
Finance
What Is A Profit And Loss Balance Sheet
Published: December 27, 2023
Learn about the key elements of a profit and loss balance sheet in finance, including income, expenses, and net profit. Gain insights into managing your financial statements.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
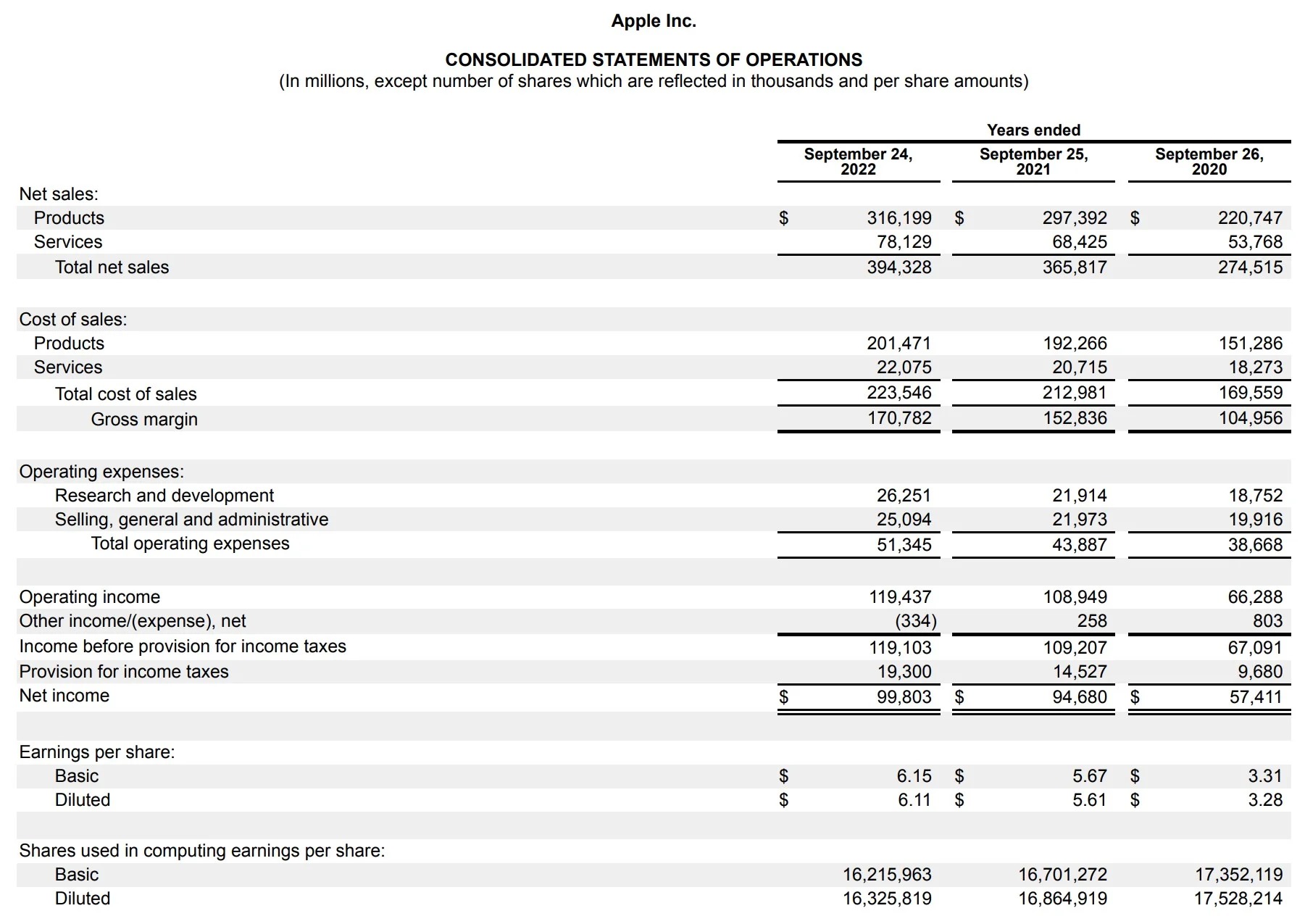
When it comes to understanding the financial health of a business, one of the fundamental documents is the Profit and Loss Balance Sheet. This essential financial statement provides valuable insights into the revenue, expenses, and overall profitability of a company. By analyzing this statement, entrepreneurs, investors, and stakeholders can assess the effective management of a business and make informed decisions.
The Profit and Loss Balance Sheet, also known as the income statement, summarizes the financial performance of a company over a specific period. It reveals whether the company has generated a profit or incurred a loss during that time. This document is crucial for businesses of all sizes and industries, as it helps monitor financial progress, identify areas of concern, and make strategic adjustments.
Understanding the intricacies of a Profit and Loss Balance Sheet is vital for entrepreneurs and those involved in financial decision-making. Through this article, we will delve deeper into the components of a Profit and Loss Balance Sheet, how revenue and expenses are accounted for, the calculation of profit or loss, the importance of this financial statement, and its limitations.
Whether you are a business owner, investor, or student of finance, by comprehending the concepts and importance of a Profit and Loss Balance Sheet, you will have a solid foundation for financial analysis and decision-making.
Definition of Profit and Loss Balance Sheet
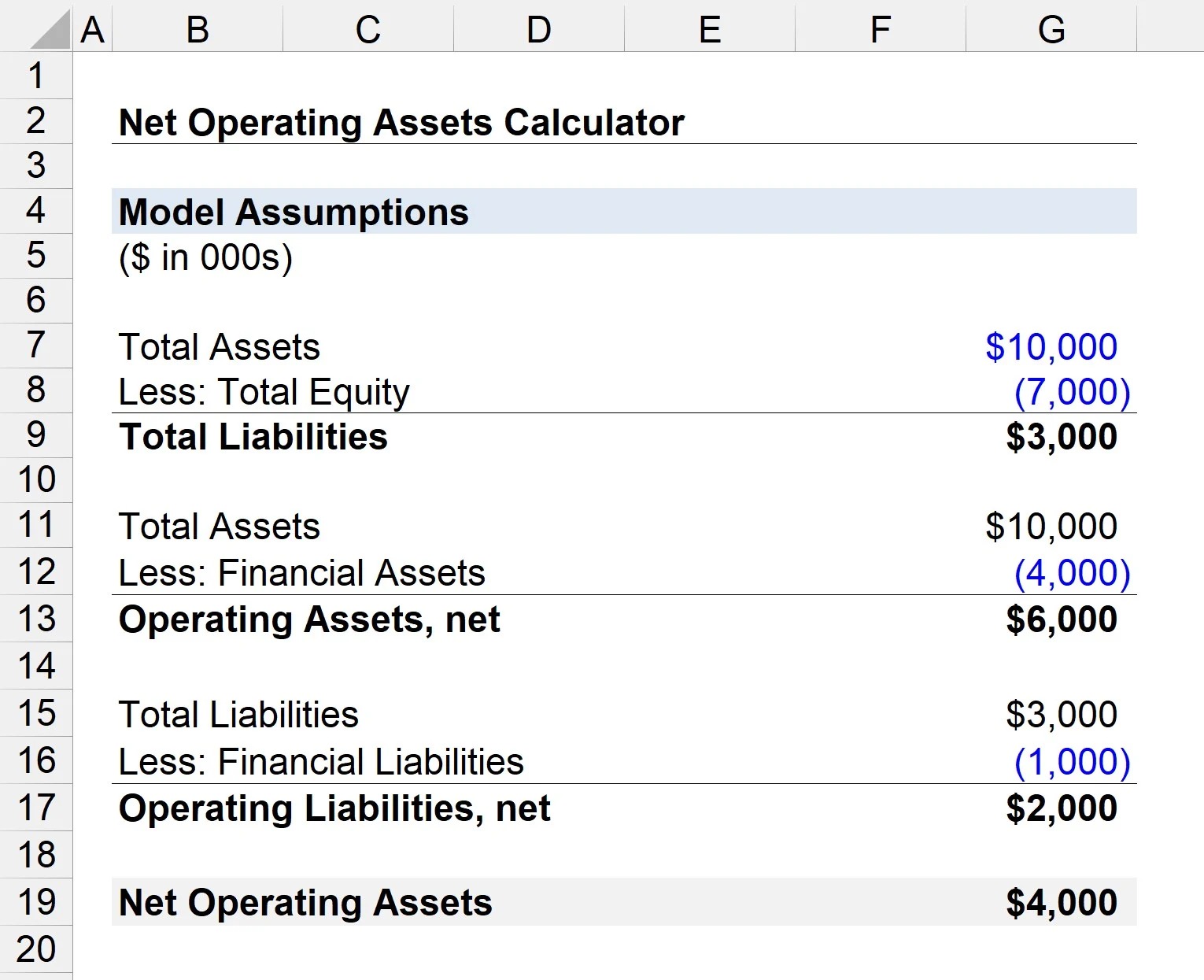
The Profit and Loss Balance Sheet, also known as the income statement, is a financial document that provides a snapshot of a company’s revenues, expenses, and profitability over a specific period. It presents a clear picture of the financial performance of a business during a specific timeframe, typically a month, quarter, or year.
The purpose of the Profit and Loss Balance Sheet is to determine whether a business has generated a profit or incurred a loss during the specified period. It showcases the business’s ability to generate revenue, manage expenses, and ultimately, its profitability. By analyzing this statement, stakeholders can gauge the financial health of a company and make informed decisions.
The Profit and Loss Balance Sheet is divided into two main sections: revenue and expenses. The revenue section lists all the income streams and sources of revenue for the business, such as sales revenue, fees earned, or interest income. On the other hand, the expenses section outlines all the costs incurred by the business to generate that revenue, including operating expenses, salaries, rent, and taxes.
At the bottom of the statement, the net profit or loss is calculated by deducting total expenses from total revenue. A positive net profit indicates that the business has generated more revenue than it has spent in expenses during that period, while a negative net loss indicates that the expenses have exceeded the revenue generated.
The Profit and Loss Balance Sheet is a dynamic document that reflects the financial performance of the business over time. It can be used for internal review, investor reporting, and regulatory compliance. By closely monitoring and analyzing this statement, business owners and stakeholders can identify trends, evaluate the effectiveness of their operations, and make strategic decisions to improve profitability.
Components of a Profit and Loss Balance Sheet
The Profit and Loss Balance Sheet, also known as the income statement, consists of several key components that provide a comprehensive overview of a company’s financial performance. By understanding these components, stakeholders can gain valuable insights into the revenue, expenses, and profitability of the business. Here are the main components:
- Revenue: This section highlights the money generated by the business through its core operations. It includes sales revenue, fees earned, interest income, and any other sources of income. Revenue is a vital component as it reflects the success and effectiveness of the business in generating income.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): In industries that involve the sale of physical products, this component represents the direct costs associated with producing or purchasing the goods being sold. It includes raw materials, labor, and overhead expenses directly tied to the production process. The COGS is subtracted from the revenue to calculate the gross profit.
- Gross Profit: This is the revenue remaining after subtracting the COGS. It represents the profit generated solely from the sale of products or services, without considering other operating expenses.
- Operating Expenses: This component includes all the costs incurred in running the business on a day-to-day basis. It encompasses expenses such as employee salaries, rent, utilities, marketing, and administrative costs. These expenses are subtracted from the gross profit to calculate the operating profit.
- Operating Profit: Also known as operating income, this represents the profit generated from core business operations before considering any interest or tax payments. It reflects the overall profitability of the business’s main activities.
- Other Income and Expenses: This component captures any income or expenses that are not directly related to the core operations of the business. It may include gains or losses from investments, interest income, or one-time extraordinary expenses.
- Net Profit or Loss: This is the final figure calculated by subtracting all expenses, including operating expenses and other income and expenses, from the revenue. A positive net profit indicates that the business has generated a profit, while a negative net loss indicates a loss.
These components collectively provide a holistic view of a company’s financial performance by detailing the inflow and outflow of revenue and expenses. Analyzing these components helps stakeholders understand the profitability of the business and identify areas for improvement.
Understanding Revenue and Expenses
Revenue and expenses are two crucial elements that form the foundation of a Profit and Loss Balance Sheet. They provide valuable insights into the financial performance and profitability of a business. Let’s take a closer look at how revenue and expenses are accounted for in this financial statement.
Revenue: Revenue represents the total income generated by a business through its primary operations. It includes sales revenue, fees earned, interest income, and any other sources of income directly related to the business’s activities. Revenue is a key indicator of the company’s ability to sell products or services and generate income.
It is important to note that revenue should only include cash or cash equivalents received or expected to be received during the specified period. It does not include future or anticipated income that has not been realized yet. Revenue recognition principles and accounting standards guide businesses to record revenue accurately.
Expenses: Expenses refer to the costs incurred by a business in its day-to-day operations. These costs can be both direct and indirect and are subtracted from the revenue to calculate the net profit or loss. Expenses are categorized into different types based on their nature and relevance to the business.
Some common types of expenses include:
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): This expense category includes the direct costs associated with producing or purchasing the goods being sold. It encompasses the cost of raw materials, direct labor, and other production-related expenses.
- Operating Expenses: These expenses cover the general operating costs of the business, such as rent, utilities, employee salaries, marketing and advertising expenses, legal fees, and other administrative costs.
- Interest Expenses: If a business has borrowed money or has outstanding loans, it will incur interest expenses on these borrowings. These expenses are subtracted from the revenue to calculate the net profit.
- Depreciation and Amortization: These expenses are associated with the gradual reduction in the value of tangible assets (depreciation) or intangible assets (amortization) over time. They reflect the wear and tear or obsolescence of assets and are recorded as expenses.
- Taxes: Businesses are obligated to pay various taxes, including income tax, sales tax, payroll tax, and property tax. These tax payments are considered expenses and are subtracted from the revenue to determine the net profit or loss.
Understanding and analyzing revenue and expenses allows businesses to evaluate the financial performance, profitability, and efficiency of their operations. By monitoring and managing these components effectively, companies can identify areas for improvement, optimize their revenue generation, and control costs to maximize their profitability.
Calculation of Profit or Loss
The calculation of profit or loss in a Profit and Loss Balance Sheet is a fundamental aspect of assessing the financial performance of a business. This calculation provides a clear indication of whether a company has generated a profit or incurred a loss during a specific period. Let’s dive into the steps involved in calculating profit or loss:
1. Calculate Revenue: The first step is to determine the total revenue generated by the business during the specified period. This includes all sources of income, such as sales revenue, fees earned, and interest income. Revenue represents the inflow of cash resulting from the business’s primary operations.
2. Calculate Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): If the business deals with the sale of physical goods, the next step is to calculate the cost of goods sold. This includes the direct costs associated with producing or purchasing the goods being sold, such as raw materials, direct labor, and other production-related expenses. Subtracting the COGS from the revenue gives us the gross profit.
3. Calculate Operating Expenses: The next step is to calculate the operating expenses of the business. These expenses include employee salaries, rent, utilities, marketing expenses, administrative costs, and other costs incurred in running the day-to-day operations. Subtracting the operating expenses from the gross profit gives us the operating profit.
4. Factor in Other Income and Expenses: Consider any additional income or expenses that are not directly related to the core operations of the business. This may include gains or losses from investments, interest income, or extraordinary one-time expenses. Adding or subtracting these items from the operating profit yields the net profit before taxes.
5. Account for Taxes: Deduct any applicable taxes, such as income tax, sales tax, or payroll tax, from the net profit before taxes. This gives us the net profit after taxes, or if the result is negative, the net loss.
The final figure obtained represents the profit or loss generated by the business during the specified period. A positive net profit indicates that the company has generated more revenue than it has incurred in expenses, resulting in a profit. Conversely, a negative net loss highlights that the expenses have exceeded the revenue, resulting in a loss.
Calculating profit or loss is vital for businesses as it helps assess their financial performance, make informed decisions, and identify areas for improvement. Regularly monitoring this calculation enables businesses to evaluate their profitability, manage expenses, and strategize for future growth.
Importance of Profit and Loss Balance Sheet
The Profit and Loss Balance Sheet, also known as the income statement, holds significant importance for businesses and stakeholders. This financial statement provides valuable insights into the financial performance, profitability, and sustainability of a company. Let’s explore the key reasons why the Profit and Loss Balance Sheet is essential:
1. Assess Financial Performance: The Profit and Loss Balance Sheet allows businesses to evaluate their financial performance over a specific period. By analyzing revenue and expenses, businesses can determine if they are generating enough income to cover their costs and make a profit. This assessment aids in identifying areas of strength and weakness, enabling businesses to make informed decisions about their operations and strategies.
2. Monitor Profitability: The Profit and Loss Balance Sheet provides a clear picture of a company’s profitability. By calculating and analyzing net profit or loss, businesses can gauge the effectiveness of their revenue generation and expense management. Monitoring profitability is crucial for the long-term sustainability and growth of a business, as it guides decision-making and helps identify opportunities for improvement.
3. Aid in Decision-Making: The information provided by the Profit and Loss Balance Sheet plays a vital role in the decision-making process. Entrepreneurs, managers, and investors use this financial statement to assess the financial health of a business and make strategic decisions. Whether it’s considering expansion plans, optimizing costs, or evaluating the success of marketing campaigns, the Profit and Loss Balance Sheet provides crucial insights for decision-makers.
4. Assist in Investor Reporting: Investors and stakeholders rely on the Profit and Loss Balance Sheet to assess the financial performance and profitability of a company. This statement helps investors understand the company’s ability to generate returns and its overall financial stability. Accurate and transparent reporting through the Profit and Loss Balance Sheet builds trust and confidence among shareholders and potential investors.
5. Facilitate Regulatory Compliance: The Profit and Loss Balance Sheet is essential for regulatory compliance. Businesses are required to prepare and disclose this financial statement as per accounting standards and regulations. It ensures transparency and accountability in financial reporting, providing accurate and reliable information to regulatory authorities and stakeholders.
6. Aid in Benchmarking and Comparisons: The Profit and Loss Balance Sheet allows businesses to benchmark their financial performance against industry peers and competitors. By comparing revenue, expenses, and profitability, businesses can identify areas where they excel or lag behind. This analysis helps set realistic goals, learn from industry best practices, and drive continuous improvement.
Overall, the Profit and Loss Balance Sheet is a key financial tool that provides crucial insights into a company’s financial performance, profitability, and viability. By analyzing this statement, businesses can make informed decisions, monitor their financial health, and drive sustainable growth in a competitive marketplace.
Limitations of Profit and Loss Balance Sheet
While the Profit and Loss Balance Sheet is a valuable financial statement, it does have certain limitations that should be considered when assessing a company’s financial health. Understanding these limitations is crucial for stakeholders to make informed decisions. Let’s explore some of the key limitations of the Profit and Loss Balance Sheet:
1. Timeframe Focus: The Profit and Loss Balance Sheet provides information for a specific period, such as a month, quarter, or year. This timeframe focus means that it may not capture long-term trends or fluctuations. To gain a more comprehensive understanding of the financial performance, it’s important to consider multiple periods or use additional financial statements.
2. Non-Cash Items: The Profit and Loss Balance Sheet only considers actual cash transactions, which means it may not account for certain non-cash items, such as depreciation and amortization. These non-cash expenses can have a significant impact on a company’s financial position but may not be adequately reflected in this statement.
3. Accrual Accounting: The Profit and Loss Balance Sheet is typically prepared using accrual accounting, which recognizes revenue when it’s earned and expenses when they are incurred, regardless of cash flow. This method can sometimes result in disparities between the timing of revenue recognition and cash inflows, which may impact the accuracy of the statement.
4. Incomplete Picture of Financial Health: While the Profit and Loss Balance Sheet focuses on revenue, expenses, and profitability, it does not provide a comprehensive view of a company’s financial health. Factors such as cash flow, liquidity, and solvency also need to be considered to gain a complete understanding of the company’s financial position.
5. Subjectivity in Expense Allocation: Allocating expenses to the appropriate category can be subjective and differ between companies. Different accounting methods and estimates may result in variations in expense recognition, making it challenging to compare financial statements of different businesses accurately.
6. External Factors: The Profit and Loss Balance Sheet does not take into account external factors that can impact a company’s financial performance. Economic conditions, industry trends, and unforeseen events, such as natural disasters or changes in government regulations, may significantly impact a company’s profitability, but may not be reflected in this statement.
Despite these limitations, the Profit and Loss Balance Sheet remains a valuable tool for understanding a company’s financial performance and profitability. It should be used in conjunction with other financial statements and analysis to gain a comprehensive view of a company’s financial health and make well-informed decisions.
Conclusion
The Profit and Loss Balance Sheet, also known as the income statement, is a crucial financial document that provides insights into a company’s revenue, expenses, and overall profitability. It allows businesses and stakeholders to assess the financial performance, make informed decisions, and monitor the sustainability of the business. By understanding the components of the Profit and Loss Balance Sheet, including revenue and expenses, businesses can evaluate their financial health, identify areas for improvement, and drive strategic growth.
While the Profit and Loss Balance Sheet has its limitations, such as its timeframe focus and potential subjective expense allocation, it remains an essential tool for financial analysis. It aids in evaluating financial performance, monitoring profitability, and facilitating investor reporting and regulatory compliance. Furthermore, it assists in benchmarking against industry peers and guides decision-making for business owners and managers.
To gain a comprehensive understanding of a company’s financial health, it’s important to consider additional financial statements, such as the balance sheet and cash flow statement, alongside the Profit and Loss Balance Sheet. These statements provide a more complete picture of a company’s financial position, liquidity, and sustainability.
In conclusion, the Profit and Loss Balance Sheet plays a critical role in assessing a company’s financial performance, profitability, and viability. By utilizing this statement effectively, businesses can make informed decisions, adapt to changing market conditions, and drive long-term success and growth in a competitive business environment.