Home>Finance>Why Did Morgan Stanley Buy Credit Default Swaps


Finance
Why Did Morgan Stanley Buy Credit Default Swaps
Published: March 4, 2024
Discover why Morgan Stanley purchased credit default swaps and the impact on the finance industry. Explore the implications and insights in this finance-focused analysis.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
The world of finance is a complex and dynamic ecosystem, often influenced by a multitude of factors that can shape the decisions of major players in the industry. One such intriguing phenomenon is the strategic purchase of Credit Default Swaps (CDS) by prominent financial institutions like Morgan Stanley. This practice has sparked widespread interest and speculation within the financial community and beyond. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of Credit Default Swaps, examine their pivotal role in the global financial crisis, and explore the motivations behind Morgan Stanley's decision to acquire these financial instruments.
The enigmatic nature of Credit Default Swaps has long been a subject of fascination and scrutiny. By unraveling the intricacies of this financial tool and analyzing its impact, we can gain valuable insights into the mechanisms that underpin the financial world. This article aims to demystify the concept of Credit Default Swaps, shed light on their historical significance, and provide a comprehensive understanding of why Morgan Stanley, a leading financial institution, made the strategic move to purchase them.
As we embark on this exploration, it is essential to approach the topic with an open mind and a willingness to delve into the complexities of the financial landscape. By doing so, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of global markets and the strategic maneuvers employed by key players such as Morgan Stanley. Let us embark on this illuminative journey to unravel the enigma of Credit Default Swaps and decipher the rationale behind Morgan Stanley's foray into this intriguing financial domain.
What are Credit Default Swaps (CDS)?
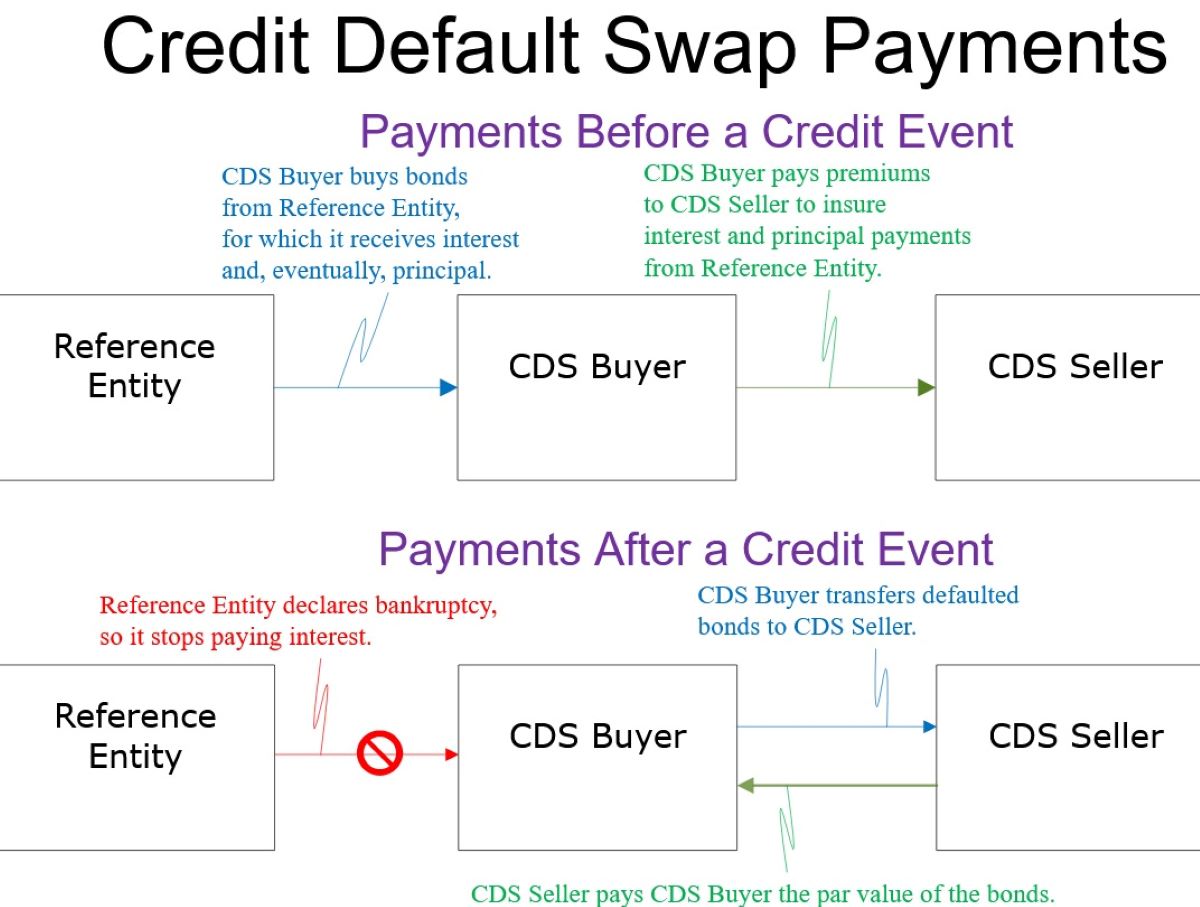
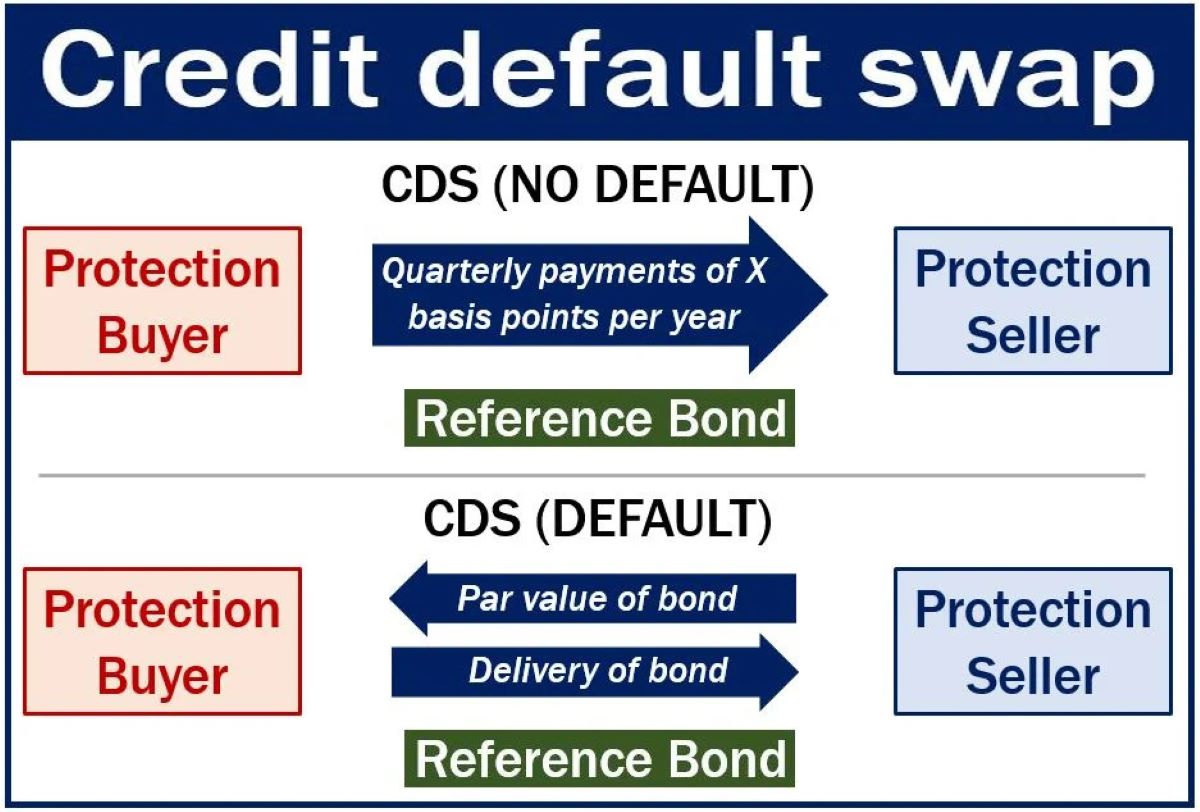
Credit Default Swaps (CDS) are derivative contracts that enable investors to mitigate the risk of default on debt instruments, such as bonds or loans. These financial instruments operate as a form of insurance against the non-payment of debt. In essence, the buyer of a CDS pays a premium to the seller in exchange for protection against potential default. If the underlying debt obligation defaults, the seller of the CDS compensates the buyer for the loss incurred.
One of the defining features of Credit Default Swaps is their flexibility and versatility. Unlike traditional insurance, CDS contracts can be traded among investors, allowing for the transfer of risk from one party to another. This characteristic has contributed to the widespread use of CDS as a risk management tool in the financial industry.
Furthermore, Credit Default Swaps are not limited to individual debt obligations. They can also be structured to cover a portfolio of debts, providing a broader scope of risk mitigation. This aspect has made CDS a valuable instrument for hedging against credit risk in diverse financial portfolios.
It is important to note that while Credit Default Swaps offer risk protection, they also introduce a degree of complexity and interconnectedness within the financial system. The trading of CDS contracts involves intricate calculations of credit risk, and the interconnected web of CDS transactions has the potential to amplify the impact of credit defaults across the market.
As we navigate the intricacies of Credit Default Swaps, it becomes evident that these financial instruments play a significant role in shaping the risk management strategies of investors and financial institutions. The evolution and widespread adoption of CDS have transformed the landscape of credit risk mitigation, making them a focal point of interest and debate within the financial domain.
The Role of Credit Default Swaps in the Financial Crisis
The global financial crisis of 2007-2008 brought to light the profound impact of Credit Default Swaps on the stability of financial markets. During this tumultuous period, the intricate web of CDS transactions became a pivotal factor in exacerbating the widespread economic turmoil.
One of the key contributors to the crisis was the proliferation of complex and opaque financial instruments, including Credit Default Swaps, which obscured the true extent of risk within the financial system. The interconnectedness of CDS transactions among major financial institutions created a domino effect, amplifying the repercussions of credit defaults and leading to systemic instability.
Furthermore, the lack of transparency and regulation in the CDS market heightened the uncertainty and unpredictability of the crisis. The opacity surrounding the valuation and exposure of CDS contracts intensified market distrust and volatility, exacerbating the severity of the financial meltdown.
The financial crisis underscored the need for enhanced oversight and regulation of Credit Default Swaps to mitigate systemic risk and safeguard the stability of the financial system. The aftermath of the crisis prompted regulatory reforms aimed at increasing transparency, standardizing CDS contracts, and imposing stricter oversight on the trading of these derivatives.
By examining the role of Credit Default Swaps in the financial crisis, we gain valuable insights into the far-reaching implications of these financial instruments and the imperative need for prudent risk management practices within the financial industry. The lessons learned from the crisis have reshaped the regulatory landscape and underscored the significance of understanding the complexities and interdependencies inherent in the trading of CDS contracts.
Why Morgan Stanley Bought Credit Default Swaps
Morgan Stanley’s decision to purchase Credit Default Swaps (CDS) stemmed from a strategic assessment of the prevailing market conditions and the firm’s risk management objectives. As a leading global financial institution, Morgan Stanley sought to navigate the complexities of the financial landscape while prudently managing its exposure to credit risk.
One of the primary motivations behind Morgan Stanley’s acquisition of Credit Default Swaps was the desire to hedge against potential credit risks associated with its investment portfolios. By purchasing CDS contracts, the firm aimed to mitigate the impact of credit defaults on its holdings, thereby safeguarding its financial stability and resilience in the face of market uncertainties.
Furthermore, the strategic utilization of Credit Default Swaps allowed Morgan Stanley to diversify its risk management strategies and enhance its overall risk-adjusted returns. The flexibility and customizable nature of CDS contracts provided the firm with an avenue to tailor its risk mitigation approach according to specific asset classes and market dynamics.
Moreover, the purchase of Credit Default Swaps enabled Morgan Stanley to optimize its capital allocation by efficiently managing its exposure to credit risk. By leveraging CDS as a risk management tool, the firm could allocate its capital resources more effectively, thereby enhancing its overall financial efficiency and stability.
It is essential to recognize that Morgan Stanley’s decision to buy Credit Default Swaps was underpinned by a comprehensive assessment of the firm’s risk appetite, market outlook, and regulatory considerations. The strategic deployment of CDS aligned with the firm’s overarching goal of prudently managing risk while maximizing its potential for sustainable growth and value creation.
By delving into the rationale behind Morgan Stanley’s acquisition of Credit Default Swaps, we gain valuable insights into the intricate risk management strategies employed by major financial institutions and the pivotal role of CDS in shaping their resilience and market positioning.
Implications of Morgan Stanley’s Decision
Morgan Stanley’s strategic decision to purchase Credit Default Swaps (CDS) carries significant implications that reverberate across the financial landscape, influencing the firm’s risk management practices, market positioning, and broader industry dynamics.
First and foremost, the acquisition of Credit Default Swaps underscores Morgan Stanley’s proactive approach to mitigating credit risk and enhancing the resilience of its investment portfolios. By leveraging CDS contracts, the firm aims to fortify its risk management framework, thereby bolstering its ability to navigate market uncertainties and credit market fluctuations.
Furthermore, the utilization of Credit Default Swaps enables Morgan Stanley to optimize its capital allocation and enhance its overall financial efficiency. By strategically hedging against potential credit defaults, the firm can allocate its capital resources more effectively, amplifying its capacity to pursue strategic initiatives and capitalize on market opportunities.
The implications of Morgan Stanley’s decision to purchase CDS extend beyond the firm’s internal risk management strategies and encompass broader implications for the financial industry. As a prominent player in the global financial landscape, Morgan Stanley’s strategic utilization of CDS sets a precedent for risk management practices and underscores the evolving dynamics of the derivatives market.
Moreover, the strategic deployment of Credit Default Swaps by Morgan Stanley contributes to the ongoing discourse surrounding the regulatory oversight and transparency of derivative instruments. The firm’s proactive approach to risk management prompts discussions about the evolving regulatory landscape and the imperative need for robust risk mitigation practices within the financial sector.
By examining the implications of Morgan Stanley’s decision to acquire Credit Default Swaps, we gain valuable insights into the evolving risk management strategies of major financial institutions and the broader impact of derivative instruments on market dynamics and regulatory considerations.
Conclusion
The strategic acquisition of Credit Default Swaps (CDS) by Morgan Stanley serves as a compelling illustration of the intricate risk management strategies employed by leading financial institutions. The decision to purchase CDS reflects the firm’s proactive approach to mitigating credit risk, optimizing capital allocation, and fortifying its resilience in the face of market uncertainties.
Throughout this exploration, we have delved into the multifaceted nature of Credit Default Swaps, unraveling their role as derivative contracts designed to hedge against potential credit defaults. The historical backdrop of the global financial crisis has underscored the far-reaching implications of CDS on market stability and regulatory reform, prompting a reevaluation of risk management practices within the financial industry.
Morgan Stanley’s strategic deployment of CDS not only enhances its internal risk management framework but also resonates with broader implications for the financial landscape. The firm’s proactive stance in utilizing derivative instruments sets a precedent for risk management practices and contributes to ongoing discussions surrounding regulatory oversight and transparency within the derivatives market.
As we conclude this exploration, it becomes evident that the strategic acquisition of Credit Default Swaps by Morgan Stanley encapsulates the evolving dynamics of risk management in the financial sector. The utilization of CDS as a risk mitigation tool underscores the imperative need for prudent risk management practices, capital efficiency, and regulatory considerations within the ever-evolving financial ecosystem.
Ultimately, the decision to purchase CDS represents a strategic maneuver that aligns with Morgan Stanley’s overarching goal of navigating market complexities, fortifying its risk management framework, and positioning itself for sustainable growth and value creation. This illuminative journey into the realm of Credit Default Swaps and the strategic decisions of financial institutions offers valuable insights into the intricate interplay of risk, resilience, and regulatory dynamics within the global financial landscape.