
Finance
How Accurate Is A FICO Score
Published: March 6, 2024
Learn about the accuracy of FICO scores and their impact on your financial standing. Understand how FICO scores are calculated and their importance in managing your finances.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to managing your finances, understanding your credit score is crucial. Your FICO score, in particular, plays a significant role in determining your creditworthiness and can impact your ability to secure loans, mortgages, and favorable interest rates. However, the accuracy of your FICO score is a topic that often raises questions and concerns among consumers.
It’s natural to wonder about the precision of a FICO score, considering the far-reaching implications it holds for your financial well-being. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of FICO scores, exploring how they are calculated, the factors that can affect their accuracy, and the importance of ensuring their reliability. Additionally, we’ll discuss strategies for monitoring and improving the accuracy of your FICO score, empowering you to take control of your financial standing.
By gaining a deeper understanding of the nuances surrounding FICO scores, you’ll be better equipped to make informed decisions and navigate the complex landscape of personal finance with confidence. So, let’s embark on this enlightening journey to unravel the mysteries of FICO score accuracy and empower ourselves with invaluable financial knowledge.
What is a FICO Score?
A FICO score is a three-digit number that represents an individual’s credit risk. This score is used by lenders to assess the likelihood of a borrower repaying their debts. The acronym “FICO” stands for Fair Isaac Corporation, the company that developed the FICO scoring model, which has become a standard tool for evaluating creditworthiness in the United States.
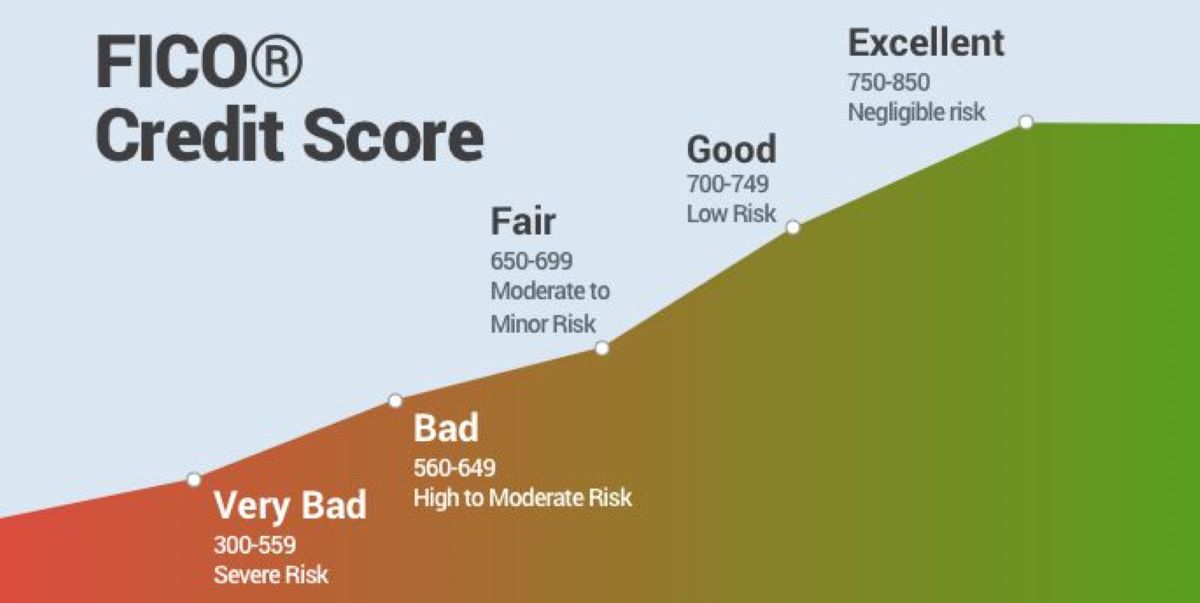
The FICO score is based on information from credit reports, which are compiled by three major credit bureaus: Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion. These reports contain details of an individual’s credit history, including their payment history, amounts owed, length of credit history, new credit, and types of credit used. FICO scores range from 300 to 850, with higher scores indicating lower credit risk and greater creditworthiness.
It’s important to note that while FICO scores are widely used, there are other credit scoring models in existence, such as VantageScore. However, FICO scores are highly prevalent and are often the focal point of discussions regarding credit scoring and lending decisions.
Understanding the significance of a FICO score is essential for anyone seeking to navigate the realms of borrowing, lending, and financial management. As we delve deeper into the world of FICO scores, we’ll uncover the mechanisms behind their calculation and the pivotal role they play in shaping individuals’ financial opportunities.
How is a FICO Score Calculated?
The calculation of a FICO score involves a complex algorithm that evaluates various aspects of an individual’s credit history to determine their creditworthiness. The specific details of this algorithm are proprietary to the Fair Isaac Corporation, but several key factors influence the calculation of a FICO score.
Payment history holds significant weight in the calculation of a FICO score. Lenders are keenly interested in whether borrowers have a history of making timely payments on their credit accounts, as this reflects their reliability in meeting financial obligations. Additionally, the amounts owed on different types of accounts, such as credit cards and loans, are taken into account. The utilization of available credit, or credit utilization ratio, is a crucial factor in this assessment.
The length of an individual’s credit history is also a determining factor in their FICO score. A longer credit history provides more data for assessing creditworthiness, while a shorter history may pose challenges in accurately gauging a borrower’s risk profile. Furthermore, the types of credit in use, such as credit cards, retail accounts, installment loans, and mortgages, contribute to the overall evaluation of credit risk.
New credit inquiries and accounts can impact a FICO score, as opening multiple new accounts within a short timeframe may raise concerns about financial stability and responsible credit management. Lastly, the mix of credit accounts, including the balance between revolving and installment accounts, is factored into the FICO score calculation.
It’s important to recognize that while these factors play a significant role in determining a FICO score, the exact weighting of each factor may vary based on an individual’s unique credit profile. By comprehending the intricacies of FICO score calculation, individuals can gain insights into the specific areas of their financial behavior that influence their credit scores.
Factors That Can Impact FICO Score Accuracy
While FICO scores are designed to provide a reliable assessment of an individual’s credit risk, several factors can potentially impact the accuracy of these scores. Understanding these influencing factors is crucial for maintaining a clear perspective on one’s creditworthiness and financial standing.
- Credit Report Errors: Inaccuracies or errors in credit reports, such as incorrect account information or unauthorized inquiries, can lead to discrepancies in FICO scores. Regularly reviewing credit reports and promptly addressing any inaccuracies is essential for ensuring score accuracy.
- Identity Theft and Fraud: Instances of identity theft or fraudulent activity can significantly impact FICO scores. Unauthorized accounts opened in a person’s name or fraudulent transactions can distort credit profiles, leading to inaccurate credit scores.
- Missing or Incomplete Information: If certain credit accounts or financial activities are not reported to the credit bureaus, it can result in incomplete data being used to calculate FICO scores. This may lead to an inaccurate representation of an individual’s credit history and creditworthiness.
- Utilization Ratio Fluctuations: Variations in credit utilization ratios, which reflect the amount of credit being used relative to the total available credit, can impact FICO scores. High utilization ratios may signal financial strain and impact credit scores, while lower ratios can positively influence scores.
- Credit Behavior Changes: Any shifts in credit behavior, such as missed payments, new credit applications, or changes in borrowing patterns, can impact FICO scores. Understanding the potential effects of these behavioral changes is crucial for maintaining score accuracy.
Recognizing these factors underscores the importance of actively monitoring one’s credit profile and taking proactive measures to address any issues that may compromise the accuracy of FICO scores. By remaining vigilant and responsive to potential influencers of score accuracy, individuals can uphold the integrity of their credit profiles and make informed decisions regarding their financial activities.
The Importance of FICO Score Accuracy
The accuracy of a FICO score holds profound significance in shaping an individual’s financial trajectory. A precise representation of creditworthiness empowers individuals to make informed decisions about borrowing, lending, and pursuing various financial opportunities. The following points underscore the critical importance of FICO score accuracy:
- Lending Decisions: Lenders heavily rely on FICO scores to assess the credit risk of potential borrowers. Accurate scores enable lenders to make fair and well-informed lending decisions, ensuring that individuals are offered suitable loan terms and interest rates based on their true creditworthiness.
- Financial Opportunities: FICO scores influence the availability of financial opportunities, such as obtaining mortgages, personal loans, and credit cards. Accurate scores open doors to favorable financial products, while inaccurate scores may limit access to these opportunities or result in less favorable terms.
- Interest Rates: The accuracy of FICO scores directly impacts the interest rates offered on loans and credit accounts. Individuals with accurate scores are more likely to secure lower interest rates, translating to significant long-term savings on interest payments.
- Financial Stability: Accurate FICO scores contribute to a clearer understanding of one’s financial standing and stability. This knowledge is essential for making sound financial decisions, planning for major life events, and maintaining overall financial well-being.
- Creditworthiness Perception: FICO scores influence how individuals are perceived by potential landlords, employers, and insurance providers. Accurate scores contribute to a positive creditworthiness perception, enhancing opportunities in various aspects of life.
By recognizing the pivotal role of FICO score accuracy, individuals can prioritize efforts to monitor and maintain the precision of their credit scores. This proactive approach not only safeguards financial opportunities and stability but also fosters a deeper sense of control and confidence in managing one’s financial future.
Ways to Monitor and Improve FICO Score Accuracy
Monitoring and actively managing the accuracy of a FICO score is essential for ensuring a reliable representation of one’s creditworthiness. By employing effective strategies for monitoring and improving FICO score accuracy, individuals can take proactive steps to safeguard their financial standing. Here are key approaches to consider:
- Regularly Check Credit Reports: Monitoring credit reports from the three major credit bureaus—Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion—is crucial for identifying any errors or discrepancies that may impact FICO scores. Annual credit report reviews are recommended, and individuals are entitled to free credit reports annually.
- Address Inaccuracies Promptly: Upon identifying errors in credit reports, individuals should promptly dispute and address these inaccuracies with the respective credit bureaus. Resolving these issues can help ensure the accuracy of credit information used in FICO score calculations.
- Practice Responsible Credit Management: Maintaining a consistent record of timely payments, managing credit utilization ratios, and avoiding excessive new credit applications are fundamental aspects of responsible credit management. These practices positively influence FICO scores and contribute to score accuracy.
- Utilize Credit Monitoring Services: Subscribing to credit monitoring services can provide ongoing insights into changes in credit reports, alerting individuals to potential inaccuracies or fraudulent activities that may impact FICO scores. These services offer added layers of vigilance and security.
- Understand Score Factors: Gaining a comprehensive understanding of the factors that influence FICO scores empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their financial behaviors. This knowledge enables proactive adjustments to credit management practices to positively impact score accuracy.
- Seek Professional Guidance: Consulting with financial advisors or credit counseling services can offer valuable guidance on improving credit management practices and addressing factors that may impact FICO score accuracy. Professional insight can help individuals navigate complex credit-related challenges.
By integrating these strategies into their financial management approach, individuals can actively monitor and enhance the accuracy of their FICO scores, ultimately fortifying their financial well-being and positioning themselves for favorable lending and credit opportunities.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of FICO scores and their accuracy is paramount for anyone seeking to navigate the terrain of personal finance. The significance of FICO score accuracy extends far beyond a mere numerical representation; it permeates lending decisions, financial opportunities, and the overall stability of individuals’ financial lives.
As we’ve explored the factors influencing FICO score accuracy and strategies for monitoring and improving score precision, it’s evident that proactive engagement with one’s credit profile is essential. Regularly reviewing credit reports, addressing inaccuracies, and practicing responsible credit management are foundational steps in ensuring the reliability of FICO scores.
Moreover, the impact of accurate FICO scores reverberates throughout various facets of life, influencing access to loans, favorable interest rates, and opportunities that hinge on creditworthiness. By embracing a proactive stance in managing FICO score accuracy, individuals empower themselves to make informed financial decisions and secure a stable financial future.
Ultimately, the journey toward maintaining accurate FICO scores is a journey toward financial empowerment and resilience. Armed with knowledge, vigilance, and a proactive mindset, individuals can navigate the complex landscape of credit with confidence, leveraging their accurate FICO scores to unlock a myriad of financial opportunities and build a solid foundation for long-term financial well-being.