Home>Finance>What Is Better: Debt Consolidation Or Bankruptcy?


Finance
What Is Better: Debt Consolidation Or Bankruptcy?
Published: March 6, 2024
Learn about the pros and cons of debt consolidation and bankruptcy to make informed financial decisions. Understand the impact on your finances and credit. #Finance
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
In the realm of personal finance, individuals often encounter challenging situations that can lead to overwhelming debt. When faced with this predicament, it's crucial to explore viable solutions that can help alleviate financial strain and pave the way toward a brighter future. Two common avenues for addressing substantial debt are debt consolidation and bankruptcy. Each option carries its own set of advantages and considerations, and determining the most suitable path requires a comprehensive understanding of both approaches. By delving into the intricacies of debt consolidation and bankruptcy, individuals can make informed decisions that align with their unique financial circumstances and long-term goals.
Debt consolidation and bankruptcy represent distinct strategies for managing and resolving debt-related challenges. While debt consolidation involves combining multiple debts into a single, more manageable payment plan, bankruptcy entails a legal process that aims to discharge or restructure debts under the protection of the court. Both avenues offer potential relief from overwhelming financial burdens, but they differ significantly in their implications and long-term effects.
Navigating the complexities of debt management can be daunting, and it's essential for individuals to grasp the intricacies of debt consolidation and bankruptcy before determining the most suitable course of action. By analyzing the merits and drawbacks of each approach, individuals can gain clarity and confidence in addressing their financial difficulties, ultimately paving the way for a more stable and secure financial future.
Understanding Debt Consolidation
Debt consolidation is a financial strategy that involves combining multiple debts, such as credit card balances, personal loans, or medical bills, into a single, more manageable loan or payment plan. This approach is designed to streamline debt repayment by consolidating various obligations into a unified structure, often resulting in lower interest rates and more favorable terms. There are several methods of consolidating debt, including obtaining a consolidation loan, utilizing a balance transfer credit card, or enrolling in a debt management program offered by credit counseling agencies.
One of the primary benefits of debt consolidation is the potential reduction of interest rates, particularly when consolidating high-interest debts into a single, lower-rate loan. By securing a more favorable interest rate, individuals can potentially save money over the long term and expedite the process of debt repayment. Additionally, consolidating multiple debts into a single monthly payment can simplify financial management, making it easier to track progress and stay organized.
It’s important to note that debt consolidation does not eliminate the total amount of debt owed; rather, it restructures existing obligations to facilitate more manageable repayment. As such, individuals considering debt consolidation should exercise prudence in managing their finances to avoid accruing additional debt while repaying the consolidated amount. Moreover, the efficacy of debt consolidation hinges on the individual’s ability to adhere to the revised payment plan and make consistent, timely payments.
While debt consolidation offers compelling advantages in terms of simplified repayment and potential interest savings, it is essential for individuals to assess their financial habits and commitments before pursuing this option. By gaining a clear understanding of debt consolidation and its implications, individuals can make informed decisions that align with their financial well-being and long-term stability.
Understanding Bankruptcy
Bankruptcy is a legal process designed to provide individuals and businesses with a fresh financial start by either discharging or restructuring their debts under the protection of the court. In the United States, bankruptcy is governed by federal law and offers different chapters, each serving distinct purposes. The most common types of bankruptcy for individuals are Chapter 7 and Chapter 13. Chapter 7 bankruptcy, often referred to as “liquidation,” involves the sale of non-exempt assets to repay creditors, after which remaining qualifying debts are discharged. On the other hand, Chapter 13 bankruptcy, known as “reorganization,” allows individuals to create a court-approved repayment plan to settle their debts over a specified period, typically three to five years.
Bankruptcy provides a legal framework for individuals to address overwhelming debt and regain financial stability. By filing for bankruptcy, individuals can halt creditor harassment, wage garnishment, and other adverse collection activities through an automatic stay, which offers immediate relief and protection. Additionally, bankruptcy can offer the opportunity to restructure debts, potentially reducing the total amount owed and establishing a more manageable repayment plan.
However, it’s important to note that bankruptcy carries significant implications, including long-term effects on creditworthiness and financial standing. A bankruptcy filing can remain on an individual’s credit report for several years, impacting their ability to obtain credit, secure favorable interest rates, or make significant financial decisions. Furthermore, certain assets may be subject to liquidation in Chapter 7 bankruptcy, and individuals must meet specific eligibility criteria and adhere to court-mandated requirements throughout the bankruptcy process.
Before considering bankruptcy as a debt relief option, individuals are encouraged to seek guidance from qualified professionals, such as bankruptcy attorneys or financial advisors, to assess their unique circumstances and explore alternative solutions. Understanding the intricacies of bankruptcy and its potential ramifications is essential for individuals navigating financial challenges and seeking a path toward sustainable debt resolution.
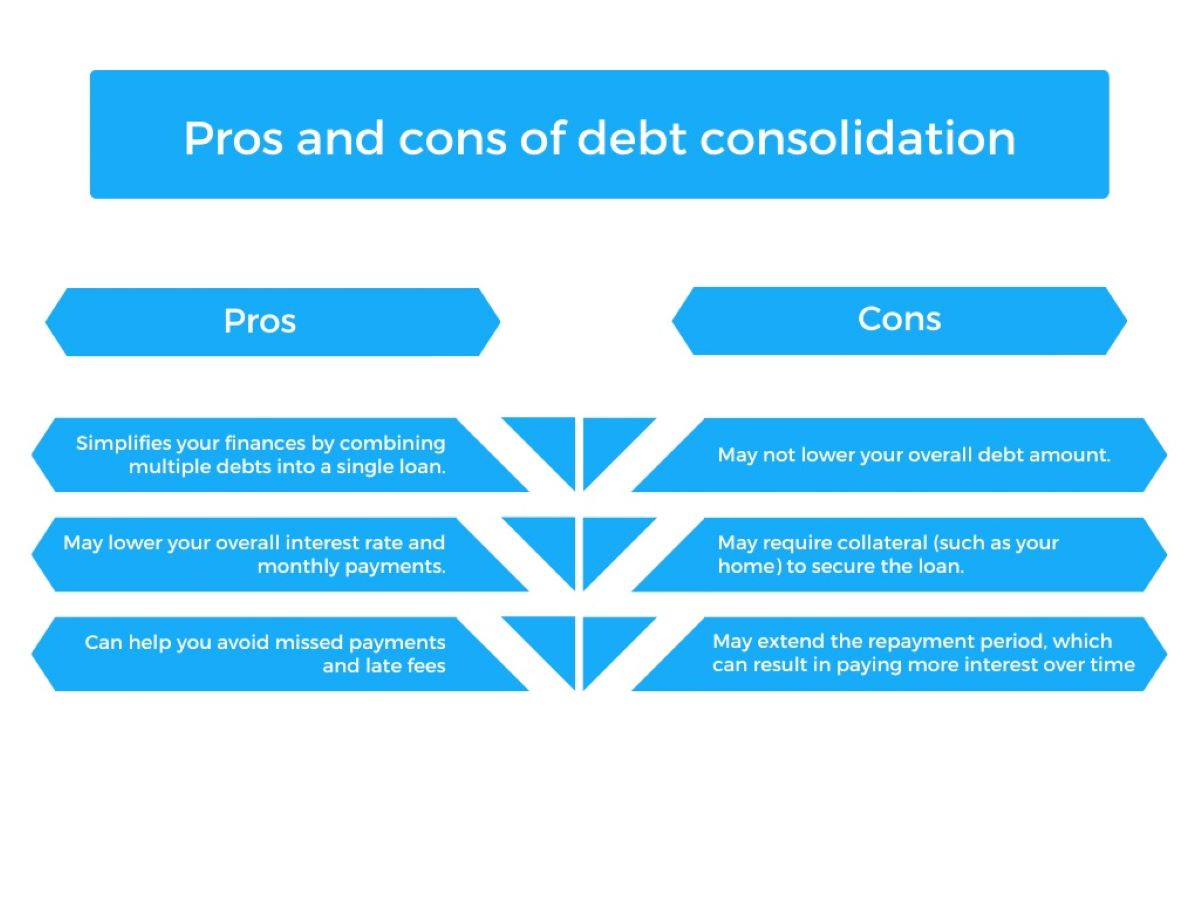
Pros and Cons of Debt Consolidation
Debt consolidation offers several potential advantages for individuals grappling with multiple sources of debt. One of the primary benefits is the simplification of repayment through the consolidation of various obligations into a single, more manageable payment plan. This streamlined approach can reduce the administrative burden of managing multiple payments, making it easier for individuals to stay organized and track their progress toward debt resolution. Additionally, debt consolidation may lead to lower interest rates, especially when consolidating high-interest debts into a single, more favorable loan or payment structure. By securing a reduced interest rate, individuals can potentially save money over time and expedite the process of debt repayment.
Another advantage of debt consolidation is the potential improvement in credit scores for individuals who effectively manage their consolidated debts. By making consistent, on-time payments and reducing overall debt balances, individuals may enhance their creditworthiness over time, which can open doors to more favorable financial opportunities in the future.
However, it’s important to consider the potential drawbacks of debt consolidation. While it can simplify repayment and reduce interest rates, individuals must exercise discipline and responsible financial management to avoid accumulating additional debt. Without addressing the root causes of indebtedness, individuals may find themselves in a more precarious financial situation if they continue to accrue new debts while repaying the consolidated amount. Moreover, some debt consolidation methods may incur fees or require collateral, necessitating a thorough evaluation of the associated costs and risks.
Before pursuing debt consolidation, individuals should carefully assess their financial habits, obligations, and the terms of the consolidation arrangement to ensure that it aligns with their long-term financial well-being. By weighing the potential benefits and considerations of debt consolidation, individuals can make informed decisions that support their journey toward sustainable debt management and financial stability.
Pros and Cons of Bankruptcy
Bankruptcy offers a structured legal framework for individuals facing overwhelming debt, providing both advantages and considerations that warrant careful evaluation. One of the primary benefits of bankruptcy is the immediate relief it offers through an automatic stay, which halts creditor harassment, wage garnishment, and other adverse collection activities. This legal protection can alleviate the emotional and financial strain associated with persistent creditor demands, offering individuals a respite to assess their financial situation and explore debt resolution options.
Additionally, bankruptcy provides the opportunity for debt restructuring, particularly through Chapter 13 bankruptcy, allowing individuals to create a court-approved repayment plan to settle their debts over a specified period, typically three to five years. This reorganization process can facilitate more manageable debt repayment, potentially reducing the total amount owed and offering a structured path toward financial recovery.
However, it’s essential to consider the potential drawbacks of bankruptcy, including its long-term impact on creditworthiness and financial standing. A bankruptcy filing can remain on an individual’s credit report for several years, affecting their ability to obtain credit, secure favorable interest rates, or make significant financial decisions. Furthermore, certain assets may be subject to liquidation in Chapter 7 bankruptcy, and individuals must meet specific eligibility criteria and adhere to court-mandated requirements throughout the bankruptcy process.
While bankruptcy provides a legal avenue for debt relief, it is crucial for individuals to approach this option with careful consideration and seek guidance from qualified professionals, such as bankruptcy attorneys or financial advisors. By understanding the potential benefits and implications of bankruptcy, individuals can make informed decisions that align with their unique financial circumstances and long-term goals.
Which Option Is Better for You?
When navigating the complexities of debt management, determining the most suitable option between debt consolidation and bankruptcy hinges on a thorough assessment of individual financial circumstances, goals, and considerations. Both approaches offer distinct advantages and implications, and selecting the appropriate path requires careful evaluation and informed decision-making.
For individuals with manageable levels of debt stemming from multiple sources, debt consolidation may present an appealing solution. By consolidating various debts into a single, more manageable payment plan, individuals can streamline their repayment process and potentially benefit from lower interest rates. Debt consolidation is particularly advantageous for those who possess the financial discipline to avoid accruing additional debt while adhering to the revised payment plan. Additionally, individuals who seek to simplify their financial obligations and improve their credit scores over time may find debt consolidation to be a favorable option.
On the other hand, individuals facing overwhelming debt and seeking a structured path toward financial recovery may find bankruptcy to be a more suitable avenue. Bankruptcy provides immediate relief through an automatic stay, offering protection from creditor harassment and wage garnishment. Furthermore, the reorganization opportunities presented by Chapter 13 bankruptcy can facilitate a structured and court-approved repayment plan, potentially reducing the total amount owed and providing a clear path toward debt resolution.
It’s important to recognize that the decision between debt consolidation and bankruptcy is not a one-size-fits-all proposition. Each individual’s financial situation is unique, and the most suitable option depends on factors such as the total amount of debt, the types of debts involved, income level, credit history, and long-term financial goals. Seeking guidance from qualified professionals, such as financial advisors or bankruptcy attorneys, can provide invaluable insights and assistance in evaluating the best course of action.
Ultimately, the determination of whether debt consolidation or bankruptcy is better suited to an individual’s needs requires a comprehensive understanding of the benefits, considerations, and potential ramifications associated with each approach. By carefully assessing their financial landscape and seeking expert guidance, individuals can make informed decisions that align with their long-term financial well-being and pave the way toward a more stable and secure future.
Conclusion
Debt consolidation and bankruptcy represent pivotal strategies for individuals grappling with overwhelming debt, each offering distinct avenues toward financial relief and stability. By understanding the intricacies of these approaches, individuals can make informed decisions that align with their unique financial circumstances and long-term goals.
Debt consolidation presents a compelling option for individuals seeking to streamline their repayment process and potentially benefit from lower interest rates. This strategy can simplify financial management and offer the opportunity to enhance credit scores through responsible debt repayment. However, the efficacy of debt consolidation hinges on individuals’ ability to exercise financial discipline and avoid accruing additional debt.
Conversely, bankruptcy provides a legal framework for individuals to address overwhelming debt and regain financial stability. Through an automatic stay and the potential for debt reorganization, bankruptcy offers immediate relief and a structured path toward debt resolution. Nonetheless, individuals must carefully consider the long-term implications of bankruptcy, including its impact on creditworthiness and financial standing.
The decision between debt consolidation and bankruptcy necessitates a comprehensive assessment of individual financial circumstances, goals, and considerations. Seeking guidance from qualified professionals is crucial in evaluating the most suitable option and charting a course toward sustainable debt management and financial recovery.
Ultimately, both debt consolidation and bankruptcy offer viable solutions for individuals navigating challenging financial situations. By weighing the benefits, considerations, and potential ramifications of each approach, individuals can make empowered decisions that support their long-term financial well-being and pave the way toward a more stable and secure future.