing for businesses. These fees are incurred each time a customer makes a purchase using a credit or debit card, and they are typically calculated as a percentage of the transaction amount along with a flat fee. The prevalence of electronic payment methods in modern commerce underscores the significance of comprehending merchant fees and their impact on a company’s financial dynamics.
It is imperative for businesses to grasp the underlying components of merchant fees, which often include interchange fees, assessment fees, and payment processor markups. Interchange fees are set by card networks such as Visa and Mastercard and are paid to the cardholder’s bank. Assessment fees, on the other hand, are collected by the card networks for card usage. Additionally, payment processors levy markups to cover their operational costs and generate revenue. Understanding these elements is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize their cost structures and pricing strategies.
Moreover, the structure of merchant fees can vary based on factors such as the type of card used, the method of card acceptance (in-store, online, or mobile), and the business’s industry. Different card types, such as rewards cards or corporate cards, often incur higher processing fees due to their associated perks and benefits. Furthermore, the manner in which a card is processed, whether through a physical terminal or an online gateway, can influence the fee structure. Businesses must navigate this landscape adeptly to mitigate the impact of merchant fees on their profitability.
By comprehending the intricacies of merchant fees, businesses can strategize effectively to mitigate their financial impact. This entails evaluating the feasibility of passing on the fees to customers, implementing pricing adjustments, or negotiating favorable terms with payment processors. Additionally, leveraging technology and data analytics can aid in identifying cost-saving opportunities and optimizing payment processing methods.
Understanding the multifaceted nature of merchant fees empowers businesses to make informed decisions that align with their financial objectives. By delving into the intricacies of these fees, businesses can navigate the complexities of electronic payment processing and position themselves for sustained profitability and growth.
Calculating Merchant Fees
Calculating merchant fees involves a nuanced assessment of the various components that contribute to the overall cost of processing electronic payments. The primary factors influencing the calculation of merchant fees include the transaction amount, the type of card used, the method of card acceptance, and the fee structure set by the payment processor. Understanding these elements is essential for businesses seeking to ascertain the true cost of accepting electronic payments and integrating these expenses into their financial analyses.
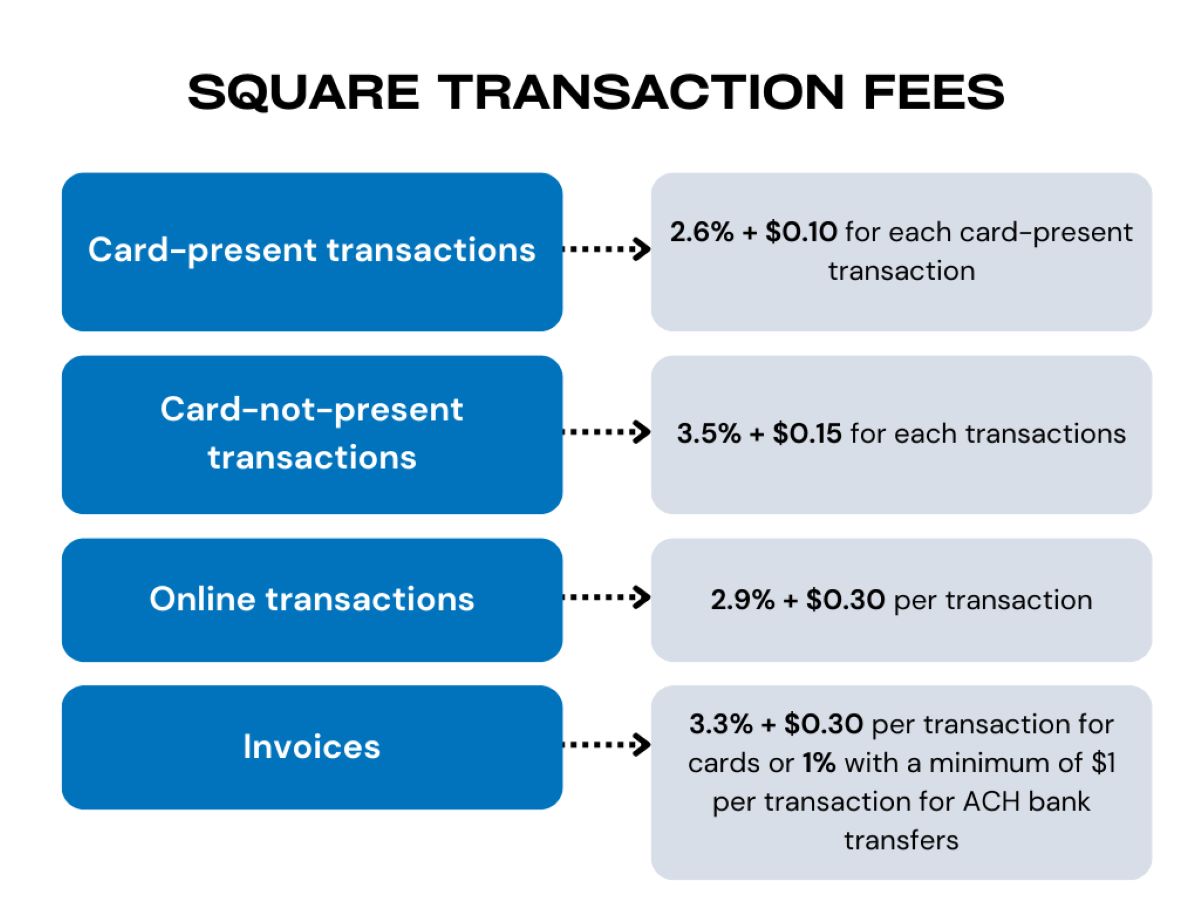
The calculation of merchant fees typically involves two primary components: a percentage of the transaction amount and a flat fee. The percentage, often referred to as the discount rate, is predetermined based on the type of card used and the terms negotiated with the payment processor. This percentage is applied to the transaction amount, thereby constituting a variable component of the merchant fee. Additionally, a flat fee, also known as a transaction fee, is charged for each transaction processed, irrespective of the transaction amount.
Businesses can calculate the total merchant fee for a transaction by combining the percentage fee and the flat fee. For example, if the discount rate is 2.5% and the flat fee is $0.30, the total fee for a $100 transaction would amount to $2.80 ($2.50 from the percentage fee and $0.30 from the flat fee). This calculation provides businesses with a clear understanding of the expenses incurred for each electronic payment processed.
Moreover, the type of card used for the transaction influences the fee calculation, as different card categories carry varying processing costs. For instance, rewards cards and corporate cards often entail higher processing fees due to their associated perks and benefits. Businesses must consider these nuances when calculating merchant fees to accurately reflect the cost of processing different types of cards.
Furthermore, the method of card acceptance, whether in-store, online, or mobile, can impact the fee structure. Online transactions and mobile payments may entail distinct fee arrangements compared to in-store transactions. Understanding these distinctions is vital for businesses to gauge the cost implications of different payment acceptance methods.
By delving into the intricacies of calculating merchant fees, businesses can gain clarity on the financial implications of electronic payment processing. This insight enables businesses to make informed decisions regarding pricing strategies, cost management, and negotiations with payment processors, ultimately fostering financial prudence and profitability.
Incorporating Merchant Fees into Cost of Goods
Integrating merchant fees into the cost of goods is a pivotal aspect of comprehensive cost analysis for businesses. By factoring in the expenses associated with electronic payment processing, businesses can derive a more accurate representation of their true cost of sales and make informed pricing decisions. This integration involves a strategic approach to ensure that the impact of merchant fees is appropriately distributed across the cost of goods, thereby aligning with the business’s financial objectives.
When incorporating merchant fees into the cost of goods, businesses must consider the direct and indirect implications of these expenses on their pricing strategies and overall profitability. Direct implications encompass the immediate impact of merchant fees on the cost of goods sold (COGS), necessitating a meticulous assessment of the fees incurred for each transaction processed. This entails calculating the total merchant fees for a given sales volume and determining the proportion of these expenses attributable to the cost of goods.
Indirect implications revolve around the broader financial ramifications of merchant fees, encompassing their influence on pricing structures, profit margins, and competitive positioning. Businesses must evaluate the feasibility of absorbing these fees within their existing pricing models or passing them on to customers through transparent pricing strategies. Additionally, the integration of merchant fees into the cost of goods necessitates aligning pricing decisions with the business’s value proposition and market positioning to ensure a harmonious balance between cost recovery and customer value perception.
Furthermore, leveraging technology and data analytics can aid in identifying patterns in electronic payment processing costs and optimizing the allocation of these expenses within the cost of goods. By analyzing transaction data and payment processing methods, businesses can discern opportunities to streamline processes, mitigate unnecessary costs, and enhance the accuracy of cost allocation. This proactive approach empowers businesses to adapt their cost structures in response to evolving market dynamics and consumer preferences.
Effectively incorporating merchant fees into the cost of goods requires a holistic understanding of the business’s financial landscape and a strategic outlook toward cost management. By integrating these fees into the cost analysis framework, businesses can refine their pricing strategies, improve cost visibility, and fortify their financial resilience in an increasingly competitive market environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the integration of merchant fees into the cost of goods is a fundamental facet of financial management for businesses. By comprehending the nuances of merchant fees, calculating these expenses accurately, and strategically incorporating them into the cost structure, businesses can optimize their pricing strategies and bolster their profitability. The intricate nature of merchant fees necessitates a comprehensive understanding of their direct and indirect implications on cost analysis and pricing decisions.
Understanding merchant fees entails delving into the components that contribute to these expenses, including interchange fees, assessment fees, and payment processor markups. Businesses must navigate this landscape adeptly to mitigate the impact of merchant fees on their profitability. Calculating merchant fees involves assessing the transaction amount, card type, method of card acceptance, and fee structure, enabling businesses to derive a clear understanding of the costs associated with electronic payment processing.
Integrating merchant fees into the cost of goods requires a strategic approach to ensure that these expenses are accurately distributed across the cost structure. This involves evaluating the direct and indirect implications of merchant fees on pricing strategies, profit margins, and competitive positioning. By leveraging technology and data analytics, businesses can optimize the allocation of these expenses within the cost of goods, fostering financial prudence and adaptability in a dynamic market environment.
Ultimately, the seamless integration of merchant fees into the cost analysis framework empowers businesses to make informed pricing decisions, enhance cost visibility, and fortify their financial resilience. By aligning their cost structures with market dynamics and consumer preferences, businesses can position themselves for sustained profitability and growth in the ever-evolving landscape of commerce.
Embracing a proactive approach to understanding, calculating, and incorporating merchant fees into the cost of goods equips businesses with the insights and strategies necessary to navigate the complexities of electronic payment processing and optimize their financial performance. As businesses strive to maintain a competitive edge in the market, the astute integration of merchant fees into cost analysis stands as a cornerstone of financial prudence and strategic decision-making.